Abstract
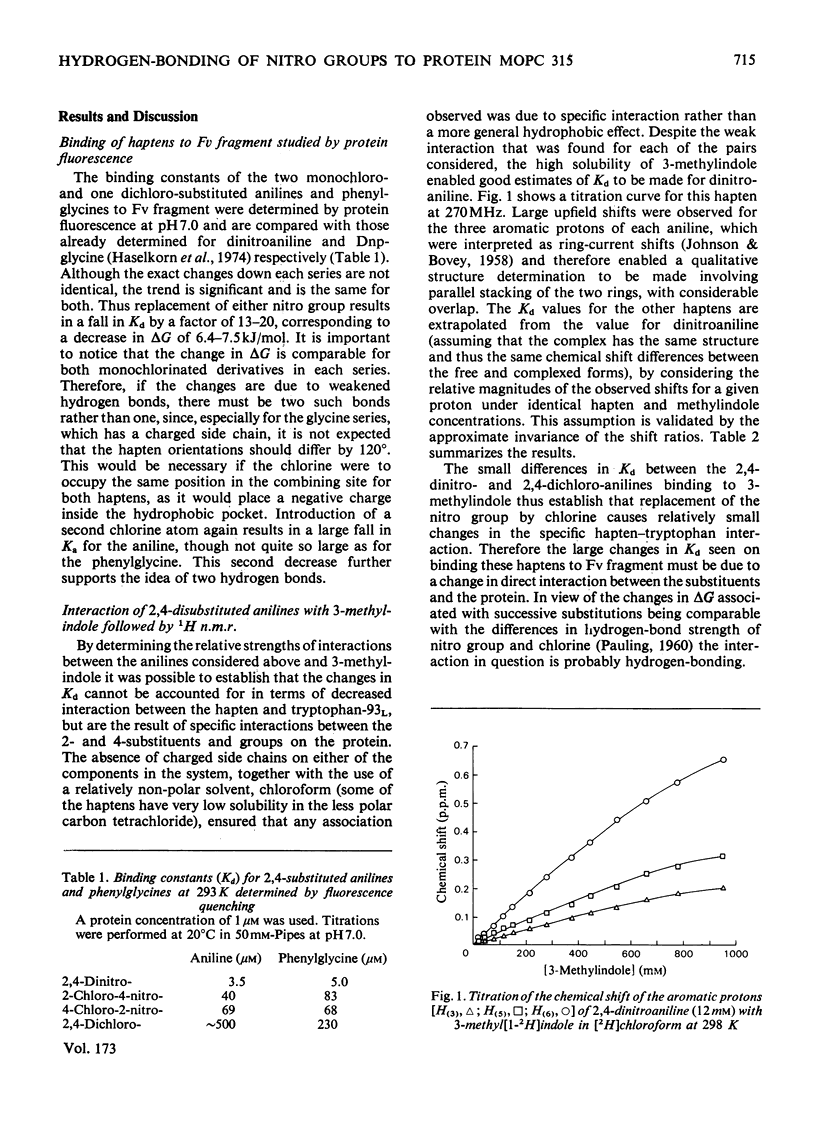
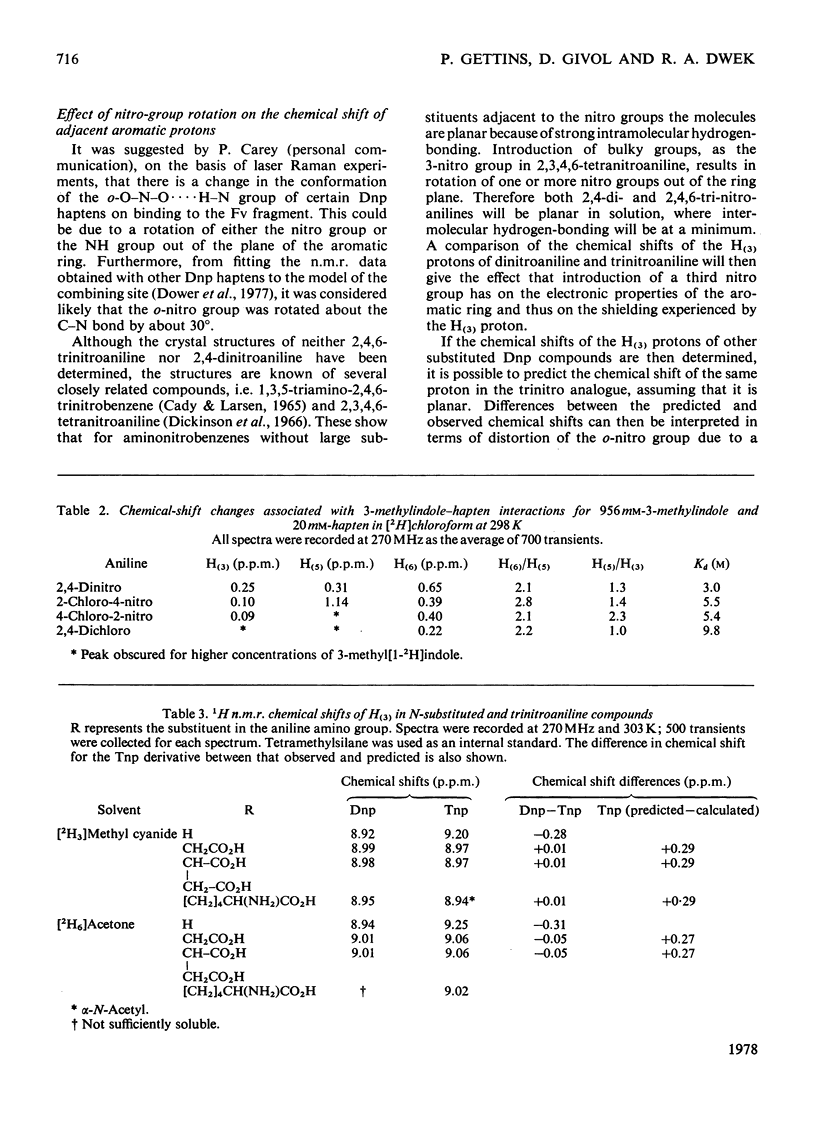
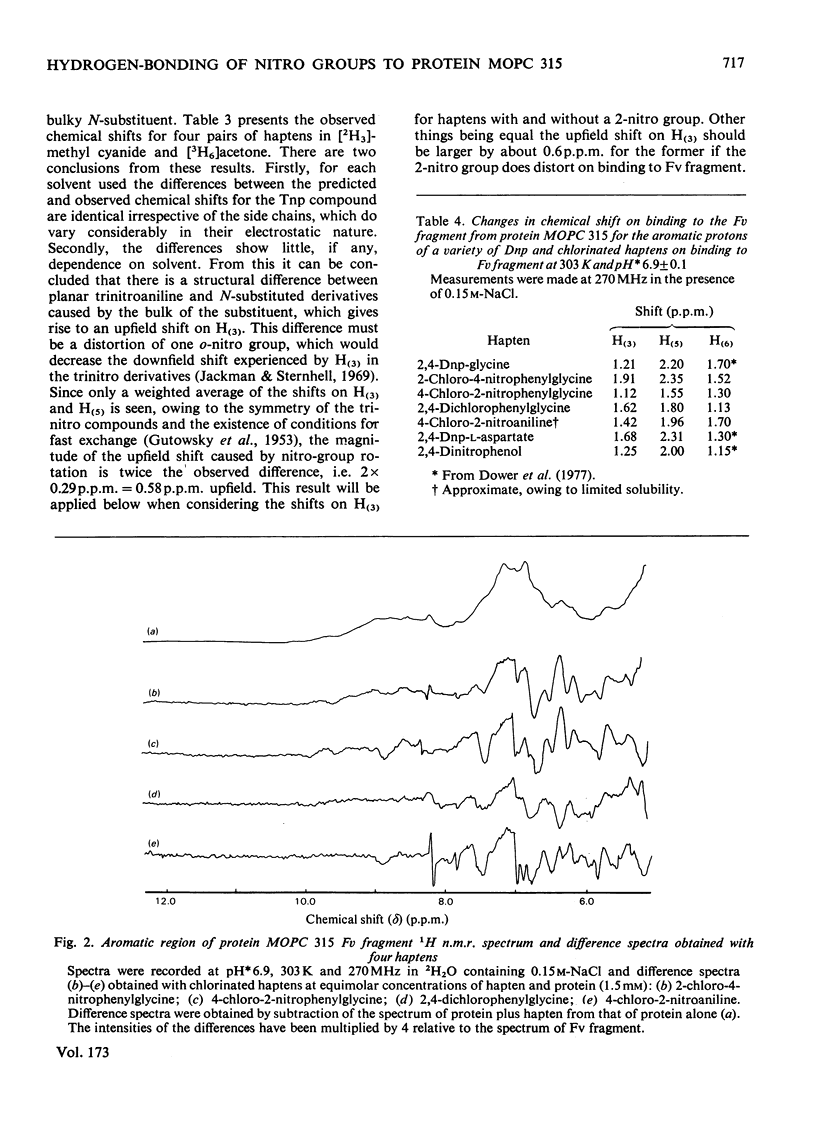
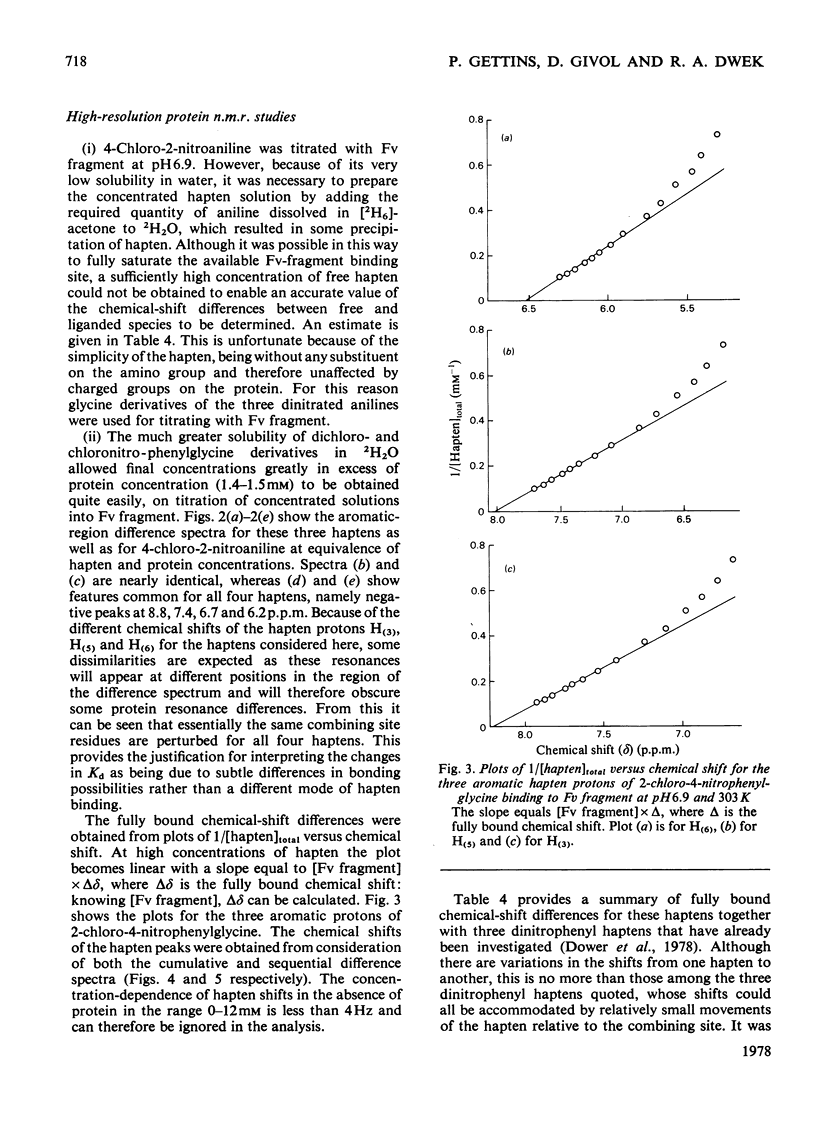
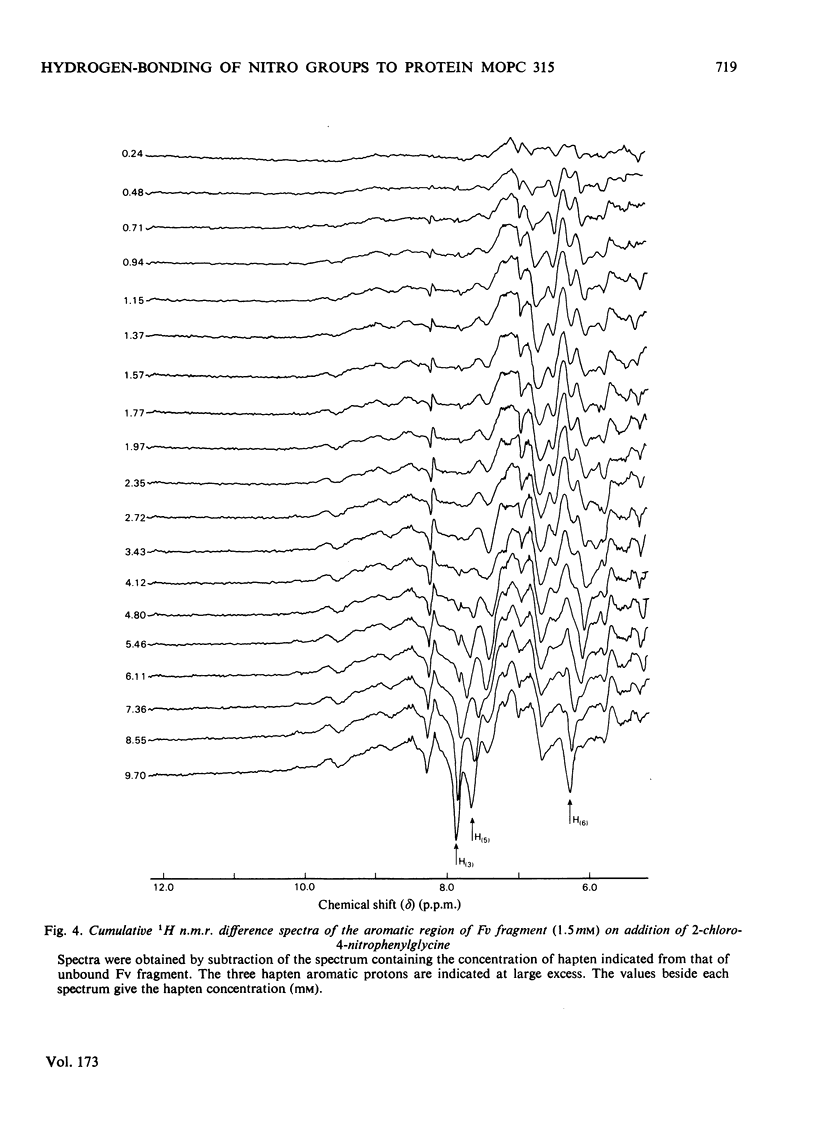
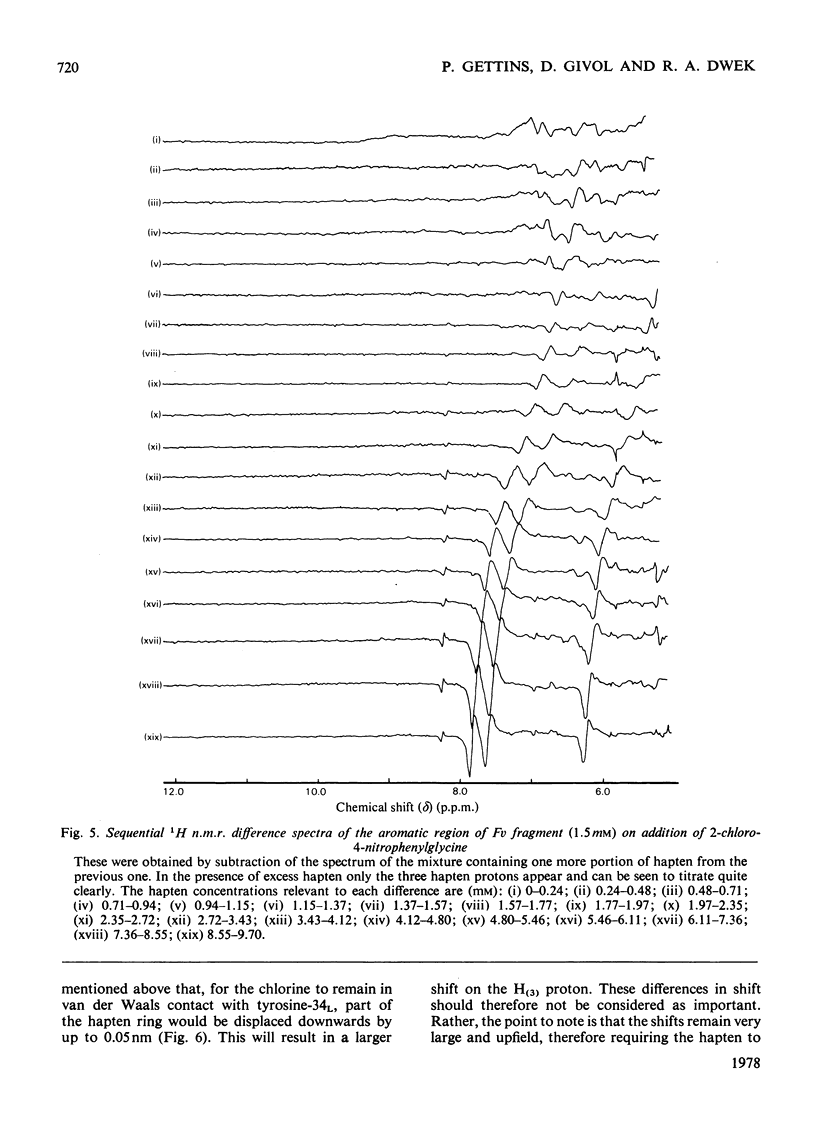
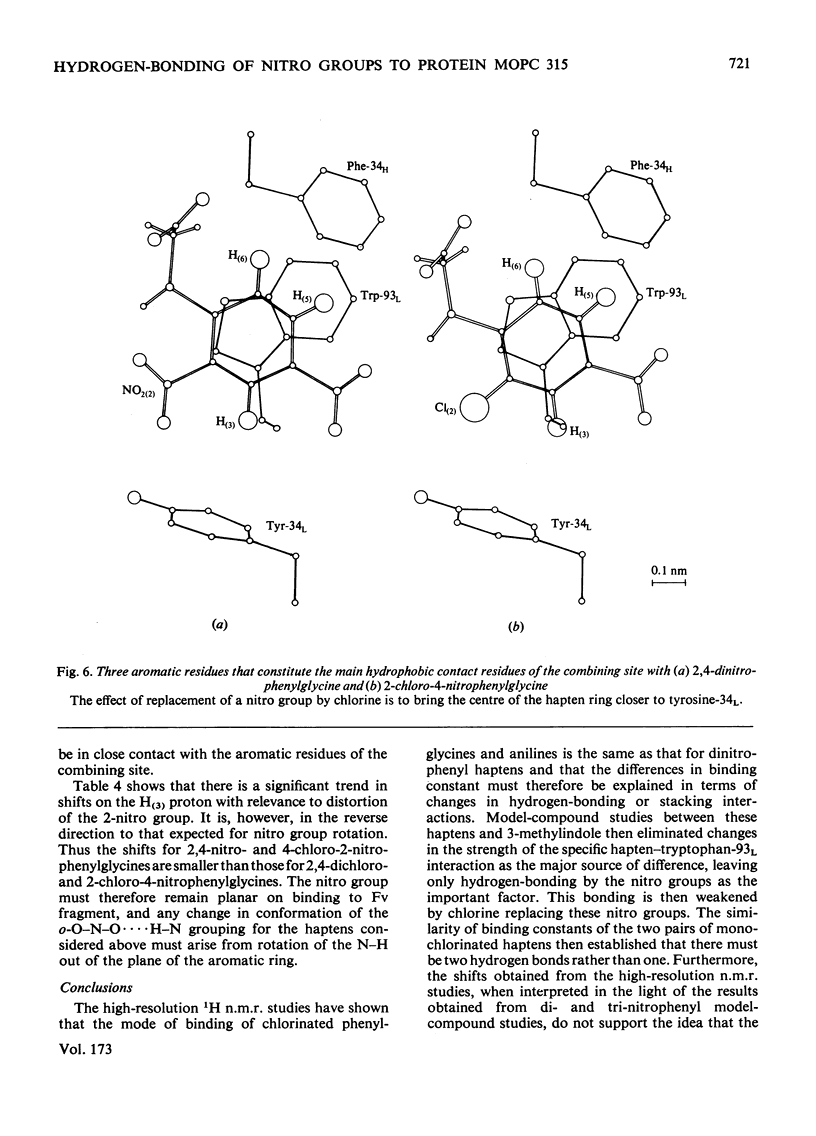
Two series of dinitrophenyl haptens, in which chlorine replaces one or both nitro groups, were used to investigate, by a combination of high-resolution 1H n.m.r. and fluorescence quenching, the presence of groups in the combining site of protein MOPC 315, which form hydrogen bonds to the aromatic-ring substituents of the hapten. The large differences in binding constants on successive replacement of nitro groups were shown to be due to specific hapten-substituent-protein interactions by (a) showing that there was little difference in the interaction between these haptens and 3-methylindole (a model for the residue tryptophan-93L with which the hapten stacks in protein MOPC 315), (b) proving by 1H n.m.r. that the mode of hapten binding is constant and (c) showing that the differences in Kd were consistent with the relative hydrogen-bonding capacities of chlorine and the nitro moiety. In this way it was established that each nitro group forms a hydrogen bond. Furthermore, from consideration of the 1H n.m.r. chemical shifts of several dinitrophenyl haptens and their trinitrophenyl analogues, it was shown that there is no distortion of the o-nitro group on binding to the variable fragment of protein MOPC 315.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dower S. K., Gettins P., Jackson R., Dwek R. A., Givol D. The binding of 2,4,6-trinitrophenyl derivatives to the mouse myeloma immunoglobulin A protein MOPC 315. Biochem J. 1978 Jan 1;169(1):179–188. doi: 10.1042/bj1690179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dower S. K., Wain-Hobson S., Gettins P., Givol D., Jackson W. R., Perkins S. J., Sunderland C. A., Sutton B. J., Wright C. E., Dwek R. A. The combining site of the dinitrophenyl-binding immunoglobulin A myeloma protein MOPC 315. Biochem J. 1977 Aug 1;165(2):207–223. doi: 10.1042/bj1650207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwek R. A., Givol D., Jones R., McLaughlin A. C., Wain-Hobson S., White A. I., Wright C. Interactions of the lanthanide- and hapten-binding sites in the Fv fragment from the myeloma protein MOPC 315. Biochem J. 1976 Apr 1;155(1):37–53. doi: 10.1042/bj1550037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haselkorn D., Friedman S., Givol D., Pecht I. Kinetic mapping of the antibody combining site by chemical relaxation spectrometry. Biochemistry. 1974 May 7;13(10):2210–2222. doi: 10.1021/bi00707a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochman J., Inbar D., Givol D. An active antibody fragment (Fv) composed of the variable portions of heavy and light chains. Biochemistry. 1973 Mar 13;12(6):1130–1135. doi: 10.1021/bi00730a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padlan E. A., Davies D. R., Pecht I., Givol D., Wright C. Model-building studies of antigen-binding sites: the hapten-binding site of mopc-315. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1977;41(Pt 2):627–637. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1977.041.01.072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


