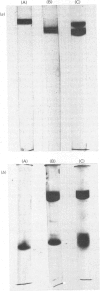
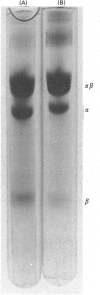
Abstract
Bacillus megaterium N.C.T.C. no. 10342 exhibits glutamate synthetase (EC 2.6.1.53) and glutamate dehydrogenase (EC 1.4.1.4) activities. Concentrations of glutamate synthase were high when the bacteria were grown on 3mM-NH4Cl and low when they were grown on 100mM-NH4Cl, whereas glutamate dehydrogenase concentrations were higher when the bacteria were grown on 100mM-NH4Cl than on 3mM-NH4Cl. Glutamate synthase and glutamate dehydrogenase were purified to homogeneity from B. megaterium grown in 10mM-glucose/10mM-NH4Cl. The purified enzymes had mol.wts. 840000 and 270000 for glutamate synthase and glutamate dehydrogenase respectively. The Km values for substrates with NADPH and coenzyme were (glutamate synthase activity shown first) 9 micron and 360 micron for 2-oxoglutarate, 7.1 micron and 8.7 micron for NADPH, and 0.2 mM for glutamine and 22 mM for NH4Cl, similar values to those of enzymes from Escherichia coli. Glutamate synthase contained NH3-dependent activity (different from authentic glutamate dehydrogenase), which was enhanced 4-fold during treatment at pH 4.6 NH3-dependent activity was generally about 2% of the glutamine-dependent activity. Amidination of glutamate synthase by the bi-functional cross-linking reagent dimethyl suberimidate inactivated glutamine-dependent glutamate synthase activity, but increased NH3-dependent activity. A cross-linked structure of mol.wt. approx 200000 was the main product formed.
Full text
PDF

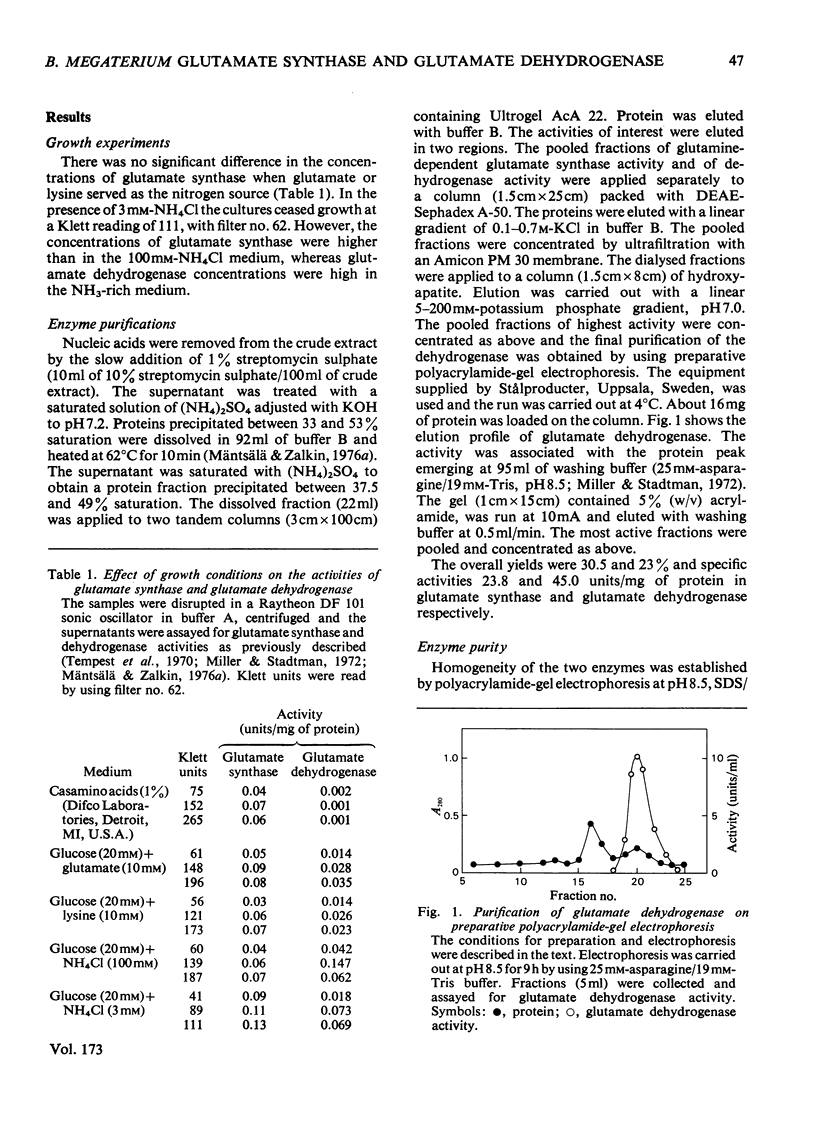

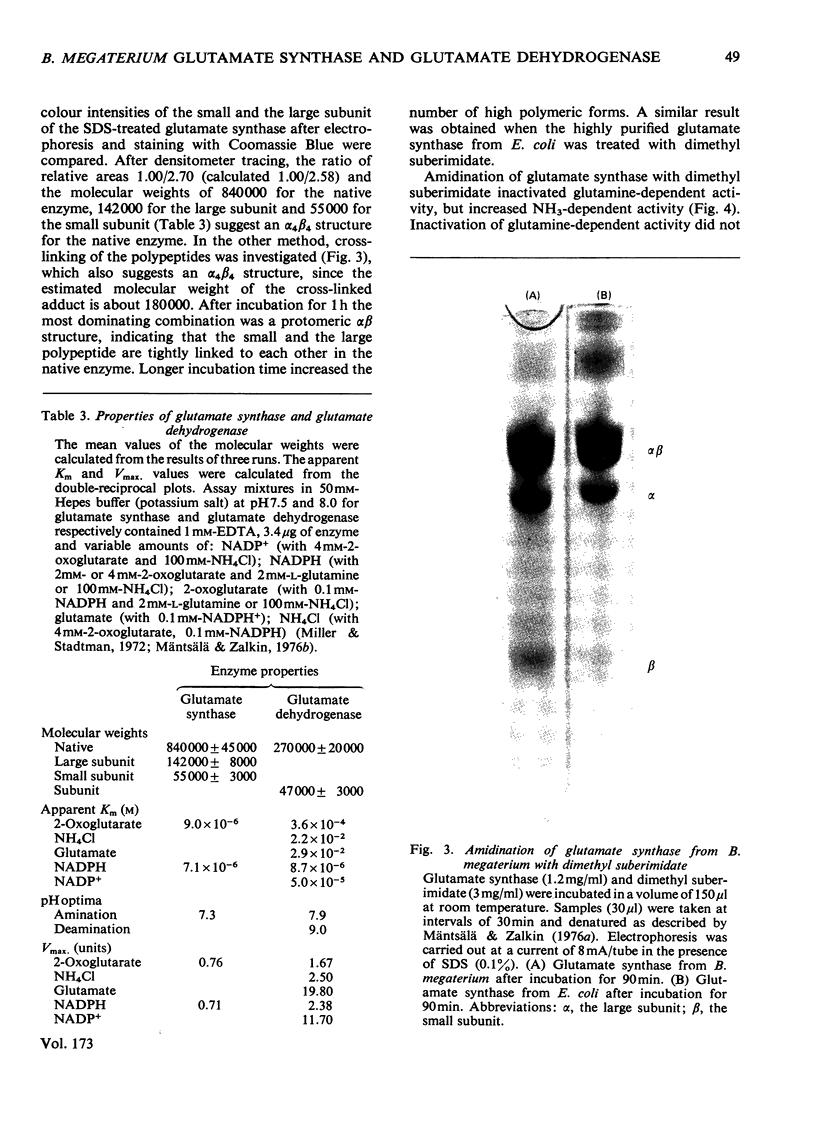


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker J. J., Jeng I., Barker H. A. Purification and properties of L-erythro-3,5-diaminohexanoate dehydrogenase from a lysine-fermenting Clostridium. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 10;247(23):7724–7734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulton J. W., Kapoor M. Purification and some properties of the glutamate dehydrogenase of Salmonella typhimurium. Can J Microbiol. 1973 Apr;19(4):427–438. doi: 10.1139/m73-071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curthoys N. P., Weiss R. F. Regulation of renal ammoniagenesis. Subcellular localization of rat kidney glutaminase isoenzymes. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 25;249(10):3261–3266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies G. E., Stark G. R. Use of dimethyl suberimidate, a cross-linking reagent, in studying the subunit structure of oligomeric proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jul;66(3):651–656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.3.651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmerich C., Aubert J. P. Synthesis of glutamate by a glutamine: 2-oxo-glutarate amidotransferase (NADP oxidoreductase) in Bacillus megaterium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Feb 5;42(3):371–376. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90380-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein I., Grossowicz N. Purification and properties of glutamate dehydrogenase from a thermophilic bacillus. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jun;122(3):1257–1264. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.3.1257-1264.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geary L. E., Meister A. On the mechanism of glutamine-dependent reductive amination of alpha-ketoglutarate catalyzed by glutamate synthase. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 25;252(10):3501–3508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. M., Westlake D. W. Purification and characterization of glutamic acid dehydrogenase and -ketoglutaric acid reductase from Peptococcus aerogenes. Can J Microbiol. 1972 Jun;18(6):881–892. doi: 10.1139/m72-136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAGERKVIST U. Biosynthesis of guanosine 5'-phosphate. II. Amination of xanthosine 5'-phosphate by purified enzyme from pigeon liver. J Biol Chem. 1958 Jul;233(1):143–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meers J. L., Pedersen L. K. Nitrogen assimilation by bacillus licheniformis organisms growning in chemostat cultures. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Apr;70(2):277–286. doi: 10.1099/00221287-70-2-277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meers J. L., Tempest D. W., Brown C. M. 'Glutamine(amide):2-oxoglutarate amino transferase oxido-reductase (NADP); an enzyme involved in the synthesis of glutamate by some bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Dec;64(2):187–194. doi: 10.1099/00221287-64-2-187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. E., Stadtman E. R. Glutamate synthase from Escherichia coli. An iron-sulfide flavoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 25;247(22):7407–7419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäntsälä P., Zalkin H. Glutamate synthase. Properties of the glutamine-dependent activity. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jun 10;251(11):3294–3299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäntsälä P., Zalkin H. Properties of apoglutamate synthase and comparison with glutamate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jun 10;251(11):3300–3305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagano H., Zalkin H., Henderson E. J. The anthranilate synthetase-anthranilate-5-phosphorribosylpyrophosphate phosphoribosyltransferase aggregate. On the reaction mechanism of anthranilate synthetase from Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1970 Aug 10;245(15):3810–3820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phibbs P. V., Jr, Bernlohr R. W. Purification, properties, and regulation of glutamic dehydrogenase of Bacillus licheniformis. J Bacteriol. 1971 May;106(2):375–385. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.2.375-385.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto N., Kotre A. M., Savageau M. A. Glutamate dehydrogenase from Escherichia coli: purification and properties. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):775–783. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.775-783.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro A. L., Viñuela E., Maizel J. V., Jr Molecular weight estimation of polypeptide chains by electrophoresis in SDS-polyacrylamide gels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Sep 7;28(5):815–820. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90391-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempest D. W., Meers J. L., Brown C. M. Synthesis of glutamate in Aerobacter aerogenes by a hitherto unknown route. Biochem J. 1970 Apr;117(2):405–407. doi: 10.1042/bj1170405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trotta P. P., Burt M. E., Haschemeyer R. H., Meister A. Reversible dissociation of carbamyl phosphate synthetase into a regulated synthesis subunit and a subunit required for glutamine utilization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Oct;68(10):2599–2603. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.10.2599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veronese F. M., Boccu E., Conventi L. Glutamate dehydrogenase from Escherichia coli: induction, purification and properties of the enzyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Feb 19;377(2):217–228. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90304-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]