Abstract
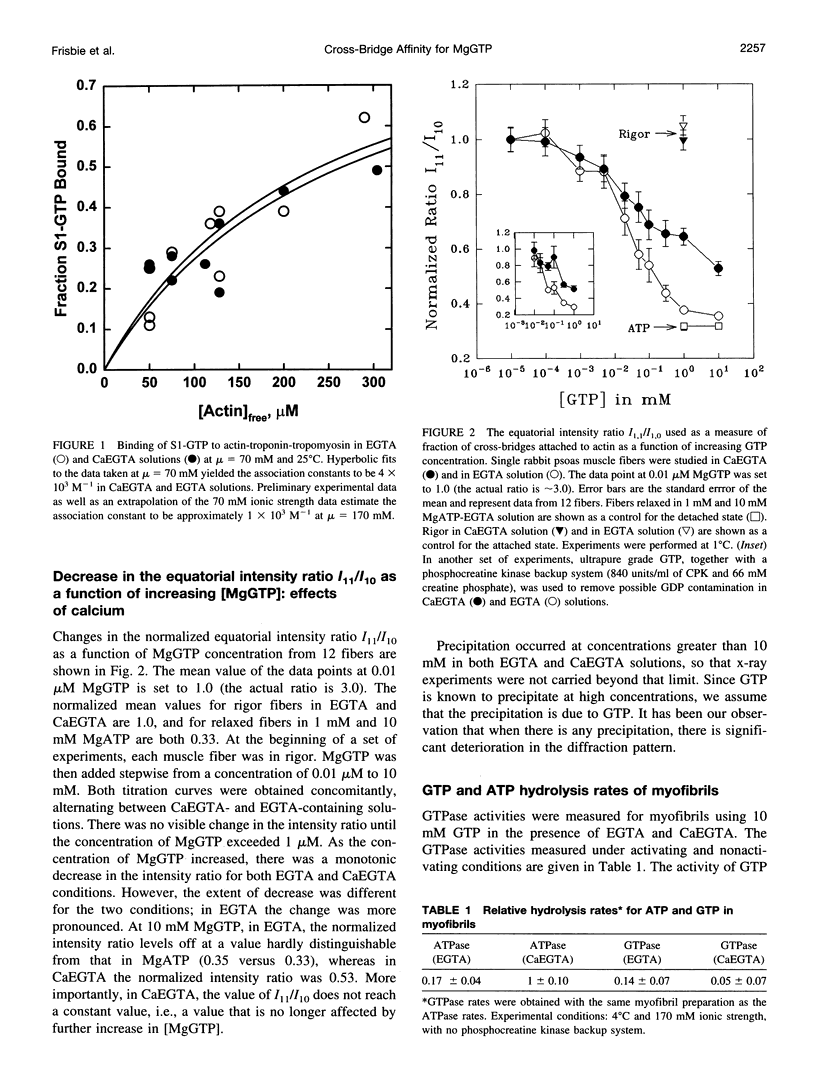
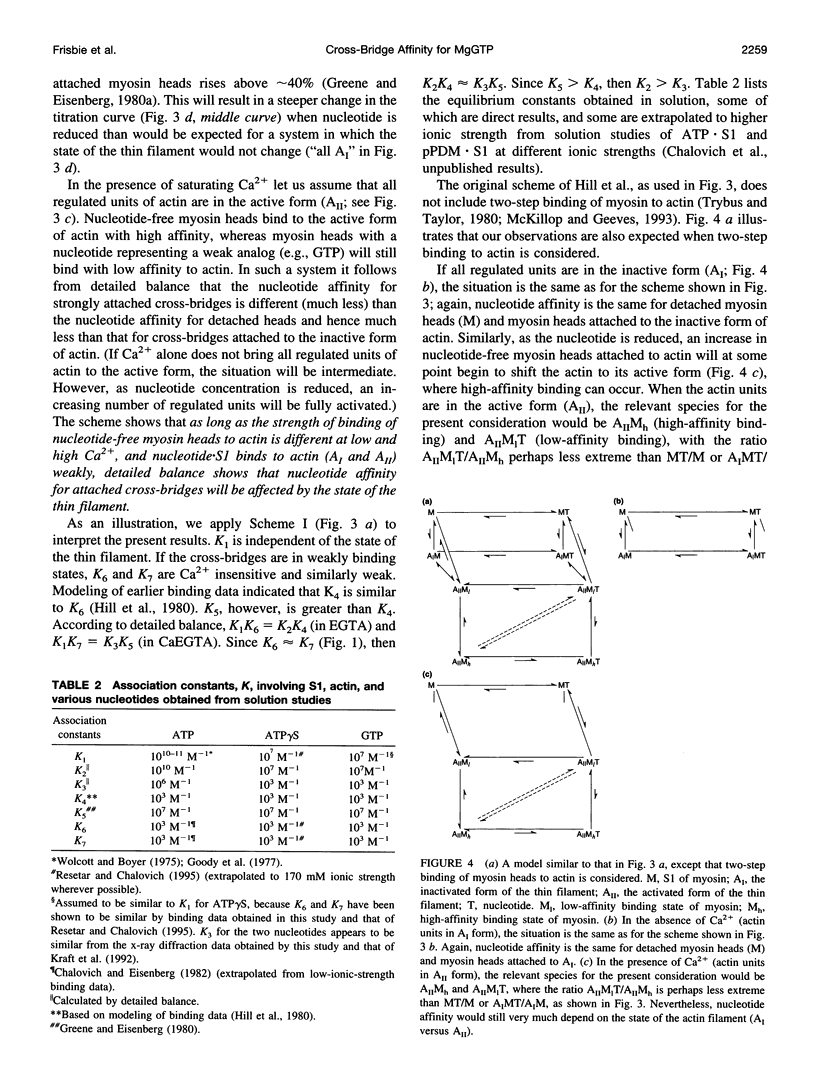
Previously we reported that saturation of cross-bridges with MgATP gamma S in skinned muscle fibers was calcium sensitive. In the present study we investigate whether this observation can be generalized to other nucleotides by studying saturation of cross-bridges with MgGTP. In solution, myosin-subfragment 1 (S1) in the presence of 10 mM MgGTP was found to bind to actin with low affinity, similar to that in the presence of MgATP and MgATP gamma S. In EGTA buffer, the equatorial x-ray diffraction intensity ratio I11/I10 recorded in single skinned fibers decreased upon increasing MgGTP concentration from 0 to 10 mM (1 degree C and 170 mM ionic strength). The I11/I10 ratio leveled off at 10 mM MgGTP, indicating full saturation of cross-bridges with the nucleotide. Under these conditions, the value of I11/I10 is indistinguishable from that obtained in the presence of saturating [MgATP]. In CaEGTA buffer, however, the decrease in I11/I10 occurs over a wider range of concentrations, and there is no indication of I11/I10 leveling off at 10 mM MgGTP, suggesting that full saturation is not reached. The Ca2+ dependence of GTP binding appears to be a direct consequence of the differences in the affinities of the strongly bound cross-bridges to actin versus weakly bound cross-bridges to actin. A biochemical scheme that could qualitatively explain the titration behavior of ATP gamma S and GTP is presented.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brenner B., Schoenberg M., Chalovich J. M., Greene L. E., Eisenberg E. Evidence for cross-bridge attachment in relaxed muscle at low ionic strength. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7288–7291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B., Yu L. C., Chalovich J. M. Parallel inhibition of active force and relaxed fiber stiffness in skeletal muscle by caldesmon: implications for the pathway to force generation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5739–5743. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B., Yu L. C., Podolsky R. J. X-ray diffraction evidence for cross-bridge formation in relaxed muscle fibers at various ionic strengths. Biophys J. 1984 Sep;46(3):299–306. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84026-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalovich J. M. Actin mediated regulation of muscle contraction. Pharmacol Ther. 1992;55(2):95–148. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(92)90013-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalovich J. M., Eisenberg E. Inhibition of actomyosin ATPase activity by troponin-tropomyosin without blocking the binding of myosin to actin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2432–2437. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dantzig J. A., Walker J. W., Trentham D. R., Goldman Y. E. Relaxation of muscle fibers with adenosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate (ATP[gamma S]) and by laser photolysis of caged ATP[gamma S]: evidence for Ca2+-dependent affinity of rapidly detaching zero-force cross-bridges. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6716–6720. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg E., Hill T. L. Muscle contraction and free energy transduction in biological systems. Science. 1985 Mar 1;227(4690):999–1006. doi: 10.1126/science.3156404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goody R. S., Hofmann W., Mannherz G. H. The binding constant of ATP to myosin S1 fragment. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Sep;78(2):317–324. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11742.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. E., Eisenberg E. Dissociation of the actin.subfragment 1 complex by adenyl-5'-yl imidodiphosphate, ADP, and PPi. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 25;255(2):543–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. E., Eisenberg E. Relationship between regulated actomyosin ATPase activity and cooperative binding of myosin to regulated actin. Cell Biophys. 1988 Jan-Jun;12:59–71. doi: 10.1007/BF02918350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. L., Eisenberg E., Chalovich J. M. Theoretical models for cooperative steady-state ATPase activity of myosin subfragment-1 on regulated actin. Biophys J. 1981 Jul;35(1):99–112. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84777-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. L., Eisenberg E., Greene L. Theoretical model for the cooperative equilibrium binding of myosin subfragment 1 to the actin-troponin-tropomyosin complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3186–3190. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. L. Theoretical formalism for the sliding filament model of contraction of striated muscle. Part I. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1974;28:267–340. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(74)90020-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraft T., Chalovich J. M., Yu L. C., Brenner B. Parallel inhibition of active force and relaxed fiber stiffness by caldesmon fragments at physiological ionic strength and temperature conditions: additional evidence that weak cross-bridge binding to actin is an essential intermediate for force generation. Biophys J. 1995 Jun;68(6):2404–2418. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80423-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraft T., Yu L. C., Kuhn H. J., Brenner B. Effect of Ca2+ on weak cross-bridge interaction with actin in the presence of adenosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11362–11366. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lymn R. W. Myosin subfragment-1 attachment to actin. Expected effect on equatorial reflections. Biophys J. 1978 Jan;21(1):93–98. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85510-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malinchik S., Yu L. C. Analysis of equatorial x-ray diffraction patterns from muscle fibers: factors that affect the intensities. Biophys J. 1995 May;68(5):2023–2031. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80379-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKillop D. F., Geeves M. A. Regulation of the interaction between actin and myosin subfragment 1: evidence for three states of the thin filament. Biophys J. 1993 Aug;65(2):693–701. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81110-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pate E., Franks-Skiba K., White H., Cooke R. The use of differing nucleotides to investigate cross-bridge kinetics. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 15;268(14):10046–10053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pate E., Nakamaye K. L., Franks-Skiba K., Yount R. G., Cooke R. Mechanics of glycerinated muscle fibers using nonnucleoside triphosphate substrates. Biophys J. 1991 Mar;59(3):598–605. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82275-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resetar A. M., Chalovich J. M. Adenosine 5'-(gamma-thiotriphosphate): an ATP analog that should be used with caution in muscle contraction studies. Biochemistry. 1995 Dec 12;34(49):16039–16045. doi: 10.1021/bi00049a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trybus K. M., Taylor E. W. Kinetic studies of the cooperative binding of subfragment 1 to regulated actin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7209–7213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D., Pate E., Cooke R., Yount R. Synthesis of non-nucleotide ATP analogues and characterization of their chemomechanical interaction with muscle fibres. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1993 Oct;14(5):484–497. doi: 10.1007/BF00297211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolcott R. G., Boyer P. D. Isotopic probes of catalytic steps of myosin adenosine triphosphatase. J Supramol Struct. 1975;3(2):154–161. doi: 10.1002/jss.400030208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu L. C., Brenner B. Structures of actomyosin crossbridges in relaxed and rigor muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1989 Mar;55(3):441–453. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82838-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


