Abstract
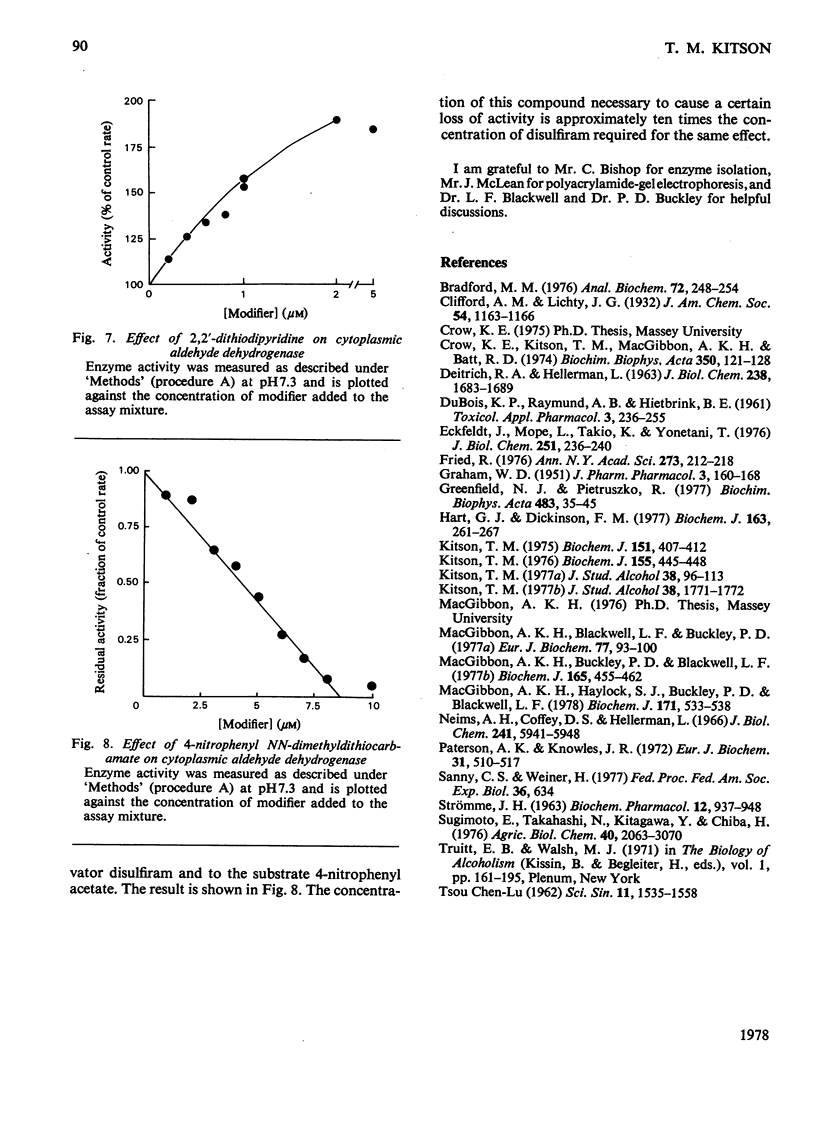
The effect of disulfiram, [1-14C]disulfiram and some other thiol reagents on the activity of cytoplasmic aldehyde dehydrogenase from sheep liver was studied. The results are consistent with a rapid covalent interaction between disulfiram and the enzyme, and inconsistent with the notion that disulfiram is a reversible competitive inhibitor of cytoplasmic aldehyde dehydrogenase. There is a non-linear relationship between loss of about 90% of the enzyme activity and amount of disulfiram added; possible reasons for this are discussed. The remaining approx. 10% of activity is relatively insensitive to disulfiram. It is found that modification of only a small number of groups (one to two) per tetrameric enzyme molecule is responsible for the observed loss of activity. The dehydrogenase activity of the enzyme is affected more severely by disulfiram than is the esterase activity. Negatively charged thiol reagents have little or no effect on cytoplasmic aldehyde dehydrogenase. 2,2'-Dithiodipyridine is an activator of the enzyme.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crow K. E., Kitson T. M., MacGibbon A. K., Batt R. D. Intracellular localisation and properties of aldehyde dehydrogenases from sheep liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 May 20;350(1):121–128. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(74)90209-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEITRICH R. A., HELLERMAN L. Diphosphopridine nucleotide-linked aldehyde dehydrogenase. II. Inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1963 May;238:1683–1689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOIS K. P., RAYMUND A. B., HIETBRINK B. E. Inhibitory action of dithiocarbamates on enzymes of animal tissues. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1961 Mar;3:236–255. doi: 10.1016/s0041-008x(61)80009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckfeldt J., Mope L., Takio K., Yonetani T. Horse liver aldehyde dehydrogenase. Purification and characterization of two isozymes. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jan 10;251(1):236–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried R. Enzymatic oxidation of diethyldithiocarbamate by xanthine oxidase and its colorimetric assay. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1976;273:212–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1976.tb52884.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAHAM W. D. In vitro inhibition of liver aldehyde dehydrogenase by tetraethylthiuram disulphide. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1951 Mar;3(3):160–168. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1951.tb13056.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenfield N. J., Pietruszko R. Two aldehyde dehydrogenases from human liver. Isolation via affinity chromatography and characterization of the isozymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jul 8;483(1):35–45. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(77)90005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart G. J., Dickinson F. M. Some properties of aldehyde dehydrogenase from sheep liver mitochondria. Biochem J. 1977 May 1;163(2):261–267. doi: 10.1042/bj1630261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitson T. M. Reinvestigation of the chemical reaction between disulfiram and ethanol. J Stud Alcohol. 1977 Sep;38(9):1771–1772. doi: 10.15288/jsa.1977.38.1771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitson T. M. The disulfiram--ethanol reaction: a review. J Stud Alcohol. 1977 Jan;38(1):96–113. doi: 10.15288/jsa.1977.38.96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitson T. M. The effect of disulfiram on the aldehyde dehydrogenases of sheep liver. Biochem J. 1975 Nov;151(2):407–412. doi: 10.1042/bj1510407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitson T. M. The effect of some analogues of disulfiram on the aldehyde dehydrogenases of sheep liver. Biochem J. 1976 May 1;155(2):445–448. doi: 10.1042/bj1550445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGibbon A. K., Blackwell L. F., Buckley P. D. Kinetics of sheep-liver cytoplasmic aldehyde dehydrogenase. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jul 1;77(1):93–100. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11645.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGibbon A. K., Buckley P. D., Blackwell L. F. Evidence for two-step binding of reduced nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide to aldehyde dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1977 Sep 1;165(3):455–462. doi: 10.1042/bj1650455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGibbon A. K., Haylock S. J., Buckley P. D., Blackwell L. F. Kinetic studies on the esterase activity of cytoplasmic sheep liver aldehyde dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1978 Jun 1;171(3):533–538. doi: 10.1042/bj1710533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neims A. H., Coffey D. S., Hellerman L. Interaction between tetraethylthiuram disulfide and the sulfhydryl groups of D-amino acid oxidase and of hemoglobin. J Biol Chem. 1966 Dec 25;241(24):5941–5948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson A. K., Knowles J. R. The number of catalytically essential carboxyl groups in pepsin. Modification of the enzyme by trimethyloxonium fluoroborate. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Dec 18;31(3):510–517. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02559.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STROEMME J. H. METHAEMOGLOBIN FORMATION INDUCED BY THIOLS. Biochem Pharmacol. 1963 Sep;12:937–948. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(63)90016-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TSOU C. L. Relation between modification of functional groups of proteins and their biological activity. I.A graphical method for the determination of the number and type of essential groups. Sci Sin. 1962 Nov;11:1535–1558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]