Abstract
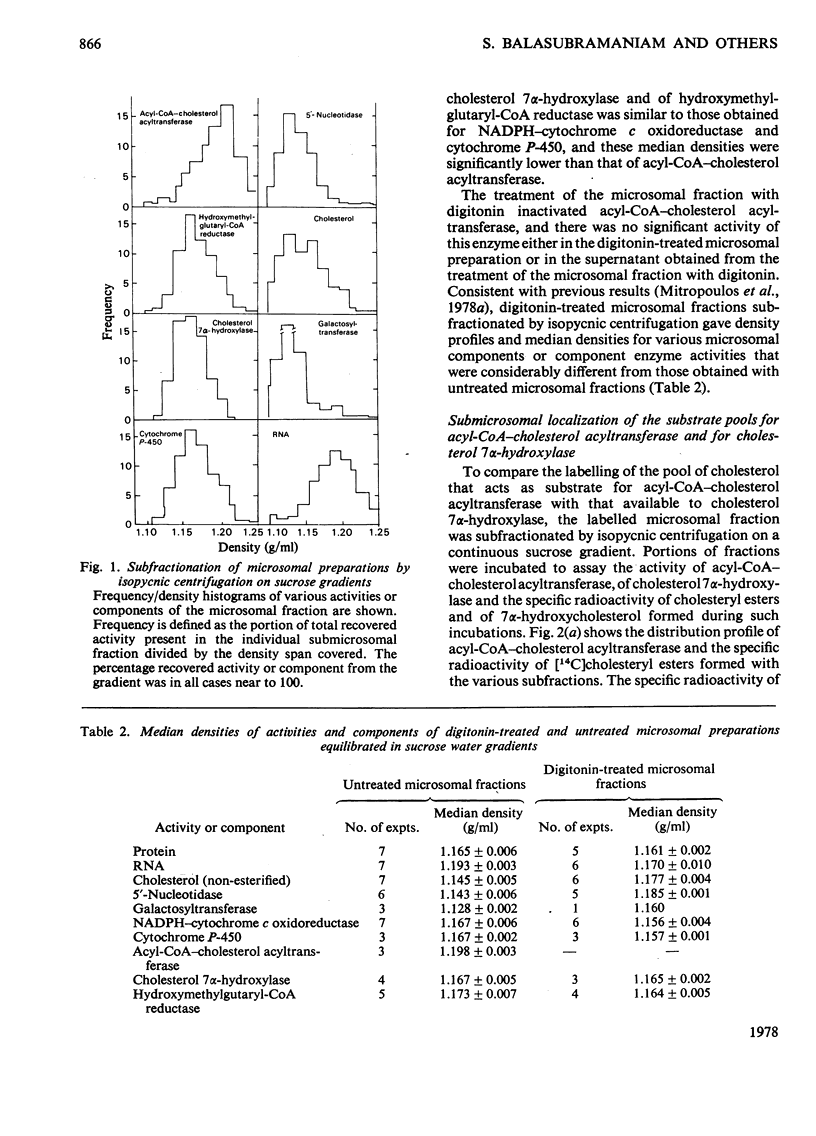
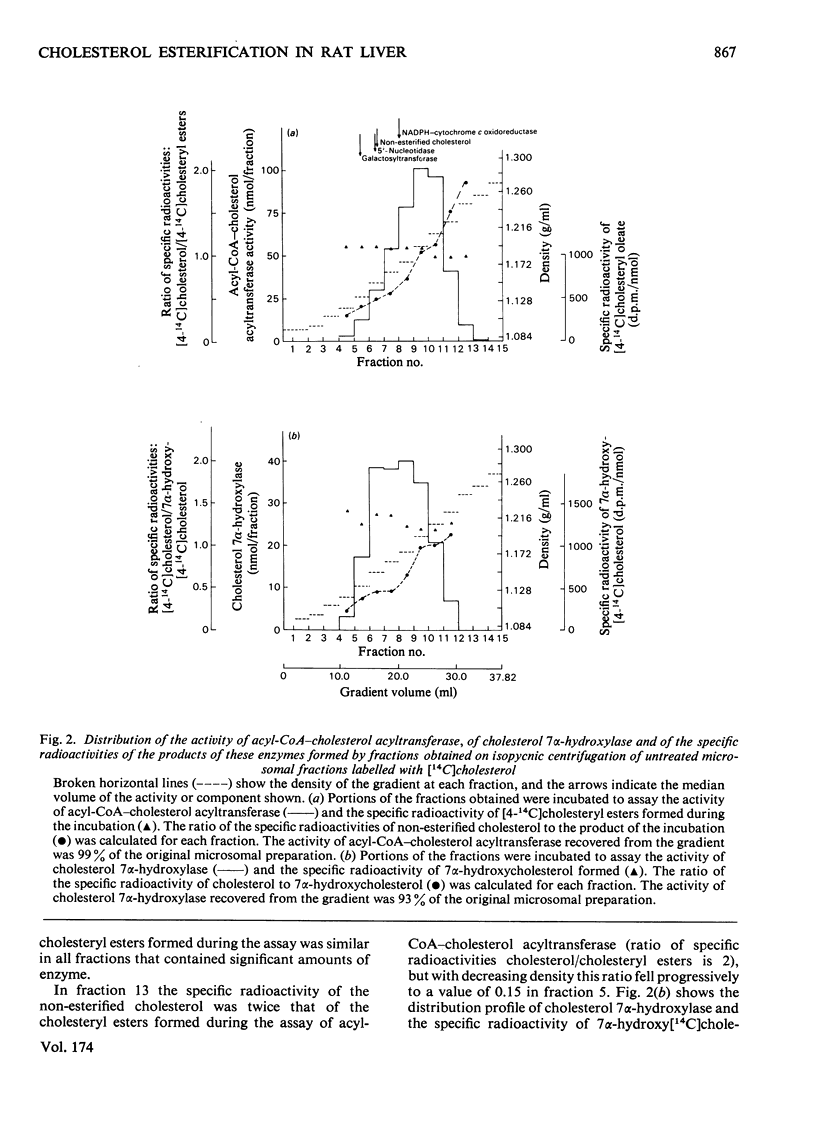
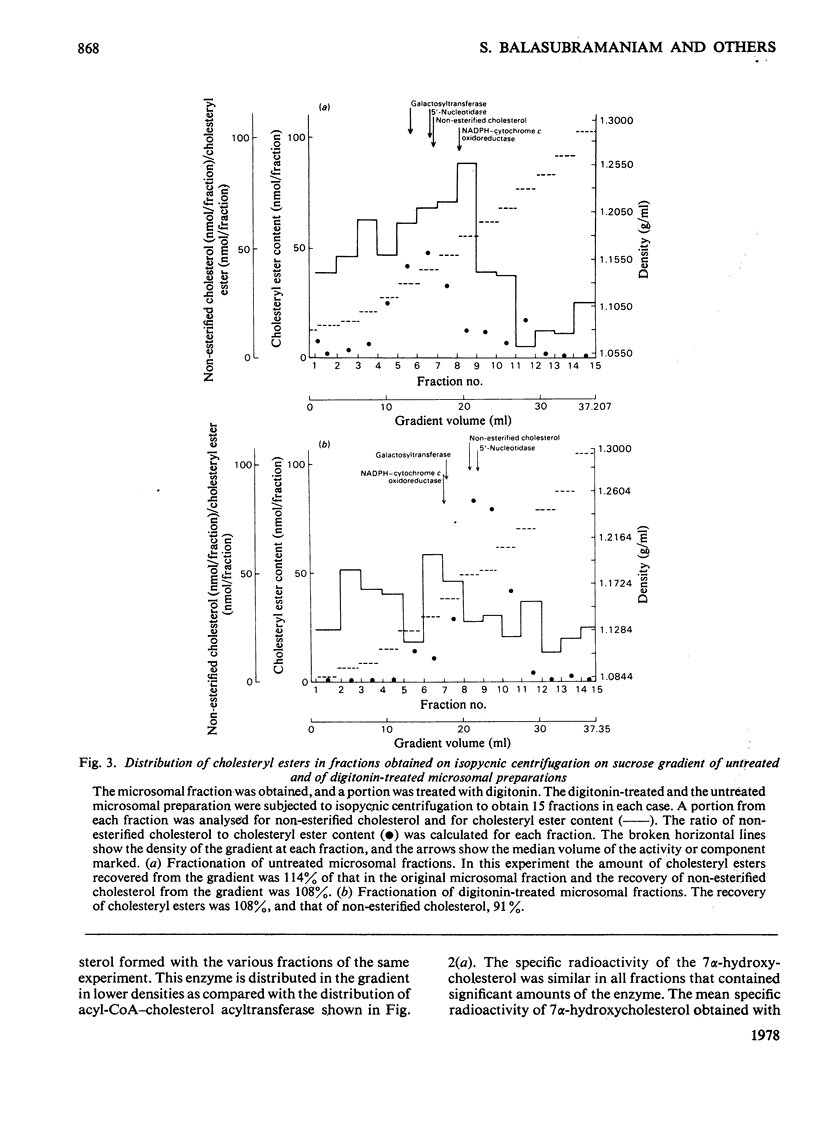
To determine the submicrosomal distribution of acyl-CoA–cholesterol acyltransferase and of cholesteryl esters, the microsomal fraction and the digitonin-treated microsomal preparation of rat liver were subjected to analytical centrifugation on sucrose density gradients. With untreated microsomal fractions the distribution profile and the median density of acyl-CoA–cholesterol acyltransferase were very similar to those of RNA. This is in contrast with hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase and cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase, which are confined to endoplasmic reticulum membranes with low ribosomal coating. In digitonin-treated microsomal preparations activity of acyl-CoA–cholesterol acyltransferase was not detectable. The labelling of untreated microsomal fractions with trace amounts of [14C]cholesterol followed by subfractionation of the labelled microsomal fraction showed that the specific radioactivity of cholesteryl esters obtained in vitro by the various subfractions was similar with all subfractions but different from the specific radioactivity of the 7α-hydroxycholesterol obtained in vitro by the same subfraction. These results demonstrate the existence of two pools of cholesterol confined to membranes from the endoplasmic reticulum, one acting as substrate for cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase and the other acting as substrate for acyl-CoA–cholesterol acyltransferase. The major part of cholesteryl esters present in both untreated and digitonin-treated microsomal fractions was distributed at densities similar to those of membranes from the smooth endoplasmic reticulum and at densities lower than those of smooth membranes from Golgi apparatus. The ratio of the concentrations of non-esterified to esterified cholesterol in the subfractions from both untreated and digitonin-treated microsomal fractions was highest at the maximum distribution of plasma membranes.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amar-Costesec A., Beaufay H., Wibo M., Thinès-Sempoux D., Feytmans E., Robbi M., Berthet J. Analytical study of microsomes and isolated subcellular membranes from rat liver. II. Preparation and composition of the microsomal fraction. J Cell Biol. 1974 Apr;61(1):201–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.61.1.201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balasubramaniam S., Goldstein J. L., Faust J. R., Brunschede G. Y., Brown M. S. Lipoprotein-mediated regulation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase activity and cholesteryl ester metabolism in the adrenal gland of the rat. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 10;252(5):1771–1779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balasubramaniam S., Mitropoulos K. A., Myant N. B. Evidence for the compartmentation of cholesterol in rat-liver microsomes. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Apr 2;34(1):77–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02730.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balasubramaniam S., Mitropoulos K. A., Myant N. B. The substrate for cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jul 22;398(1):172–177. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(75)90180-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesterton C. J. Distribution of cholesterol precursors and other lipids among rat liver intracellular structures. J Biol Chem. 1968 Mar 25;243(6):1147–1151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielsson H., Einarsson K., Johansson G. Effect of biliary drainage on individual reactions in the conversion of cholesterol to taurochlic acid. Bile acids and steroids 180. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Jul;2(1):44–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1967.tb00103.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depierre J. W., Dallner G. Structural aspects of the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Dec 29;415(4):411–472. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietschy J. M., Brown M. S. Effect of alterations of the specific activity of the intracellular acetyl CoA pool on apparent rates of hepatic cholesterogenesis. J Lipid Res. 1974 Sep;15(5):508–516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODMAN D. S., DEYKIN D., SHIRATORI T. THE FORMATION OF CHOLESTEROL ESTERS WITH RAT LIVER ENZYMES. J Biol Chem. 1964 May;239:1335–1345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidez L. I., Roheim P. S., Eder H. A. Turnover of cholesteryl esters of plasma lipoproteins in the rat. J Lipid Res. 1967 Jan;8(1):7–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRAOKA T., GLICK D. Studies in histochemistry. LXXI. Measurement of protein in millimicrogram amounts by quenching of dye fluorescence. Anal Biochem. 1963 Jun;5:497–504. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(63)90069-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R. L., Regen D. M., Gray M. E., LeQuire V. S. Lipid transport in liver. I. Electron microscopic identification of very low density lipoproteins in perfused rat liver. Lab Invest. 1967 Feb;16(2):305–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel R. J. Lipoproteins and lipid transport. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1975;63:37–59. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3258-9_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones A. L., Ruderman N. B., Herrera M. G. Electron microscopic and biochemical study of lipoprotein synthesis in the isolated perfused rat liver. J Lipid Res. 1967 Sep;8(5):429–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Pecq J. B., Paoletti C. A new fluorometric method for RNA and DNA determination. Anal Biochem. 1966 Oct;17(1):100–107. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90012-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitropoulos K. A., Balasubramaniam S. Cholesterol 7 -hydroxylase in rat liver microsomal preparations. Biochem J. 1972 Jun;128(1):1–9. doi: 10.1042/bj1280001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitropoulos K. A., Balasubramaniam S., Myant N. B. The effect of interruption of the enterophecatic circulation of bile acids and of cholesterol feeding on cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase in relation to the diurnal rhythm in its activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Dec 20;326(3):428–438. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(73)90143-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitropoulos K. A., Balasubramaniam S. The role of glucocorticoids in the regulation of the diurnal rhythm of hepatic beta-hydroxy-beta-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase and cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase. Biochem J. 1976 Oct 15;160(1):49–55. doi: 10.1042/bj1600049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitropoulos K. A., Venkatesan S., Balasubramaniam S., Peters T. J. The submicrosomal localization of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme-A reductase, cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase and cholesterol in rat liver. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jan 16;82(2):419–429. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12036.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitropoulos K. A., Venkatesan S. The influence of cholesterol on the activity, on the isothermic kinetics and on the temperature-induced kinetics of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme a reductase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Oct 24;489(1):126–142. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(77)90239-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson L. H., Hultman E. Liver and muscle glycogen in man after glucose and fructose infusion. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1974 Feb;33(1):5–10. doi: 10.3109/00365517409114190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PALADE G. E., SIEKEVITZ P. Liver microsomes; an integrated morphological and biochemical study. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1956 Mar 25;2(2):171–200. doi: 10.1083/jcb.2.2.171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachter H., Jabbal I., Hudgin R. L., Pinteric L., McGuire E. J., Roseman S. Intracellular localization of liver sugar nucleotide glycoprotein glycosyltransferases in a Golgi-rich fraction. J Biol Chem. 1970 Mar 10;245(5):1090–1100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumaker V. N., Adams G. H. Circulating lipoproteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1969;38:113–136. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.38.070169.000553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shefer S., Hauser S., Bekersky I., Mosbach E. H. Biochemical site of regulation of bile acid biosynthesis in the rat. J Lipid Res. 1970 Sep;11(5):404–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solyom A., Trams E. G. Enzyme markers in characterization of isolated plasma membranes. Enzyme. 1972;13(5-6):329–372. doi: 10.1159/000459682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokke K. T., Norum K. R. Subcellular distribution of acyl-CoA: cholesterol acyltransferase in rat liver cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jun 9;210(1):202–204. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(70)90082-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilleray J., Peters T. J. Analytical subfractionation of microsomal fractions from the livers of control and Gunn-strain rats. Biochem Soc Trans. 1976;4(2):248–250. doi: 10.1042/bst0040248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Cantfort J., Gielen J. Cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase. 2. Biochemical properties and participation of endogenous cholesterol in the assay in vitro. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jun 16;55(1):33–40. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02135.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


