Abstract
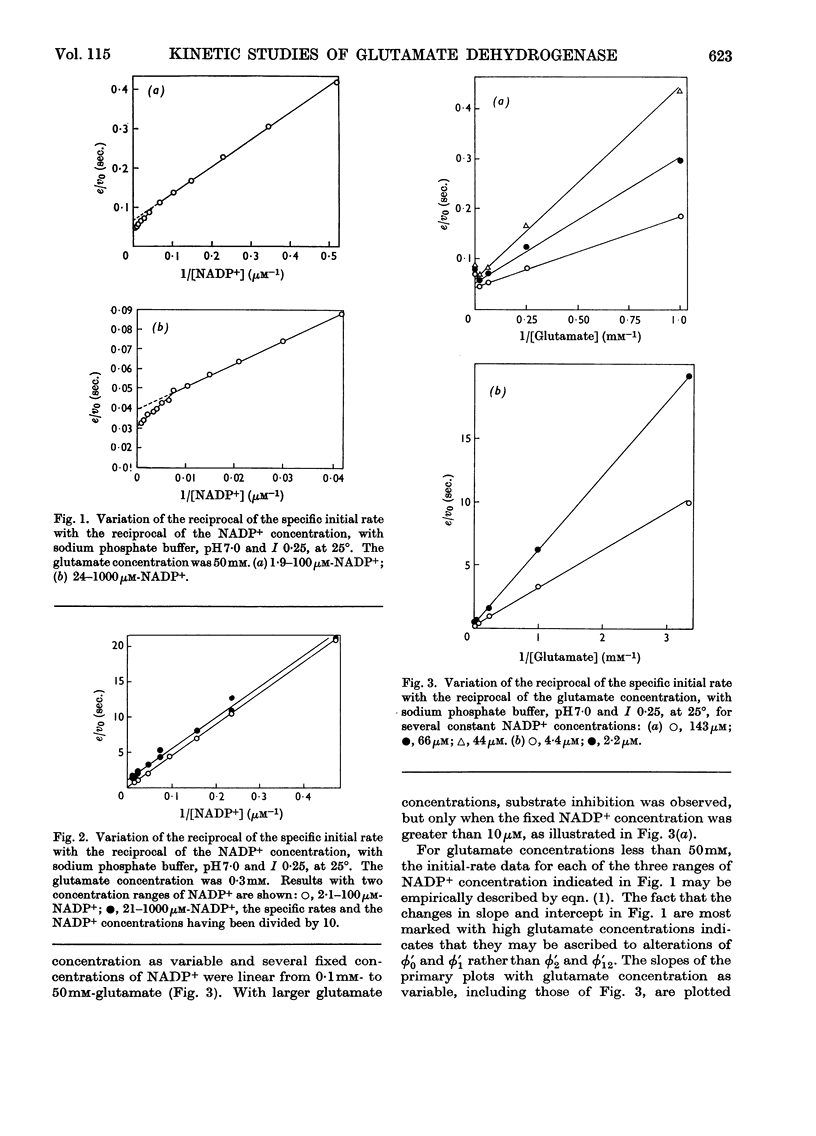
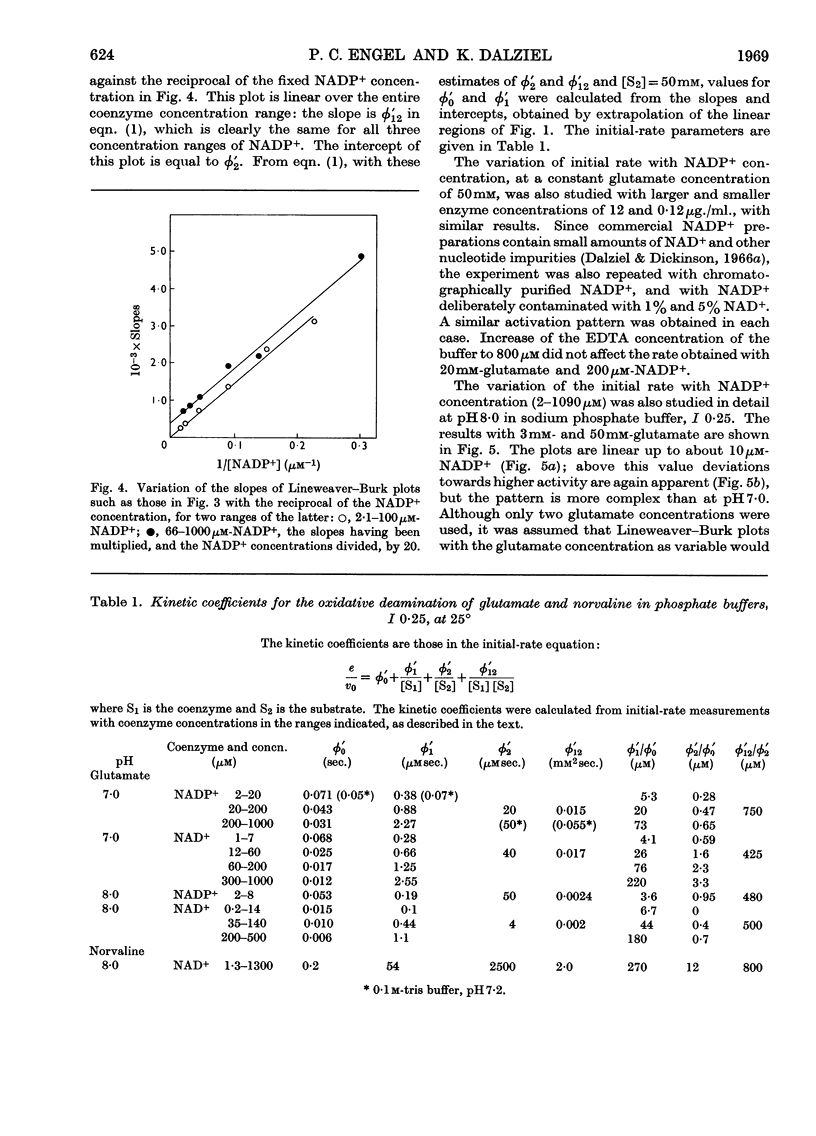
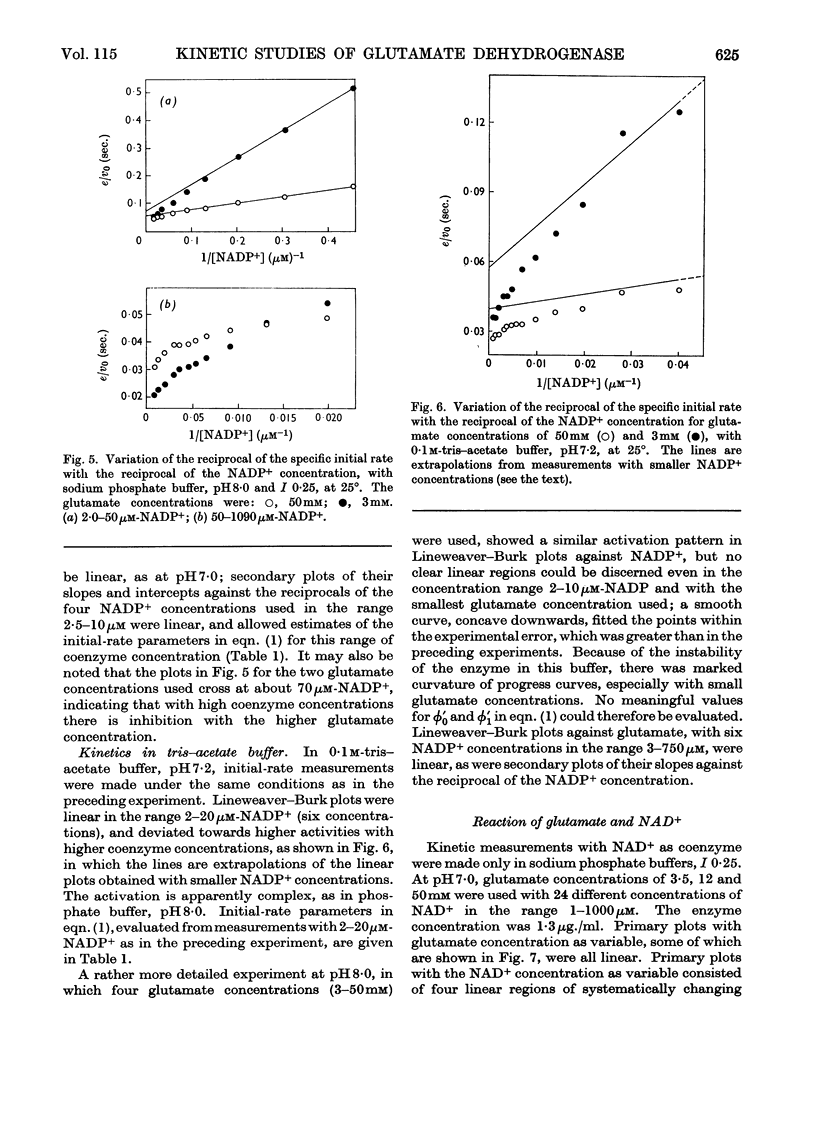
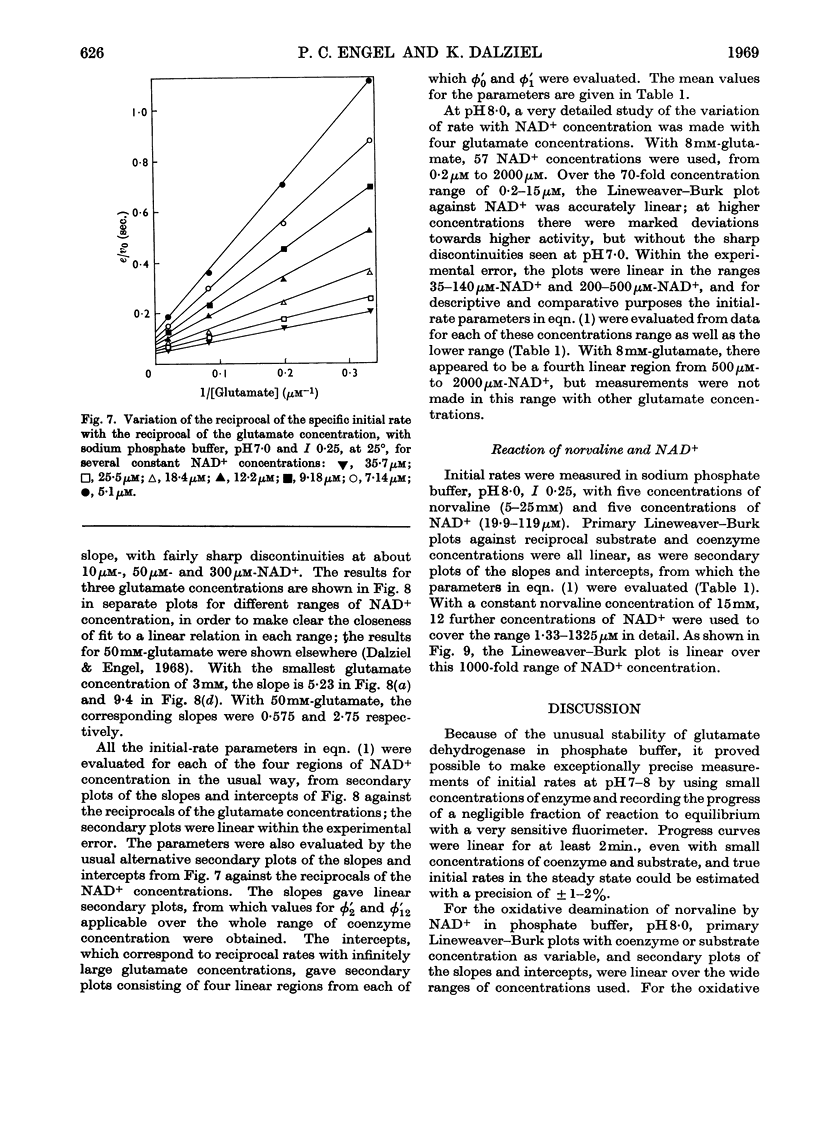
1. Kinetic studies of glutamate dehydrogenase were made with wide concentration ranges of the coenzymes NAD+ and NADP+ and the substrates glutamate and norvaline. Initial-rate parameters were evaluated. 2. Deviations from Michaelis–Menten behaviour towards higher activity were observed with increasing concentrations of either coenzyme with glutamate as substrate, but not with norvaline as substrate. 3. In phosphate buffer, pH7·0, Lineweaver–Burk plots with either coenzyme as variable and a constant, large glutamate concentration showed three or four linear regions of different slope with relatively sharp discontinuities. Maximum rates obtained by extrapolation and Michaelis constants for the coenzymes increased in steps with increase of coenzyme concentration. 4. In the absence of evidence of heterogeneity of the enzyme and coenzyme preparations, the results are interpreted in terms of negative homotropic interactions between the enzyme subunits. It is suggested that sharp discontinuities in Lineweaver–Burk plots or reciprocal binding plots may be characteristic of this new type of interaction, which can be explained in terms of an Adair–Koshland model, but not by the model of Monod, Wyman & Changeux.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson B. M., Reynolds M. L. Inhibition of glutamic dehydrogenase by N-1-alkylnicotinamide chlorides. J Biol Chem. 1966 Apr 25;241(8):1688–1693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CIOTTI M. M., KAPLAN N. O., STOLZENBACH F. E. Reaction of pyridine nucleotide analogues with dehydrogenases. J Biol Chem. 1956 Aug;221(2):833–844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway A., Koshland D. E., Jr Negative cooperativity in enzyme action. The binding of diphosphopyridine nucleotide to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Biochemistry. 1968 Nov;7(11):4011–4023. doi: 10.1021/bi00851a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DALZIEL K. Kinetic studies of liver alcohol dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1962 Aug;84:244–254. doi: 10.1042/bj0840244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DALZIEL K. The preparation and properties of crystalline alcohol dehydrogenase from liver. Biochem J. 1961 Aug;80:440–445. doi: 10.1042/bj0800440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIPRISCO G., ARFIN S. M., STRECKER H. J. STUDIES ON THE NATURE OF THE INHIBITION OF GLUTAMIC DEHYDROGENASE BY N-2-FLUORENYLACETAMIDE AND OTHER COMPOUNDS. J Biol Chem. 1965 Apr;240:1611–1615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalziel K., Dickinson F. M. The kinetics and mechanism of liver alcohol dehydrogenase with primary and secondary alcohols as substrates. Biochem J. 1966 Jul;100(1):34–46. doi: 10.1042/bj1000034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalziel K. The interpretation of kinetic data for enzyme-catalysed reactions involving three substrates. Biochem J. 1969 Sep;114(3):547–556. doi: 10.1042/bj1140547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalziel Keith, Engel Paul C. Antagonistic homotropic interactions as a possible explanation of coenzyme activation of glutamate dehydrogenase. FEBS Lett. 1968 Oct;1(5):349–352. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(68)80153-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Prisco G. Desensitization of the allosteric sites of glutamate dehydrogenase by fluorodinitrobenzene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Jan 23;26(2):148–152. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90226-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel P. C., Dalziel K. The equilibrium constants of the glutamate dehydrogenase systems. Biochem J. 1967 Nov;105(2):691–695. doi: 10.1042/bj1050691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDEN C. GLUTAMATE DEHYDROGENASE. V. THE RELATION OF ENZYME STRUCTURE TO THE CATALYTIC FUNCTION. J Biol Chem. 1963 Oct;238:3286–3299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDEN C. Glutamic dehydrogenase. I. The effect of coenzyme on the sedimentation velocity and kinetic behavior. J Biol Chem. 1959 Apr;234(4):809–814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDEN C. Glutamic dehydrogenase. III. The order of substrate addition in the enzymatic reaction. J Biol Chem. 1959 Nov;234:2891–2896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYES J. E., Jr, VELICK S. F. Yeast alcohol dehydrogenase: molecular weight, coenzyme binding, and reaction equilibria. J Biol Chem. 1954 Mar;207(1):225–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwatsubo M., Pantaloni D. Régulation de l'activité de la glutamate déshydrogènase par les effecteurs GTP et ADP: étude par "stopped flow". Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1967 Dec 18;49(11):1563–1572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. I., Vaage O., Zimmer T. L., Frøholm L. O., Laland S. G. The presence of protein bound intermediates in the biosynthesis of gramicidin S. FEBS Lett. 1968 Oct;1(5):346–348. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(68)80152-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshland D. E., Jr, Némethy G., Filmer D. Comparison of experimental binding data and theoretical models in proteins containing subunits. Biochemistry. 1966 Jan;5(1):365–385. doi: 10.1021/bi00865a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARLER E., TANFORD C. THE MOLECULAR WEIGHT OF THE POLYPEPTIDE CHAINS OF L-GLUTAMATE DEHYDROGENASE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Dec;239:4217–4218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLSON J. A., ANFINSEN C. B. Kinetic and equilibrium studies on crystalline 1-glutamic acid dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1953 Jun;202(2):841–856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLSON J. A., ANFINSEN C. B. The crystallization and characterization of L-glutamic acid dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1952 May;197(1):67–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROGERS K. S., HELLERMAN L., THOMPSON T. E. L-GLUTAMATE DEHYDROGENASE. 3. MOLECULAR SIZE OF BOVINE GLUTAMATE DEHYDROGENASE AND THE METHYLMERCURIC BROMIDE-ACTIVATED ENZYME IN THE CONCENTRATION RANGE OF ENZYMATIC ASSAY. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jan;240:198–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SILVERSTEIN E., BOYER P. D. EQUILIBRIUM REACTION RATES AND THE MECHANISMS OF LIVER AND YEAST ALCOHOL DEHYDROGENASE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Nov;239:3908–3914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRECKER H. J. Glutamic dehydrogenase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1953 Sep;46(1):128–140. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(53)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRUCK J., Jr, SIZER I. W. The substrate specificity of glutamic acid dehydrogenase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1960 Feb;86:260–266. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(60)90415-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sund H., Burchard W. Sedimentation coefficient and molecular weight of beef liver glutamate dehydrogenase at the microgram and the milligram level. Eur J Biochem. 1968 Nov;6(2):202–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb00438.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomkins G. M., Yielding K. L., Curran J. F., Summers M. R., Bitensky M. W. The dependence of the substrate specificity on the conformation of crystalline glutamate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1965 Oct;240(10):3793–3798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


