Abstract
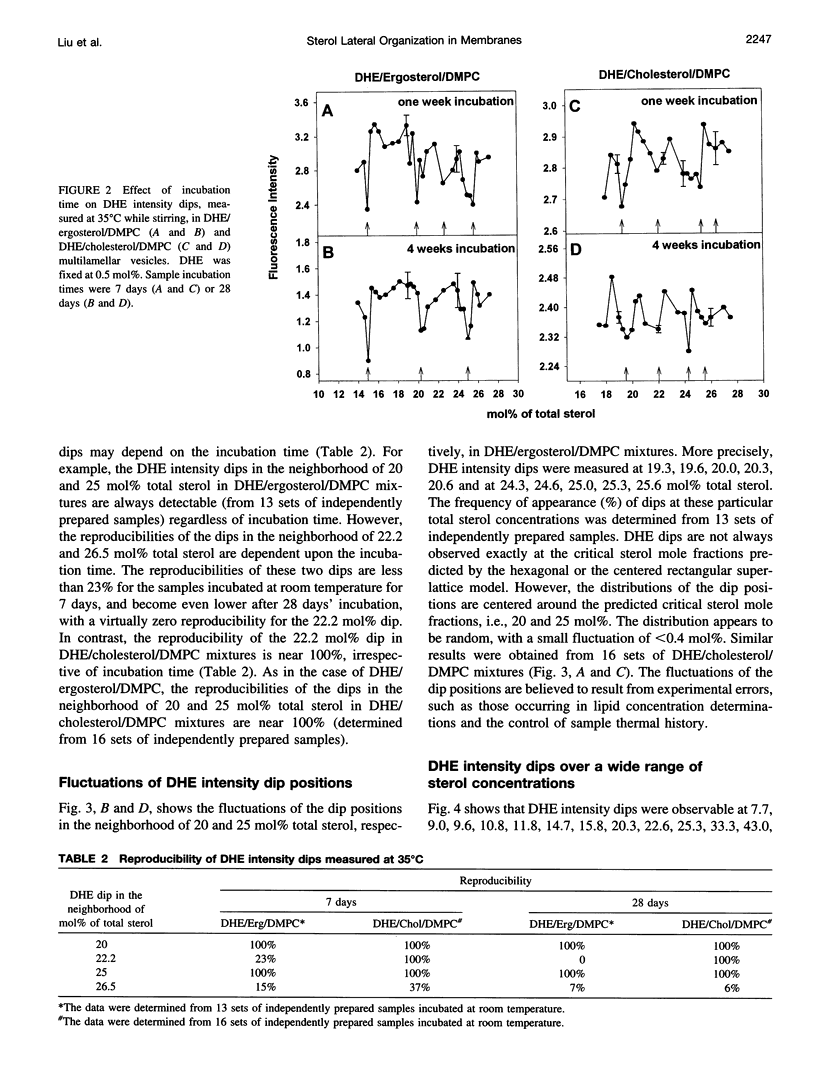
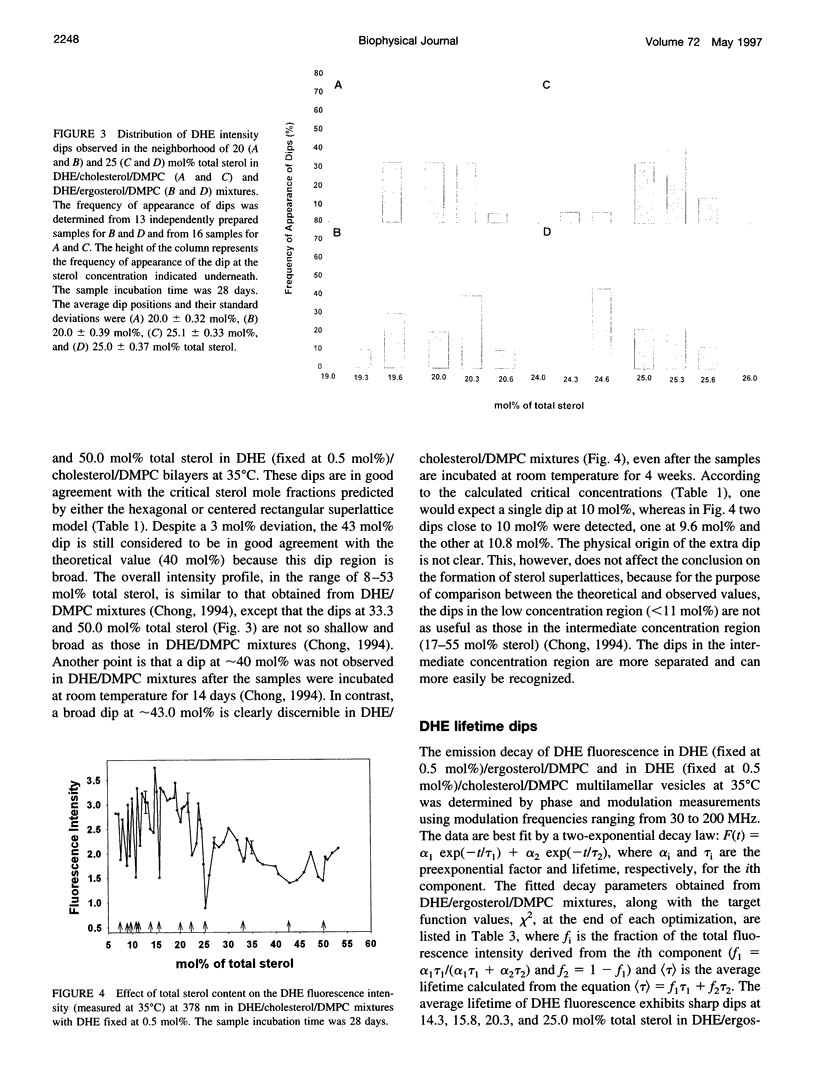
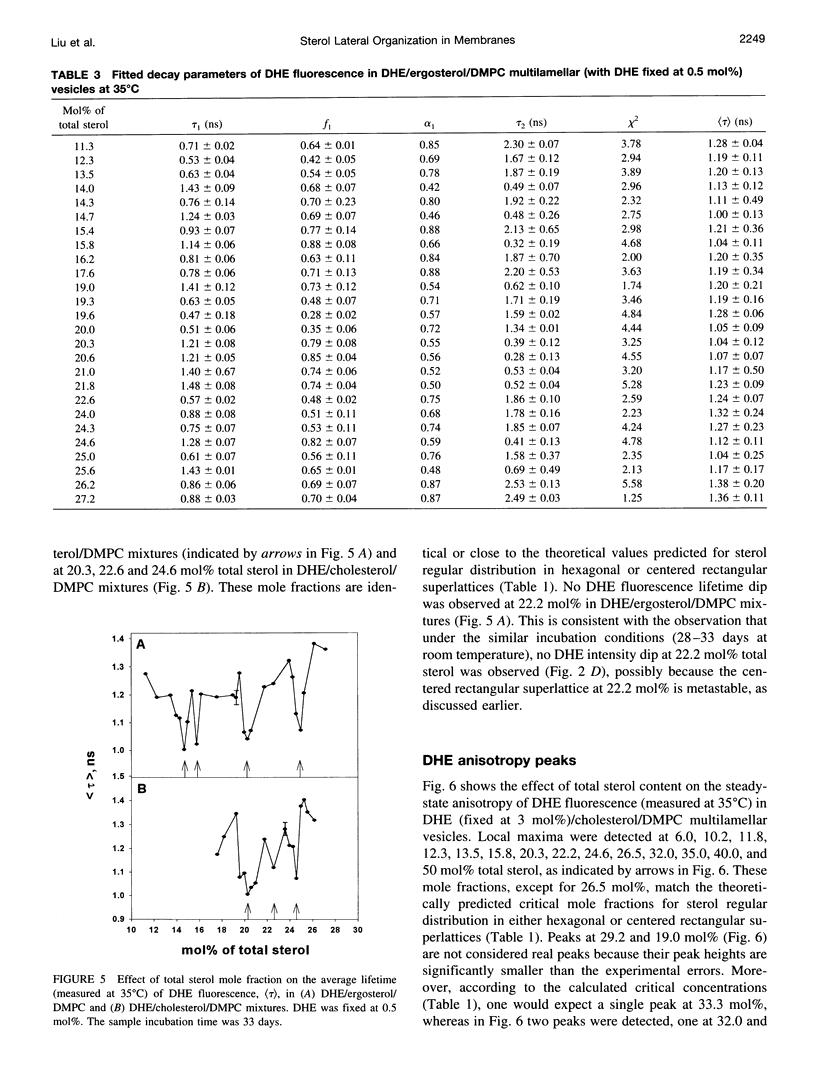
We have examined the fractional sterol concentration dependence of dehydroergosterol (DHE) fluorescence in DHE/cholesterol/dimyristoyl-L-alpha-phosphatidylcholine (DMPC), DHE/ergosterol/DMPC and DHE/cholesterol/dipalmitoyl-L-alpha-phosphatidylcholine (DPPC) liquid-crystalline bilayers. Fluorescence intensity and lifetime exhibit local minima (dips) whenever the total sterol mole fraction, irrespective of the DHE content, is near the critical mole fractions predicted for sterols being regularly distributed in hexagonal superlattices. This result provides evidence that all three of these naturally occurring sterols (e.g., cholesterol, ergosterol, and DHE) can be regularly distributed in the membrane and that the bulky tetracyclic ring of the sterols is the cause of regular distribution. Moreover, at the critical sterol mole fractions, the steady-state anisotropy of DHE fluorescence and the calculated rotational relaxation times exhibit distinct peaks, suggesting that membrane free volume reaches a local minimum at critical sterol mole fractions. This, combined with the well-known sterol condensing effect on lipid acyl chains, provides a new understanding of how variations in membrane sterol content change membrane free volume. In addition to the fluorescence dips/peaks corresponding to hexagonal superlattices, we have observed intermediate fluorescence dips/peaks at concentrations predicted by the centered rectangular superlattice model. However, the 22.2 mol% dip for centered rectangular superlattices in DHE/ergosterol/DMPC mixtures becomes diminished after long incubation (4 weeks), whereas on the same time frame the 22.2 mol% dip in DHE/cholesterol/DMPC mixtures remains discernible, suggesting that although all three of these sterols can be regularly distributed, subtle differences in sterol structure cause changes in lateral sterol organization in the membrane.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almeida P. F., Vaz W. L., Thompson T. E. Lateral diffusion in the liquid phases of dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine/cholesterol lipid bilayers: a free volume analysis. Biochemistry. 1992 Jul 28;31(29):6739–6747. doi: 10.1021/bi00144a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez E., Ruiz-Gutiérrez V., Santa María C., Machado A. Age-dependent modification of lipid composition and lipid structural order parameter of rat peritoneal macrophage membranes. Mech Ageing Dev. 1993 Oct 1;71(1-2):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0047-6374(93)90030-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar L. K., Chong P. L., Barenholz Y., Thompson T. E. Spontaneous transfer between phospholipid bilayers of dehydroergosterol, a fluorescent cholesterol analog. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jul 24;983(1):109–112. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90386-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broadley C., Dawidowicz E., Chong P. L., Hoover R. Modulation of membrane cholesterol levels: effects on endothelial cell function. Exp Cell Res. 1991 Mar;193(1):144–150. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(91)90548-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W. C., Bittman R. Kinetics of association of amphotericin B with vesicles. Biochemistry. 1977 Sep 20;16(19):4145–4149. doi: 10.1021/bi00638a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong P. L. Evidence for regular distribution of sterols in liquid crystalline phosphatidylcholine bilayers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Oct 11;91(21):10069–10073. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.21.10069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong P. L., Tang D., Sugar I. P. Exploration of physical principles underlying lipid regular distribution: effects of pressure, temperature, and radius of curvature on E/M dips in pyrene-labeled PC/DMPC binary mixtures. Biophys J. 1994 Jun;66(6):2029–2038. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80996-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong P. L., Thompson T. E. Depolarization of dehydroergosterol in phospholipid bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Dec 1;863(1):53–62. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90386-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davenport L., Dale R. E., Bisby R. H., Cundall R. B. Transverse location of the fluorescent probe 1,6-diphenyl-1,3,5-hexatriene in model lipid bilayer membrane systems by resonance excitation energy transfer. Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 16;24(15):4097–4108. doi: 10.1021/bi00336a044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes M. P., Chong P. L., Buckley H. R., Pieringer R. A. Fluorescence studies on the molecular action of amphotericin B on susceptible and resistant fungal cells. Biochemistry. 1996 Jun 18;35(24):7983–7992. doi: 10.1021/bi952910c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heiniger H. J., Kandutsch A. A., Chen H. W. Depletion of L-cell sterol depresses endocytosis. Nature. 1976 Oct 7;263(5577):515–517. doi: 10.1038/263515a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoover R. L., Dawidowicz E. A., Robinson J. M., Karnovsky M. J. Role of cholesterol in the capping of surface immunoglobulin receptors on murine lymphocytes. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;97(1):73–80. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.1.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyslop P. A., Morel B., Sauerheber R. D. Organization and interaction of cholesterol and phosphatidylcholine in model bilayer membranes. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 30;29(4):1025–1038. doi: 10.1021/bi00456a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ipsen J. H., Karlström G., Mouritsen O. G., Wennerström H., Zuckermann M. J. Phase equilibria in the phosphatidylcholine-cholesterol system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Nov 27;905(1):162–172. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90020-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jähnig F. Structural order of lipids and proteins in membranes: evaluation of fluorescence anisotropy data. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6361–6365. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao Y. L., Chong P. L., Huang C. H. Time-resolved fluorometric and differential scanning calorimetric investigation of dehydroergosterol in 1-stearoyl-2-caprylphosphatidylcholine bilayers. Biochemistry. 1990 Feb 6;29(5):1315–1322. doi: 10.1021/bi00457a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly S. L., Lamb D. C., Taylor M., Corran A. J., Baldwin B. C., Powderly W. G. Resistance to amphotericin B associated with defective sterol delta 8-->7 isomerase in a Cryptococcus neoformans strain from an AIDS patient. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1994 Sep 15;122(1-2):39–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1994.tb07140.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakowicz J. R., Cherek H., Balter A. Correction of timing errors in photomultiplier tubes used in phase-modulation fluorometry. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1981 Sep;5(3):131–146. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(81)90012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lentz B. R., Barrow D. A., Hoechli M. Cholesterol-phosphatidylcholine interactions in multilamellar vesicles. Biochemistry. 1980 Apr 29;19(9):1943–1954. doi: 10.1021/bi00550a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin H., Huang C. Eutectic phase behavior of 1-stearoyl-2-caprylphosphatidylcholine and dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine mixtures. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Dec 8;946(1):178–184. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90471-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mabrey S., Mateo P. L., Sturtevant J. M. High-sensitivity scanning calorimetric study of mixtures of cholesterol with dimyristoyl- and dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholines. Biochemistry. 1978 Jun 13;17(12):2464–2468. doi: 10.1021/bi00605a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason J. T. Properties of phosphatidylcholine bilayers as revealed by mixed-acyl phospholipid fluorescent probes containing n-(9-anthroyloxy) fatty acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Aug 24;1194(1):99–108. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(94)90207-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeod A. J., Suckling K. E., Walton P. L., Johnson M. Effects of in vitro incorporation of cholesterol and cholesterol analogues into rat platelets. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jun 14;688(2):581–585. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90369-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMullen T. P., McElhaney R. N. New aspects of the interaction of cholesterol with dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine bilayers as revealed by high-sensitivity differential scanning calorimetry. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995 Mar 8;1234(1):90–98. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(94)00266-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melchior D. L., Scavitto F. J., Steim J. M. Dilatometry of dipalmitoyllecithin-cholesterol bilayers. Biochemistry. 1980 Oct 14;19(21):4828–4834. doi: 10.1021/bi00562a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muczynski K. A., Stahl W. L. Incorporation of danyslated phospholipids and dehydroergosterol into membranes using a phospholipid exchange protein. Biochemistry. 1983 Dec 6;22(25):6037–6048. doi: 10.1021/bi00294a052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pal R., Wiener J. R., Barenholz Y., Wagner R. R. Influence of the membrane glycoprotein and cholesterol of vesicular stomatitis virus on the dynamics of viral and model membranes: fluorescence studies. Biochemistry. 1983 Jul 19;22(15):3624–3630. doi: 10.1021/bi00284a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parasassi T., Giusti A. M., Raimondi M., Gratton E. Abrupt modifications of phospholipid bilayer properties at critical cholesterol concentrations. Biophys J. 1995 May;68(5):1895–1902. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80367-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quintão E., Grundy S. M., Ahrens E. H., Jr Effects of dietary cholesterol on the regulation of total body cholesterol in man. J Lipid Res. 1971 Mar;12(2):233–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes Mateo C., Ulises Acuña A., Brochon J. C. Liquid-crystalline phases of cholesterol/lipid bilayers as revealed by the fluorescence of trans-parinaric acid. Biophys J. 1995 Mar;68(3):978–987. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80273-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J., Lee A. G., Wilton D. C. The organisation of cholesterol and ergosterol in lipid bilayers based on studies using non-perturbing fluorescent sterol probes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Mar 23;552(1):23–37. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90243-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder F., Barenholz Y., Gratton E., Thompson T. E. A fluorescence study of dehydroergosterol in phosphatidylcholine bilayer vesicles. Biochemistry. 1987 May 5;26(9):2441–2448. doi: 10.1021/bi00383a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder F., Jefferson J. R., Kier A. B., Knittel J., Scallen T. J., Wood W. G., Hapala I. Membrane cholesterol dynamics: cholesterol domains and kinetic pools. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1991 Mar;196(3):235–252. doi: 10.3181/00379727-196-43185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somerharju P. J., Virtanen J. A., Eklund K. K., Vainio P., Kinnunen P. K. 1-Palmitoyl-2-pyrenedecanoyl glycerophospholipids as membrane probes: evidence for regular distribution in liquid-crystalline phosphatidylcholine bilayers. Biochemistry. 1985 May 21;24(11):2773–2781. doi: 10.1021/bi00332a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang D., Chong P. L. E/M dips. Evidence for lipids regularly distributed into hexagonal super-lattices in pyrene-PC/DMPC binary mixtures at specific concentrations. Biophys J. 1992 Oct;63(4):903–910. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81672-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang D., Wieb van der Meer B., Chen S. Y. Evidence for a regular distribution of cholesterol in phospholipid bilayers from diphenylhexatriene fluorescence. Biophys J. 1995 May;68(5):1944–1951. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80371-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virtanen J. A., Ruonala M., Vauhkonen M., Somerharju P. Lateral organization of liquid-crystalline cholesterol-dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine bilayers. Evidence for domains with hexagonal and centered rectangular cholesterol superlattices. Biochemistry. 1995 Sep 12;34(36):11568–11581. doi: 10.1021/bi00036a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vist M. R., Davis J. H. Phase equilibria of cholesterol/dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine mixtures: 2H nuclear magnetic resonance and differential scanning calorimetry. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 16;29(2):451–464. doi: 10.1021/bi00454a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whetton A. D., Houslay M. D. 5'-Nucleotidase is activated upon cholesterol-depletion of liver plasma membranes. FEBS Lett. 1983 Jun 27;157(1):70–74. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)81118-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeagle P. L., Martin R. B., Lala A. K., Lin H. K., Bloch K. Differential effects of cholesterol and lanosterol on artificial membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4924–4926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




