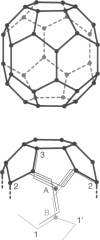
Abstract
The process of clathrin self-assembly into closed shells with the Fullerene structure is investigated. It is argued that the shell size distribution is governed by the kinetics of assembly and depends on the rate of growth controlled by the free clathrin concentration. The particularly abundant small structures—the “tennis ball” and the “hexagonal barrel”—are found to have a certain unique property that makes them ubiquitous in the process of slow growth. A thermal ratchet-type mechanism of the coated vesicle assembly on the membrane is proposed, and possible experimental tests are suggested.
Full text
PDF
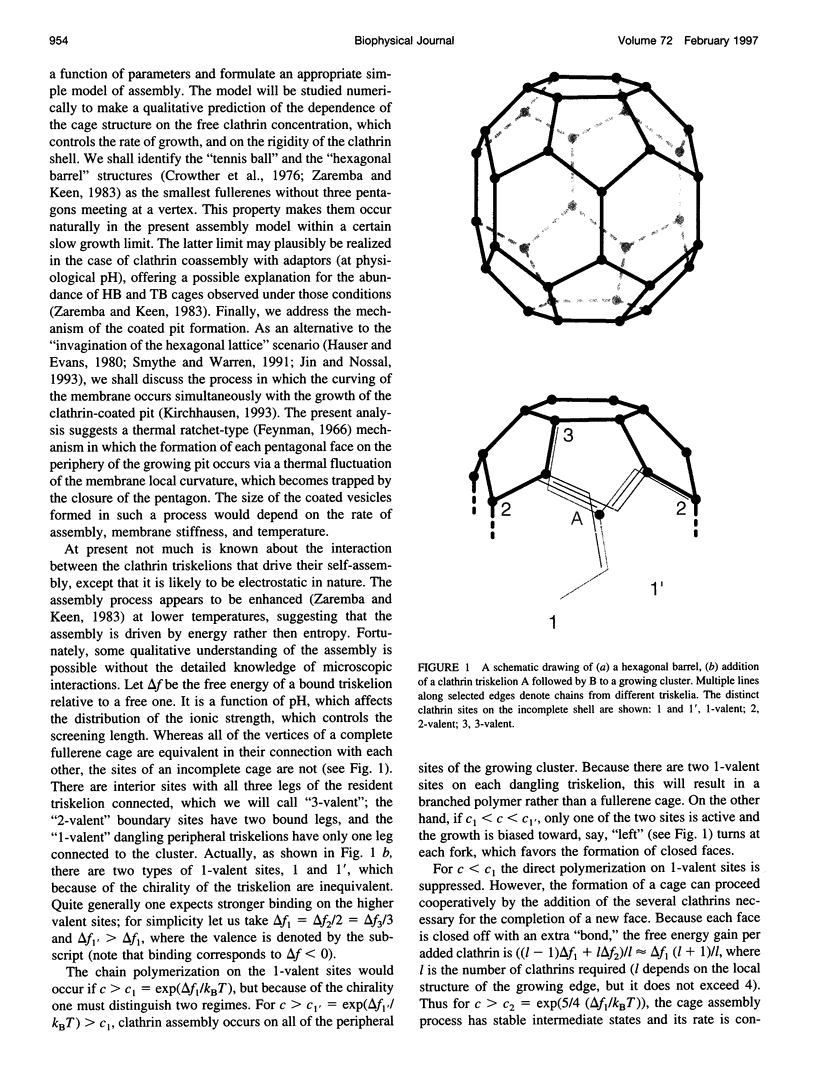


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brodsky F. M. Living with clathrin: its role in intracellular membrane traffic. Science. 1988 Dec 9;242(4884):1396–1402. doi: 10.1126/science.2904698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowther R. A., Finch J. T., Pearse B. M. On the structure of coated vesicles. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jun 5;103(4):785–798. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90209-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowther R. A., Pearse B. M. Assembly and packing of clathrin into coats. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 1):790–797. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuser J. Three-dimensional visualization of coated vesicle formation in fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1980 Mar;84(3):560–583. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.3.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin A. J., Nossal R. Topological mechanisms involved in the formation of clathrin-coated vesicles. Biophys J. 1993 Oct;65(4):1523–1537. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81189-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keen J. H. Clathrin and associated assembly and disassembly proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:415–438. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.002215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keen J. H., Willingham M. C., Pastan I. H. Clathrin-coated vesicles: isolation, dissociation and factor-dependent reassociation of clathrin baskets. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):303–312. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90007-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchhausen T., Harrison S. C. Protein organization in clathrin trimers. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):755–761. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90439-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patzer E. J., Schlossman D. M., Rothman J. E. Release of clathrin from coated vesicles dependent upon a nucleoside triphosphate and a cytosol fraction. J Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;93(1):230–236. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.1.230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse B. M., Robinson M. S. Clathrin, adaptors, and sorting. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:151–171. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.001055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid S. L. The mechanism of receptor-mediated endocytosis: more questions than answers. Bioessays. 1992 Sep;14(9):589–596. doi: 10.1002/bies.950140903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smythe E., Warren G. The mechanism of receptor-mediated endocytosis. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Dec 18;202(3):689–699. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaremba S., Keen J. H. Assembly polypeptides from coated vesicles mediate reassembly of unique clathrin coats. J Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;97(5 Pt 1):1339–1347. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.5.1339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]