Abstract
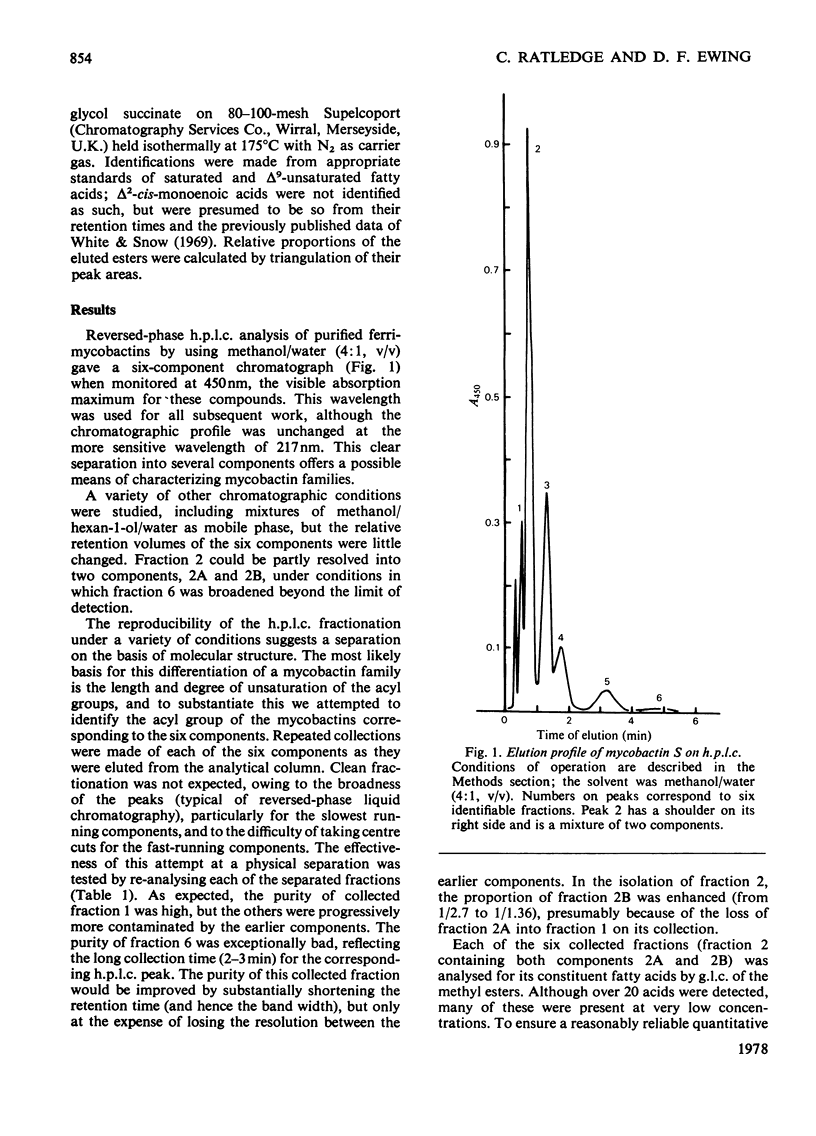
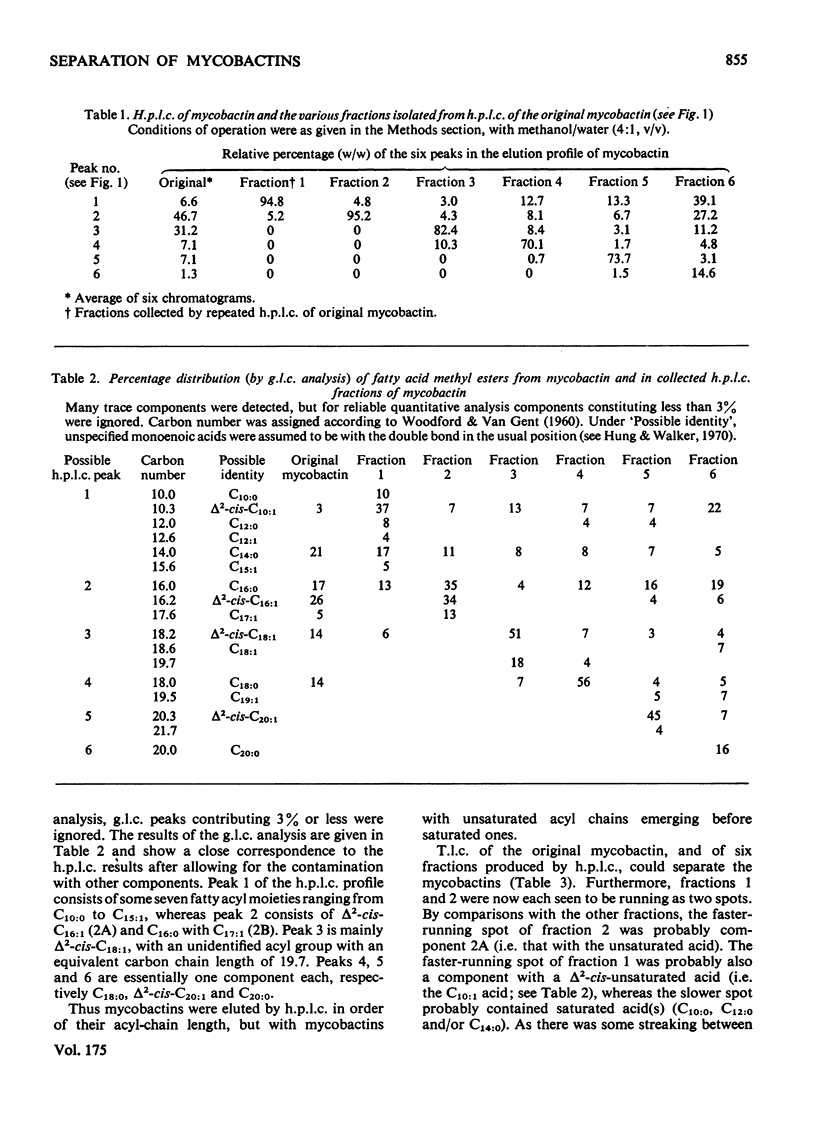
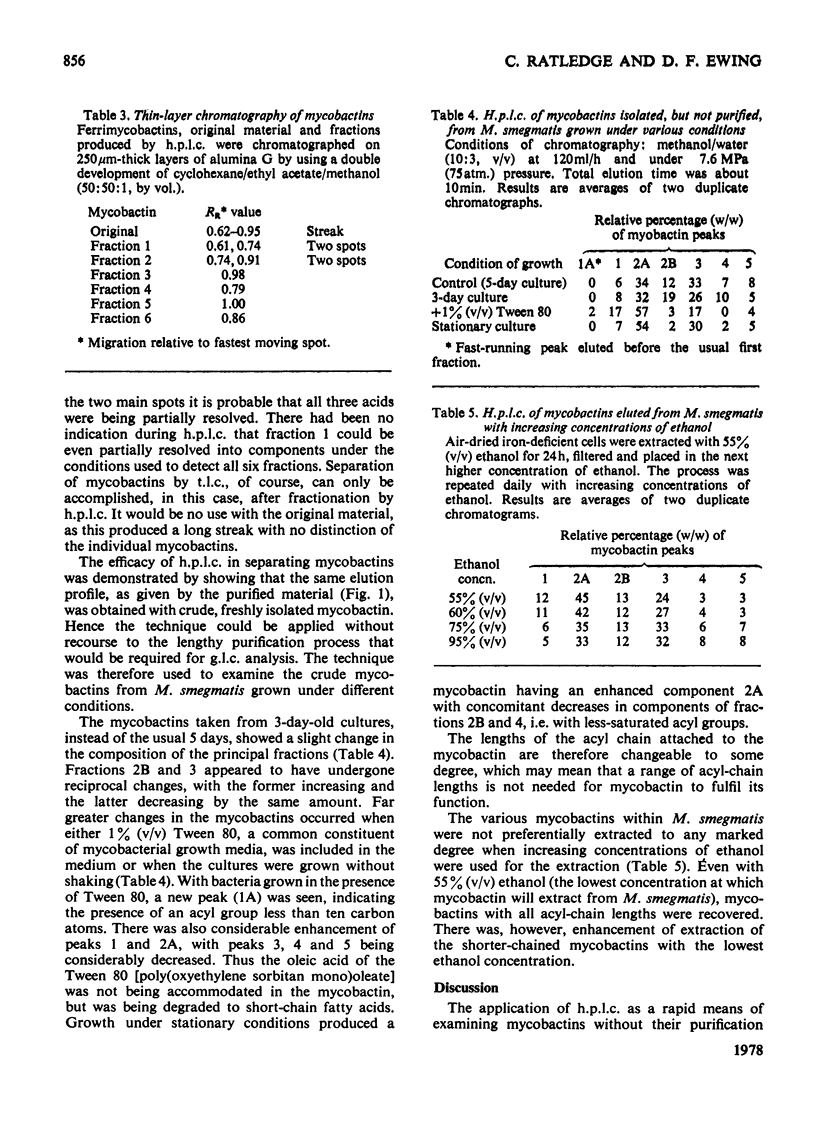
The family of mycobactins from Mycobacterium smegmatis were resolved into seven fractions by high-pressure liquid chromatography. This separation was by virtue of the differences in length and character of the long acyl substituents as shown by g.l.c. of the methyl esters of the isolated fatty acids from the fractions. As t.l.c. could also resolve the individual mycobactin fractions, it too must rely on the same differences to effect separation. As the lengths of the acyl chains were modulated by the growth conditions, a specific range of acyl groups may not be needed for mycobactin to function. This technique provides a simple means of rapidly characterizing crude mycobactins from all mycobacteria.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hung J. G., Walker R. W. Unsaturated fatty acids of Mycobacteria. Lipids. 1970 Aug;5(8):720–722. doi: 10.1007/BF02531442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratledge C., Hall M. J. Influence of metal ions on the formation of mycobactin and salicylic acid in Mycobacterium smegmatis grown in static culture. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):314–319. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.314-319.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratledge C., Patel P. V. Isolation, properties and taxonomic relevance of lipid-soluble, iron-binding compounds (the nocobactins) from Nocardia. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Mar;93(1):141–152. doi: 10.1099/00221287-93-1-141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratledge C., Snow G. A. Isolation and structure of nocobactin NA, a lipid-soluble iron-binding compound from Nocardia asteroides. Biochem J. 1974 May;139(2):407–413. doi: 10.1042/bj1390407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snow G. A. Mycobactins: iron-chelating growth factors from mycobacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1970 Jun;34(2):99–125. doi: 10.1128/br.34.2.99-125.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White A. J., Snow G. A. Isolation of mycobactinss from various mycobacteria. The properties of mycobactin S and H. Biochem J. 1969 Mar;111(5):785–792. doi: 10.1042/bj1110785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


