Abstract
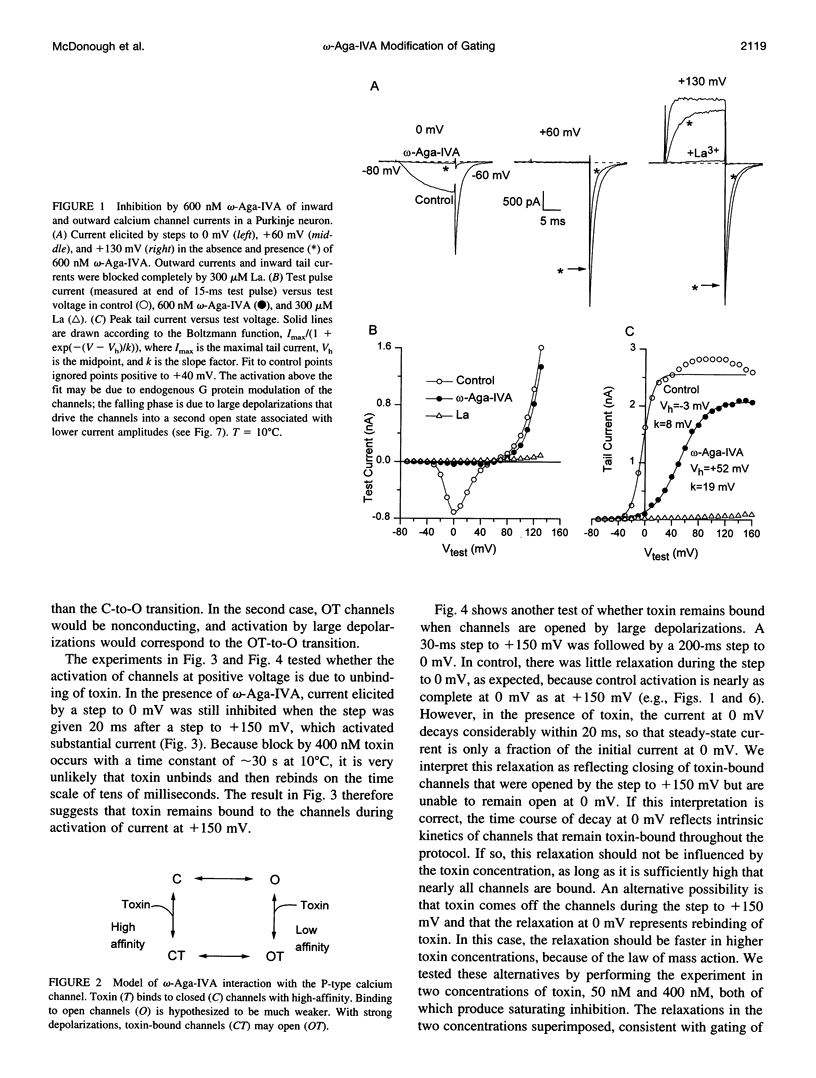
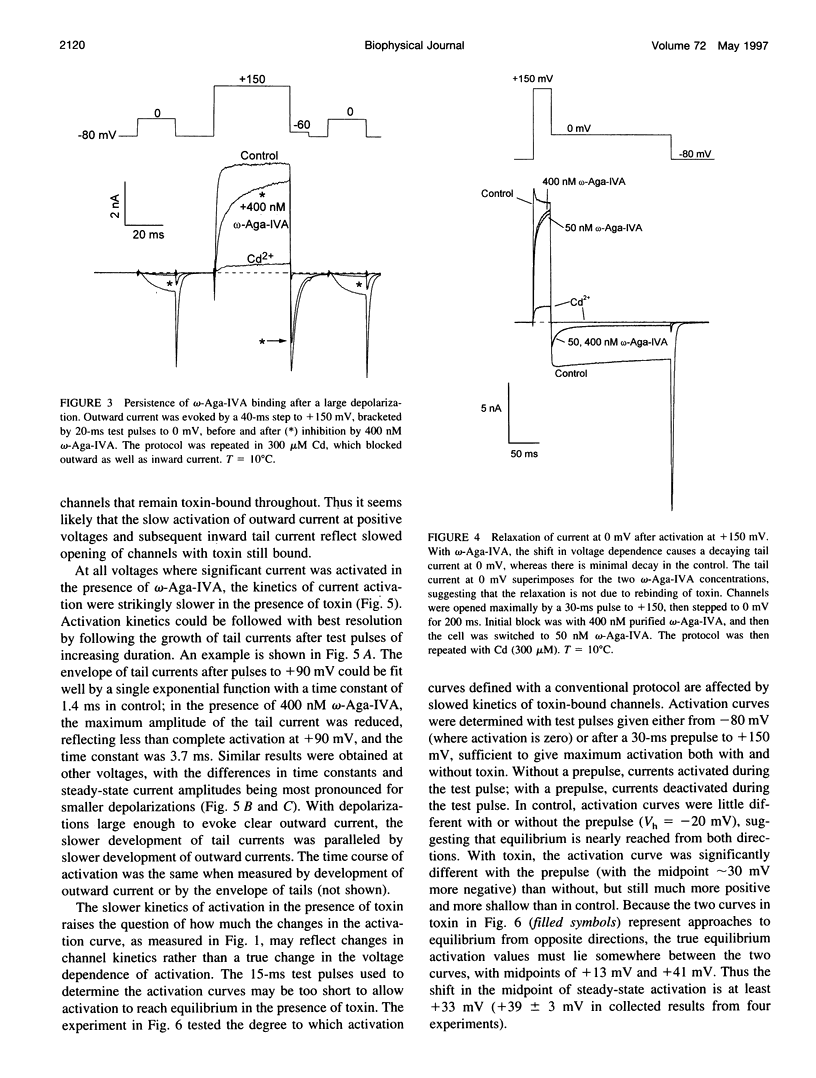
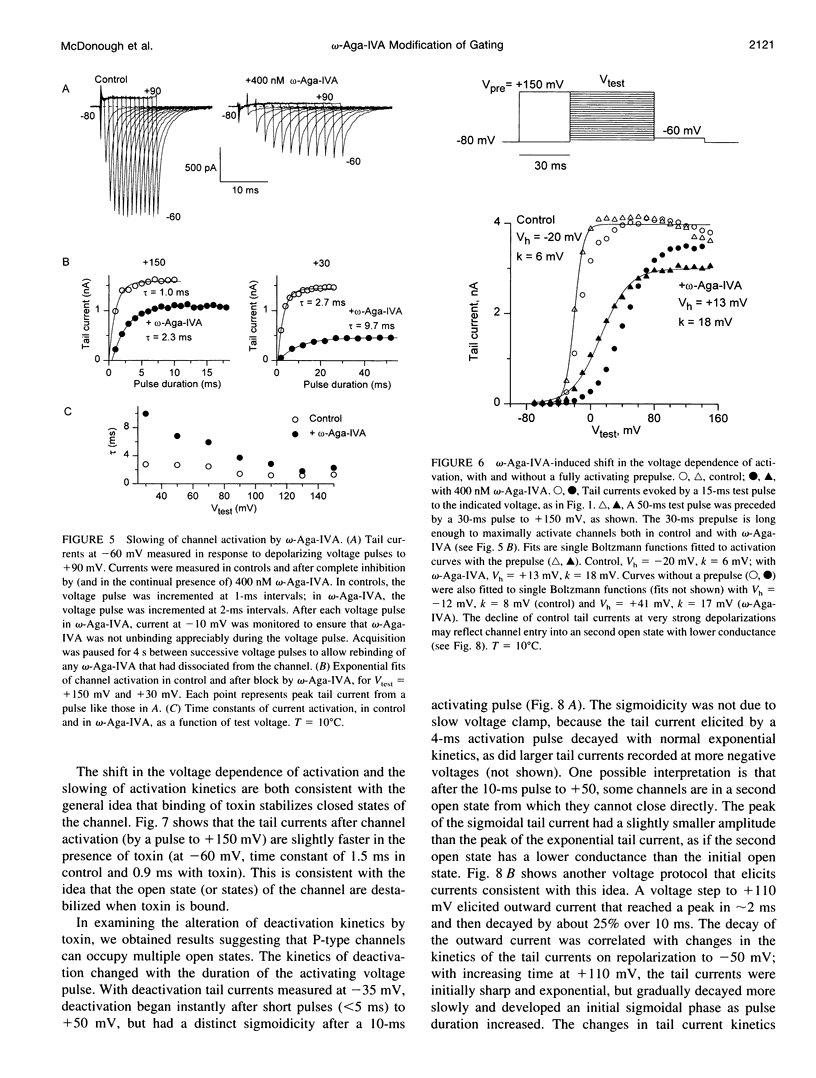
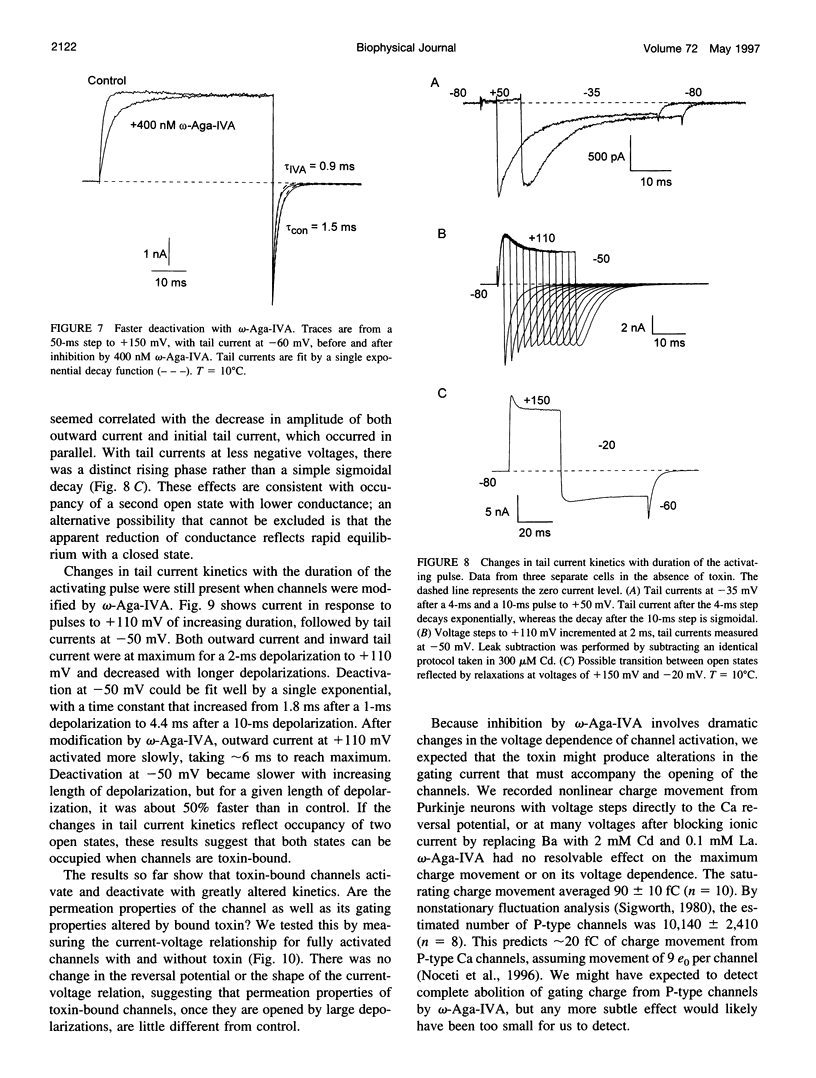
We studied the mechanism of inhibition of P-type calcium channels in rat cerebellar Purkinje neurons by the peptide toxin omega-Aga-IVA. Saturating concentrations of omega-Aga-IVA (> 50 nM) inhibited inward current carried by 2-5 mM Ba almost completely. However, outward current at depolarizations of > +60 mV, carried by internal Cs, was inhibited much less, as was the tail current after such depolarizations. omega-Aga-IVA shifted the midpoint of the tail current activation curve by about +50 mV and made the curve less steep. The inactivation curve was also shifted in the depolarized direction and was made less steep. With omega-Aga-IVA, channels activated more slowly and deactivated more quickly than in control. Trains of repeated large depolarizations relieved the inhibition of current (as tested with moderate depolarizations), probably reflecting the unbinding of toxin. The relief of inhibition was faster with increasing depolarization, but did not require internal permeant ions. We conclude that omega-Aga-IVA alters voltage-dependent gating by stabilizing closed states of the channel and that omega-Aga-IVA dissociates much more rapidly from open channels than from closed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams M. E., Mintz I. M., Reily M. D., Thanabal V., Bean B. P. Structure and properties of omega-agatoxin IVB, a new antagonist of P-type calcium channels. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Oct;44(4):681–688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargas J., Howe A., Eberwine J., Cao Y., Surmeier D. J. Cellular and molecular characterization of Ca2+ currents in acutely isolated, adult rat neostriatal neurons. J Neurosci. 1994 Nov;14(11 Pt 1):6667–6686. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-11-06667.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bean B. P. Neurotransmitter inhibition of neuronal calcium currents by changes in channel voltage dependence. Nature. 1989 Jul 13;340(6229):153–156. doi: 10.1038/340153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boland L. M., Bean B. P. Modulation of N-type calcium channels in bullfrog sympathetic neurons by luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone: kinetics and voltage dependence. J Neurosci. 1993 Feb;13(2):516–533. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-02-00516.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boland L. M., Morrill J. A., Bean B. P. omega-Conotoxin block of N-type calcium channels in frog and rat sympathetic neurons. J Neurosci. 1994 Aug;14(8):5011–5027. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-08-05011.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callewaert G., Eilers J., Konnerth A. Axonal calcium entry during fast 'sodium' action potentials in rat cerebellar Purkinje neurones. J Physiol. 1996 Sep 15;495(Pt 3):641–647. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carabelli V., Lovallo M., Magnelli V., Zucker H., Carbone E. Voltage-dependent modulation of single N-Type Ca2+ channel kinetics by receptor agonists in IMR32 cells. Biophys J. 1996 May;70(5):2144–2154. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79780-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbone E., Prestipino G., Spadavecchia L., Franciolini F., Possani L. D. Blocking of the squid axon K+ channel by noxiustoxin: a toxin from the venom of the scorpion Centruroides noxius. Pflugers Arch. 1987 May;408(5):423–431. doi: 10.1007/BF00585064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliot L. S., Johnston D. Multiple components of calcium current in acutely dissociated dentate gyrus granule neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1994 Aug;72(2):762–777. doi: 10.1152/jn.1994.72.2.762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellinor P. T., Zhang J. F., Horne W. A., Tsien R. W. Structural determinants of the blockade of N-type calcium channels by a peptide neurotoxin. Nature. 1994 Nov 17;372(6503):272–275. doi: 10.1038/372272a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmslie K. S., Zhou W., Jones S. W. LHRH and GTP-gamma-S modify calcium current activation in bullfrog sympathetic neurons. Neuron. 1990 Jul;5(1):75–80. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90035-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert C. D. Horizontal integration and cortical dynamics. Neuron. 1992 Jul;9(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90215-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herlitze S., Garcia D. E., Mackie K., Hille B., Scheuer T., Catterall W. A. Modulation of Ca2+ channels by G-protein beta gamma subunits. Nature. 1996 Mar 21;380(6571):258–262. doi: 10.1038/380258a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillyard D. R., Monje V. D., Mintz I. M., Bean B. P., Nadasdi L., Ramachandran J., Miljanich G., Azimi-Zoonooz A., McIntosh J. M., Cruz L. J. A new Conus peptide ligand for mammalian presynaptic Ca2+ channels. Neuron. 1992 Jul;9(1):69–77. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90221-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda S. R. Double-pulse calcium channel current facilitation in adult rat sympathetic neurones. J Physiol. 1991 Aug;439:181–214. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda S. R. Voltage-dependent modulation of N-type calcium channels by G-protein beta gamma subunits. Nature. 1996 Mar 21;380(6571):255–258. doi: 10.1038/380255a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. C., Bean B. P. G-protein modulation of ion permeation through N-type calcium channels. Nature. 1993 Sep 16;365(6443):258–262. doi: 10.1038/365258a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Sugimori M., Lin J. W., Cherksey B. Blocking and isolation of a calcium channel from neurons in mammals and cephalopods utilizing a toxin fraction (FTX) from funnel-web spider poison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1689–1693. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Sugimori M., Simon S. M. Transmission by presynaptic spike-like depolarization in the squid giant synapse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2415–2419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKinnon R., Miller C. Mechanism of charybdotoxin block of the high-conductance, Ca2+-activated K+ channel. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Mar;91(3):335–349. doi: 10.1085/jgp.91.3.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnelli V., Pollo A., Sher E., Carbone E. Block of non-L-, non-N-type Ca2+ channels in rat insulinoma RINm5F cells by omega-agatoxin IVA and omega-conotoxin MVIIC. Pflugers Arch. 1995 Apr;429(6):762–771. doi: 10.1007/BF00374799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchetti C., Carbone E., Lux H. D. Effects of dopamine and noradrenaline on Ca channels of cultured sensory and sympathetic neurons of chick. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Feb;406(2):104–111. doi: 10.1007/BF00586670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCobb D. P., Beam K. G. Action potential waveform voltage-clamp commands reveal striking differences in calcium entry via low and high voltage-activated calcium channels. Neuron. 1991 Jul;7(1):119–127. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90080-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonough S. I., Swartz K. J., Mintz I. M., Boland L. M., Bean B. P. Inhibition of calcium channels in rat central and peripheral neurons by omega-conotoxin MVIIC. J Neurosci. 1996 Apr 15;16(8):2612–2623. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-08-02612.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarlane M. B. Depolarization-induced slowing of Ca2+ channel deactivation in squid neurons. Biophys J. 1997 Apr;72(4):1607–1621. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(97)78807-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarlane M. B., Gilly W. F. Spatial localization of calcium channels in giant fiber lobe neurons of the squid (Loligo opalescens). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 May 14;93(10):5067–5071. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.10.5067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. The charybdotoxin family of K+ channel-blocking peptides. Neuron. 1995 Jul;15(1):5–10. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90057-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mintz I. M., Bean B. P. Block of calcium channels in rat neurons by synthetic omega-Aga-IVA. Neuropharmacology. 1993 Nov;32(11):1161–1169. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(93)90010-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mintz I. M., Venema V. J., Swiderek K. M., Lee T. D., Bean B. P., Adams M. E. P-type calcium channels blocked by the spider toxin omega-Aga-IVA. Nature. 1992 Feb 27;355(6363):827–829. doi: 10.1038/355827a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noceti F., Baldelli P., Wei X., Qin N., Toro L., Birnbaumer L., Stefani E. Effective gating charges per channel in voltage-dependent K+ and Ca2+ channels. J Gen Physiol. 1996 Sep;108(3):143–155. doi: 10.1085/jgp.108.3.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patil P. G., de Leon M., Reed R. R., Dubel S., Snutch T. P., Yue D. T. Elementary events underlying voltage-dependent G-protein inhibition of N-type calcium channels. Biophys J. 1996 Nov;71(5):2509–2521. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79444-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penington N. J., Kelly J. S., Fox A. P. Action potential waveforms reveal simultaneous changes in ICa and IK produced by 5-HT in rat dorsal raphe neurons. Proc Biol Sci. 1992 May 22;248(1322):171–179. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1992.0059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfrieger F. W., Gottmann K., Lux H. D. Kinetics of GABAB receptor-mediated inhibition of calcium currents and excitatory synaptic transmission in hippocampal neurons in vitro. Neuron. 1994 Jan;12(1):97–107. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90155-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall A., Tsien R. W. Pharmacological dissection of multiple types of Ca2+ channel currents in rat cerebellar granule neurons. J Neurosci. 1995 Apr;15(4):2995–3012. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-04-02995.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
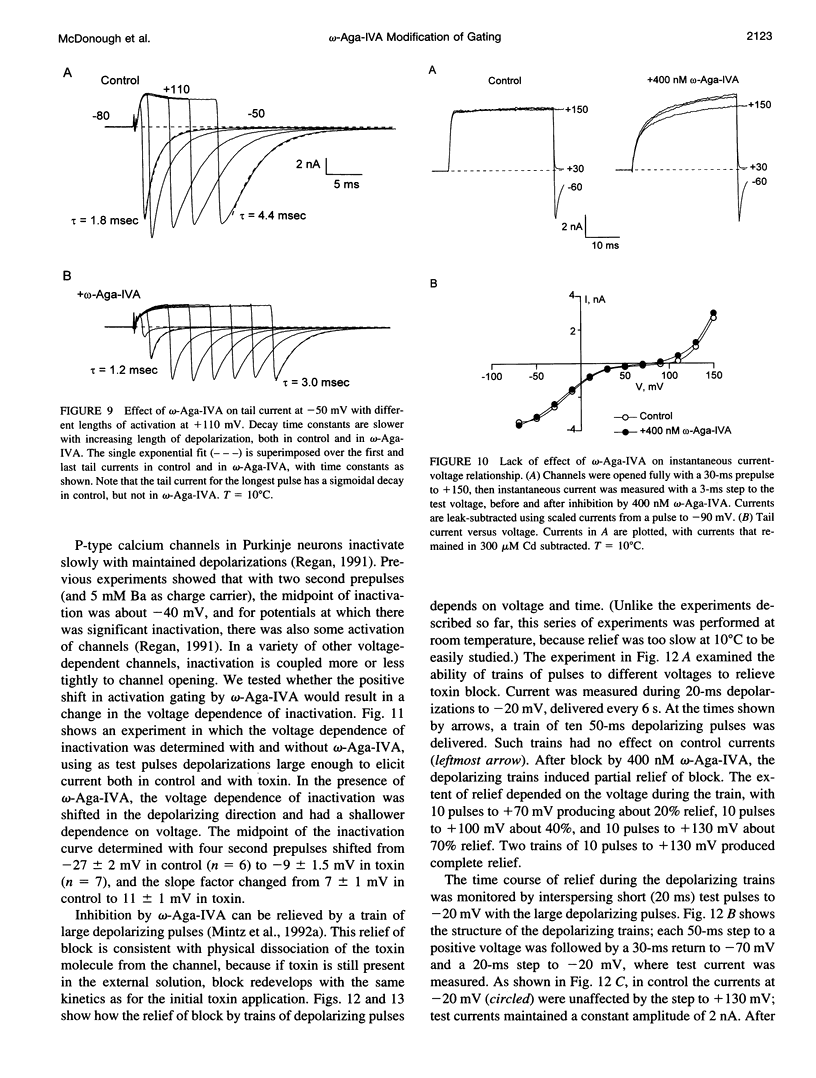
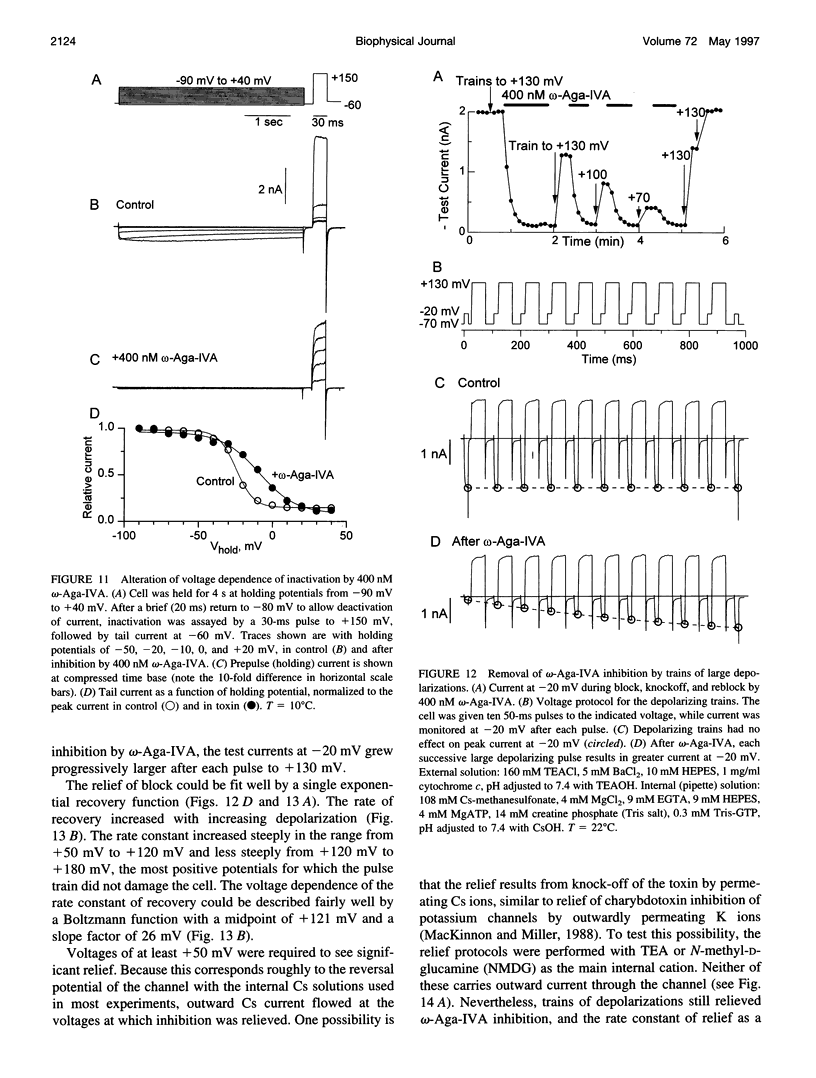
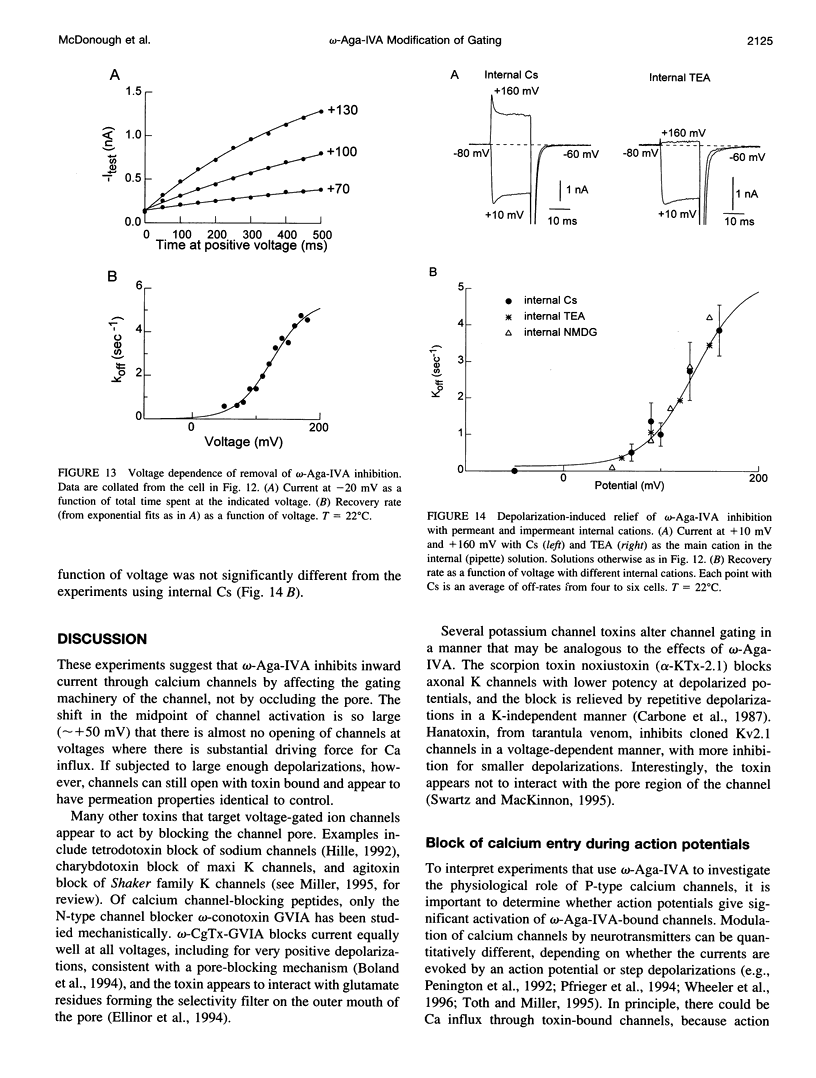
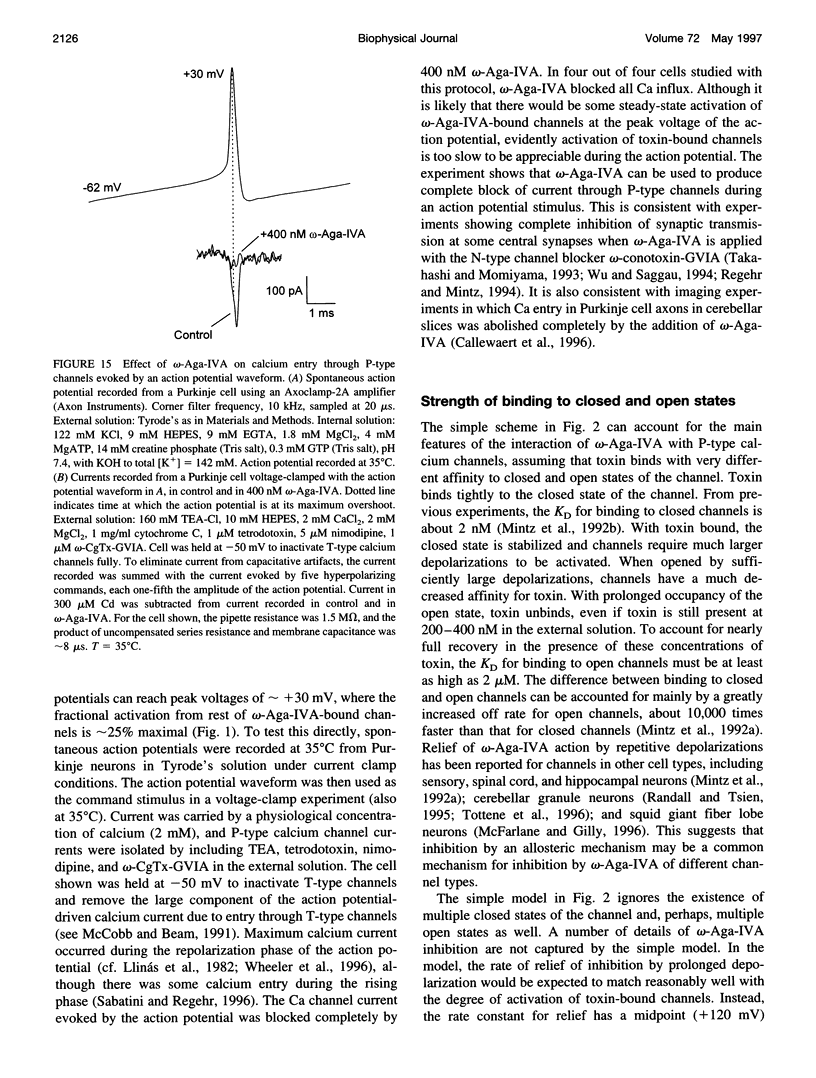
- Regan L. J. Voltage-dependent calcium currents in Purkinje cells from rat cerebellar vermis. J Neurosci. 1991 Jul;11(7):2259–2269. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-07-02259.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regehr W. G., Mintz I. M. Participation of multiple calcium channel types in transmission at single climbing fiber to Purkinje cell synapses. Neuron. 1994 Mar;12(3):605–613. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90216-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabatini B. L., Regehr W. G. Timing of neurotransmission at fast synapses in the mammalian brain. Nature. 1996 Nov 14;384(6605):170–172. doi: 10.1038/384170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigworth F. J. The variance of sodium current fluctuations at the node of Ranvier. J Physiol. 1980 Oct;307:97–129. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swartz K. J., MacKinnon R. An inhibitor of the Kv2.1 potassium channel isolated from the venom of a Chilean tarantula. Neuron. 1995 Oct;15(4):941–949. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90184-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., Momiyama A. Different types of calcium channels mediate central synaptic transmission. Nature. 1993 Nov 11;366(6451):156–158. doi: 10.1038/366156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toth P. T., Miller R. J. Calcium and sodium currents evoked by action potential waveforms in rat sympathetic neurones. J Physiol. 1995 May 15;485(Pt 1):43–57. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tottene A., Moretti A., Pietrobon D. Functional diversity of P-type and R-type calcium channels in rat cerebellar neurons. J Neurosci. 1996 Oct 15;16(20):6353–6363. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-20-06353.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner T. J., Adams M. E., Dunlap K. Calcium channels coupled to glutamate release identified by omega-Aga-IVA. Science. 1992 Oct 9;258(5080):310–313. doi: 10.1126/science.1357749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usowicz M. M., Sugimori M., Cherksey B., Llinás R. P-type calcium channels in the somata and dendrites of adult cerebellar Purkinje cells. Neuron. 1992 Dec;9(6):1185–1199. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90076-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler D. B., Randall A., Tsien R. W. Changes in action potential duration alter reliance of excitatory synaptic transmission on multiple types of Ca2+ channels in rat hippocampus. J Neurosci. 1996 Apr 1;16(7):2226–2237. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-07-02226.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler D. B., Randall A., Tsien R. W. Roles of N-type and Q-type Ca2+ channels in supporting hippocampal synaptic transmission. Science. 1994 Apr 1;264(5155):107–111. doi: 10.1126/science.7832825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L. G., Saggau P. Pharmacological identification of two types of presynaptic voltage-dependent calcium channels at CA3-CA1 synapses of the hippocampus. J Neurosci. 1994 Sep;14(9):5613–5622. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-09-05613.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


