Abstract
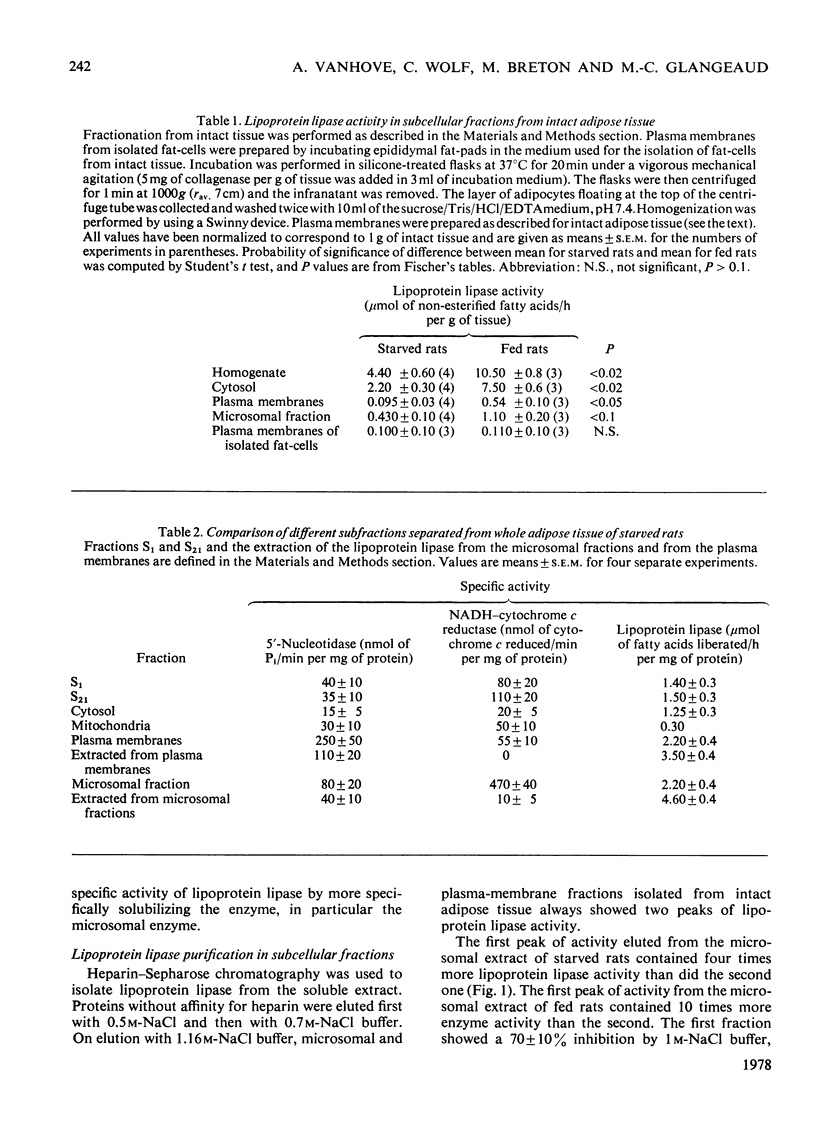
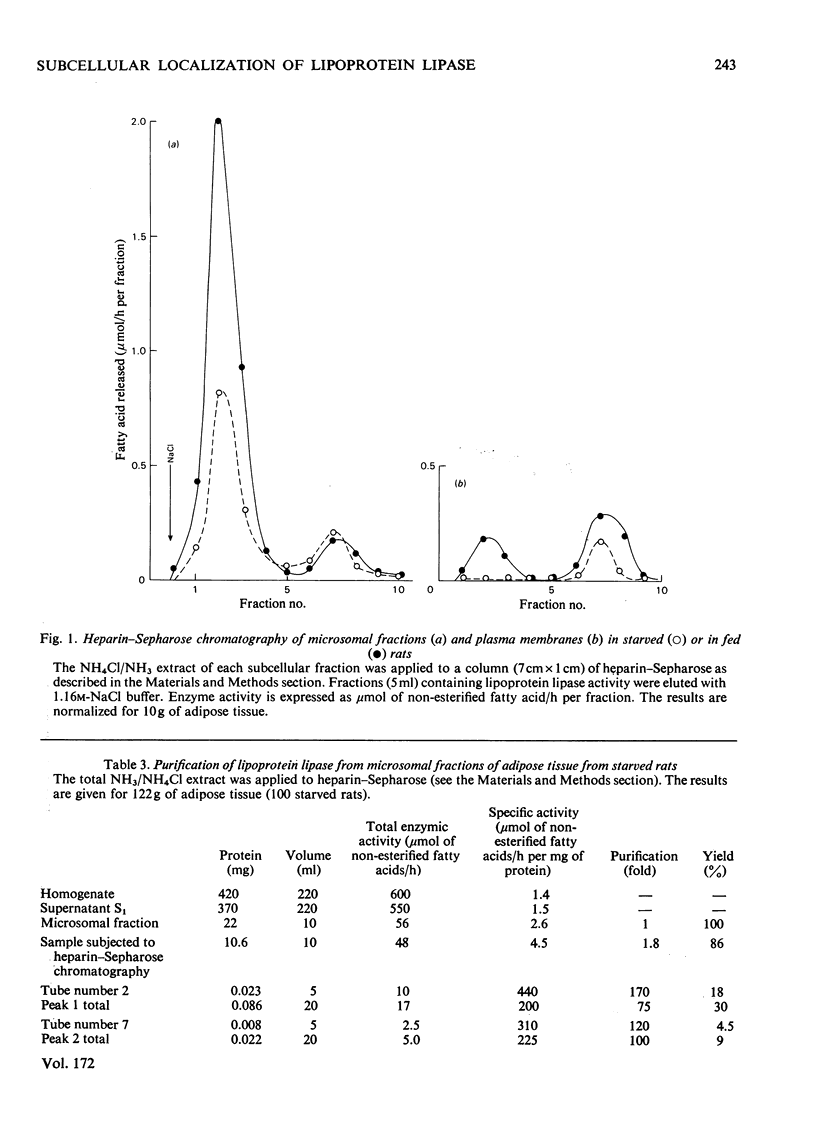
This study supports the possibility for multiple subcellular forms of lipoprotein lipase. 1. The total activity of lipoprotein lipase per g of intact epididymal adipose tissue from fed rats is much higher than that from starved rats. 2. The isolated fat-cells of fed and of starved rats have lipoprotein lipase of almost the same activity per g of fat-pads. The isolated fat-cells of starved rats have a much higher proportion of total activity per g of the intact tissue than do those of fed rats. 3. Under the conditions of homogenization used, only a small proportion of the total activity per g of intact tissue from fed rats was associated with the fat layer which floated to the top of the homogenate during low-speed centrifugation. The different proportions of the specific enzyme activity found in each subcellular fraction are described. 4. Lipoprotein lipase from plasma membranes and microsomal fractions from starved and fed rats was purified by affinity chromatography. 5. The total activity of microsomal lipoprotein lipase per g of intact adipose tissue is enhanced by a normal diet. 6. In intact epididymal adipose tissue from fed rats, the activity per g of tissue of lipoprotein lipase of plasma membranes is much higher than that in the same fraction from starved rats. By contrast, the activities per g of tissue in plasma membranes obtained from starved or from fed rats by collagenase treatment were similar.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avruch J., Wallach D. F. Preparation and properties of plasma membrane and endoplasmic reticulum fragments from isolated rat fat cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Apr 13;233(2):334–347. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90331-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer A., Davies P., Williams E. R., Robinson D. S. The clearing-factor lipase activity of isolated fat-cells. Biochem J. 1975 Feb;146(2):481–488. doi: 10.1042/bj1460481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham V. J., Robinson D. S. Clearing-factor lipase in adipose tissue. Distinction of different states of the enzyme and the possible role of the fat cell in the maintenance of tissue activity. Biochem J. 1969 Apr;112(2):203–209. doi: 10.1042/bj1120203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON T. F., PURDOM M. Serum 5-nucleotidase. J Clin Pathol. 1954 Nov;7(4):341–343. doi: 10.1136/jcp.7.4.341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOLE V. P. A relation between non-esterified fatty acids in plasma and the metabolism of glucose. J Clin Invest. 1956 Feb;35(2):150–154. doi: 10.1172/JCI103259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P., Cryer A., Robinson D. S. Hormonal control of adipose tissue clearing factor lipase activity. FEBS Lett. 1974 Sep 1;45(1):271–275. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80860-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etienne J., Breton M., Vanhove A., Polonovski J. Purification de la lipoprotéine lipase de tissu adipeux humain par chromatographie d'affinité. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1974 Oct 21;279(17):1487–1490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etienne J., Breton M., Vanhove A., Polonovski J. Purification of rat adipose tissue lipoprotein lipase by affinity chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Mar 11;429(1):198–204. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90042-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garfinkel A. S., Schotz M. C. Separation of molecular species of lipoprotein lipase from adipose tissue. J Lipid Res. 1972 Jan;13(1):63–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garfinkel A. S., Schotz M. C. Sequential induction of two species of lipoprotein lipase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 13;306(1):128–133. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(73)90216-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giacobino J. P., Chmelar M. Comparison of plasma membranes and endoplasmic reticulum fractions obtained from whole white adipose tissue and isolated adipocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Sep 16;406(1):68–82. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90043-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greten H., Walter B. Purification of rat adipose tissue lipoprotein lipase. FEBS Lett. 1973 Sep 1;35(1):36–40. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80571-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho S. J., Ho R. J., Meng H. C. Comparison of heparin-released and epinephrine-sensitive lipases in rat adipose tissue. Am J Physiol. 1967 Feb;212(2):284–290. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.212.2.284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iverius P. H. Coupling of glycosaminoglycans to agarose beads (sepharose 4B). Biochem J. 1971 Oct;124(4):677–683. doi: 10.1042/bj1240677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley T. F. Rapid assay of labeled free fatty acids in mixtures of labeled lipids. J Lipid Res. 1968 Nov;9(6):799–800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoo J. C., Jarett L., Mayer S. E., Steinberg D. Subcellular distribution of and epinephrine-induced changes in hormone-sensitive lipase, phosphorylase, and phosphorylase kinase in rat adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 10;247(15):4812–4818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laudat M. H., Pairault J., Bayer P., Martin M., Laudat P. Preparation of fat cell membrane with high sensitivity to lipolytic hormones. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Mar 17;255(3):1005–1008. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90413-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeel D. W., Jarett L. Preparation and characterization of a plasma membrane fraction from isolated fat cells. J Cell Biol. 1970 Feb;44(2):417–432. doi: 10.1083/jcb.44.2.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson-Ehle P., Garfinkel A. S., Schotz M. C. Intra- and extracellular forms of lipoprotein lipase in adipose tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 22;431(1):147–156. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(76)90269-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pokrajac N., Lossow W. J., Chaikoff I. L. The effect of nutritional state on lipoprotein lipase activity in isolated rat adipose tissue cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 May 16;139(1):123–132. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(67)90118-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODBELL M. METABOLISM OF ISOLATED FAT CELLS. I. EFFECTS OF HORMONES ON GLUCOSE METABOLISM AND LIPOLYSIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:375–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner W., Weissmann C. A rapid, sensitive, and specific method for the determination of protein in dilute solution. Anal Biochem. 1973 Dec;56(2):502–514. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90217-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schotz M. C., Garfinkel A. S. Effect of nutrition on species of lipoprotein lipase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 11;270(4):472–478. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(72)90112-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf C., Vanhove A., Breton M., Etienne J., Bereziat G., Polonovski J. Localisation sub-cellulaire de la lipoprotéine-lipase dans l'adipocyte de rat. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1975;169(5):1145–1149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


