Abstract
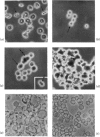
1. The fusion of human erythrocytes into multicellular bodies that is induced by microdroplets of oleoylglycerol was investigated by optical and electron microscopy, and by gel electrophoresis of membrane proteins. 2. At the highest concentrations of oleoylglycerol and Ca2+ used, at least 80% of the cells fused after 30min at 37°C and only about 5% of the cells had completely lysed; the shapes of fused multicellular bodies were usually retained in `ghosts' prepared by hypo-osmotic lysis. 3. The rate of cell fusion was related to the concentration of Ca2+, although some cells fused when no exogenous Ca2+ was present. 4. Interactions of microdroplets of oleoylglycerol with the cells led to abnormalities in the structural appearance of the erythrocyte membrane; subsequent membrane fusion occurred, at least in some instances, at the sites of the microdroplets. 5. The intramembranous particles on the P-fracture face of the treated cells were more randomly distributed, but not significantly increased in number by comparison with the control cells. 6. Gel electrophoresis of the proteins of `ghosts' prepared from fused human erythrocytes showed a production of material of very high molecular weight, the development of a new component in the band-3 region, an increased staining of bands 4.3 and 4.5, and a new component moving slightly faster than band 6. 7. Bands 2.1–2.3 were altered, band 3 was decreased and band 4.1 was lost. 8. Most, but not all, of the changes in the membrane proteins appeared to result from the entry of Ca2+ into the cell. 9. 1-Chloro-4-phenyl-3-l-toluene-p-sulphonamidobutan-2-one partially inhibited both cell fusion and the associated decrease in band-3 protein. 10. The possibility that proteolytic degradation of membrane proteins may be involved in cell fusion induced by oleoylglycerol is considered, and some implications of this possibility are discussed.
Full text
PDF




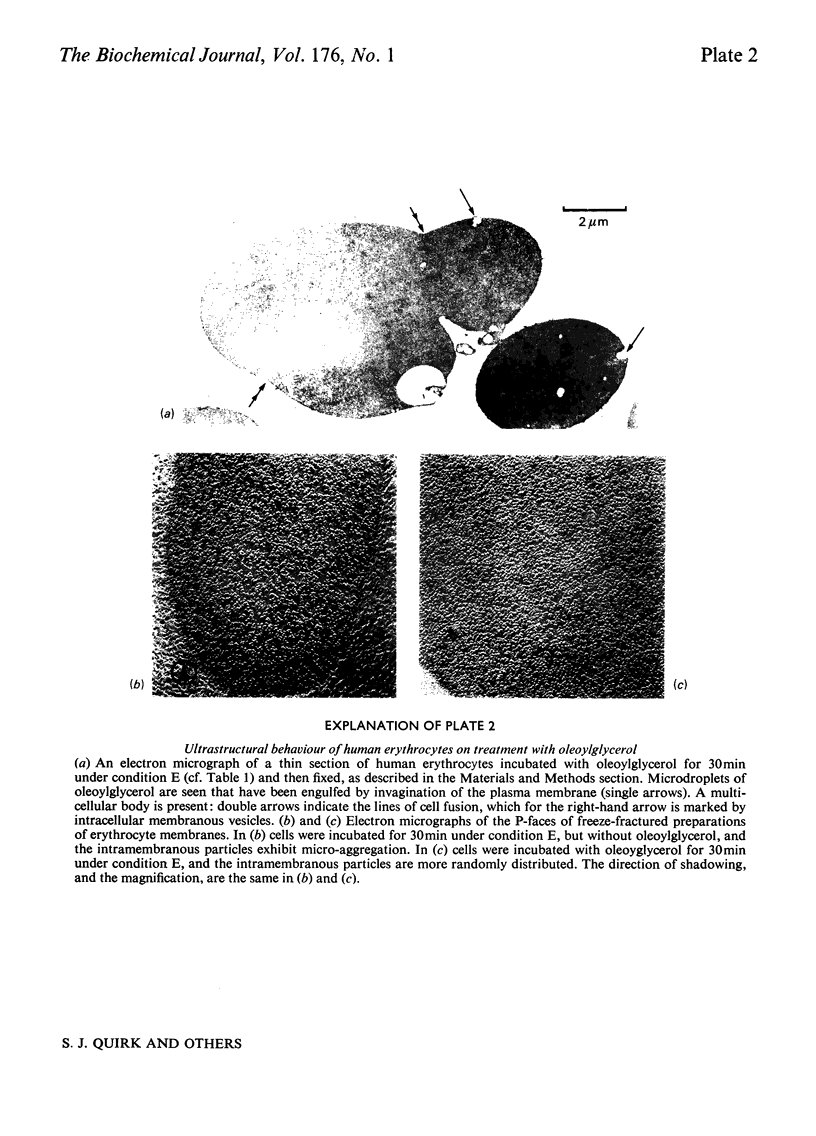
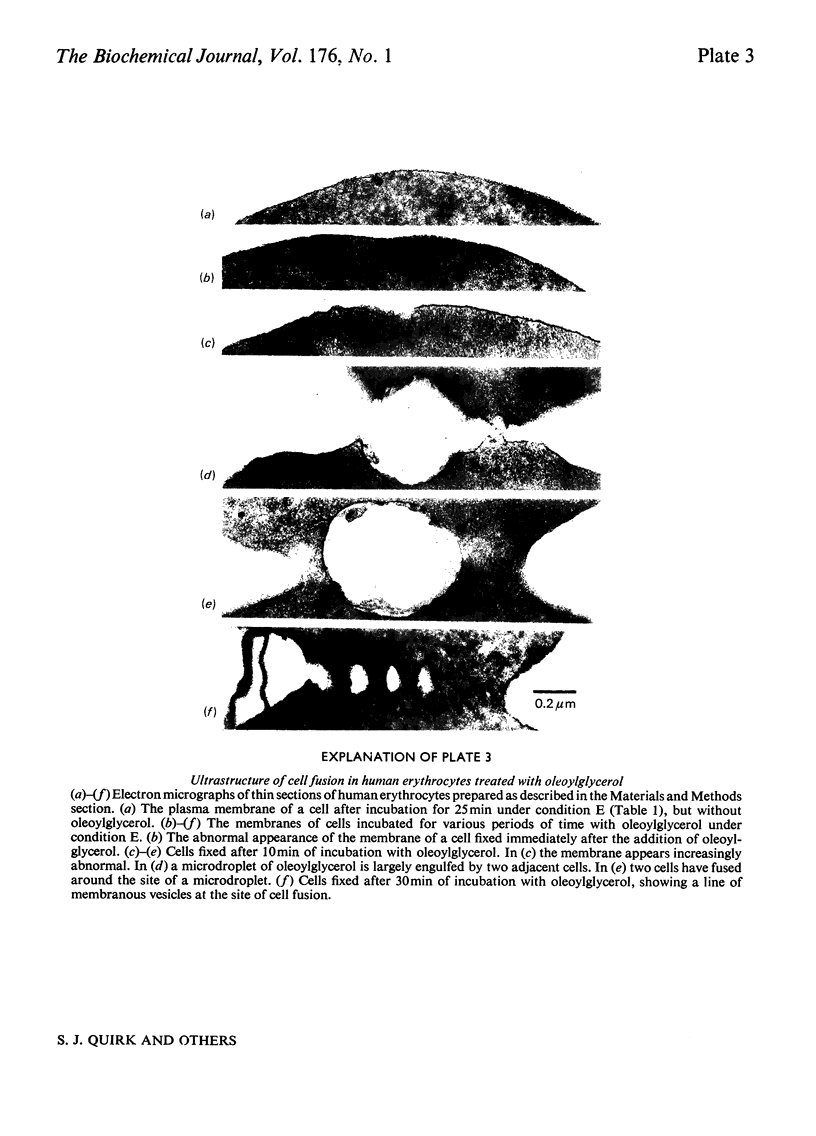
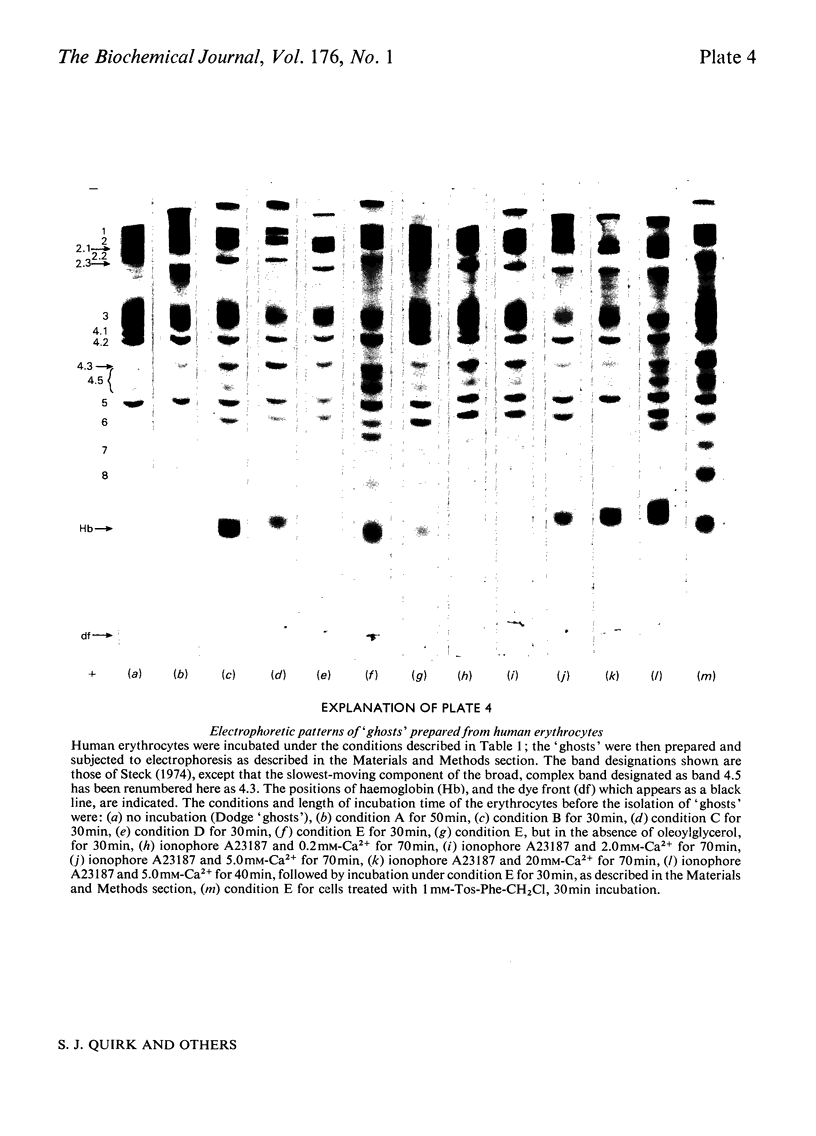





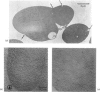
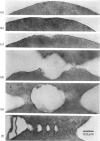
Images in this article
Selected References
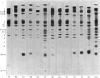
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahkong Q. F., Fisher D., Tampion W., Lucy J. A. Mechanisms of cell fusion. Nature. 1975 Jan 17;253(5488):194–195. doi: 10.1038/253194a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahkong Q. F., Fisher D., Tampion W., Lucy J. A. The fusion of erythrocytes by fatty acids, esters, retinol and alpha-tocopherol. Biochem J. 1973 Sep;136(1):147–155. doi: 10.1042/bj1360147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan D., Billah M. M., Finean J. B., Michell R. H. Release of diacylglycerol-enriched vesicles from erythrocytes with increased intracellular (Ca2+). Nature. 1976 May 6;261(5555):58–60. doi: 10.1038/261058a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender W. W., Garan H., Berg H. C. Proteins of the human erythrocyte membrane as modified by pronase. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jun 28;58(3):783–797. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90040-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blow A. M., Botham G. M., Lucy J. A. Entry of calcium into hen erythrocytes on treatment with fusogenic chemicals [proceedings]. Biochem Soc Trans. 1978;6(1):284–285. doi: 10.1042/bst0060284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branton D., Bullivant S., Gilula N. B., Karnovsky M. J., Moor H., Mühlethaler K., Northcote D. H., Packer L., Satir B., Satir P. Freeze-etching nomenclature. Science. 1975 Oct 3;190(4209):54–56. doi: 10.1126/science.1166299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabantchik Z. I., Rothstein A. Membrane proteins related to anion permeability of human red blood cells. II. Effects of proteolytic enzymes on disulfonic stilbene sites of surface proteins. J Membr Biol. 1974;15(3):227–248. doi: 10.1007/BF01870089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway K. L., Triplett R. B., Anderson D. R. Calcium-promoted aggregation of erythrocyte membrane proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Feb 27;379(2):571–581. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90163-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chi E. Y., Lagunoff D., Koehler J. K. Freeze-fracture study of mast cell secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2823–2827. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DODGE J. T., MITCHELL C., HANAHAN D. J. The preparation and chemical characteristics of hemoglobin-free ghosts of human erythrocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Jan;100:119–130. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drickamer L. K. Fragmentation of the 95,000-dalton transmembrane polypeptide in human erythrocyte membranes. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 10;251(17):5115–5123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgsaeter A., Branton D. Intramembrane particle aggregation in erythrocyte ghosts. I. The effects of protein removal. J Cell Biol. 1974 Dec;63(3):1018–1036. doi: 10.1083/jcb.63.3.1018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgsaeter A., Shotton D. M., Branton D. Intramembrane particle aggregation in erythrocyte ghosts. II. The influence of spectrin aggregation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Feb 19;426(1):101–122. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90433-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend D. S., Orci L., Perrelet A., Yanagimachi R. Membrane particle changes attending the acrosome reaction in guinea pig spermatozoa. J Cell Biol. 1977 Aug;74(2):561–577. doi: 10.1083/jcb.74.2.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy A., Rice-Evans C. A spectrofluorimetric study of the interaction of glycerol mono-oleate with human erythrocyte ghosts. FEBS Lett. 1976 Oct 15;69(1):45–50. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80650-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King L. E., Jr, Morrison M. Calcium effects on human erythrocyte membrane proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Nov 15;471(1):162–168. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90404-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk R. G., Tosteson D. C. Cation transport and membrane morphology. J Membr Biol. 1973;12(3):273–285. doi: 10.1007/BF01870005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson D., Raff M. C., Gomperts B., Fewtrell C., Gilula N. B. Molecular events during membrane fusion. A study of exocytosis in rat peritoneal mast cells. J Cell Biol. 1977 Feb;72(2):242–259. doi: 10.1083/jcb.72.2.242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lentz B. R., Barenholz Y., Thompson T. E. Fluorescence depolarization studies of phase transitions and fluidity in phospholipid bilayers. 2 Two-component phosphatidylcholine liposomes. Biochemistry. 1976 Oct 5;15(20):4529–4537. doi: 10.1021/bi00665a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorand L., Weissmann L. B., Epel D. L., Bruner-Lorand J. Role of the intrinsic transglutaminase in the Ca2+-mediated crosslinking of erythrocyte proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4479–4481. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggio B., Lucy J. A. Polar-group behaviour in mixed monolayers of phospholipids and fusogenic lipids. Biochem J. 1976 May 1;155(2):353–364. doi: 10.1042/bj1550353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggio B., Lucy J. A. Studies on mixed monolayers of phospholipids and fusogenic lipids. Biochem J. 1975 Sep;149(3):597–608. doi: 10.1042/bj1490597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Perrelet A., Friend D. S. Freeze-fracture of membrane fusions during exocytosis in pancreatic B-cells. J Cell Biol. 1977 Oct;75(1):23–30. doi: 10.1083/jcb.75.1.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L. The organization of proteins in the human red blood cell membrane. A review. J Cell Biol. 1974 Jul;62(1):1–19. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triplett R. B., Carraway K. L. Proteolytic digestion of erythrocytes, resealed ghosts, and isolated membranes. Biochemistry. 1972 Jul 18;11(15):2897–2903. doi: 10.1021/bi00765a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triplett R. B., Wingate J. M., Carraway K. L. Calcium effects on erythrocyte membrane proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Nov 15;49(4):1014–1020. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90313-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tökés Z. A., Chambers S. M. Proteolytic activity associated with human erythrocyte membranes. Self-digestion of isolated human erythrocyte membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 May 6;389(2):325–338. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90325-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vos J., Ahkong Q. F., Botham G. M., Quirk S. J., Lucy J. A. Changes in the distribution of intramembranous particles in hen erythrocytes during cell fusion induced by the bivalent-cation ionophore A23187. Biochem J. 1976 Sep 15;158(3):651–653. doi: 10.1042/bj1580651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidekamm E., Brdiczka D., Di Pauli G., Wildermuth M. Biochemical characterization of segreated membrane vesicles from human erythrocytes with increased intracellular Ca2+. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Mar;179(2):486–494. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90137-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu J., Branton D. Reconstitution of intramembrane particles in recombinants of erythrocyte protein band 3 and lipid: effects of spectrin-actin association. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3891–3895. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakai N., Kulka R. G., Loyter A. Fusion of human erythrocyte ghosts promoted by the combined action of calcium and phosphate ions. Nature. 1976 Oct 21;263(5579):696–699. doi: 10.1038/263696a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]