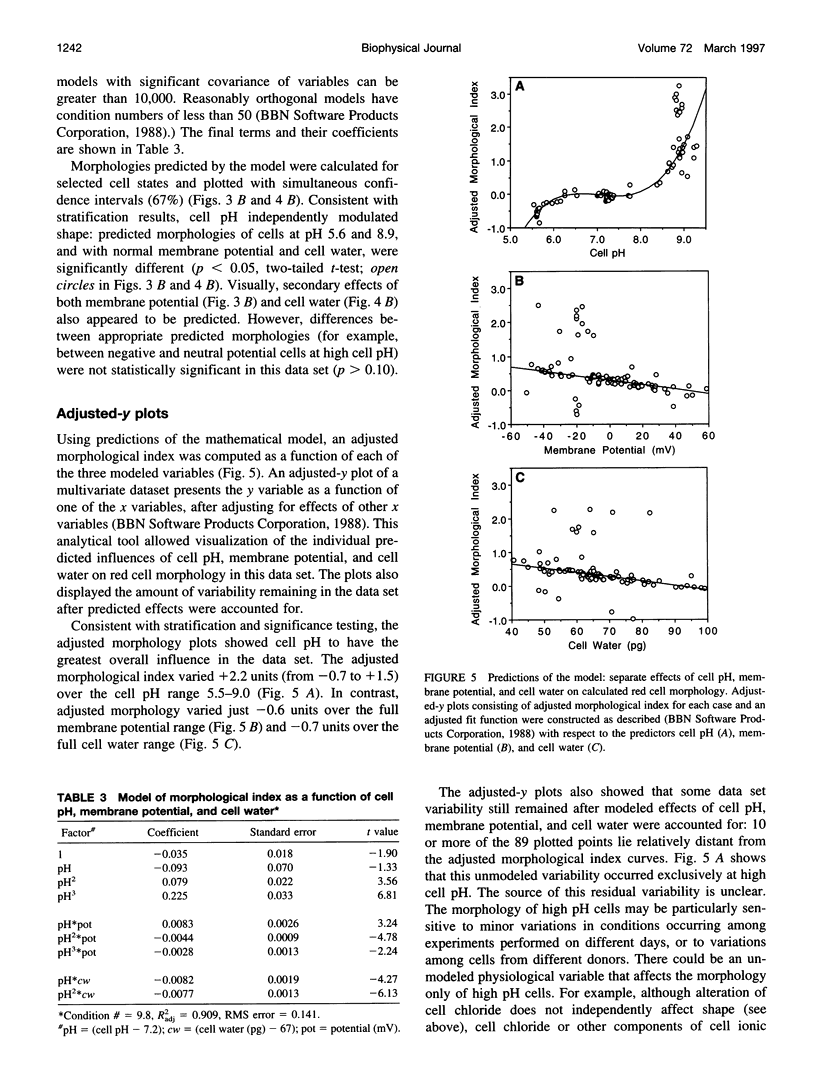
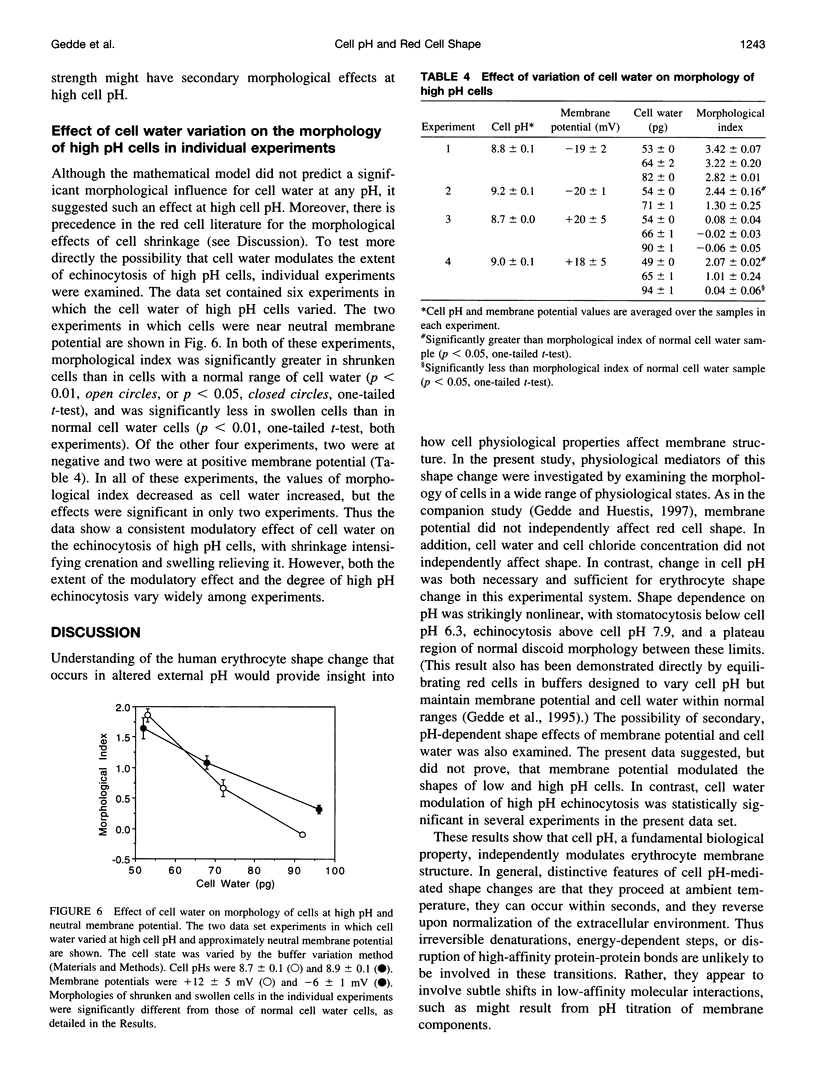
Abstract
Altered external pH transforms human erythrocytes from discocytes to stomatocytes (low pH) or echinocytes (high pH). The mechanism of this transformation is unknown. The preceding companion study (Gedde and Huestis) demonstrated that these shape changes are not mediated by changes in membrane potential, as has been reported. The aim of this study was to identify the physiological properties that mediate this shape change. Red cells were placed in a wide range of physiological states by manipulation of buffer pH, chloride concentration, and osmolality. Morphology and four potential predictor properties (cell pH, membrane potential, cell water, and cell chloride concentration) were assayed. Analysis of the data set by stratification and nonlinear multivariate modeling showed that change in neither cell water nor cell chloride altered the morphology of normal pH cells. In contrast, change in cell pH caused shape change in normal-range membrane potential and cell water cells. The results show that change in cytoplasmic pH is both necessary and sufficient for the shape changes of human erythrocytes equilibrated in altered pH environments.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernhardt I., Donath E., Glaser R. Influence of surface charge and transmembrane potential on rubidium-86 efflux of human red blood cells. J Membr Biol. 1984;78(3):249–255. doi: 10.1007/BF01925972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernhardt I., Erdmann A., Vogel R., Glaser R. Factors involved in the increase of K+ efflux of erythrocytes in low chloride media. Biomed Biochim Acta. 1987;46(2-3):S36–S40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessis M., Prenant M. Topographie de l'apparition des spicules dans les érythrocytes crénelés (échinocytes. Nouv Rev Fr Hematol. 1972 May-Jun;12(3):351–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busa W. B. Mechanisms and consequences of pH-mediated cell regulation. Annu Rev Physiol. 1986;48:389–402. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.48.030186.002133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busa W. B., Nuccitelli R. Metabolic regulation via intracellular pH. Am J Physiol. 1984 Apr;246(4 Pt 2):R409–R438. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1984.246.4.R409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgsaeter A., Branton D. Intramembrane particle aggregation in erythrocyte ghosts. I. The effects of protein removal. J Cell Biol. 1974 Dec;63(3):1018–1036. doi: 10.1083/jcb.63.3.1018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgsaeter A., Shotton D. M., Branton D. Intramembrane particle aggregation in erythrocyte ghosts. II. The influence of spectrin aggregation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Feb 19;426(1):101–122. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90433-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgsaeter A., Stokke B. T., Mikkelsen A., Branton D. The molecular basis of erythrocyte shape. Science. 1986 Dec 5;234(4781):1217–1223. doi: 10.1126/science.3775380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrell J. E., Jr, Lee K. J., Huestis W. H. Membrane bilayer balance and erythrocyte shape: a quantitative assessment. Biochemistry. 1985 Jun 4;24(12):2849–2857. doi: 10.1021/bi00333a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman J. C., Hoffman J. F. Ionic and osmotic equilibria of human red blood cells treated with nystatin. J Gen Physiol. 1979 Aug;74(2):157–185. doi: 10.1085/jgp.74.2.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gedde M. M., Yang E., Huestis W. H. Shape response of human erythrocytes to altered cell pH. Blood. 1995 Aug 15;86(4):1595–1599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser R. The shape of red blood cells as a function of membrane potential and temperature. J Membr Biol. 1979 Dec 31;51(3-4):217–228. doi: 10.1007/BF01869085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann A., Müller P. Ionic strength-dependent alterations of membrane structure of red blood cells. Biosci Rep. 1986 Nov;6(11):1007–1015. doi: 10.1007/BF01114978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huestis W. H., Raftery M. A. Observation of cooperative ionizations in hemoglobin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1887–1891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. M., Taylor G., Meyer D. B. Shape and volume changes in erythrocyte ghosts and spectrin-actin networks. J Cell Biol. 1980 Aug;86(2):371–376. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.2.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. S., Knauf P. A. Mechanism of the increase in cation permeability of human erythrocytes in low-chloride media. Involvement of the anion transport protein capnophorin. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Nov;86(5):721–738. doi: 10.1085/jgp.86.5.721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange Y., Hadesman R. A., Steck T. L. Role of the reticulum in the stability and shape of the isolated human erythrocyte membrane. J Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;92(3):714–721. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.3.714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohandas N., Chasis J. A., Shohet S. B. The influence of membrane skeleton on red cell deformability, membrane material properties, and shape. Semin Hematol. 1983 Jul;20(3):225–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mombers C., de Gier J., Demel R. A., van Deenen L. L. Spectrin-phospholipid interaction. A monolayer study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Dec 2;603(1):52–62. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90390-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao M., Jinbu Y., Sato S., Ishigami Y., Nakao T., Ito-Ueno E., Wake K. Structure and function of red cell cytoskeleton. Biomed Biochim Acta. 1987;46(2-3):S5–S9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinto da Silva P. Translational mobility of the membrane intercalated particles of human erythrocyte ghosts. pH-dependent, reversible aggregation. J Cell Biol. 1972 Jun;53(3):777–787. doi: 10.1083/jcb.53.3.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAND R. P., BURTON A. C. MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF THE RED CELL MEMBRANE. I. MEMBRANE STIFFNESS AND INTRACELLULAR PRESSURE. Biophys J. 1964 Mar;4:115–135. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(64)86773-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheetz M. P., Singer S. J. Biological membranes as bilayer couples. A molecular mechanism of drug-erythrocyte interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4457–4461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiffer K. A., Goerke J., Düzgüneş N., Fedor J., Shohet S. B. Interaction of erythrocyte protein 4.1 with phospholipids. A monolayer and liposome study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jan 22;937(2):269–280. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90249-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shviro Y., Zilber I., Shaklai N. The interaction of hemoglobin with phosphatidylserine vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Apr 23;687(1):63–70. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90170-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St-Onge D., Gicquaud C. Research on the mechanism of interaction between actin and membrane lipids. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Feb 28;167(1):40–47. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91727-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokke B. T., Mikkelsen A., Elgsaeter A. Spectrin, human erythrocyte shapes, and mechanochemical properties. Biophys J. 1986 Jan;49(1):319–327. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83644-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svetina S., Zeks B. Membrane bending energy and shape determination of phospholipid vesicles and red blood cells. Eur Biophys J. 1989;17(2):101–111. doi: 10.1007/BF00257107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szebeni J., Hauser H., Eskelson C. D., Watson R. R., Winterhalter K. H. Interaction of hemoglobin derivatives with liposomes. Membrane cholesterol protects against the changes of hemoglobin. Biochemistry. 1988 Aug 23;27(17):6425–6434. doi: 10.1021/bi00417a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TROTTER W. D. The slide-coverslip disc-sphere transformation in mammalian erythrocytes. Br J Haematol. 1956 Jan;2(1):65–74. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1956.tb06685.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tocanne J. F., Teissié J. Ionization of phospholipids and phospholipid-supported interfacial lateral diffusion of protons in membrane model systems. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Feb 28;1031(1):111–142. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(90)90005-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


