Abstract
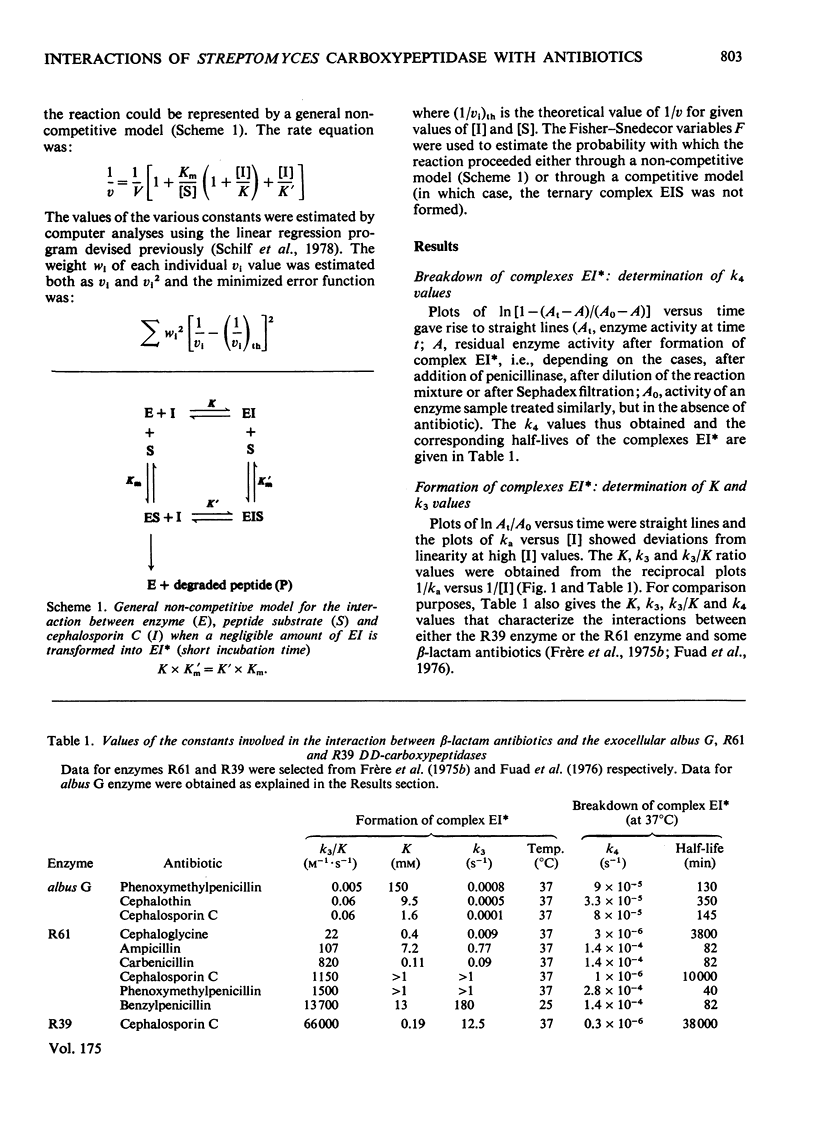
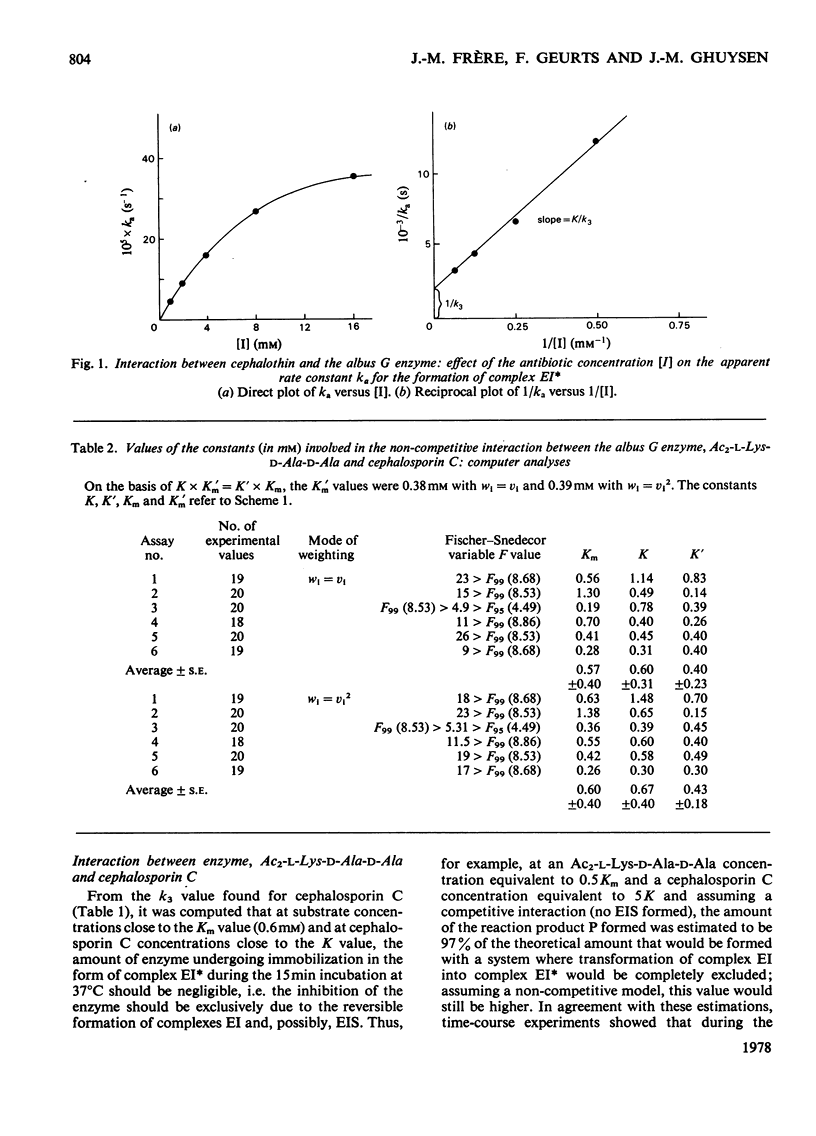
Kinetically, the three-step model proposed for the interaction between beta-lactam antibiotics and the exocellular DD-carboxypeptidases-transpeptidases of Streptomyces R61 and Actinomadura R39 [Frère, Ghuysen & Iwatsubo (1975) Eur. J. Biochem. 57, 343--357; Fuad, Frère, Ghuysen, Duez & Iwatsubo (1976) Biochem. J. 155, 623--629] applies to the interaction between the much less penicillin-sensitive exocellular DD-carboxypeptidase-endopeptidase of Streptomyces albus G and at least phenoxymethylpenicillin, cephalothin and cephalosporin C. The penicillin resistance of the albus G enzyme is mainly due to the low efficiency with which the first reversible complex formed with the antibiotic (complex EI) undergoes transformation into a second more stable complex EI*. Analysis of the ternary interaction between enzyme, NalphaNepsilon-diacetyl-L-lysyl-D-alanyl-D-alanine (Ac2-L-Lys-D-Ala-D-Ala) and cephalosporin C indicates a non-competitive mechanism.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adriaens P., Meesschaert B., Frère J. M., Vanderhaeghe H., Degelaen J., Ghuysen J. M., Eyssen H. Stability of D-5,5-dimethyl-delta2-thiazoline-4-carboxylic acid in relation to its possible occurrence as a degradation product of penicillin by the exocellular DD-carboxypeptidase-transpeptidase from Streptomyces R61 and the membrane-bound dd-carboxypeptidase from Bacillus stearothermophilus. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 25;253(10):3660–3665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duez C., Frère J. M., Geurts F., Ghuysen J. M., Dierickx L., Delcambe L. The exocellular DD-carboxypeptidase-endopeptidase from Streptomyces albus G. Purification and chemical properties. Biochem J. 1978 Dec 1;175(3):793–800. doi: 10.1042/bj1750793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frere J., Ghuysen J., Degelaen J., Loffet A., Perkins H. R. Fragmentation of benzylpenicillin after interaction with the exocellular DD-carboxypeptidase-transpeptidases of Streptomyces R61 and R39. Nature. 1975 Nov 13;258(5531):168–170. doi: 10.1038/258168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frere J., Ghuysen J., Vanderhaeghe H., Adriaens P., Degelaen J., De Graeve J. Fate of thiazolidine ring during fragmentation of penicillin by exocellular DD-carboxypeptidase-transpeptidase of Streptomyces R61. Nature. 1976 Apr 1;260(5550):451–454. doi: 10.1038/260451a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frère J. M., Ghuysen J. M., Iwatsubo M. Kinetics of interaction between the exocellular DD-carboxypeptidase-transpeptidase from Streptomyces R61 and beta-lactam antibiotics. A choice of models. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Sep 15;57(2):343–351. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02307.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frére J. M., Leyh-Bouille M., Ghuysen J. M., Nieto M., Perkins H. R. Exocellular DD-carboxypeptidases-transpeptidases from Streptomyces. Methods Enzymol. 1976;45:610–636. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(76)45054-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuad N., Frère J. M., Ghuysen J. M., Duez C., Iwatsubo M. Mode of interaction between beta-lactam antibiotics and the exocellular DD-carboxypeptidase--transpeptidase from Streptomyces R39. Biochem J. 1976 Jun 1;155(3):623–629. doi: 10.1042/bj1550623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leyh-Bouille M., Ghuysen J. M., Nieto M., Perkins H. R., Schleifer K. H., Kandler O. On the Streptomyces albus G DD carboxypeptidase mechanism of action of penicillin, vancomycin, and ristocetin. Biochemistry. 1970 Jul 21;9(15):2971–2975. doi: 10.1021/bi00817a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin H. H., Schilf W., Maskos C. Purification of the membrane-bound DD-carboxypeptidase of the unstable spheroplast L-form of Proteus mirabilis by affinity chromatography. Non-competitive inhibition of the enzyme by penicillins and low stability of the enzyme-inhibitor complex. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Dec 11;71(2):585–593. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb11149.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rando R. R. On the mechanism of action of antibiotics which act as irreversible enzyme inhibitors. Biochem Pharmacol. 1975 Jun 15;24(11-12):1153–1160. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(75)90055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schilf W., Frère P., Frère J. M., Martin H. H., Ghuysen J. M., Adriaens P., Meesschaert B. Interaction between penicillin and the DD-carboxypeptidase of the unstable L-form of Proteus mirabilis strain 19. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Apr 17;85(2):325–330. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12242.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


