Abstract
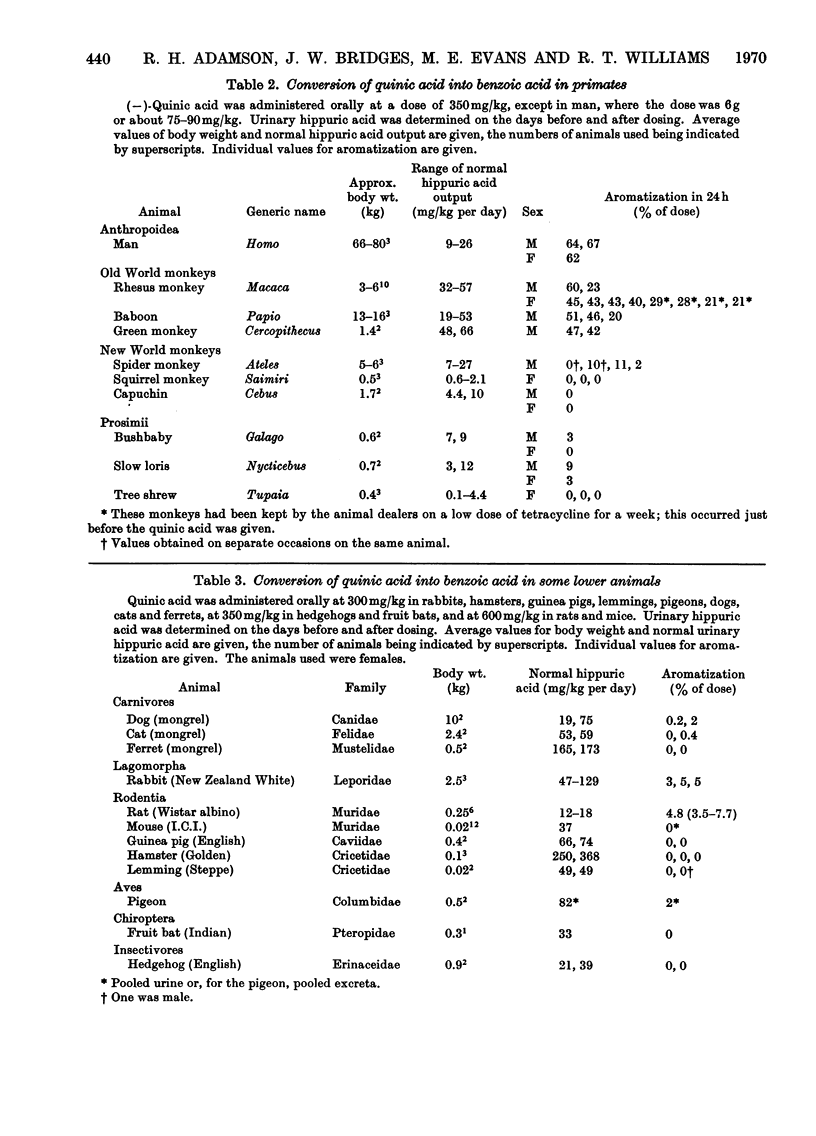
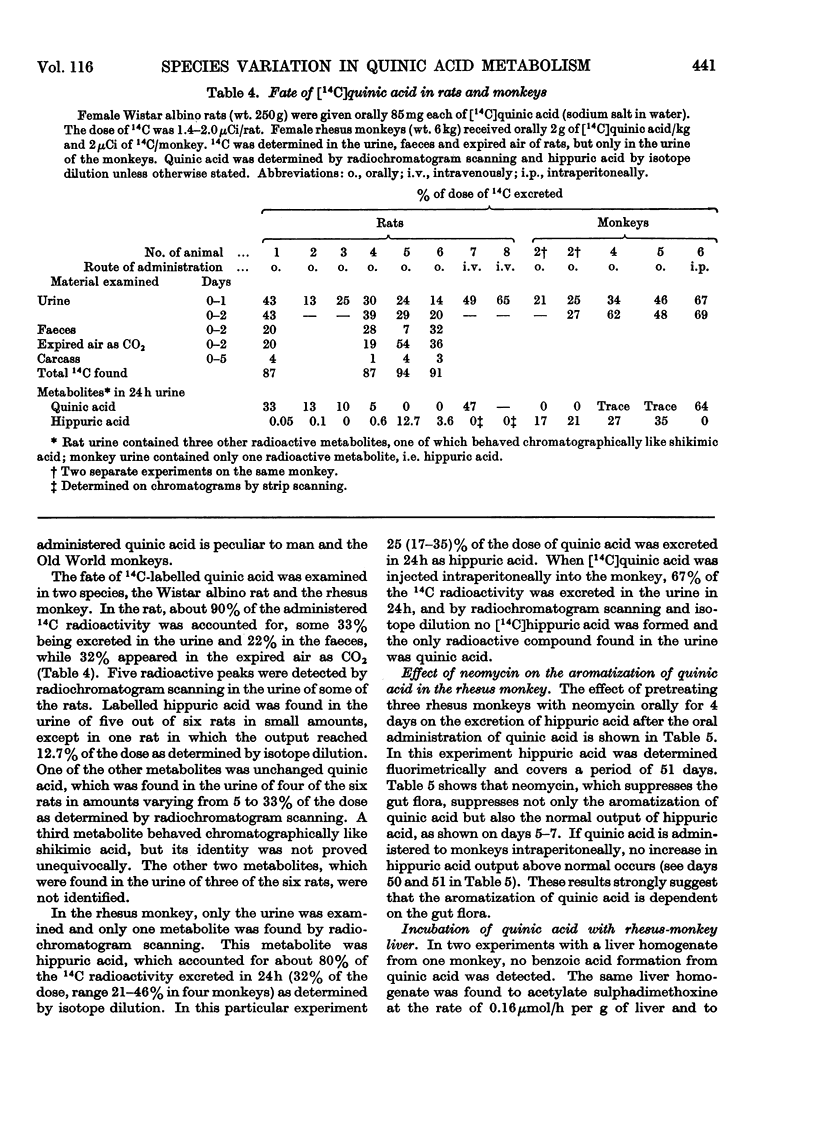
1. The fate of (−)-quinic acid has been investigated in 22 species of animals including man. 2. In man and three species of Old World monkeys, i.e. rhesus monkey, baboon and green monkey, oral quinic acid was extensively aromatized (20–60%) and excreted in the urine as hippuric acid, which was determined fluorimetrically. 3. In three species of New World monkeys, i.e. squirrel monkey, spider monkey and capuchin, in three species of lemurs, i.e. bushbaby, slow loris and tree shrew, in the dog, cat, ferret, rabbit, rat, mouse, guinea pig, hamster, lemming, fruit bat, hedgehog and pigeon, oral quinic acid was not extensively aromatized (0–5%). 4. In the rhesus monkey, injected quinic acid was not aromatized, but largely excreted unchanged. 5. In rhesus monkeys pretreated with neomycin to suppress gut flora, the aromatization of oral quinic acid was considerably suppressed. 6. In rats and rhesus monkeys [14C]quinic acid was used and this confirmed its low aromatization in rats and its high aromatization in the monkeys. 7. Shikimic acid given orally was excreted as hippuric acid (26–56%) in rhesus monkeys, but not in rats. 8. The results support the view that quinic acid and shikimic acid are aromatized by the gut flora in man and the Old World monkeys.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
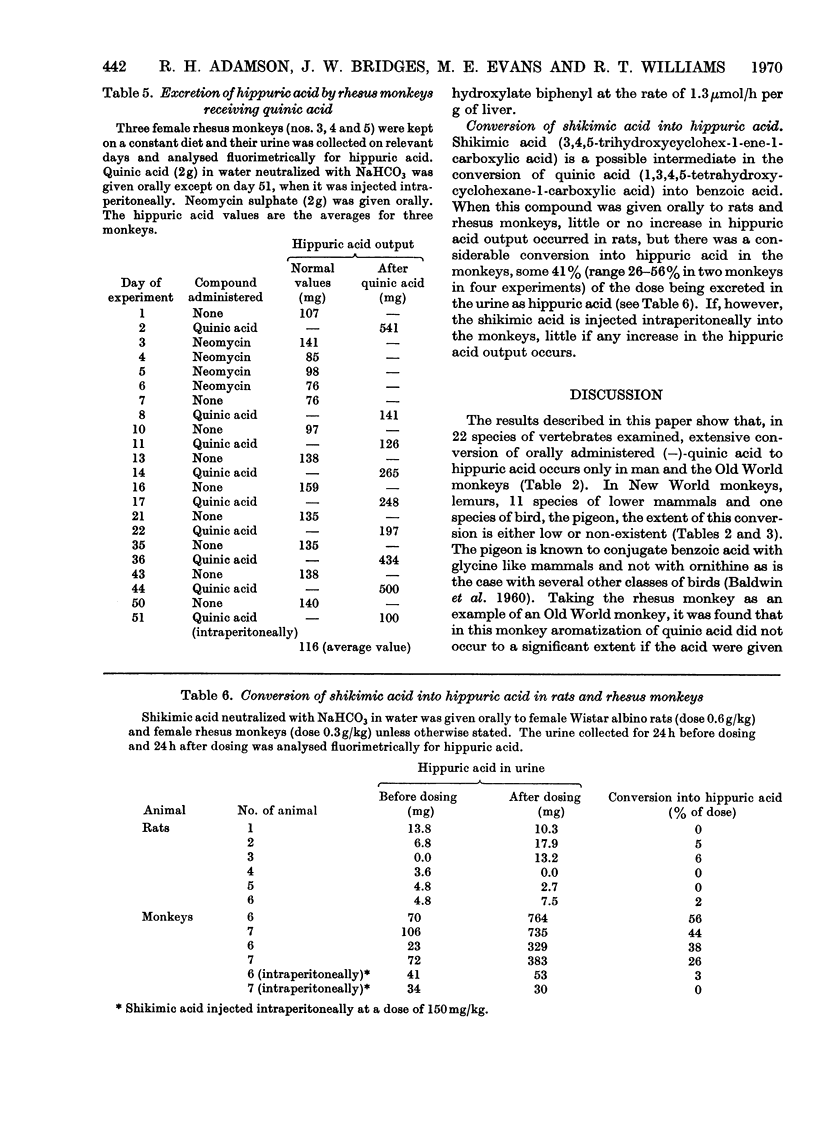
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASATOOR A. M. AROMATISATION OF QUINIC ACID AND SHIKIMIC ACID BY BACTERIA AND THE PRODUCTION OF URINARY HIPPURATE. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Apr 12;100:290–292. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90455-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALDWIN B. C., ROBINSON D., WILLIAMS R. T. Studies in detoxication. 82. The fate of benzoic acid in some domestic and other birds. Biochem J. 1960 Sep;76:595–600. doi: 10.1042/bj0760595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEER C. T., DICKENS F., PEARSON J. The aromatization of hydrogenated derivatives of benzoic acid in animal tissues. Biochem J. 1951 Feb;48(2):222–237. doi: 10.1042/bj0480222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babior B. M., Bloch K. Aromatization of cyclohexanecarboxylic acid. J Biol Chem. 1966 Aug 25;241(16):3643–3651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridges J. W., Kibby M. R., Walker S. R., Williams R. T. Structure and species as factors affecting the metabolism of some methoxy-6-sulphanilamidopyrimidines. Biochem J. 1969 Jan;111(2):167–172. doi: 10.1042/bj1110167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridges J. W., Kibby M. R., Williams R. T. The structure of the glucuronide of sulphadimethoxine formed in man. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):829–836. doi: 10.1042/bj0960829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COTRAN R., KENDRICK M. I., KASS E. H. Role of intestinal bacteria in aromatization of quinic acid in man and guinea pig. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Jul;104:424–426. doi: 10.3181/00379727-104-25860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creaven P. J., Parke D. V., Williams R. T. A fluorimetric study of the hydroxylation of biphenyl in vitro by liver preparations of various species. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):879–885. doi: 10.1042/bj0960879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. D., WEISS U. Aromatic biosynthesis. VIII. The roles of 5-dehydroquinic acid and quinic acid. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1953;220(1-2):1–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutton P. L., Evans W. C. The metabolism of aromatic compounds by Rhodopseudomonas palustris. A new, reductive, method of aromatic ring metabolism. Biochem J. 1969 Jul;113(3):525–536. doi: 10.1042/bj1130525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLMAN G. L., BURKHALTER A., LADOU J. A fluorometric method for the determination of hippuric acid. J Lab Clin Med. 1961 May;57:813–818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITOMA C., POSNER H. S., LEONARD F. Aromatization of hexahydrobenzoic acid by mamalian liver mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Jan;27(1):156–160. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90302-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. T. Comparative patterns of drug metabolism. Fed Proc. 1967 Jul-Aug;26(4):1029–1039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


