Abstract
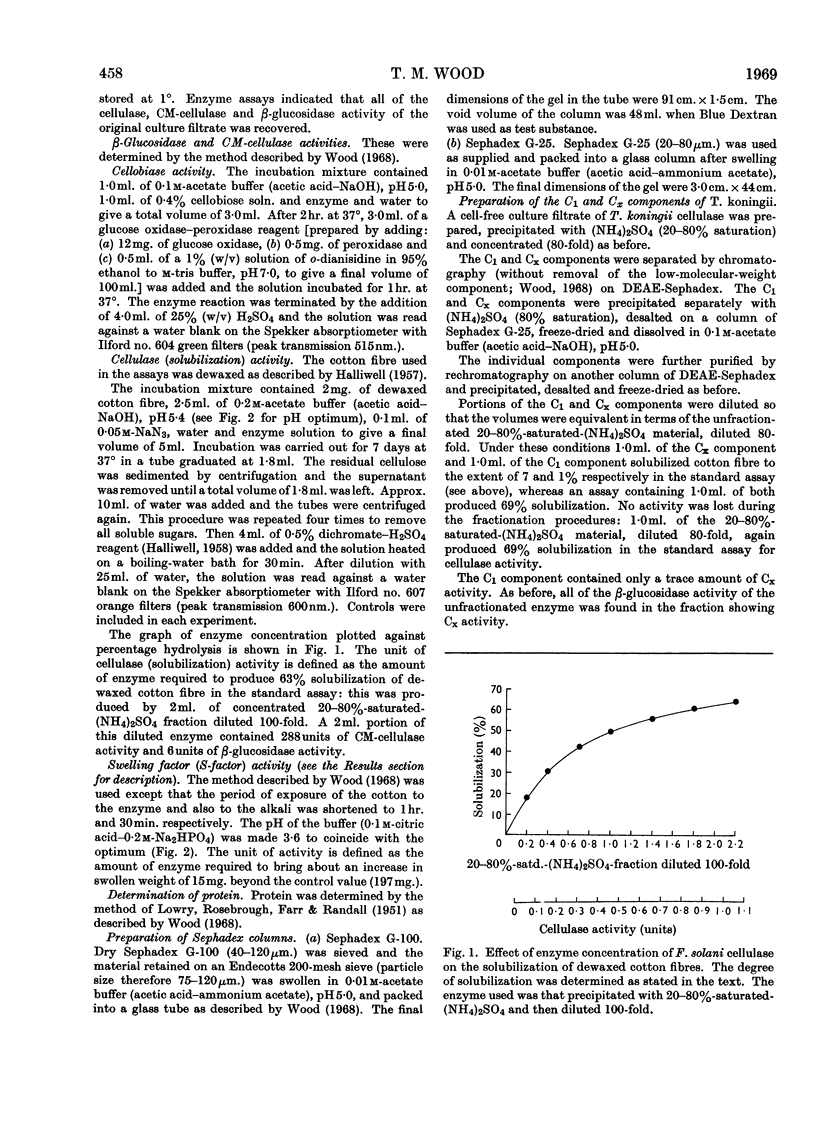
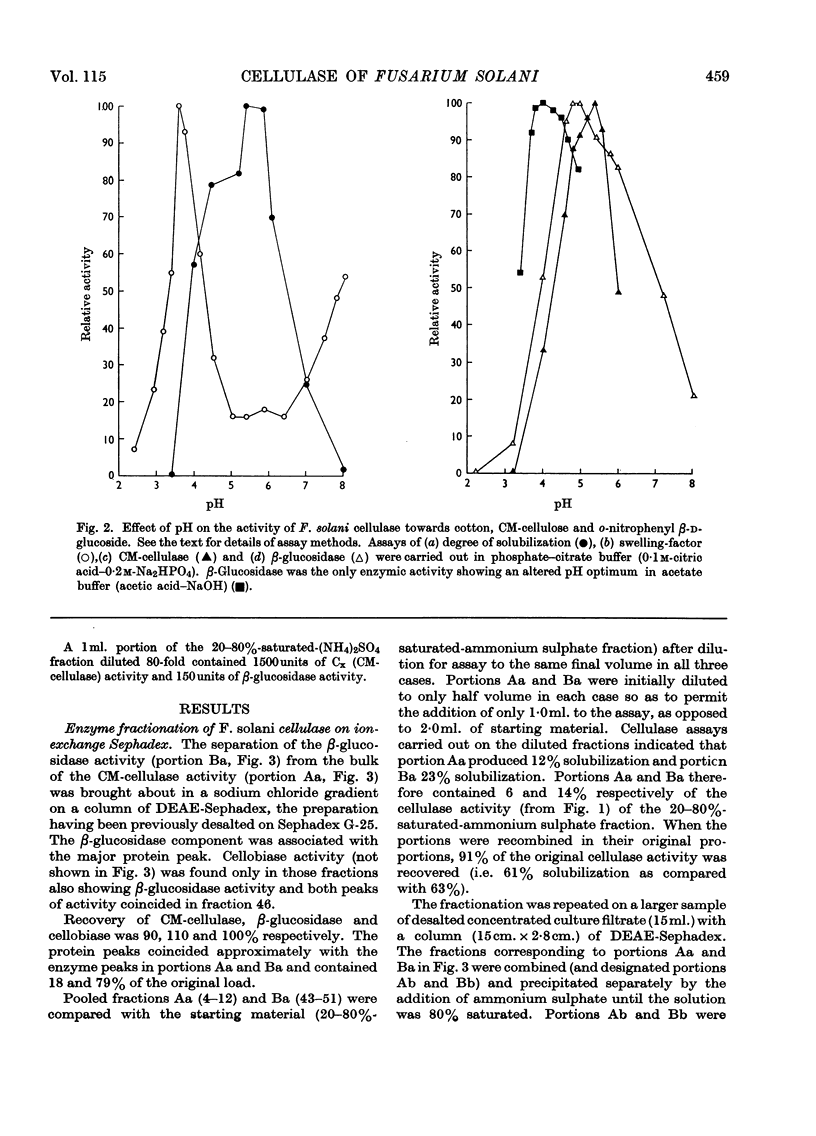
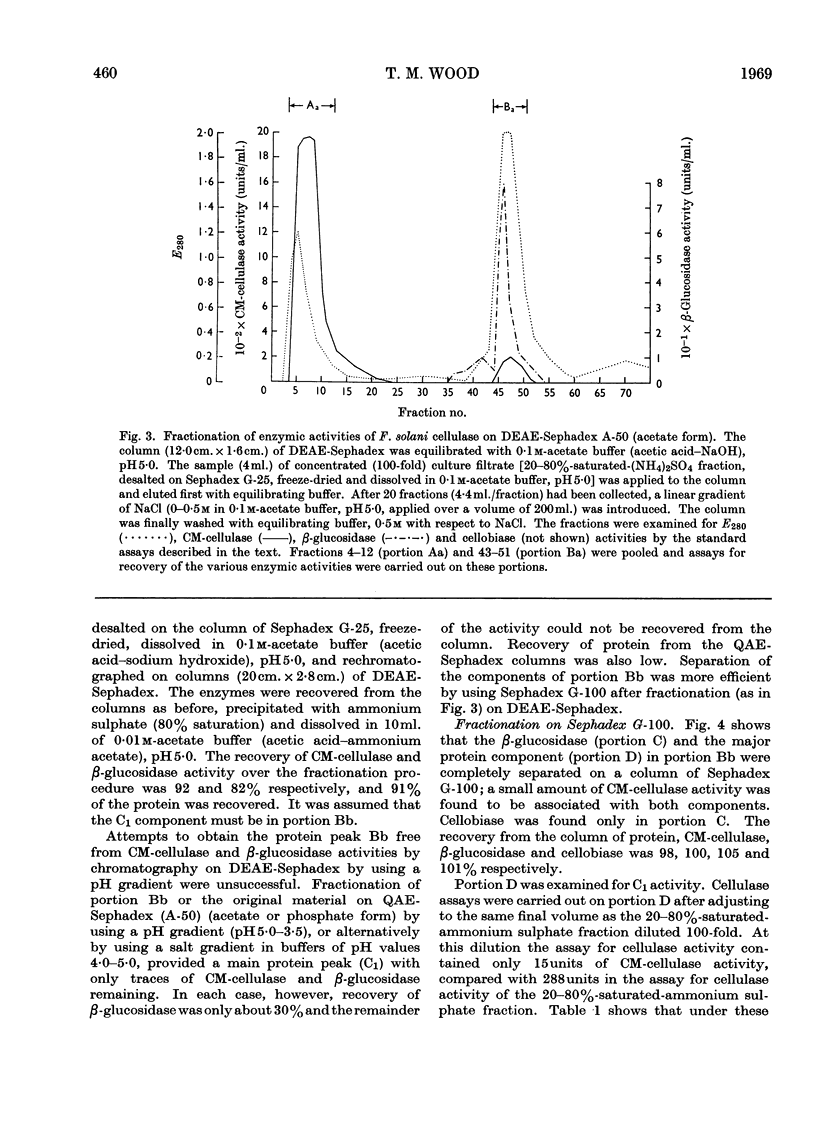
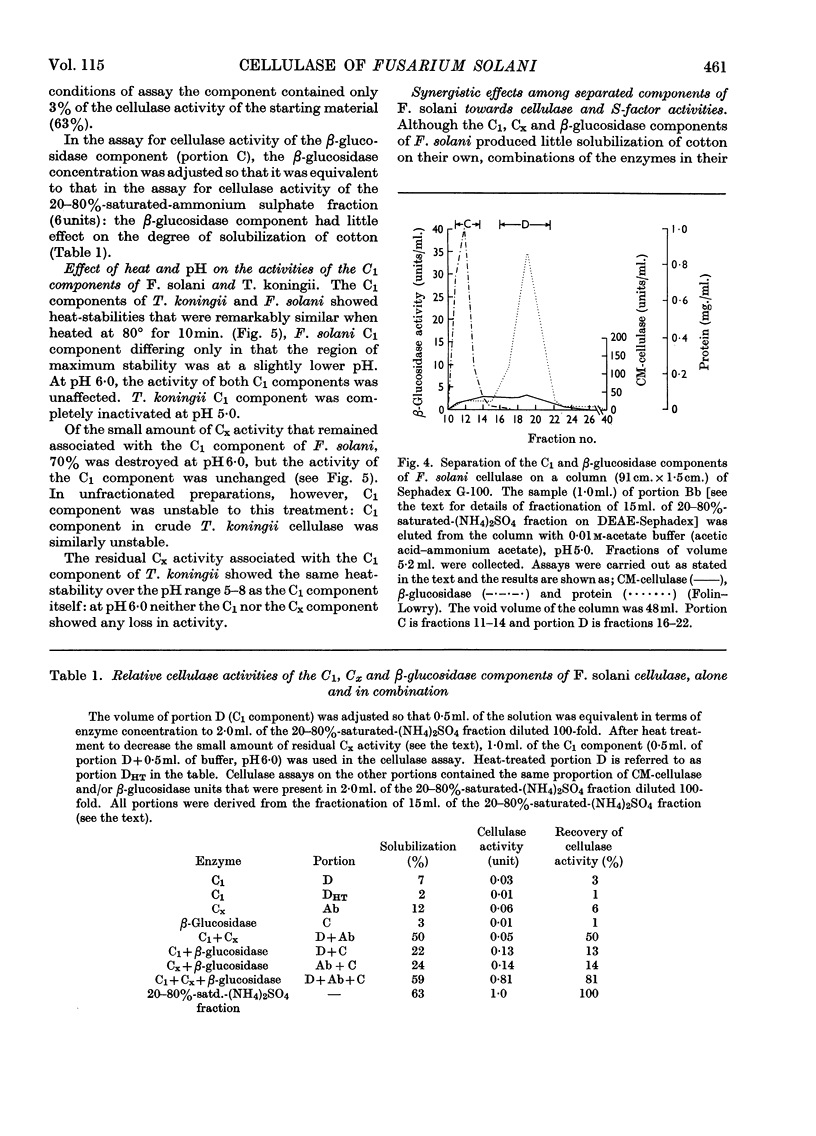
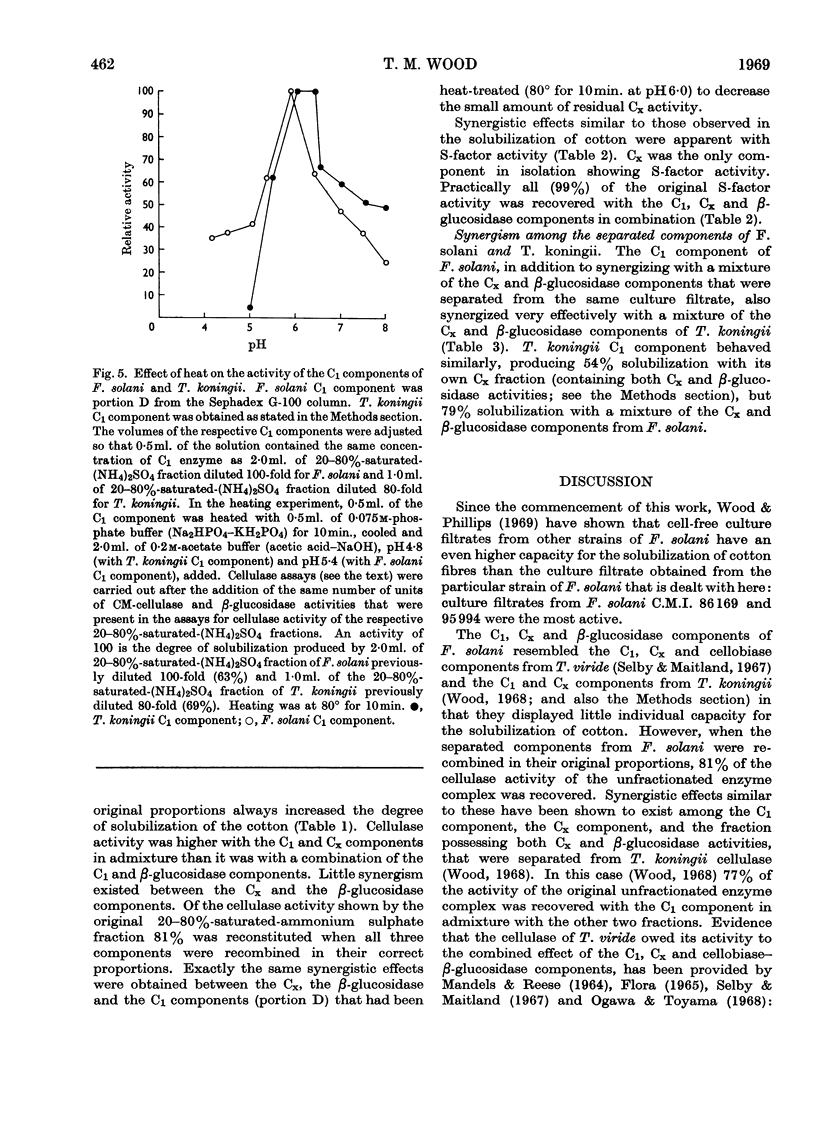
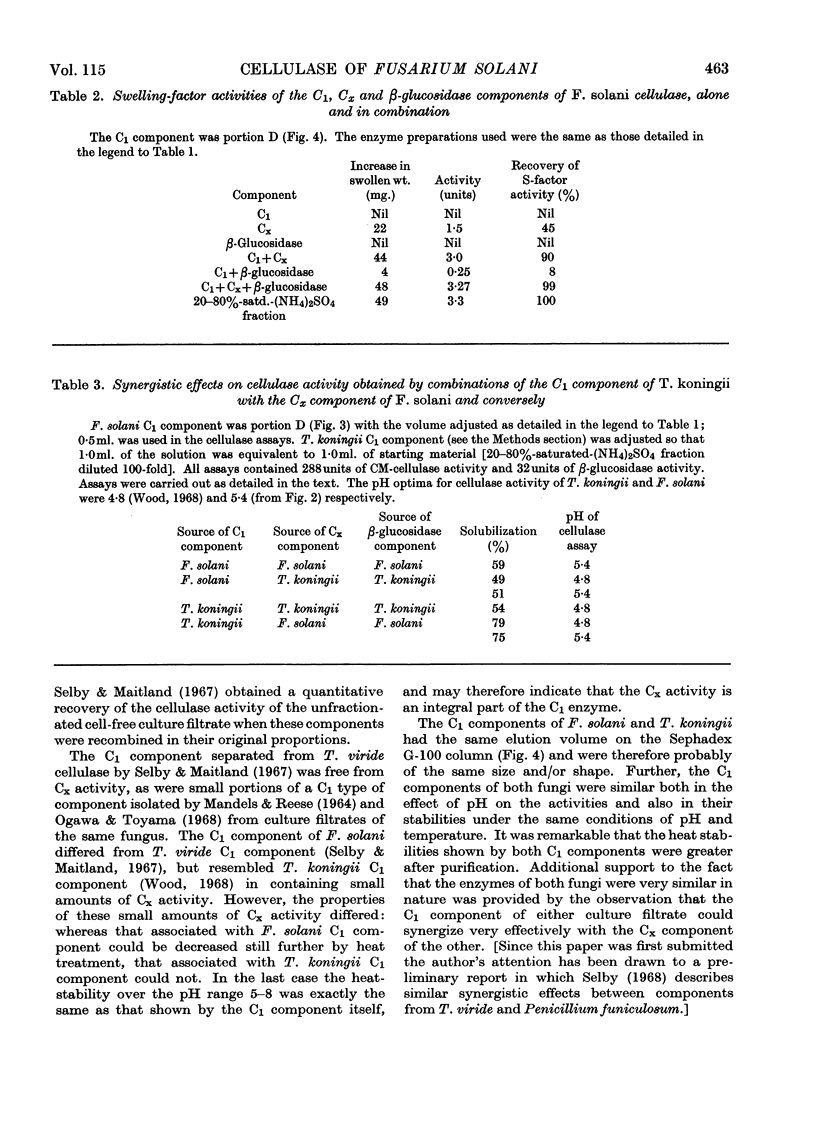
1. Culture filtrates from Fusarium solani were fractionated by ion-exchange chromatography on DEAE-Sephadex, followed by gel chromatography on Sephadex G-100, into a C1 component, a Cx component (CM-cellulase) and a β-glucosidase (cellobiase) component. 2. The individual components showed little capacity for the solubilization of cotton fibre (cellulase activity), but when recombined in their original proportions 81% of the original cellulase activity was recovered. 3. The C1 components of F. solani and Trichoderma koningii were similar in their pH optima, heat stabilities over the pH range 5–8 and elution volumes on Sephadex G-100. 4. The C1 component of F. solani synergized with the Cx component of T. koningii and conversely. 5. The C1 and the β-glucosidase components of F. solani were devoid of the swelling-factor (S-factor) activity associated with the Cx component.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- HALLIWELL G. A microdetermination of cellulose in studies with cellulase. Biochem J. 1958 Apr;68(4):605–610. doi: 10.1042/bj0680605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALLIWELL G. Cellulolysis by rumen micro-organisms. J Gen Microbiol. 1957 Aug;17(1):153–165. doi: 10.1099/00221287-17-1-153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALLIWELL G. HYDROLYSIS OF FIBROUS COTTON AND REPRECIPITATED CELLULOSE BY CELLULOLYTIC ENZYMES FROM SOIL MICRO-ORGANISMS. Biochem J. 1965 Apr;95:270–281. doi: 10.1042/bj0950270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REESE E. T., SIU R. G. H., LEVINSON H. S. The biological degradation of soluble cellulose derivatives and its relationship to the mechanism of cellulose hydrolysis. J Bacteriol. 1950 Apr;59(4):485–497. doi: 10.1128/jb.59.4.485-497.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby K., Maitland C. C. The cellulase of Trichoderma viride. Separation of the components involved in the solubilization of cotton. Biochem J. 1967 Sep;104(3):716–724. doi: 10.1042/bj1040716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood T. M. Cellulolytic enzyme system of Trichoderma koningii. Separation of components attacking native cotton. Biochem J. 1968 Sep;109(2):217–227. doi: 10.1042/bj1090217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood T. M., Phillips D. R. Another source of cellulase. Nature. 1969 Jun 7;222(5197):986–987. doi: 10.1038/222986b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


