Abstract
Although the statistical thermodynamics of noncovalent binding has been considered in a number of theoretical papers, few methods of computing binding affinities are derived explicitly from this underlying theory. This has contributed to uncertainty and controversy in certain areas. This article therefore reviews and extends the connections of some important computational methods with the underlying statistical thermodynamics. A derivation of the standard free energy of binding forms the basis of this review. This derivation should be useful in formulating novel computational methods for predicting binding affinities. It also permits several important points to be established. For example, it is found that the double-annihilation method of computing binding energy does not yield the standard free energy of binding, but can be modified to yield this quantity. The derivation also makes it possible to define clearly the changes in translational, rotational, configurational, and solvent entropy upon binding. It is argued that molecular mass has a negligible effect upon the standard free energy of binding for biomolecular systems, and that the cratic entropy defined by Gurney is not a useful concept. In addition, the use of continuum models of the solvent in binding calculations is reviewed, and a formalism is presented for incorporating a limited number of solvent molecules explicitly.
Full text
PDF




















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ajay, Murcko M. A. Computational methods to predict binding free energy in ligand-receptor complexes. J Med Chem. 1995 Dec 22;38(26):4953–4967. doi: 10.1021/jm00026a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. R., Craik D. J., Martin J. L. Functional group contributions to drug-receptor interactions. J Med Chem. 1984 Dec;27(12):1648–1657. doi: 10.1021/jm00378a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appelt K., Bacquet R. J., Bartlett C. A., Booth C. L., Freer S. T., Fuhry M. A., Gehring M. R., Herrmann S. M., Howland E. F., Janson C. A. Design of enzyme inhibitors using iterative protein crystallographic analysis. J Med Chem. 1991 Jul;34(7):1925–1934. doi: 10.1021/jm00111a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bash P. A., Singh U. C., Langridge R., Kollman P. A. Free energy calculations by computer simulation. Science. 1987 May 1;236(4801):564–568. doi: 10.1126/science.3576184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Shaul A., Ben-Tal N., Honig B. Statistical thermodynamic analysis of peptide and protein insertion into lipid membranes. Biophys J. 1996 Jul;71(1):130–137. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79208-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge D. L., DiCapua F. M. Free energy via molecular simulation: applications to chemical and biomolecular systems. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1989;18:431–492. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.18.060189.002243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhm H. J. The development of a simple empirical scoring function to estimate the binding constant for a protein-ligand complex of known three-dimensional structure. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 1994 Jun;8(3):243–256. doi: 10.1007/BF00126743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chothia C., Janin J. Principles of protein-protein recognition. Nature. 1975 Aug 28;256(5520):705–708. doi: 10.1038/256705a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen N. C., Blaney J. M., Humblet C., Gund P., Barry D. C. Molecular modeling software and methods for medicinal chemistry. J Med Chem. 1990 Mar;33(3):883–894. doi: 10.1021/jm00165a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman P. M. Structure-based drug design. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1994 Dec;4(6):868–874. doi: 10.1016/0959-440x(94)90268-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg D., McLachlan A. D. Solvation energy in protein folding and binding. Nature. 1986 Jan 16;319(6050):199–203. doi: 10.1038/319199a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson H. P. Co-operativity in protein-protein association. The structure and stability of the actin filament. J Mol Biol. 1989 Apr 5;206(3):465–474. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90494-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein A. V., Janin J. The price of lost freedom: entropy of bimolecular complex formation. Protein Eng. 1989 Oct;3(1):1–3. doi: 10.1093/protein/3.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilson M. K. Multiple-site titration and molecular modeling: two rapid methods for computing energies and forces for ionizable groups in proteins. Proteins. 1993 Mar;15(3):266–282. doi: 10.1002/prot.340150305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greer J., Erickson J. W., Baldwin J. J., Varney M. D. Application of the three-dimensional structures of protein target molecules in structure-based drug design. J Med Chem. 1994 Apr 15;37(8):1035–1054. doi: 10.1021/jm00034a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross M., Jaenicke R. Proteins under pressure. The influence of high hydrostatic pressure on structure, function and assembly of proteins and protein complexes. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Apr 15;221(2):617–630. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb18774.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtzer A. The "cratic correction" and related fallacies. Biopolymers. 1995 Jun;35(6):595–602. doi: 10.1002/bip.360350605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton N., Lewis M. Calculation of the free energy of association for protein complexes. Protein Sci. 1992 Jan;1(1):169–181. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560010117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janin J., Chothia C. Role of hydrophobicity in the binding of coenzymes. Appendix. Translational and rotational contribution to the free energy of dissociation. Biochemistry. 1978 Jul 25;17(15):2943–2948. doi: 10.1021/bi00608a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janin J. Elusive affinities. Proteins. 1995 Jan;21(1):30–39. doi: 10.1002/prot.340210105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAUZMANN W. Some factors in the interpretation of protein denaturation. Adv Protein Chem. 1959;14:1–63. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60608-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthew J. B., Gurd F. R., Garcia-Moreno B., Flanagan M. A., March K. L., Shire S. J. pH-dependent processes in proteins. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1985;18(2):91–197. doi: 10.3109/10409238509085133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto S., Kollman P. A. Absolute and relative binding free energy calculations of the interaction of biotin and its analogs with streptavidin using molecular dynamics/free energy perturbation approaches. Proteins. 1993 Jul;16(3):226–245. doi: 10.1002/prot.340160303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto S., Kollman P. A. What determines the strength of noncovalent association of ligands to proteins in aqueous solution? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8402–8406. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morild E. The theory of pressure effects on enzymes. Adv Protein Chem. 1981;34:93–166. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60519-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
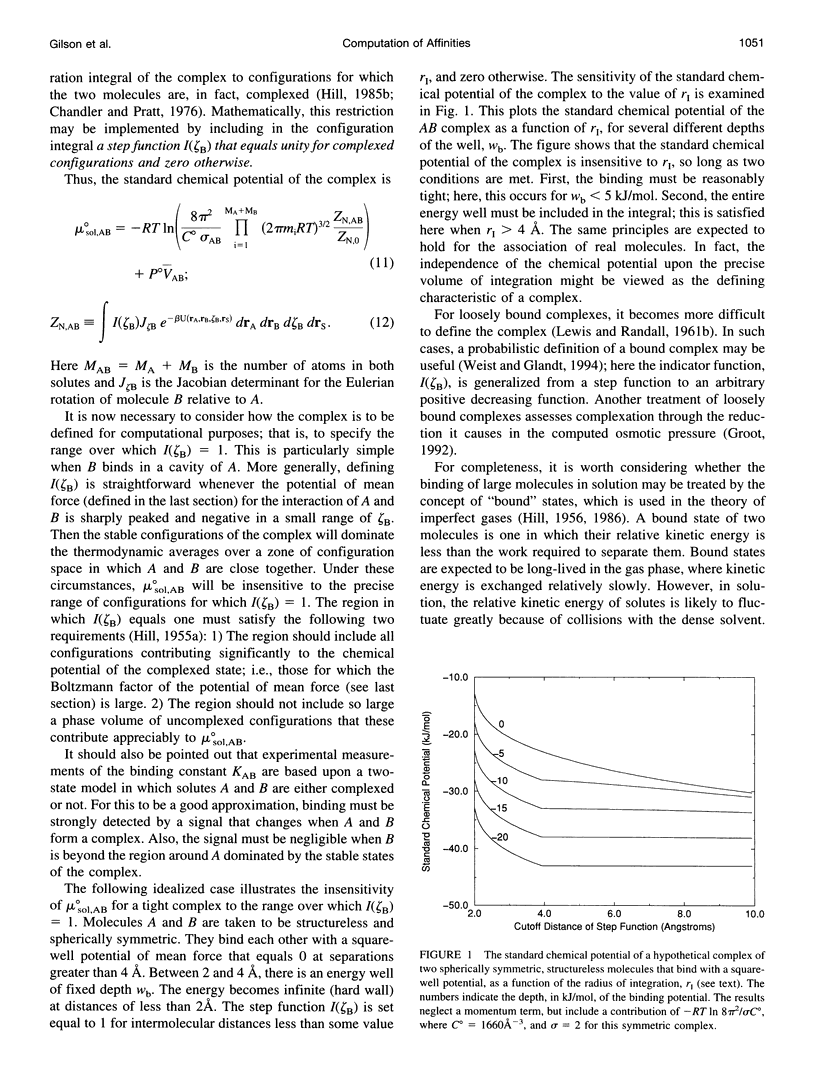
- Morton A., Baase W. A., Matthews B. W. Energetic origins of specificity of ligand binding in an interior nonpolar cavity of T4 lysozyme. Biochemistry. 1995 Jul 11;34(27):8564–8575. doi: 10.1021/bi00027a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy K. P., Xie D., Garcia K. C., Amzel L. M., Freire E. Structural energetics of peptide recognition: angiotensin II/antibody binding. Proteins. 1993 Feb;15(2):113–120. doi: 10.1002/prot.340150203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy K. P., Xie D., Thompson K. S., Amzel L. M., Freire E. Entropy in biological binding processes: estimation of translational entropy loss. Proteins. 1994 Jan;18(1):63–67. doi: 10.1002/prot.340180108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller K., Lüdemann H. D., Jaenicke R. Pressure-induced structural changes of pig heart lactic dehydrogenase. Biophys Chem. 1981 Oct;14(2):101–110. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(81)85011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotny J., Bruccoleri R. E., Saul F. A. On the attribution of binding energy in antigen-antibody complexes McPC 603, D1.3, and HyHEL-5. Biochemistry. 1989 May 30;28(11):4735–4749. doi: 10.1021/bi00437a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page M. I., Jencks W. P. Entropic contributions to rate accelerations in enzymic and intramolecular reactions and the chelate effect. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Aug;68(8):1678–1683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.8.1678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux B., Nina M., Pomès R., Smith J. C. Thermodynamic stability of water molecules in the bacteriorhodopsin proton channel: a molecular dynamics free energy perturbation study. Biophys J. 1996 Aug;71(2):670–681. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79267-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEINBERG I. Z., SCHERAGA H. A. Entropy changes accompanying association reactions of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1963 Jan;238:172–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schade B. C., Lüdemann H. D., Rudolph R., Jaenicke R. Kinetics of reconstitution of porcein muscle lactic dehydrogenase after reversible high pressure dissociation. Biophys Chem. 1980 Apr;11(2):257–263. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(80)80028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schade B. C., Rudolph R., Lüdemann H. D., Jaenicke R. Reversible high-pressure dissociation of lactic dehydrogenase from pig muscle. Biochemistry. 1980 Mar 18;19(6):1121–1126. doi: 10.1021/bi00547a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoup D., Szabo A. Role of diffusion in ligand binding to macromolecules and cell-bound receptors. Biophys J. 1982 Oct;40(1):33–39. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84455-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sneddon S. F., Tobias D. J., Brooks C. L., 3rd Thermodynamics of amide hydrogen bond formation in polar and apolar solvents. J Mol Biol. 1989 Oct 20;209(4):817–820. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90609-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spolar R. S., Record M. T., Jr Coupling of local folding to site-specific binding of proteins to DNA. Science. 1994 Feb 11;263(5148):777–784. doi: 10.1126/science.8303294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tidor B., Karplus M. The contribution of vibrational entropy to molecular association. The dimerization of insulin. J Mol Biol. 1994 May 6;238(3):405–414. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WYMAN J. THE BINDING POTENTIAL, A NEGLECTED LINKAGE CONCEPT. J Mol Biol. 1965 Mar;11:631–644. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80017-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weng Z., Vajda S., Delisi C. Prediction of protein complexes using empirical free energy functions. Protein Sci. 1996 Apr;5(4):614–626. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560050406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang A. S., Honig B. On the pH dependence of protein stability. J Mol Biol. 1993 May 20;231(2):459–474. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang L., Hermans J. Hydrophilicity of cavities in proteins. Proteins. 1996 Apr;24(4):433–438. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0134(199604)24:4<433::AID-PROT3>3.0.CO;2-F. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng C., Wong C. F., McCammon J. A., Wolynes P. G. Quantum simulation of ferrocytochrome c. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):726–728. doi: 10.1038/334726a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Freyberg B., Richmond T. J., Braun W. Surface area included in energy refinement of proteins. A comparative study on atomic solvation parameters. J Mol Biol. 1993 Sep 20;233(2):275–292. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


