Abstract
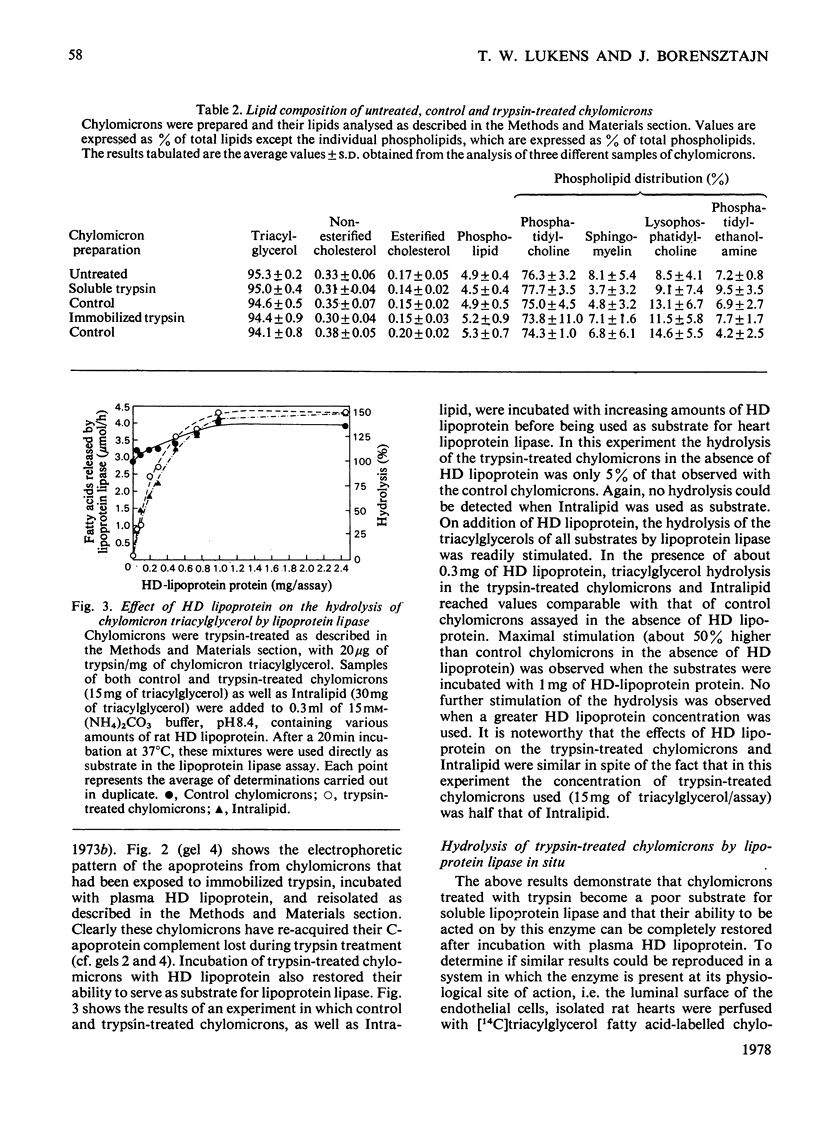
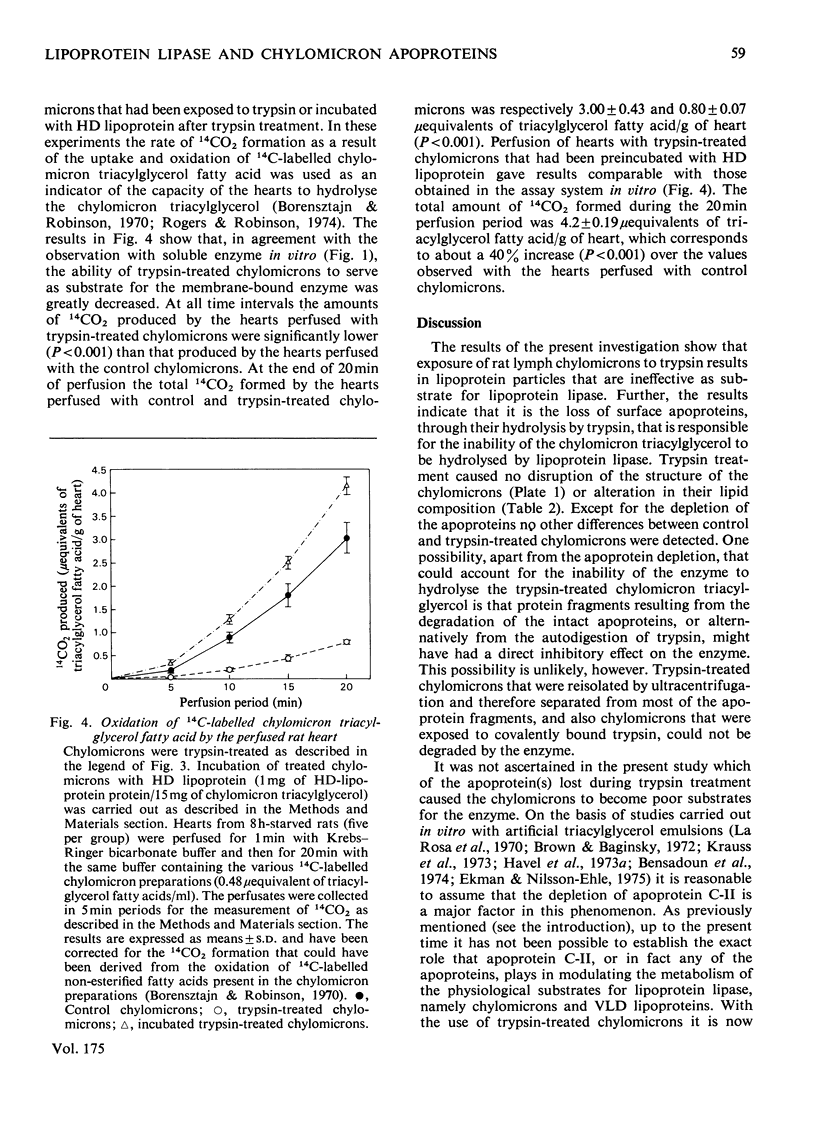
1. Rat lymph chylomicrons were exposed to soluble and to immobilized trypsin. This treatment caused no detectable changes in the chylomicron structure or lipid composition, but did result in virtually total depletion of all their tetramethylurea-soluble apoproteins. 2. The capacity of these apoprotein-depleted chylomicrons to act as substrate for lipoprotein lipase in vitro and in situ (i.e. isolated perfused rat heart) was decreased by about 90 and 75% respectively, compared with intact chylomicrons. 3. On incubation with rat plasma high-density lipoproteins, trypsin-treated chylomicrons readily acquired a full apoprotein complement. This resulted in the complete restoration of their capacity to act as substrate for lipoprotein lipase both in vitro and in situ. 4. It is suggested that with the use of try,sin-treated chylomicrons it is now possible for the first time to investigate the physiological role that individual apoproteins play in the catabolism of triacylglycerol-rich lipoproteins by lipoprotein lipase.
Full text
PDF


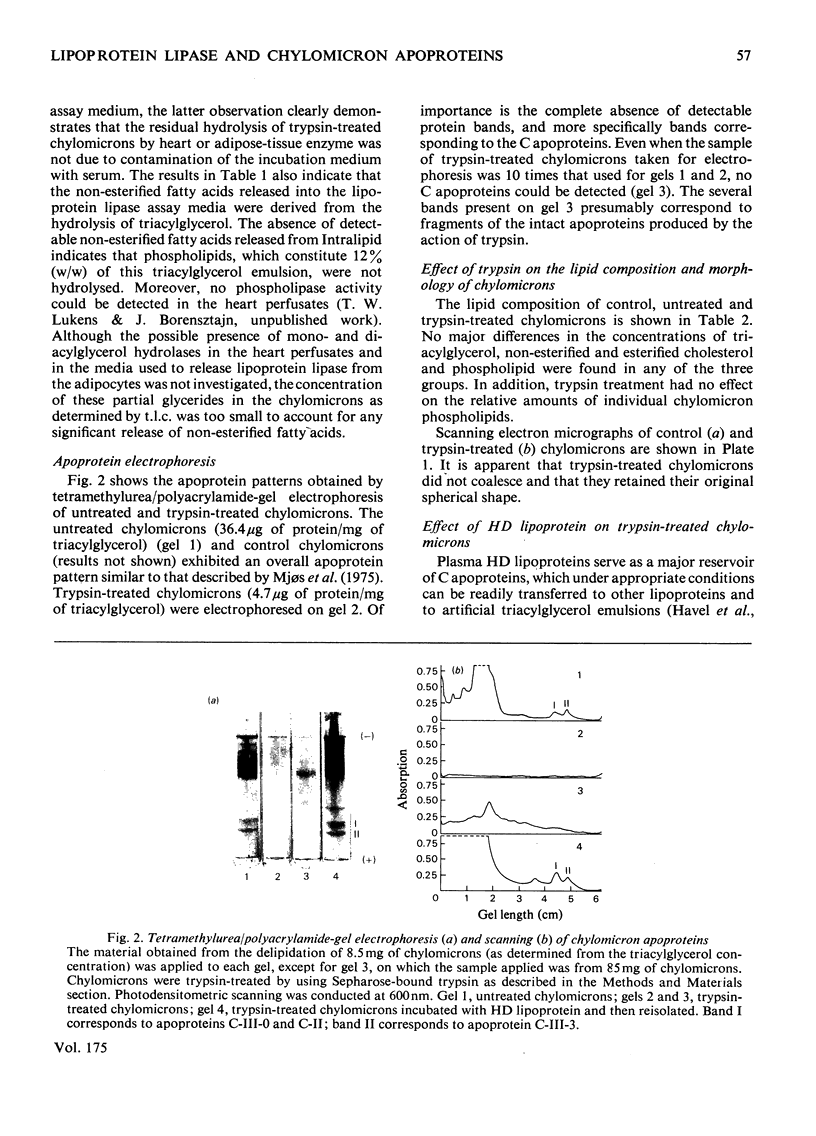


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERNFELD P., KELLEY T. F. PROTEOLYSIS OF HUMAN SERUM BETA-LIPOPROTEIN. J Biol Chem. 1964 Oct;239:3341–3346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-On H., Roheim P. S., Eder H. A. Serum lipoproteins and apolipoproteins in rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. J Clin Invest. 1976 Mar;57(3):714–721. doi: 10.1172/JCI108329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensadoun A., Ehnholm C., Steinberg D., Brown W. V. Purification and characterization of lipoprotein lipase from pig adipose tissue. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 10;249(7):2220–2227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaton V., Vandamme D., Peeters H. Activation of lipoprotein lipase in vitro by unsaturated phospholipids. FEBS Lett. 1974 Aug 25;44(2):185–188. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80722-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borensztajn J., Otway S., Robinson D. S. Effect of fasting on the clearing factor lipase (lipoprotein lipase) activity of fresh and defatted preparations of rat heart muscle. J Lipid Res. 1970 Mar;11(2):102–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borensztajn J., Robinson D. S. The effect of fasting on the utilization of chylomicron triglyceride fatty acids in relation to clearing factor lipase (lipoprotein lipase) releasable by heparin in the perfused rat heart. J Lipid Res. 1970 Mar;11(2):111–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. V., Baginsky M. L. Inhibition of lipoprotein lipase by an apoprotein of human very low density lipoprotein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jan 31;46(2):375–382. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(72)80149-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung J., Scanu A. M. Isolation, molecular properties, and kinetic characterization of lipoprotein lipase from rat heart. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 25;252(12):4202–4209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung J., Scanu A. M., Reman F. Effect of phospholipids on lipoprotein lipase activation in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jan 19;296(1):116–123. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(73)90050-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P., Parikh I. Adsorbents for affinity chromatography. Use of N-hydroxysuccinimide esters of agarose. Biochemistry. 1972 Jun 6;11(12):2291–2299. doi: 10.1021/bi00762a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERLANGER B. F., KOKOWSKY N., COHEN W. The preparation and properties of two new chromogenic substrates of trypsin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 Nov;95:271–278. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90145-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egelrud T., Olivecrona T. Purified bovine milk (lipoprotein) lipase: activity against lipid substrates in the absence of exogenous serum factors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 13;306(1):115–127. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(73)90215-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehnholm C., Kinnunen P. K., Huttunen J. K., Nikkilä E. A., Ota M. Purification and characterization of lipoprotein lipase from pig myocardium. Biochem J. 1975 Sep;149(3):649–655. doi: 10.1042/bj1490649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekman R., Nilsson-Ehle P. Effects of apolipoproteins on lipoprotein lipase activity of human adipose tissue. Clin Chim Acta. 1975 Aug 18;63(1):29–35. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(75)90374-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher M. J. A colorimetric method for estimating serum triglycerides. Clin Chim Acta. 1968 Nov;22(3):393–397. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(68)90041-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganesan D., Bass H. B. Isolation of C-I and C-II activated lipoprotein lipases and protamine insensitive triglyceride lipase by heparin-sepharose affinity chromatography. FEBS Lett. 1975 Apr 15;53(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80667-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganesan D., Bass H. B., McConathy W. J., Alaupovic P. Is decreased activity of C-II activated lipoprotein lipase in type III hyperlipoproteinemia (broad-beta-disease) a cause or an effect of increased apolipoprotein E levels? Metabolism. 1976 Nov;25(11):1189–1195. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(76)80001-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganesan D., Bradford R. H., Alaupovic P., McConathy W. J. Differential activation of lipoprotein lipase from human post-heparin plasma, milk and adipose tissue by polypeptides of human serum Apolipoprotein C. FEBS Lett. 1971 Jun 24;15(3):205–208. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80312-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glickman R. M., Kirsch K. Lymph chylomicron formation during the inhibition of protein synthesis. Studies of chylomicron apoproteins. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2910–2920. doi: 10.1172/JCI107487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel R. J., Fielding C. J., Olivecrona T., Shore V. G., Fielding P. E., Egelrud T. Cofactor activity of protein components of human very low density lipoproteins in the hydrolysis of triglycerides by lipoproteins lipase from different sources. Biochemistry. 1973 Apr 24;12(9):1828–1833. doi: 10.1021/bi00733a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel R. J., Kane J. P., Kashyap M. L. Interchange of apolipoproteins between chylomicrons and high density lipoproteins during alimentary lipemia in man. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jan;52(1):32–38. doi: 10.1172/JCI107171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel R. J., Shore V. G., Shore B., Bier D. M. Role of specific glycopeptides of human serum lipoproteins in the activation of lipoprotein lipase. Circ Res. 1970 Oct;27(4):595–600. doi: 10.1161/01.res.27.4.595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heaf D. J., Carlson L. A. The effect of lysolecithin on the release of oleate from triolein by human post-heparin lipase. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1976 Nov;36(7):693–695. doi: 10.3109/00365517609054498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane J. P. A rapid electrophoretic technique for identification of subunit species of apoproteins in serum lipoproteins. Anal Biochem. 1973 Jun;53(2):350–364. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90081-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krauss R. M., Herbert P. N., Levy R. I., Fredrickson D. S. Further observations on the activation and inhibition of lipoprotein lipase by apolipoproteins. Circ Res. 1973 Oct;33(4):403–411. doi: 10.1161/01.res.33.4.403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaRosa J. C., Levy R. I., Herbert P., Lux S. E., Fredrickson D. S. A specific apoprotein activator for lipoprotein lipase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Oct 9;41(1):57–62. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90468-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis S., Langdon R. G. Studies on human serum beta-1-lipoprotein. 3. Enzymatic modifications. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jan 25;241(2):485–493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. L., Smith L. C. Activation of lipoprotein lipase by apolipoprotein glutamic acid. Formation of a stable surface film. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 10;248(9):3359–3362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mjos O. D., Faergeman O., Hamilton R. L., Havel R. J. Characterization of remnants produced during the metabolism of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins of blood plasma and intestinal lymph in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1975 Sep;56(3):603–615. doi: 10.1172/JCI108130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostlund-Lindqvist A. M., Iverius P. H. Activation of highly purified lipoprotein lipase from bovine milk. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Aug 18;65(4):1447–1455. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80391-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quarfordt S. H., Hilderman H., Greenfield M. R., Shelburne F. A. The effect of human arginine rich apoprotein on rat adipose lipoprotein lipase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Sep 9;78(1):302–308. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91254-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers M. P., Barnett D., Robinson D. S. Clearing factor lipase (lipoprotein lipase) activator. A method for the measurement of the net activating ability of human sera. Atherosclerosis. 1976 Sep;24(3):551–564. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(76)90147-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers M. P., Robinson D. S. Effects of cold exposure on heart clearing factor lipase and triglyceride utilization in the rat. J Lipid Res. 1974 May;15(3):263–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPERRY W. M., WEBB M. A revision of the Schoenheimer-Sperry method for cholesterol determination. J Biol Chem. 1950 Nov;187(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schonfeld G., Weidman S. W., Witztum J. L., Bowen R. M. Alterations in levels and interrelations of plasma apolipoproteins induced by diet. Metabolism. 1976 Mar;25(3):261–275. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(76)90084-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen B. W., Scanu A. M., Kézdy F. J. Structure of human serum lipoproteins inferred from compositional analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):837–841. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skipski V. P., Peterson R. F., Barclay M. Quantitative analysis of phospholipids by thin-layer chromatography. Biochem J. 1964 Feb;90(2):374–378. doi: 10.1042/bj0900374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twu J. S., Garfinkel A. S., Schotz M. C. Rat heart lipoprotein lipase. Atherosclerosis. 1975 Nov-Dec;22(3):463–472. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(75)90025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]