Abstract
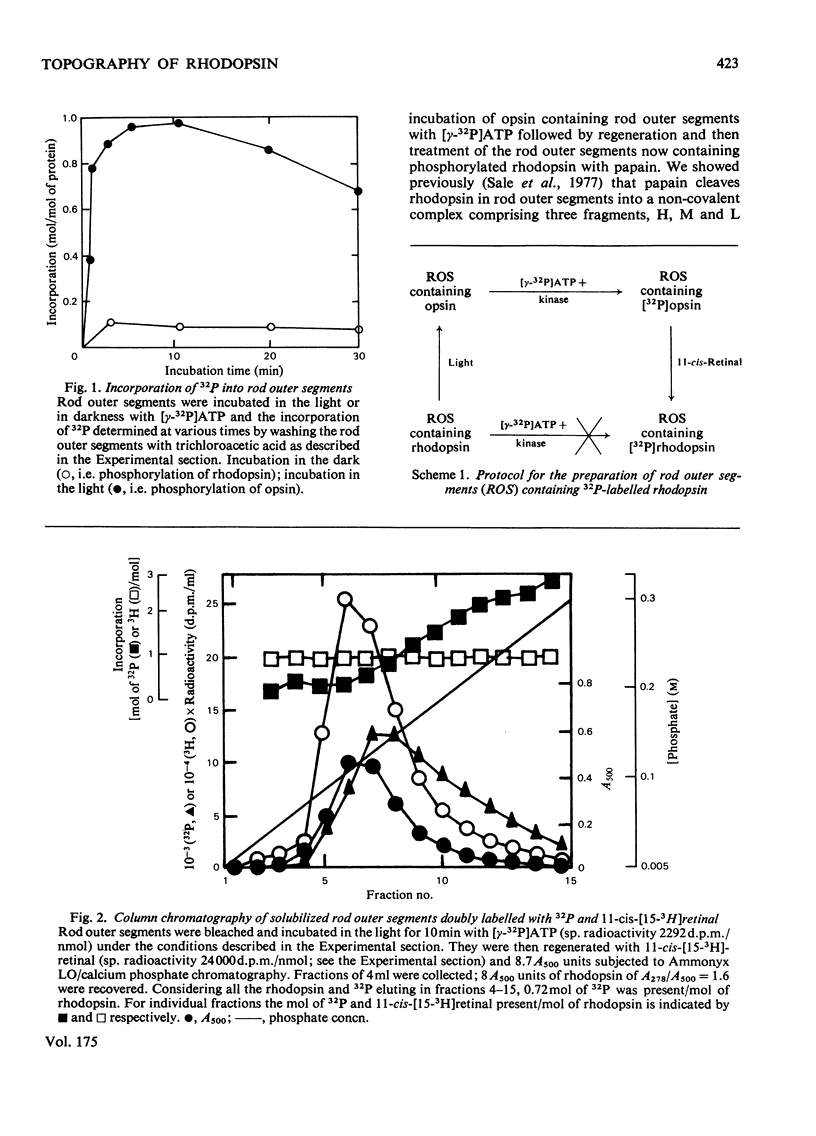
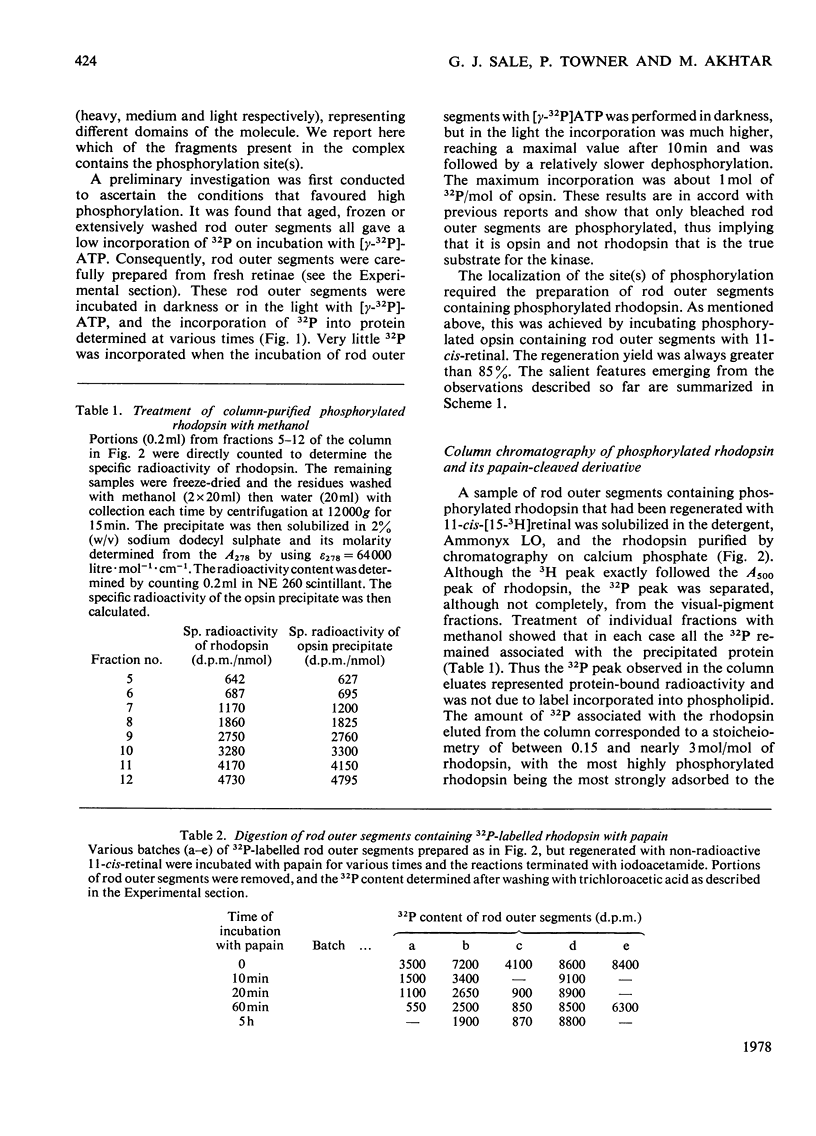
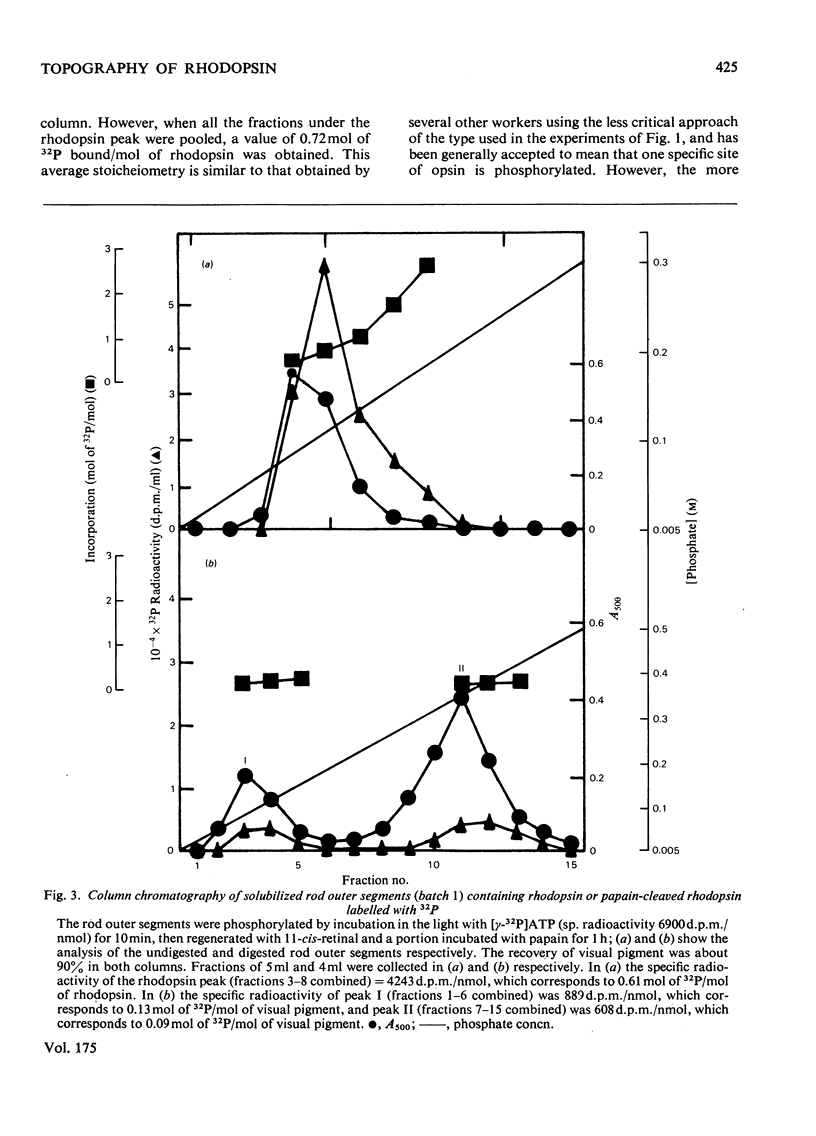
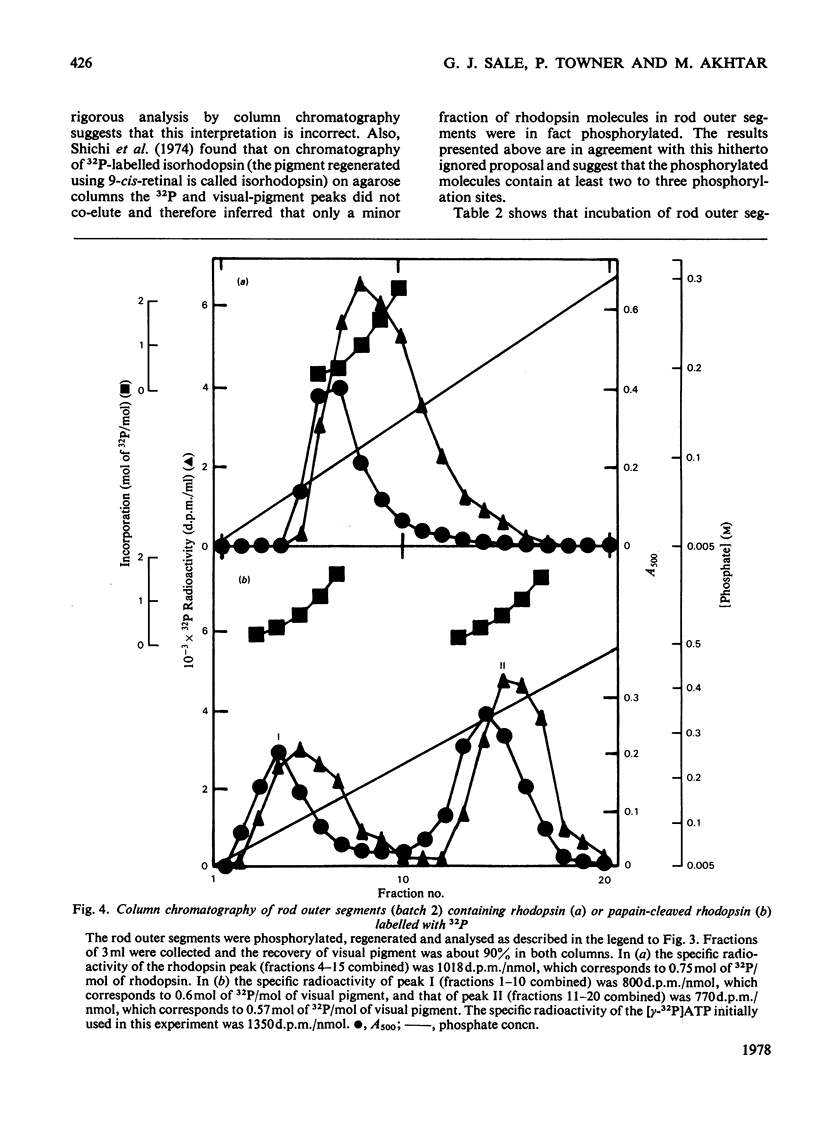
Studies on the light-stimulated phosphorylation of rod outer segments by [gamma-32P]ATP showed that although nearly 1 mol of [32P]phosphate was incorporated/mol of total opsin, only a small fraction of the molecules were phosphorylated, and these contained at least 2-3 mol of phosphate/mol. Rod outer segments containing the phosphorylated opsin were incubated with 11-cis-retinal to generate phosphorylated rhodopsin and then digested with papain to produce a cleaved complex comprising three fragments, heavy (H), medium (M) and light (L). It was shown that L-fragment of apparent mol.wt. 6000 contained all the phosphorylation sites. This suggests that one specific domain of rhodopsin is susceptible to multiple phosphorylation.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akhtar M., Blosse P. T., Dewhurst P. B. Studies on vision. The nature of the retinal-opsin linkage. Biochem J. 1968 Dec;110(4):693–702. doi: 10.1042/bj1100693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akhtar M., Blosse P. T., Dewhurst P. B. The reduction of a rhodopsin derivative. Life Sci. 1965 Jun;4(12):1221–1226. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(65)90336-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Applebury M. L., Zuckerman D. M., Lamola A. A., Jovin T. M. Rhodopsin. Purification and recombination with phospholipids assayed by the metarhodopsin I leads to metarhodopsin II transition. Biochemistry. 1974 Aug 13;13(17):3448–3458. doi: 10.1021/bi00714a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bownds D., Brodie A., Robinson W. E., Palmer R. D., Miller J., Shedlovsky A. Proceedings: Physiology and enzymology of frog photoreceptor membranes. Exp Eye Res. 1974 Mar;18(3):253–269. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(74)90153-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bownds D., Dawes J., Miller J., Stahlman M. Phosphorylation of frog photoreceptor membranes induced by light. Nat New Biol. 1972 May 24;237(73):125–127. doi: 10.1038/newbio237125a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bownds D. Site of attachment of retinal in rhodopsin. Nature. 1967 Dec 23;216(5121):1178–1181. doi: 10.1038/2161178a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank R. N., Buzney S. M. Mechanism and specificity of rhodopsin phosphorylation. Biochemistry. 1975 Nov 18;14(23):5110–5117. doi: 10.1021/bi00694a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hargrave P. A. The amino-terminal tryptic peptide of bovine rhodopsin. A glycopeptide containing two sites of oligosaccharide attachment. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 May 27;492(1):83–94. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90216-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirtenstein M. D., Akhtar M. A convenient synthesis of labelled rhodopsin and studies on its active site. Biochem J. 1970 Sep;119(3):359–366. doi: 10.1042/bj1190359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn H., Cook J. H., Dreyer W. J. Phosphorylation of rhodopsin in bovine photoreceptor membranes. A dark reaction after illumination. Biochemistry. 1973 Jun 19;12(13):2495–2502. doi: 10.1021/bi00737a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn H., Dreyer W. J. Light dependent phosphorylation of rhodopsin by ATP. FEBS Lett. 1972 Jan 15;20(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80002-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn H. Light-dependent phosphorylation of rhodopsin in living frogs. Nature. 1974 Aug 16;250(467):588–590. doi: 10.1038/250588a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATHEWS C. K., BROWN F., COHEN S. S. VIRUS-INDUCED ACQUISITION OF METABOLIC FUNCTION. VII. BIOSYNTHESIS DE NOVO OF DEOXYCYTIDYLATE HYDROXYMETHYLASE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Sep;239:2957–2963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDowell J. H., Kühn H. Light-induced phosphorylation of rhodopsin in cattle photoreceptor membranes: substrate activation and inactivation. Biochemistry. 1977 Sep 6;16(18):4054–4060. doi: 10.1021/bi00637a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. A., Paulsen R. Phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of frog rod outer segment membranes as part of the visual process. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 25;250(12):4427–4432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Röhlich P. Photoreceptor membrane carbohydrate on the intradiscal surface of retinal rod disks. Nature. 1976 Oct 28;263(5580):789–791. doi: 10.1038/263789a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sale G. J., Towner P., Akhtar M. Functional rhodopsin complex consisting of three noncovalently linked fragments. Biochemistry. 1977 Dec 13;16(25):5641–5649. doi: 10.1021/bi00644a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shichi H., Somers R. L., O'Brien P. J. Phosphorylation of rhodopsin: most rhodopsin molecules are not phosphorylated. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Nov 6;61(1):217–221. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90555-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swank R. T., Munkres K. D. Molecular weight analysis of oligopeptides by electrophoresis in polyacrylamide gel with sodium dodecyl sulfate. Anal Biochem. 1971 Feb;39(2):462–477. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90436-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towner P., Sale G. J., Akhtar M. Identification of the active site polypeptide in labeled photoreceptor membranes digested with papain. FEBS Lett. 1977 Apr 1;76(1):51–55. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virmaux N., Weller M., Mandel P. Localisation of the major site. of light stimulated phosphorylation in a region of rhodopsin distinct from the chromophore binding site. FEBS Lett. 1975 May 15;53(3):320–323. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller M., Goridis C., Viramaux N., Mandel P. Letter: A hypothetical model for the possible involvement of rhodopsin phosphorylation in light and dark adaptation in the retina. Exp Eye Res. 1975 Oct;21(4):405–408. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(75)90050-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller M., Virmaux N., Mandel P. Light-stimulated phosphorylation of rhodopsin in the retina: the presence of a protein kinase that is specific for photobleached rhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):381–385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller M., Virmaux N., Mandel P. Role of light and rhodopsin phosphorylation in control of permeability of retinal rod outer segment disks to Ca2plus. Nature. 1975 Jul 3;256(5512):68–70. doi: 10.1038/256068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


