Abstract
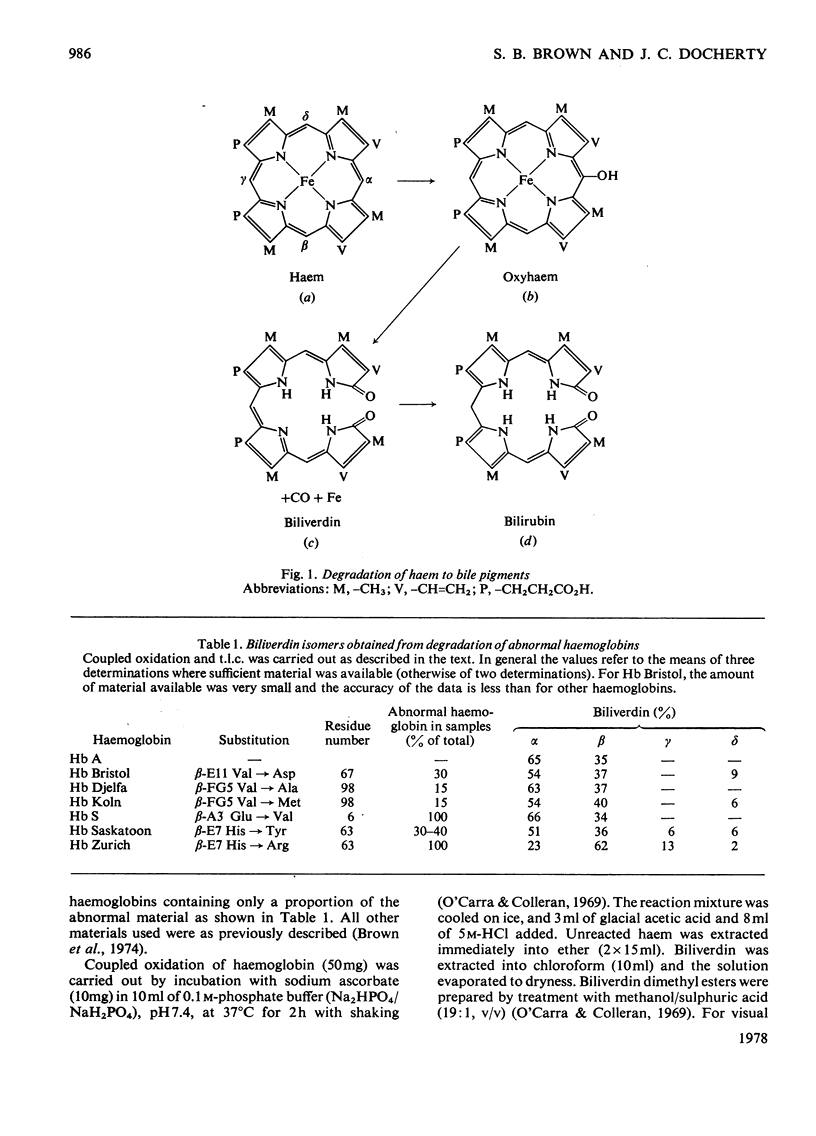
The coupled oxidation of certain abnormal haemoglobins leads to different bile-pigment isomer distributions from that of normal haemoglobin. The isomer pattern may be correlated with the structure of the abnormal haemoglobin in the neighbourhood of the haem pocket. This is support for haem degradation by an intramolecular reaction.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- 'Carra P. O., Colleran E. HAEM catabolism and coupled oxidation of haemproteins. FEBS Lett. 1969 Nov 29;5(4):295–298. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80372-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnett R., McDonagh A. F. The meso-reactivity of porphyrins and related compounds. VI. Oxidative cleavage of the haem system. The four isomeric biliverdins of the IX series. J Chem Soc Perkin 1. 1973;9:881–888. doi: 10.1039/p19730000881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown N. A., King R. F., Shillcock M. E., Brown S. B. Haemoglobin catabolism: the role of ferrihaems in studies of the degradation pathway. Biochem J. 1974 Jan;137(1):135–137. doi: 10.1042/bj1370135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. B. Stereospecific haem cleavage. A model for the formation of bile-pigment isomers in vivo and in vitro. Biochem J. 1976 Oct 1;159(1):23–27. doi: 10.1042/bj1590023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perutz M. F., Lehmann H. Molecular pathology of human haemoglobin. Nature. 1968 Aug 31;219(5157):902–909. doi: 10.1038/219902a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perutz M. F. Structure and mechanism of haemoglobin. Br Med Bull. 1976 Sep;32(3):195–208. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid R., McDonagh A. F. The enzymatic formation of bilirubin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Apr 15;244:533–552. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb41553.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenhunen R., Marver H. S., Schmid R. The enzymatic conversion of heme to bilirubin by microsomal heme oxygenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Oct;61(2):748–755. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.2.748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winterhalter K. H., Di Iorio E. E., Beetlestone J. G., Kushimo J. B., Uebelhack H., Eicher H., Mayer A. The electronic structure of the haem iron in haemoglobin Zurich beta 63his-arg. J Mol Biol. 1972 Oct 14;70(3):665–674. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90565-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winterhalter K. H., Wüthrich K. Structural investigations of modified haemoglobins by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Mol Biol. 1972 Feb 14;63(3):477–482. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90442-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


