Abstract
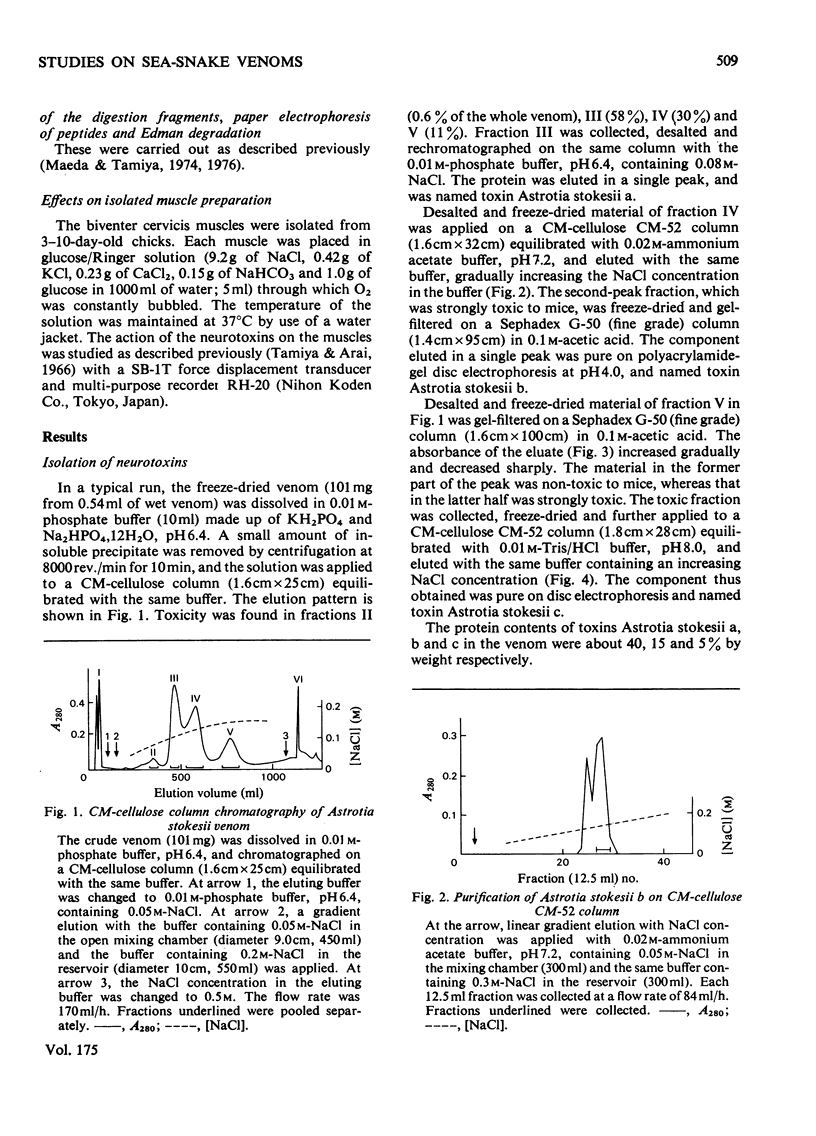
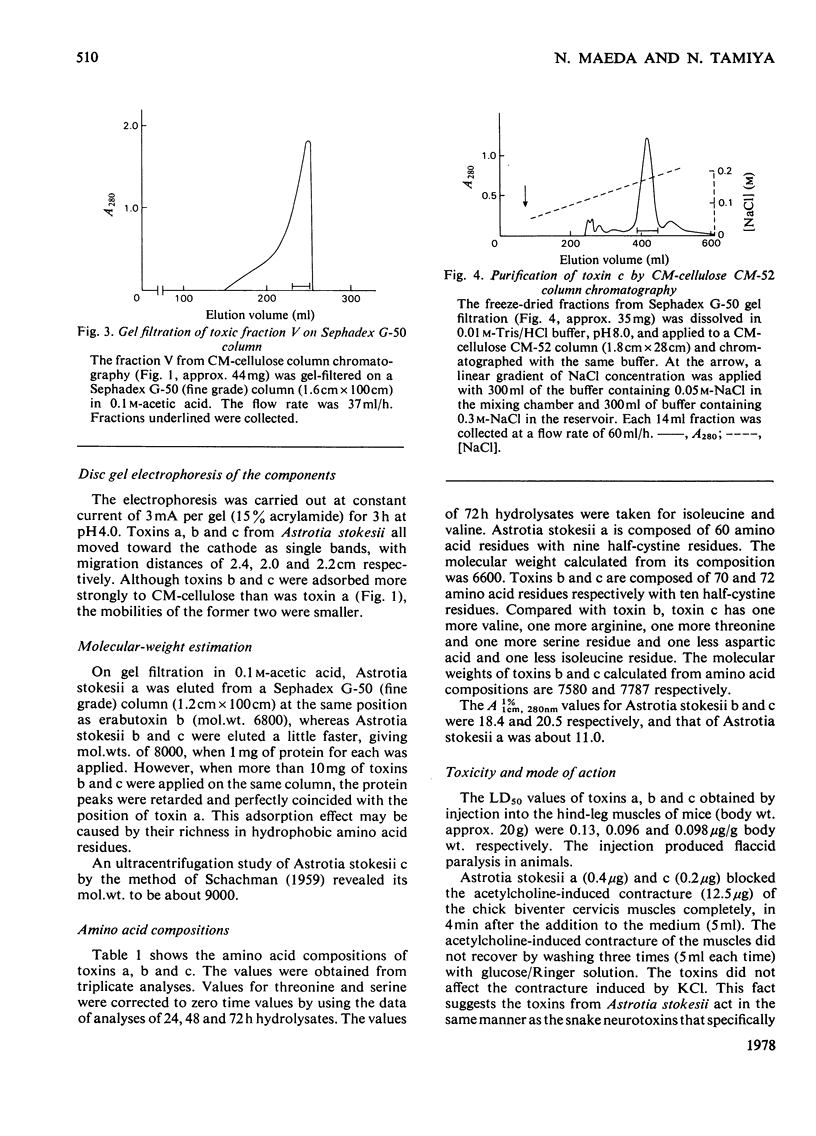
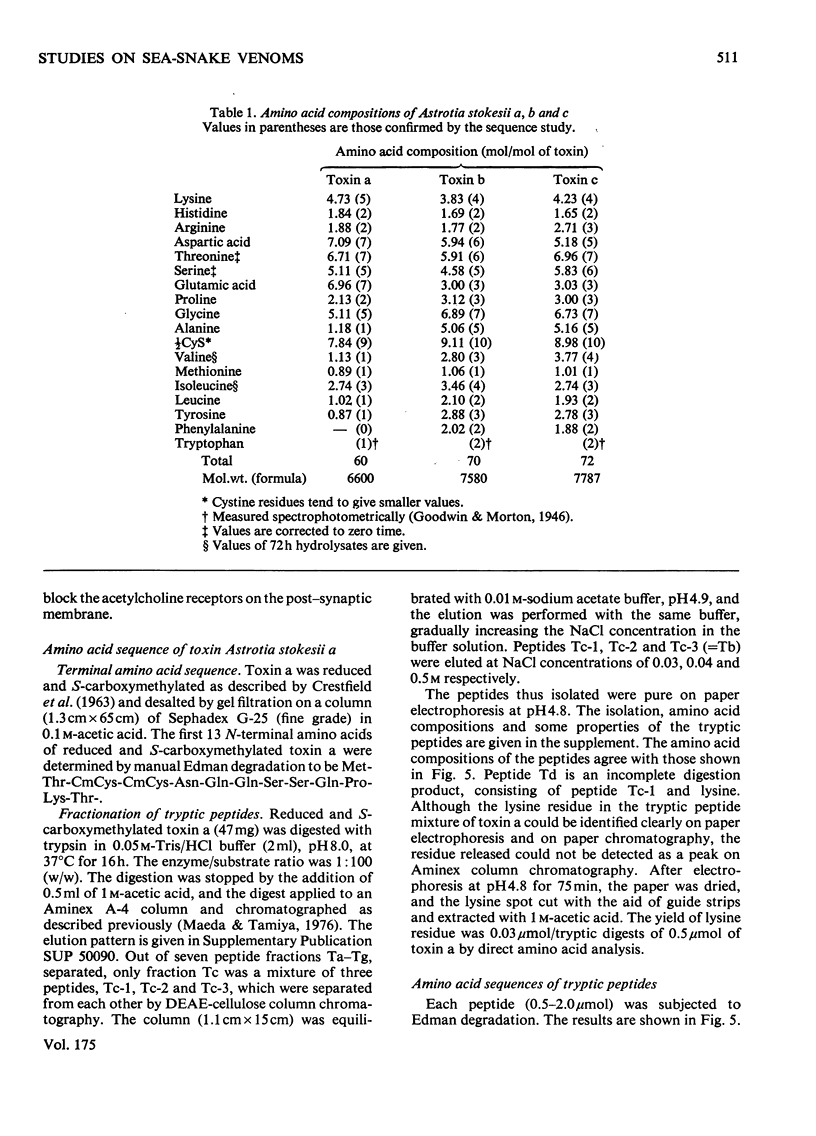
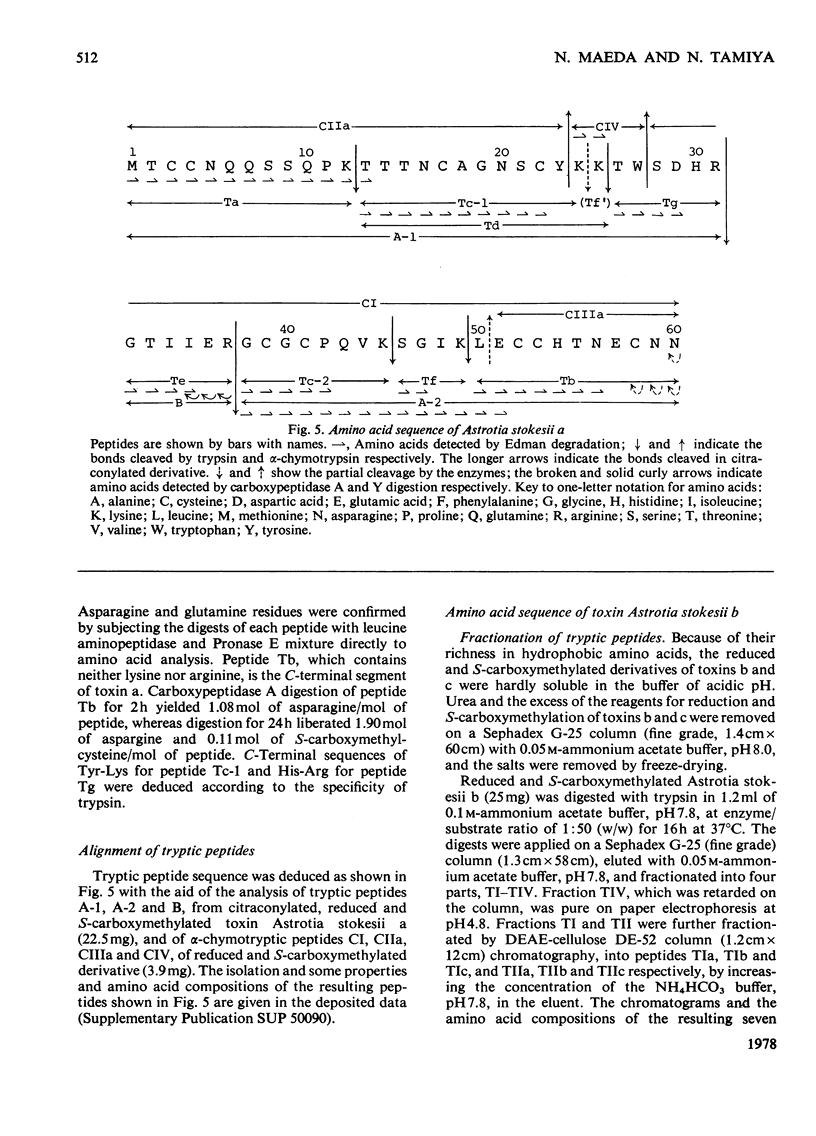
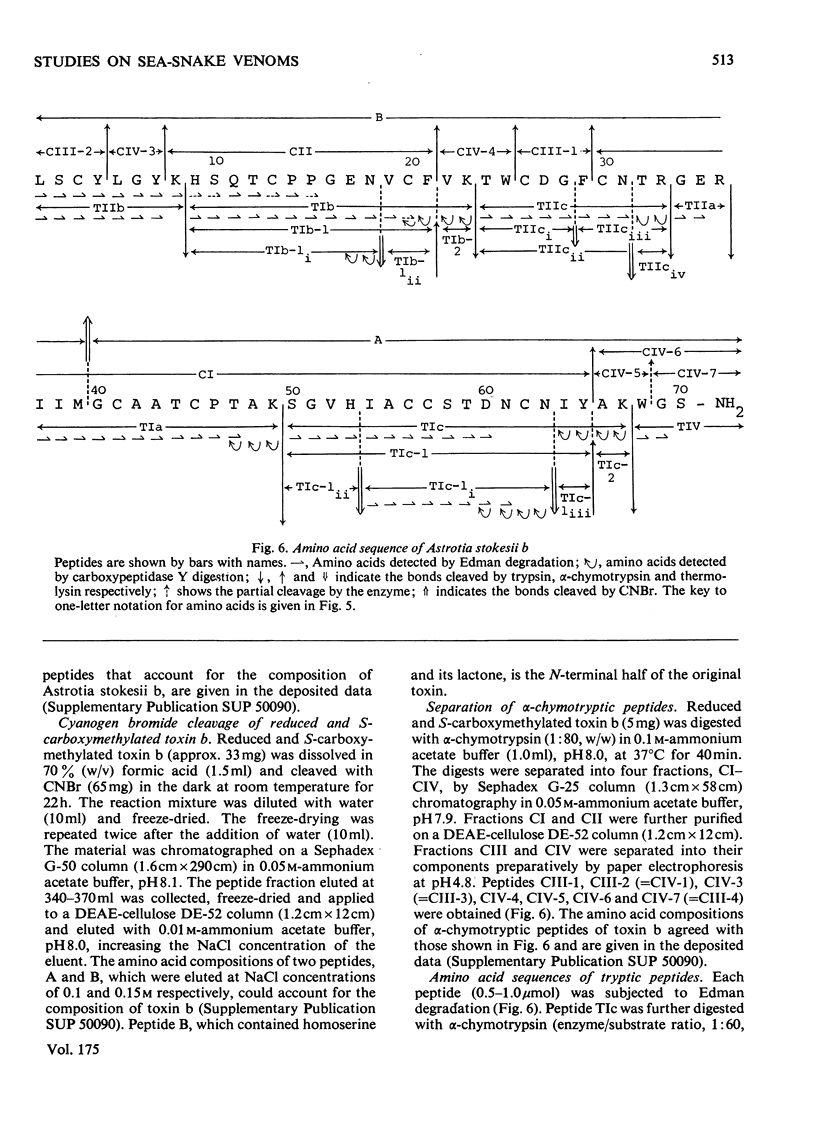
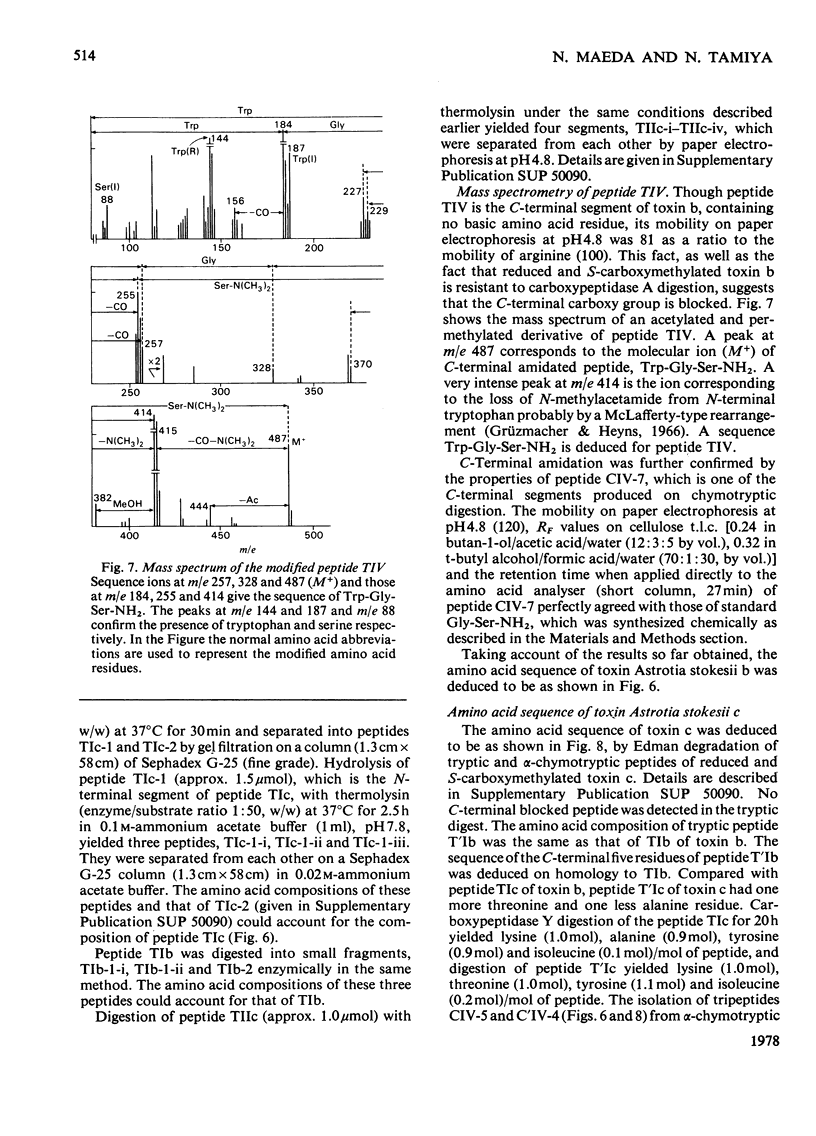
From the venom of a sea snake Astrotia stokesii three neurotoxic components, toxins Astrotia stokesii a, b and c were isolated in 40, 15 and 5% yield by weight respectively of the whole venom. Their LD50 values for 20g mice were 0.13, 0.096 and 0.098 microgram/g body wt. respectively and accounted for almost all the lethal activity of the venom. Their amino acid sequences were determined. Astrotia stokesii a was composed of 60 amino acid residues with nine half-cystine residues and was quite homologous to other sea-snake short-chain neurotoxins in its amino acid sequence. Toxins Astrotia stokesii b and c were composed of 70 and 72 amino acid residues respectively with 10 half-cystine residues. They are the first long-chain neurotoxins with high activity isolated from sea-snake venoms. The C-terminal carboxy groups of toxins b and c were found to be amidated; the amidation is known for some polypeptides, but is novel for a protein. The amide group may make a hydrogen-bond with glutamic acid-39, which replaces a lysine that has so far been found invariably in long-chain neutrotoxins. Astrotia stokesii b and c are also novel in having phenylalanine-25 and isoleucine- or valine-42. The ordinary Tyr-Glu pair, which is observed in X-ray structure [Low, Preston, Sato, Rosen, Searl, Rudko & Richardson (1976) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 73, 2991-2994] and n.m.r.study [Inagaki, Tatsumi, Miyazawa, Hori & Tamiya (1977) Abstr. Int. Congr. Pure Appl. Chem. 26th, p. 336] on erabutoxins may be replaced by a hydrophobic pair. Detailed evidence for the amino acid sequences of the proteins has been deposited as Supplementary Publication SUP 5009o (30 pages) at the British Library Lending Division, Boston Spa, Wetherby, West Yorkshire LS23 7B1, U.K., from whom copies can be obtained on the terms indicated in Biochem. J. (1978) 169, 5.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CRESTFIELD A. M., MOORE S., STEIN W. H. The preparation and enzymatic hydrolysis of reduced and S-carboxymethylated proteins. J Biol Chem. 1963 Feb;238:622–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of protein conformation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):222–245. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DU VIGNEAUD V., RESSLER C., TRIPPETT S. The sequence of amino acids in oxytocin, with a proposal for the structure of oxytocin. J Biol Chem. 1953 Dec;205(2):949–957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dufton M. J., Hider R. C. Snake toxin secondary structure predictions. Structure activity relationships. J Mol Biol. 1977 Sep 15;115(2):177–193. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90095-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin T. W., Morton R. A. The spectrophotometric determination of tyrosine and tryptophan in proteins. Biochem J. 1946;40(5-6):628–632. doi: 10.1042/bj0400628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray W. R., Del Valle U. E. Application of mass spectrometry to protein chemistry. I. Method for amino-terminal sequence analysis of proteins. Biochemistry. 1970 May 12;9(10):2134–2137. doi: 10.1021/bi00812a600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grützmacher H. F., Heyns K. Massenspektrometrische Untersuchungen, XIV. Einfluss aromatischer Aminosäuren auf die Elektronenstoss-Fragmentierung von N-Acetyl-peptiden. Justus Liebigs Ann Chem. 1966 Oct;698:24–33. doi: 10.1002/jlac.19666980104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habermann E., Jentsch J. Sequenzanalyse des Melittins aus den tryptischen und peptischen Spaltstücken. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1967 Jan;348(1):37–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low B. W., Preston H. S., Sato A., Rosen L. S., Searl J. E., Rudko A. D., Richardson J. S. Three dimensional structure of erabutoxin b neurotoxic protein: inhibitor of acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):2991–2994. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.2991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda N., Takagi K., Tamiya N., Chen Y. M., Lee C. Y. The isolation of an easily reversible post-synaptic toxin from the venom of a sea snake, Laticauda semifasciata. Biochem J. 1974 Aug;141(2):383–387. doi: 10.1042/bj1410383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda N., Tamiya N. Isolation, properties and amino acid sequences of three neurotoxins from the venom of a sea snake, Aipysurus laevis. Biochem J. 1976 Jan 1;153(1):79–87. doi: 10.1042/bj1530079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda N., Tamiya N. The primary structure of the toxin Laticauda semifasciata III, a weak and reversibly acting neurotoxin from the venom of a sea snake, Laticauda semifasciata. Biochem J. 1974 Aug;141(2):389–400. doi: 10.1042/bj1410389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris H. R., Williams D. H., Ambler R. P. Determination of the sequences of protein-derived peptides and peptide mixtures by mass spectrometry. Biochem J. 1971 Nov;125(1):189–201. doi: 10.1042/bj1250189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutt V., Jorpes J. E., Magnusson S. Structure of porcine secretin. The amino acid sequence. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Sep;15(3):513–519. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01034.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickerson P. A., Kumar V. Electron microscopic studies of acetylcholinesterase from Bungarus fasciatus venom. Toxicon. 1974 Jan;12(1):83–84. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(74)90103-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka H., Inouye K., Kanayama M., Shinozaki F. The syntheses of peptides related to the N-terminal structure of corticotropin. VII. The synthesis of peptide derivatives corresponding to positions 11 to 18 in the corticotropin molecule. Bull Chem Soc Jpn. 1966 May;39(5):882–888. doi: 10.1246/bcsj.39.882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato S., Tamiya N. Iodination of erabutoxin b: diiodohistidine formation. J Biochem. 1970 Dec;68(6):867–872. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda M., Yoshida H., Tamiya N. Biosynthesis of erabutoxins in the sea snake, Laticauda semif asciata. Toxicon. 1974 Dec;12(6):633–641. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(74)90198-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamiya N., Arai H. Studies on sea-snake venoms. Crystallization of erabutoxins a and b from Laticauda semifasciata venom. Biochem J. 1966 Jun;99(3):624–630. doi: 10.1042/bj0990624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsernoglou D., Petsko G. A. The crystal structure of a post-synaptic neurotoxin from sea snake at A resolution. FEBS Lett. 1976 Sep 15;68(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80390-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsernoglou D., Petsko G. A. Three-dimensional structure of neurotoxin a from venom of the Philippines sea snake. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):971–974. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


