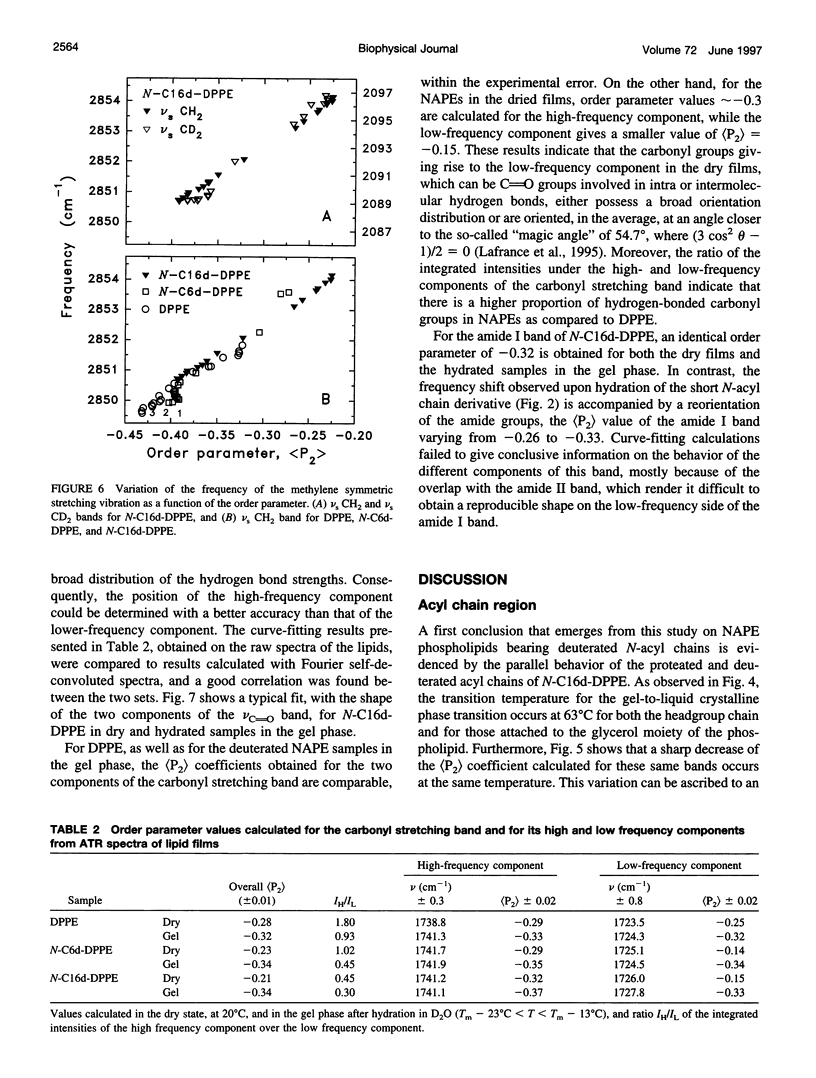
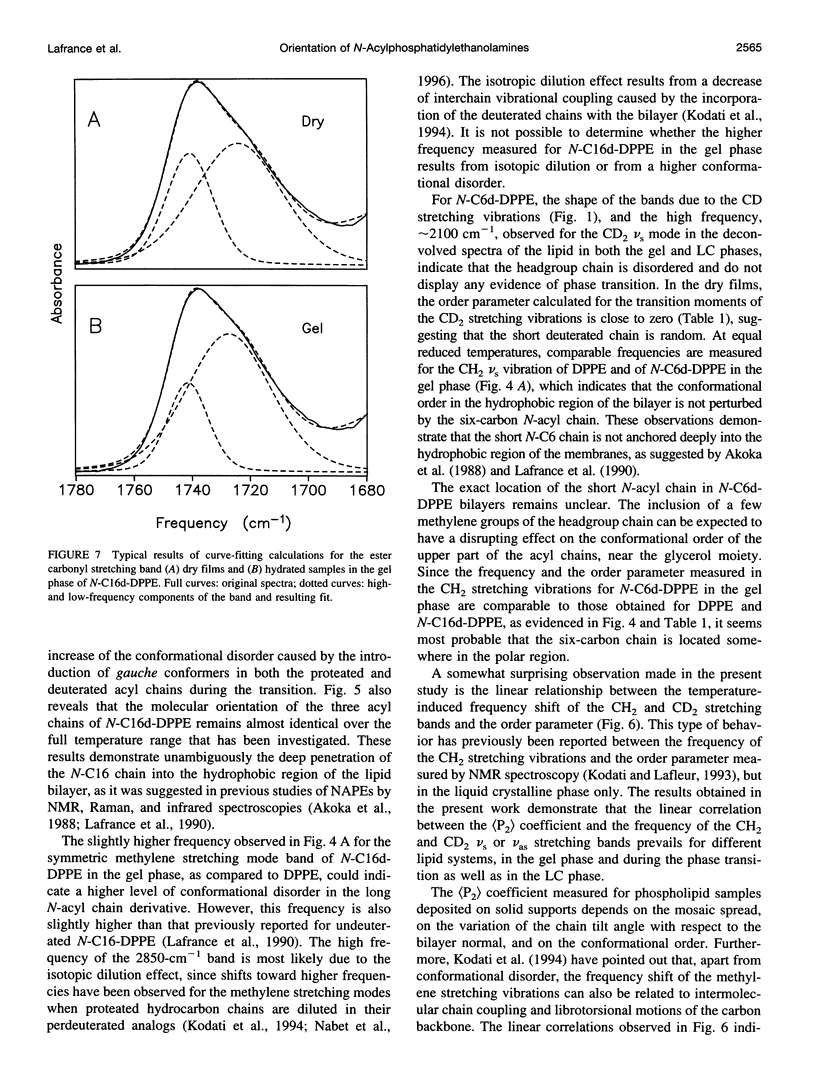
Abstract
N-Acylphosphatidylethanolamines, or NAPEs, are found in tissues involved in degenerating processes, such as dehydrated endosperm of seeds, erythrocyte membranes, or cell injury. To determine the conformation and orientation of the acyl chains of these phospholipids, NAPEs with deuterated N-acyl chains of 6 and 16 carbon atoms were synthesized and studied by transmission and attenuated total reflectance (ATR) infrared spectroscopy. For N-C16d-DPPE, the ATR measurements show that the N-acyl chain has the same orientation as the two acyl chains attached to the glycerol moiety, while the N-acyl chain of N-C6d-DPPE is randomly oriented. These results demonstrate that for N-C16d-DPPE, the N-acyl chain is embedded into the hydrophobic core of the bilayer, while for the short chain derivative the N-acyl chain remains in the lipid headgroup region. The analysis of the carbonyl stretching band and of the amide I band suggests that, for the long N-acyl chain lipid, the ester C=O and the N-H groups are linked by intermolecular hydrogen bonds.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akutsu H., Kyogoku Y. Conformational analysis of phosphatidylethanol-amine in multilayers by infrared dichroism. Chem Phys Lipids. 1975 Nov;15(2):222–242. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(75)90045-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asher I. M., Levin I. W. Effects of temperature and molecular interactions on the vibrational infrared spectra of phospholipid vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jul 4;468(1):63–72. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90151-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blume A., Hübner W., Messner G. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy of 13C = O-labeled phospholipids hydrogen bonding to carbonyl groups. Biochemistry. 1988 Oct 18;27(21):8239–8249. doi: 10.1021/bi00421a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bomstein R. A. A new class of phosphatides isolated from soft wheat flour. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Oct 8;21(1):49–54. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90424-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. M., Steers J., Hui S. W., Yeagle P. L., Silvius J. R. Role of head group structure in the phase behavior of amino phospholipids. 2. Lamellar and nonlamellar phases of unsaturated phosphatidylethanolamine analogues. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 29;25(15):4259–4267. doi: 10.1021/bi00363a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casal H. L., Mantsch H. H. Polymorphic phase behaviour of phospholipid membranes studied by infrared spectroscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Dec 4;779(4):381–401. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(84)90017-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman K. D., Moore T. S., Jr N-acylphosphatidylethanolamine synthesis in plants: occurrence, molecular composition, and phospholipid origin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1993 Feb 15;301(1):21–33. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1993.1110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark N. A., Rothschild K. J., Luippold D. A., Simon B. A. Surface-induced lamellar orientation of multilayer membrane arrays. Theoretical analysis and a new method with application to purple membrane fragments. Biophys J. 1980 Jul;31(1):65–96. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85041-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domingo J. C., Mora M., Africa de Madariaga M. Role of headgroup structure in the phase behaviour of N-acylethanolamine phospholipids: hydrogen-bonding ability and headgroup size. Chem Phys Lipids. 1994 Mar 1;69(3):229–240. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(94)90004-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fringeli U. P., Günthard H. H. Infrared membrane spectroscopy. Mol Biol Biochem Biophys. 1981;31:270–332. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-81537-9_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fringeli U. P. The structure of lipids and proteins studied by attenuated total reflection (ATR) infrared spectroscopy. II. Oriented layers of a homologous series: phosphatidylethanolamine to phosphatidylcholine. Z Naturforsch C. 1977 Jan-Feb;32(1-2):20–45. doi: 10.1515/znc-1977-1-205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser H., Pascher I., Pearson R. H., Sundell S. Preferred conformation and molecular packing of phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylcholine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jun 16;650(1):21–51. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(81)90007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. B., Mason R., Thomas K. M., Shipley G. G. Structural chemistry of 1,2 dilauroyl-DL-phosphatidylethanolamine: molecular conformation and intermolecular packing of phospholipids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):3036–3040. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.3036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodati V. R., Lafleur M. Comparison between orientational and conformational orders in fluid lipid bilayers. Biophys J. 1993 Jan;64(1):163–170. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81351-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafrance D., Marion D., Pézolet M. Study of the structure of N-acyldipalmitoylphosphatidylethanolamines in aqueous dispersion by infrared and Raman spectroscopies. Biochemistry. 1990 May 15;29(19):4592–4599. doi: 10.1021/bi00471a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. N., McElhaney R. N., Pohle W., Mantsch H. H. Components of the carbonyl stretching band in the infrared spectra of hydrated 1,2-diacylglycerolipid bilayers: a reevaluation. Biophys J. 1994 Dec;67(6):2367–2375. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80723-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantsch H. H., McElhaney R. N. Phospholipid phase transitions in model and biological membranes as studied by infrared spectroscopy. Chem Phys Lipids. 1991 Mar;57(2-3):213–226. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(91)90077-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh T. J. Differences in hydrocarbon chain tilt between hydrated phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylcholine bilayers. A molecular packing model. Biophys J. 1980 Feb;29(2):237–245. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85128-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabet A., Boggs J. M., Pézolet M. Study by infrared spectroscopy of the interdigitation of C26:0 cerebroside sulfate into phosphatidylcholine bilayers. Biochemistry. 1996 May 28;35(21):6674–6683. doi: 10.1021/bi952824c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman J. L., Stiers D. L., Anderson W. H., Schmid H. H. Phase behavior of synthetic N-acylethanolamine phospholipids. Chem Phys Lipids. 1986 Dec 31;42(4):249–260. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(86)90084-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothschild K. J., Clark N. A. Polarized infrared spectroscopy of oriented purple membrane. Biophys J. 1979 Mar;25(3):473–487. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85317-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tristram-Nagle S., Zhang R., Suter R. M., Worthington C. R., Sun W. J., Nagle J. F. Measurement of chain tilt angle in fully hydrated bilayers of gel phase lecithins. Biophys J. 1993 Apr;64(4):1097–1109. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81475-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


