Abstract
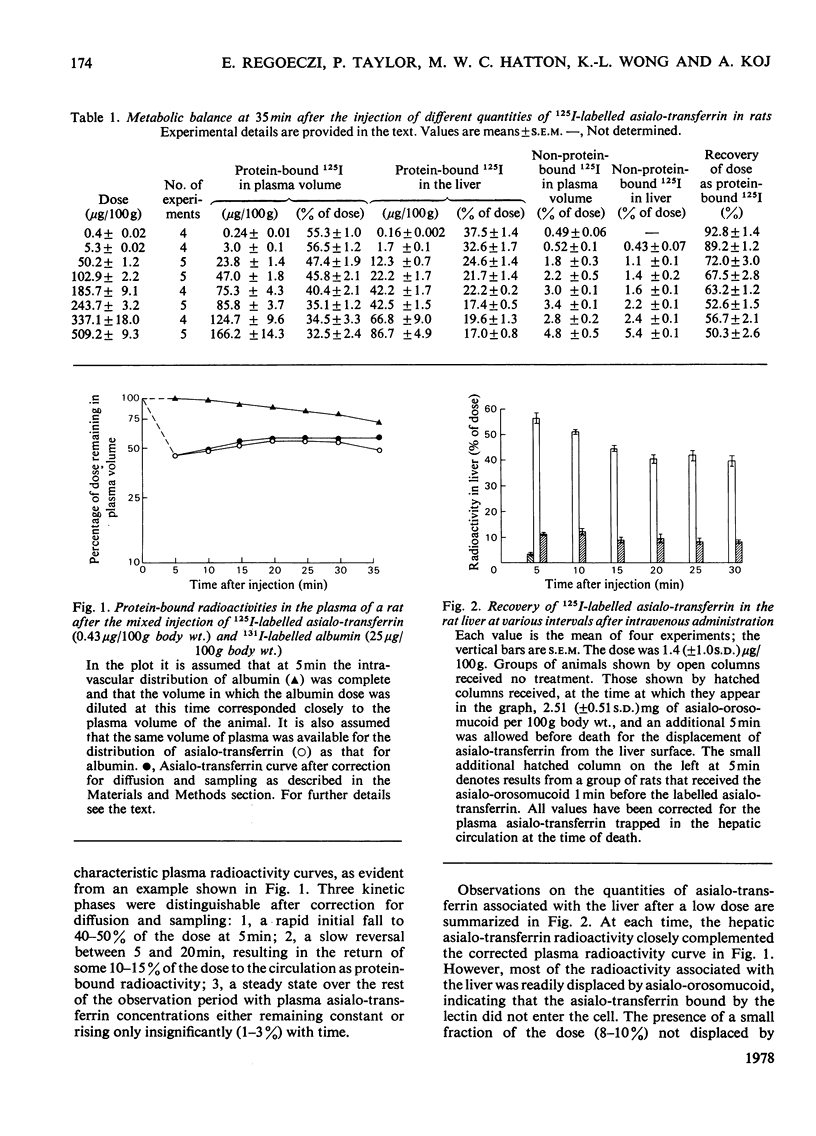
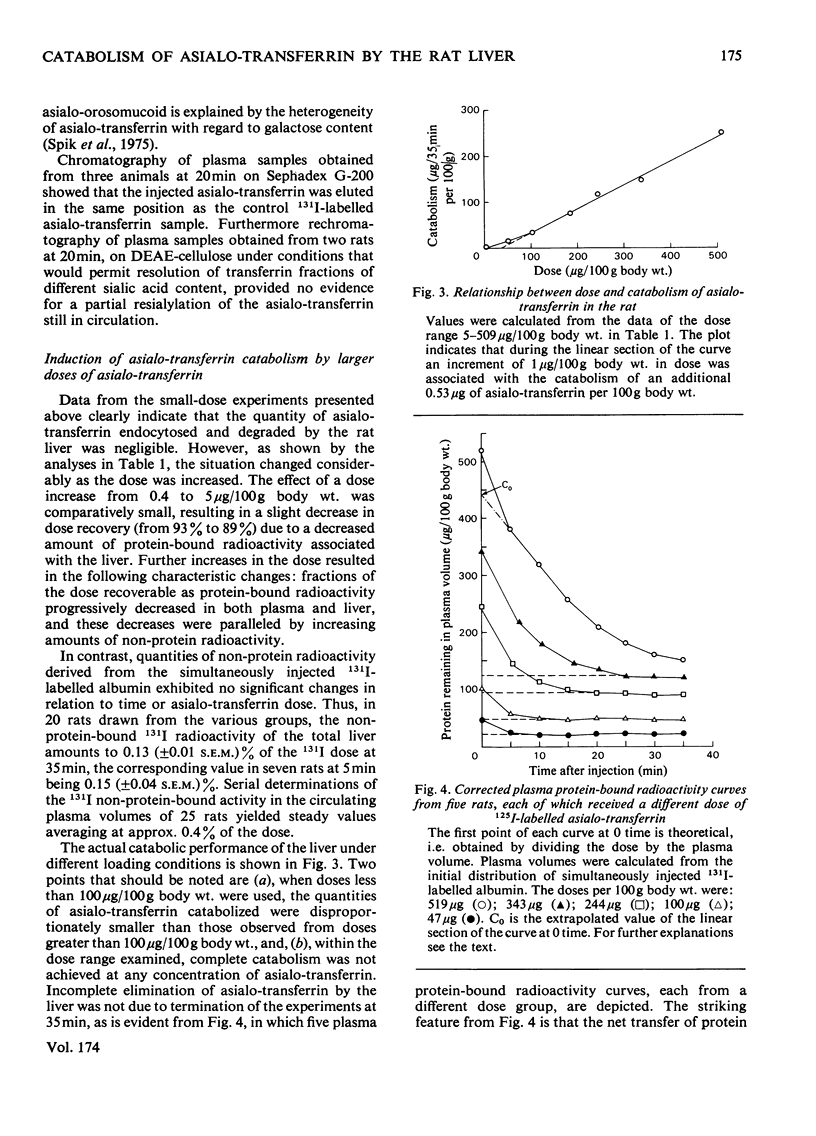
The ability of the rat liver to bind and endocytose human asialo-transferrin was investigated in vivo. Asialo-transferrin was separated from incompletely desialylated transferrin and neuraminidase by chromatography before being labelled with 125I. Plasma radioactivity curves and hepatic radioactivity contents measured over a 1270-fold dose range led to the following observation. At the lowest dose (0.4μg/100g body wt.), the distribution of asialo-transferrin between plasma and liver resembled a reversible reaction reaching equilibrium in approx. 20min. After 35min, 93% of the dose was recovered with the plasma and liver as protein-bound radioactivity. Most of the asialo-transferrin associated with the liver could be displaced by asialo-orosomucoid, indicating that binding of asialo-transferrin to the galactose-specific lectin on the plasma membrane of hepatocytes was not followed by a signal for endocytosis. A range of doses, up to an average of 509.2μg of asialo-transferrin per 100g body wt., resulted in progressive increments in asialo-transferrin catabolism, as evidenced by lower dose recoveries and increased concentrations of non-protein-associated radioactivity in the liver and plasma volume. These observations indicate that binding and endocytosis of human asialo-transferrin by the rat hepatocyte are distinct phenomena. Individual asialo-transferrin molecules, although readily bound by the hepatic lectin, lack either the quantity or spacing of terminal galactose residues necessary for triggering endocytosis. Although endocytosis is induced by several asialo-transferrin molecules acting synergistically, preliminary experiments with asialo-glycopeptides and other substances have so far failed to provide further insight into the chemical basis of the signal for endocytosis.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMINOFF D. Methods for the quantitative estimation of N-acetylneuraminic acid and their application to hydrolysates of sialomucoids. Biochem J. 1961 Nov;81:384–392. doi: 10.1042/bj0810384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashwell G., Morell A. G. The role of surface carbohydrates in the hepatic recognition and transport of circulating glycoproteins. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1974;41(0):99–128. doi: 10.1002/9780470122860.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARKE J. T. SIMPLIFIED "DISC" (POLYACRYLAMIDE GEL) ELECTROPHORESIS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:428–436. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14214.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlwood P. A. Differential sedimentation-velocity and gel-filtration measurements on human apotransferrin and iron-transferrin. Biochem J. 1971 Dec;125(4):1019–1026. doi: 10.1042/bj1251019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlwood P. A., Hatton M. W., Regoeczi E. The physicochemical and chemical properties of alpha 1-acid glycoproteins from mammalian and avian plasmas. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 26;453(1):81–92. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(76)90252-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregoriadis G., Morell A. G., Sternlieb I., Scheinberg I. H. Catabolism of desialylated ceruloplasmin in the liver. J Biol Chem. 1970 Nov 10;245(21):5833–5837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatton M. W., Regoeczi E. A simple method for the purification of commercial neuraminidase preparations free from proteases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Nov 15;327(1):114–120. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90108-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatton M. W., Regoeczi E., Kaur H. Bovine transferrin glycopeptide: the relevance of its structure to interaction with the mammalian hepatic lectin that binds asialoglycoproteins. Can J Biochem. 1978 May;56(5):339–344. doi: 10.1139/o78-053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki T., Ashwell G. Chemical and physical properties of an hepatic membrane protein that specifically binds asialoglycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 10;251(5):1296–1302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koj A., Hatton M. W., Wong K. L., Regoeczi E. Isolation and partial characterization of rabbit plasma alpha1-antitrypsin. Biochem J. 1978 Mar 1;169(3):589–596. doi: 10.1042/bj1690589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaBadie J. H., Chapman K. P., Aronson N. N., Jr Glycoprotein catabolism in rat liver: Lysosomal digestion of iodinated asialo-fetuin. Biochem J. 1975 Nov;152(2):271–279. doi: 10.1042/bj1520271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane R. S. DEAE-cellulose chromatography of human transferrin: the effect of increasing iron saturation and copper(II) binding. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Aug 27;243(2):193–202. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90076-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFARLANE A. S. Efficient trace-labelling of proteins with iodine. Nature. 1958 Jul 5;182(4627):53–53. doi: 10.1038/182053a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarlane A. S., Koj A. Short-term measurement of catabolic rates using iodine-labeled plasma protein. J Clin Invest. 1970 Oct;49(10):1903–1911. doi: 10.1172/JCI106409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore A. T., Williams K. E., Lloyd J. B. The effect of chemical treatments of albumin and orosomucoid on rate of clearance from the rat bloodstream and rate of pinocytic capture of rat yolk sac cultured in vitro. Biochem J. 1977 Jun 15;164(3):607–616. doi: 10.1042/bj1640607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morell A. G., Gregoriadis G., Scheinberg I. H., Hickman J., Ashwell G. The role of sialic acid in determining the survival of glycoproteins in the circulation. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1461–1467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoeczi E., Hatton M. W., Charlwood P. A. Carbohydrate-mediated elimination of avian plasma glycoprotein in mammals. Nature. 1975 Apr 24;254(5502):699–701. doi: 10.1038/254699a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoeczi E., Hatton M. W. Studies of the metabolism of asialotransferrins: the mechanism for the hypercatabolism of human asialotransferrin in the rabbit. Can J Biochem. 1974 Jul;52(7):645–651. doi: 10.1139/o74-092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoeczi E. Hepatic uptake of asialoglycoproteins in vivo: quantification using a dual-isotope technique. J Nucl Biol Med. 1975 Jul-Sep;19(3):149–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoeczi E., Wong K. L., Ali M., Hatton M. W. The molecular components of human transferrin type C. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1977;10(1):17–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1977.tb02772.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J. C., Kornfeld S. Hepatic uptake of proteins coupled to fetuin glycopeptide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Nov 5;45(3):622–629. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90462-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spik G., Bayard B., Fournet B., Strecker G., Bouquelet S., Montreuil J. Studies on glycoconjugates. LXIV. Complete structure of two carbohydrate units of human serotransferrin. FEBS Lett. 1975 Feb 15;50(3):296–299. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80513-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro R. G. Glycoproteins. Adv Protein Chem. 1973;27:349–467. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60451-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockert R. J., Morell A. G., Scheinberg I. H. Mammalian hepatic lectin. Science. 1974 Oct 25;186(4161):365–366. doi: 10.1126/science.186.4161.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Lenten L., Ashwell G. The binding of desialylated glycoproteins by plasma membranes of rat liver. Development of a quantitative inhibition assay. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jul 25;247(14):4633–4640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. L., Regoeczi E. Some observations on the carbohydrate composition of purified transferrin. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1977;9(4):241–248. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1977.tb03487.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


