Abstract
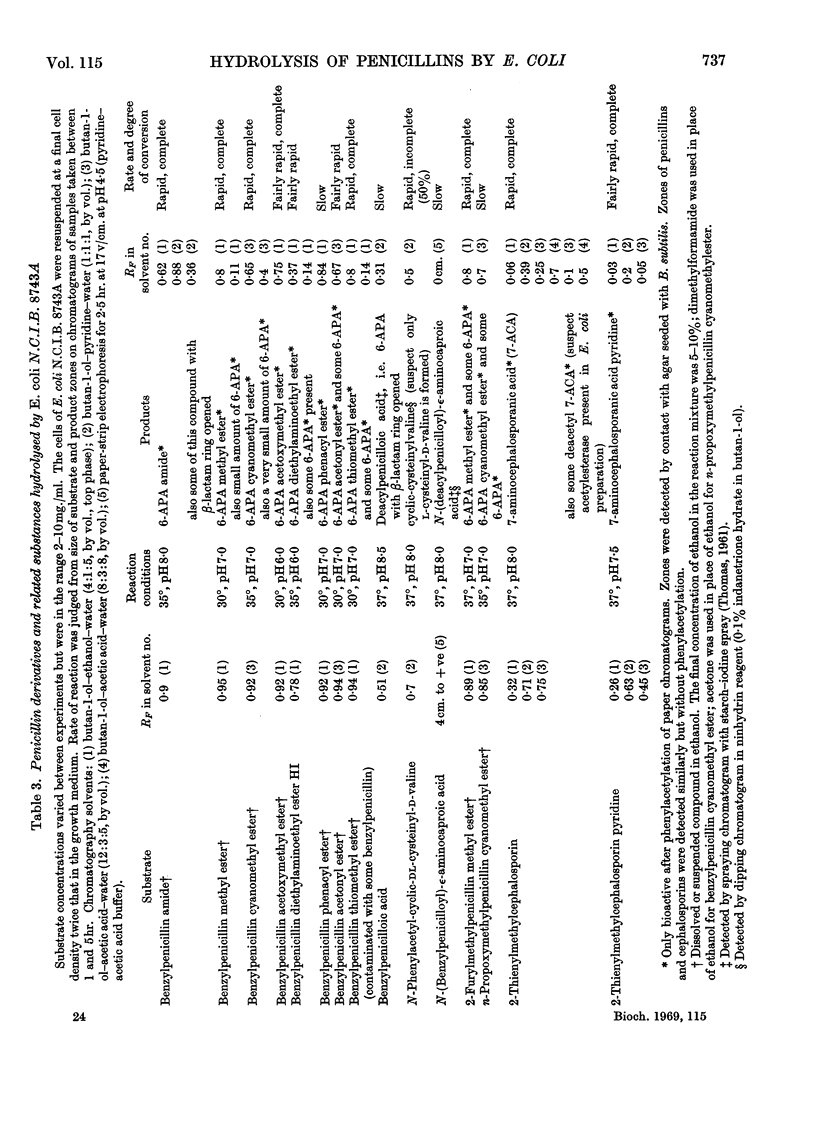
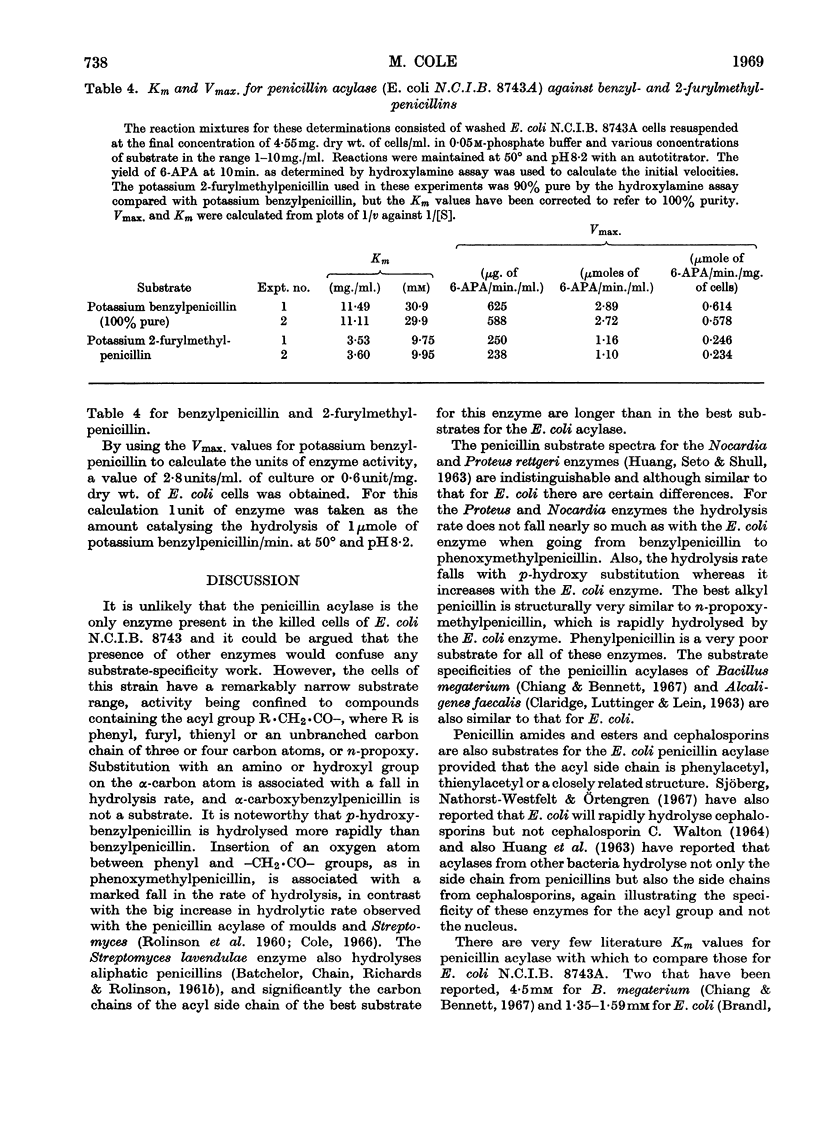
1. A method is given for the preparation of penicillin acylase by using Escherichia coli N.C.I.B. 8743 and a strain selected for higher yield. The enzyme is associated with the bacterial cells and removes the side chains of penicillins to give 6-amino-penicillanic acid and a carboxylic acid. 2. The rates of penicillin deacylation indicated that p-hydroxybenzylpenicillin was the best substrate, followed in diminishing order by benzyl-, dl-α-hydroxybenzyl-, 2-furylmethyl-, 2-thienylmethyl-, d-α-aminobenzyl-, n-propoxymethyl- and isobutoxymethyl-penicillin. Phenylpenicillin and dl-α-carboxybenzylpenicillin were not substrates and phenoxymethyl-penicillin was very poor. 3. Amides and esters of the above penicillins were also substrates for the deacylation reaction, as were cephalosporins with a thienylmethyl side chain. 4. For the deacylation of 2-furylmethylpenicillin at 21° the optimum pH was 8·2. The optimum temperature was 60° at pH7. 5. By using selection A of N.C.I.B. 8743 and determining reaction velocities by assaying yields of 6-amino-penicillanic acid in a 10min. reaction at 50° and pH8·2, the Km for benzylpenicillin was found to be about 30mm and the Km for 2-furylmethylpenicillin, about 10mm. The Vmax. values were 0·6 and 0·24μmole/min./mg. of bacterial cells respectively.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BATCHELOR F. R., CHAIN E. B., HARDY T. L., MANSFORD K. R., ROLINSON G. N. 6-Aminopenicillanic acid. III. Isolation and purification. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1961 Aug 15;154:498–508. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1961.0047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BATCHELOR F. R., CHAIN E. B., RICHARDS M., ROLINSON G. N. 6-Aminopenicillanic acid. VI. Formation of 6-aminopenicillanic acid from penicillin by enzymic hydrolysis. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1961 Aug 15;154:522–531. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1961.0050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batchelor F. R., Dewdney J. M., Gazzard D. Penicillin allergy: the formation of the penicilloyl determinant. Nature. 1965 Apr 24;206(982):362–364. doi: 10.1038/206362a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARIDGE C. A., LUTTINGER J. R., LEIN J. SPECIFICITY OF PENICILLIN AMIDASES. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Aug-Sep;113:1008–1012. doi: 10.3181/00379727-113-28559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiang C., Bennett R. E. Purification and properties of penicillin amidase from Bacillus megaterium. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jan;93(1):302–308. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.1.302-308.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole M. Factors affecting the synthesis of ampicillin and hydroxypenicillins by the cell-bound penicillin acylase of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1969 Dec;115(4):757–764. doi: 10.1042/bj1150757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole M. Formation of 6-aminopenicillanic acid, penicillins, and penicillin acylase by various fungi. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Jan;14(1):98–104. doi: 10.1128/am.14.1.98-104.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole M., Sutherland R. The role of penicillin acylase in the resistance of gram-negative bacteria to penicillins. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Mar;42(3):345–356. doi: 10.1099/00221287-42-3-345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUANG H. T., SETO T. A., SHULL G. M. Distribution and substrate specificity of benzylpenicillin acylase. Appl Microbiol. 1963 Jan;11:1–6. doi: 10.1128/am.11.1.1-6.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton-Miller J. M. Penicillinacylase. Bacteriol Rev. 1966 Dec;30(4):761–771. doi: 10.1128/br.30.4.761-771.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROLINSON G. N., BATCHELOR F. R., BUTTERWORTH D., CAMERON-WOOD J., COLE M., EUSTACE G. C., HART M. V., RICHARDS M., CHAIN E. B. Formation of 6-aminopenicillanic acid from penicillin by enzymatic hydrolysis. Nature. 1960 Jul 16;187:236–237. doi: 10.1038/187236a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöberg B., Nathorst-Westfelt L., Ortengren B. Enzymatic hydrolysis of some penicillins and cephalosporins by Escherichia coli acylase. Acta Chem Scand. 1967;21(2):547–551. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.21-0547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szentirmai A. Properties of penicillin acylase isolated from Escherichia coli. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1965;12(4):395–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS R. Colorimetric detection of penicillins and cephalosporins on paper. Nature. 1961 Sep 16;191:1161–1163. doi: 10.1038/1911161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


