Abstract
1. An enzyme extracted from Pseudomonas acidovorans was purified and shown to catalyse the simultaneous dehydration and decarboxylation of d-4-deoxy-5-oxoglucarate. It is proposed to name the enzyme d-4-deoxy-5-oxoglucarate hydro-lyase (decarboxylating), trivial name `deoxyoxoglucarate dehydratase'. 2. No added cofactors were required, and the enzyme was inactivated when incubated with its substrate in the presence of sodium borohydride. Under these conditions the substrate and enzyme appeared to be bound covalently. 3. The action of the enzyme is readily explained if it is assumed that d-4-deoxy-5-oxoglucarate forms a Schiff base with a lysine residue in the enzyme.
Full text
PDF
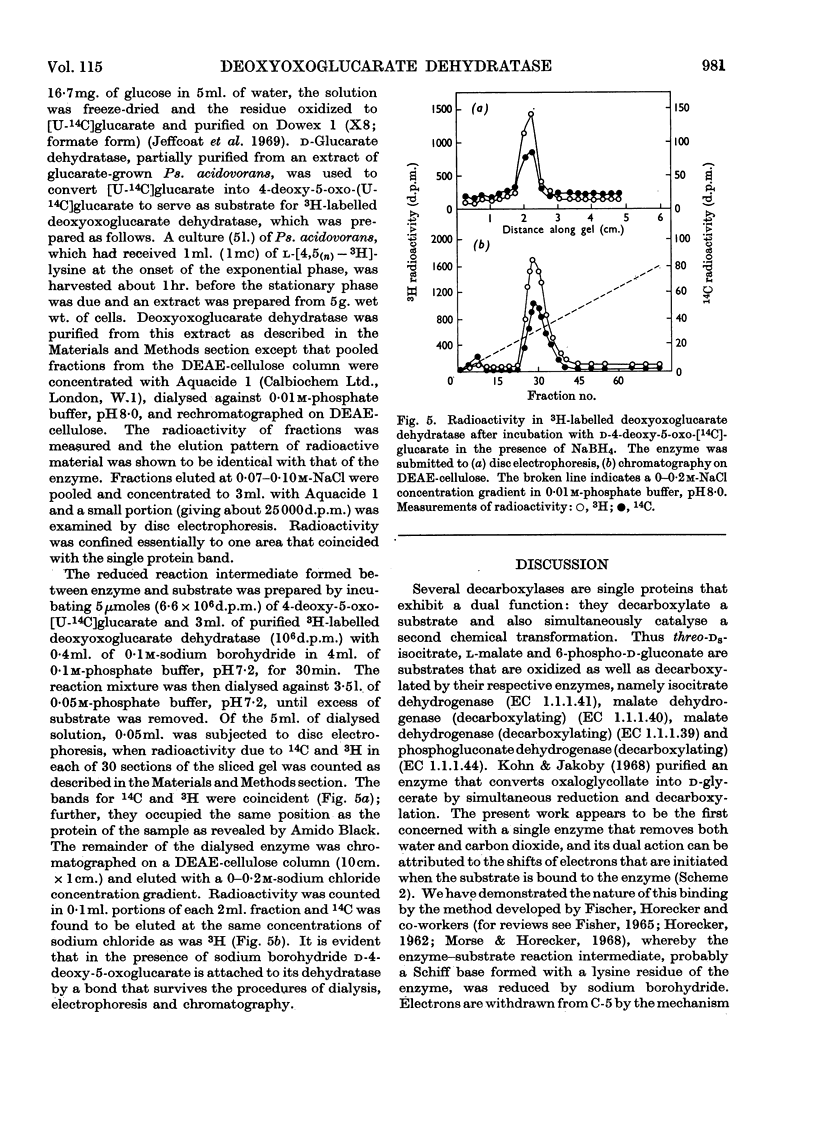
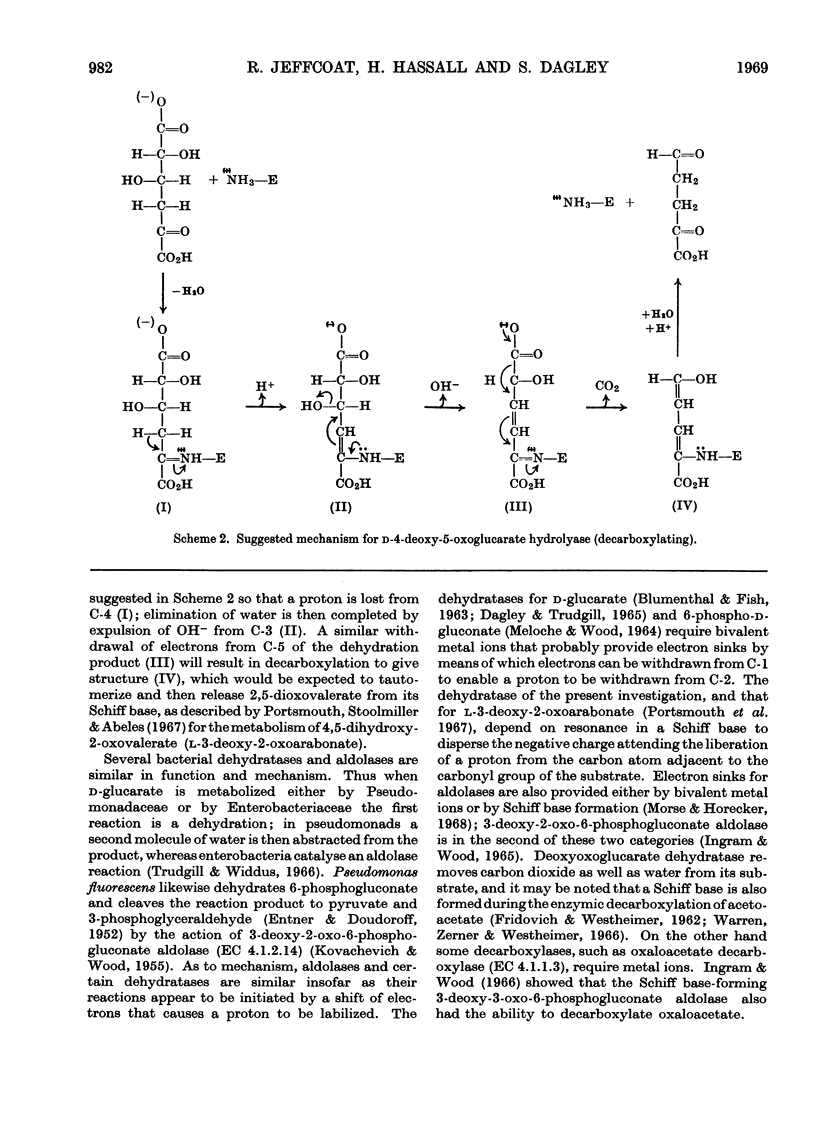

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLUMENTHAL H. J., FISH D. C. Bacterial conversion of D-glucarate to glycerate and pyruvate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1963 May 3;11:239–243. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(63)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAGLEY S., TRUDGILL P. W. THE METABOLISM OF GALACTARATE, D-GLUCARATE AND VARIOUS PENTOSES BY SPECIES OF PSEUDOMONAS. Biochem J. 1965 Apr;95:48–58. doi: 10.1042/bj0950048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagley S., Geary P. J., Wood J. M. The metabolism of protocatechuate by Pseudomonas testosteroni. Biochem J. 1968 Oct;109(4):559–568. doi: 10.1042/bj1090559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENTNER N., DOUDOROFF M. Glucose and gluconic acid oxidation of Pseudomonas saccharophila. J Biol Chem. 1952 May;196(2):853–862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingram J. M., Wood W. A. The mechanism of 2-keto-3-deoxy-6-phosphogluconic aldolase. II. Studies of the partial reactions with substrate analogues. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jul 25;241(14):3256–3261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingram J. M., Wood W. A. The role of lysine residues in the activity of 2-keto-3-deoxy-6-phosphogluconate aldolase. J Biol Chem. 1965 Nov;240(11):4146–4151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffcoat R., Hassall H., Dagley S. The metabolism of D-glucarate by Pseudomonas acidovorans. Biochem J. 1969 Dec;115(5):969–976. doi: 10.1042/bj1150969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohn L. D., Jakoby W. B. Tartaric acid metabolism. VI. Crystalline oxaloglycolate reductive decarboxylase. J Biol Chem. 1968 May 25;243(10):2486–2493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MELOCHE H. P., WOOD W. A. THE MECHANISM OF 6-PHOSPHOGLUCONIC DEHYDRASE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Oct;239:3505–3510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse D. E., Horecker B. L. The mechanism of action of aldolases. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1968;31:125–181. doi: 10.1002/9780470122761.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portsmouth D., Stoolmiller A. C., Abeles R. H. Studies on the mechanism of action of 2-keto-3-deoxy-L-arabonate dehydratase. The participation of an enzyme-substrate Schiff base in a dehydration. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jun 10;242(11):2751–2759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tishler P. V., Epstein C. J. A convenient method of preparing polyacrylamide gels for liquid scintillation spectrometry. Anal Biochem. 1968 Jan;22(1):89–98. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90262-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trudgill P. W., Widdus R. D-glucarate catabolism by pseudomonadaceae and enterobacteriaceae. Nature. 1966 Sep 3;211(5053):1097–1099. doi: 10.1038/2111097a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren S., Zerner B., Westheimer F. H. Acetoacetate decarboxylase. Identification of lysine at the active site. Biochemistry. 1966 Mar;5(3):817–823. doi: 10.1021/bi00867a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]