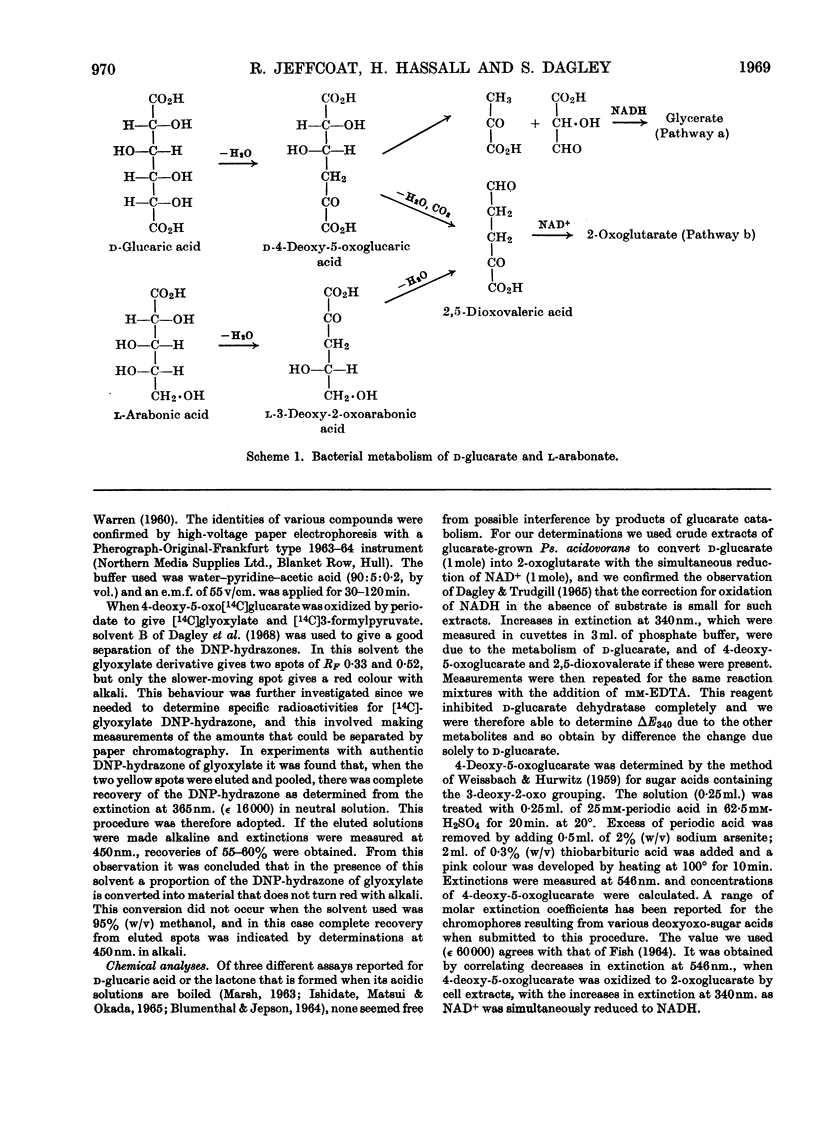
Abstract
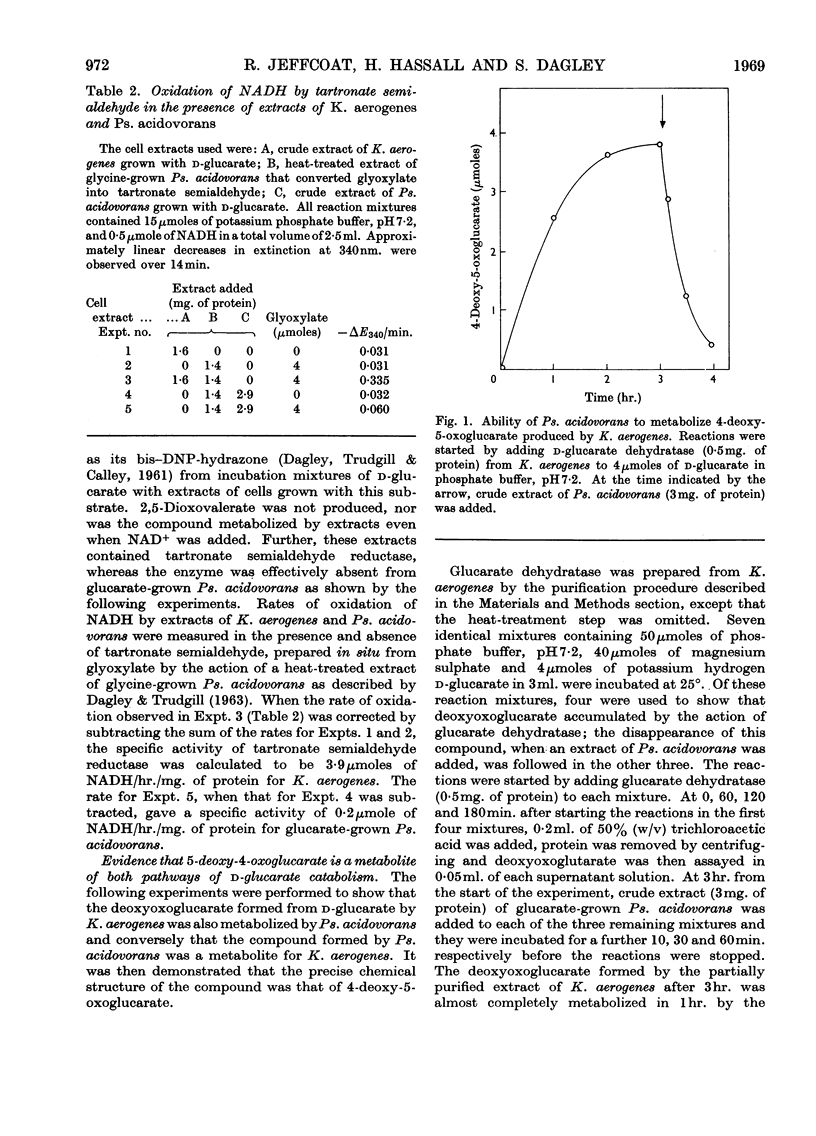
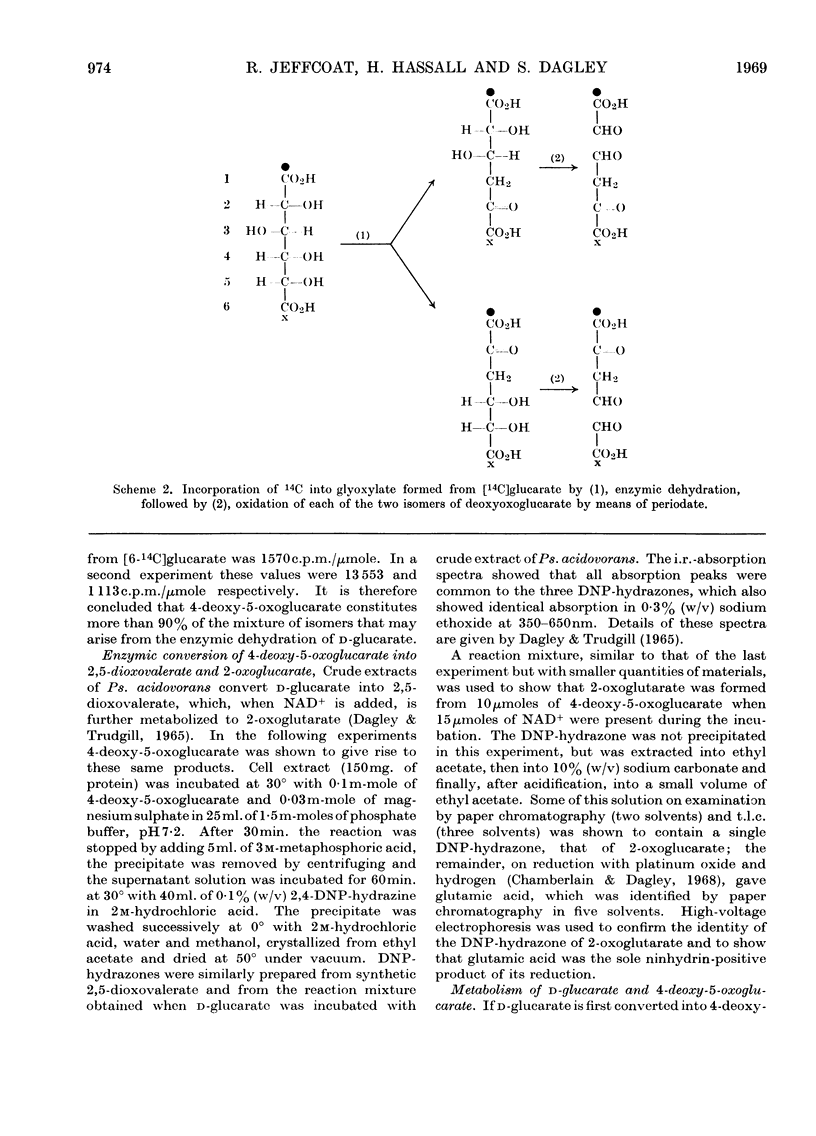
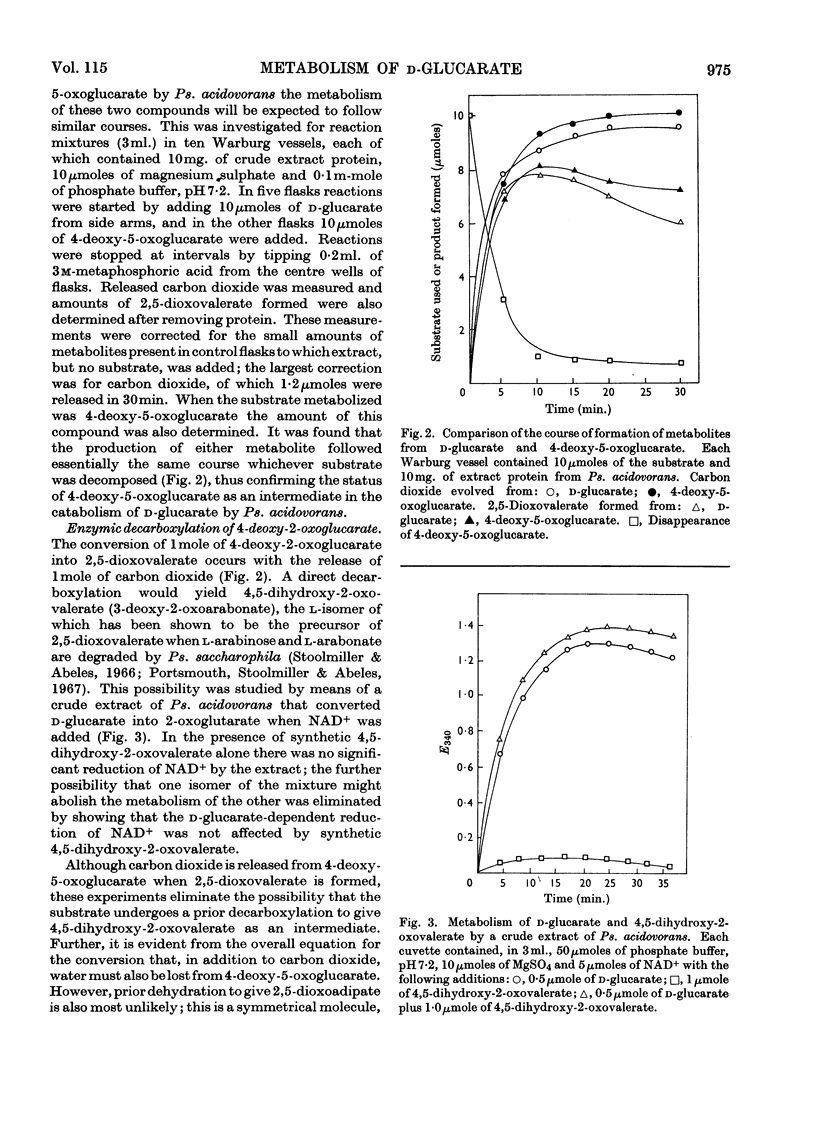
1. Dehydratases that converted d-glucarate into 4-deoxy-5-oxoglucarate were partially purified from Klebsiella aerogenes and Pseudomonas acidovorans. 2. When d-glucarate was metabolized to 2,5-dioxovalerate it appeared that water and carbon dioxide were removed from 4-deoxy-5-oxoglucarate in one enzymic step: 4,5-dihydroxy-2-oxovalerate was not an intermediate in this reaction. 3. A method for the enzymic determination of d-glucarate is described.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BACHRACH U. The aerobic breakdown of uric acid by certain pseudomonads. J Gen Microbiol. 1957 Aug;17(1):1–11. doi: 10.1099/00221287-17-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLUMENTHAL H. J., FISH D. C. Bacterial conversion of D-glucarate to glycerate and pyruvate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1963 May 3;11:239–243. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(63)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayly R. C., Dagley S., Gibson D. T. The metabolism of cresols by species of Pseudomonas. Biochem J. 1966 Nov;101(2):293–301. doi: 10.1042/bj1010293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenthal H. J., Jepson T. Asymmetric dehydration of galactarate by bacterial galactarate dehydratase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964 Oct 14;17(3):282–287. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(64)90398-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain E. M., Dagley S. The metabolism of thymol by a Pseudomonas. Biochem J. 1968 Dec;110(4):755–763. doi: 10.1042/bj1100755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAGLEY S., TRUDGILL P. W., CALLELY A. G. Synthesis of cell constituents from glycine by a Pseudomonas. Biochem J. 1961 Dec;81:623–631. doi: 10.1042/bj0810623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAGLEY S., TRUDGILL P. W. THE METABOLISM OF GALACTARATE, D-GLUCARATE AND VARIOUS PENTOSES BY SPECIES OF PSEUDOMONAS. Biochem J. 1965 Apr;95:48–58. doi: 10.1042/bj0950048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAGLEY S., TRUDGILL P. W. THE METABOLISM OF TARTARIC ACID BY A PSEUDOMONAS. A NEW PATHWAY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:22–31. doi: 10.1042/bj0890022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagley S., Geary P. J., Wood J. M. The metabolism of protocatechuate by Pseudomonas testosteroni. Biochem J. 1968 Oct;109(4):559–568. doi: 10.1042/bj1090559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEINBERG R. H., GREENBERG D. M. Studies on the enzymic decomposition of urocanic acid. J Biol Chem. 1959 Oct;234:2670–2676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGHES D. E. A press for disrupting bacteria and other micro-organisms. Br J Exp Pathol. 1951 Apr;32(2):97–109. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishidate M., Matsui M., Okada M. Biochemical studies on glucuronic acid and glucaric acid. 1. Quantitative chemical determination of D-glucaric acid in urine. Anal Biochem. 1965 May;11(2):176–189. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh C. A. Metabolism of d-glucuronolactone in mammalian systems. Identification of d-glucaric acid as a normal constituent of urine. Biochem J. 1963 Jan;86(1):77–86. doi: 10.1042/bj0860077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portsmouth D., Stoolmiller A. C., Abeles R. H. Studies on the mechanism of action of 2-keto-3-deoxy-L-arabonate dehydratase. The participation of an enzyme-substrate Schiff base in a dehydration. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jun 10;242(11):2751–2759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOOLMILLER A. C., ABELES R. H. FORMATION OF ALPHA-KETOGLUTARATE SEMIALDEHYDE. AN INTRAMOLECULAR DISMUTATION REACTION. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 May 3;19:438–443. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90143-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M. The aerobic pseudomonads: a taxonomic study. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 May;43(2):159–271. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-2-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoolmiller A. C., Abeles R. H. Formation of alpha-ketoglutaric semialdehyde from L-2-keto-3-deoxyarabonic acid and isolation of L-2-keto-3-deoxyarabonate dehydratase from Pseudomonas saccharophila. J Biol Chem. 1966 Dec 25;241(24):5764–5771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trudgill P. W., Widdus R. D-glucarate catabolism by pseudomonadaceae and enterobacteriaceae. Nature. 1966 Sep 3;211(5053):1097–1099. doi: 10.1038/2111097a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. Thiobarbituric acid spray reaction for deoxy sugars and sialic acids. Nature. 1960 Apr 16;186:237–237. doi: 10.1038/186237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISSBACH A., HURWITZ J. The formation of 2-keto-3-deoxyheptonic acid in extracts of Escherichia coli B. I. Identification. J Biol Chem. 1959 Apr;234(4):705–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


