Abstract
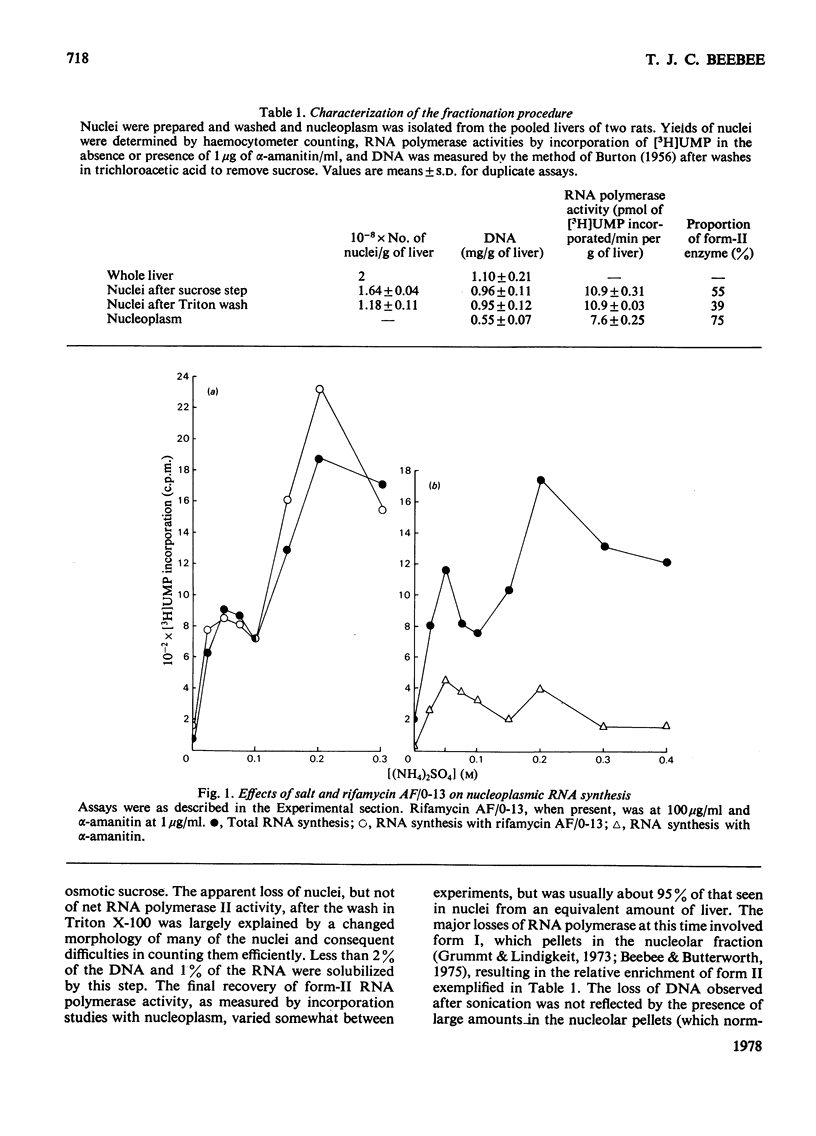
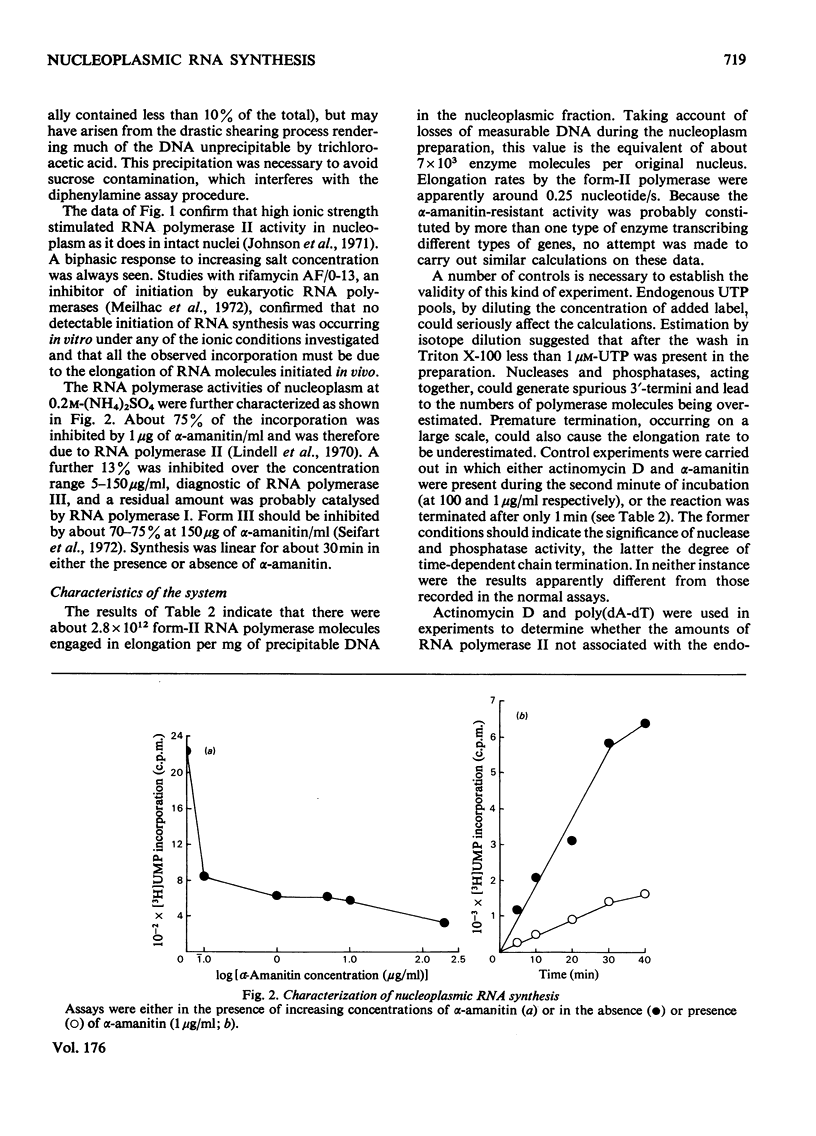
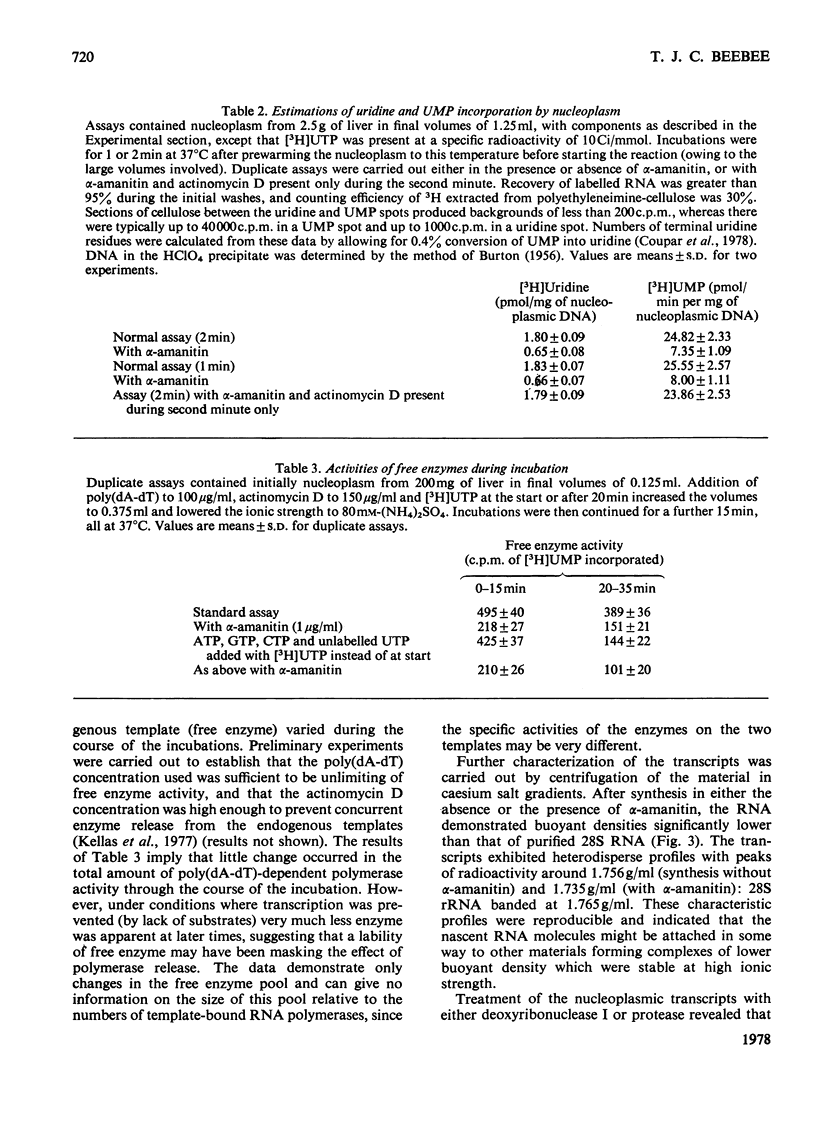
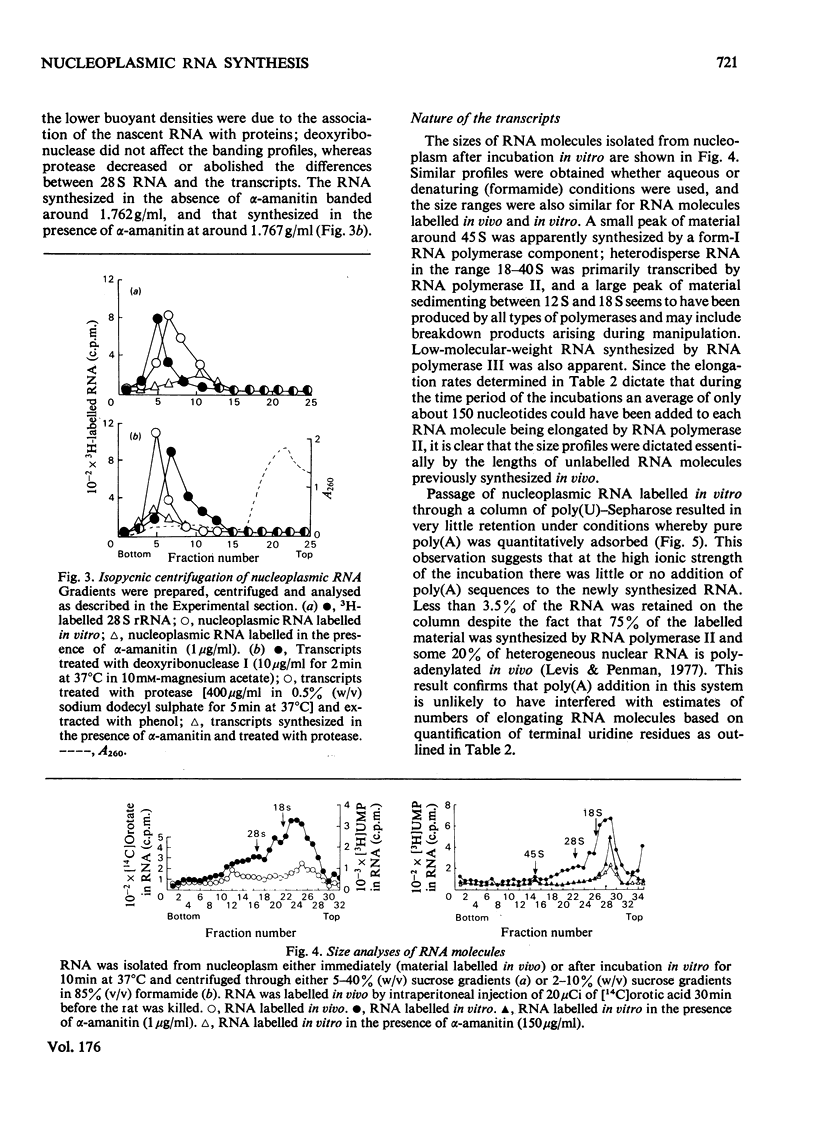
1. A nucleoplasmic fraction rich in endogenous RNA polymerase II activity was isolated from rat liver nuclei and conditions were determined under which elongation of RNA molecules initiated in vivo continued at maximal rates in vitro. 2. Elongation rates in vitro were calculated to be about 0.25 nucleotide/s and there were about 7 X 10(3) RNA molecules in the process of being elongated by form-II RNA polymerase per original nucleus. 3. Evidence was obtained suggesting that transcription-dependent release of RNA polymerase II molecules from the template occurred during the incubations in vitro. 4. The nascent RNA was tightly associated with protein and banded as ribonucleoprotein in caesium salt gradients. 5. RNA molecules labelled in vitro were up to 13000 nucleotides in length, but consisted of long unlabelled chains transcribed in vivo with only short labelled sequences added in vitro, and without significant polyadenylation. 6. Hybridization of transcripts in the presence of a vast excess of DNA demonstrated that both form-II RNA polymerase and another enzyme, resistant to low alpha-amanitin concentrations, were synthesizing RNA molecules complementary to both reiterated and unique DNA sequences in the genome.
Full text
PDF


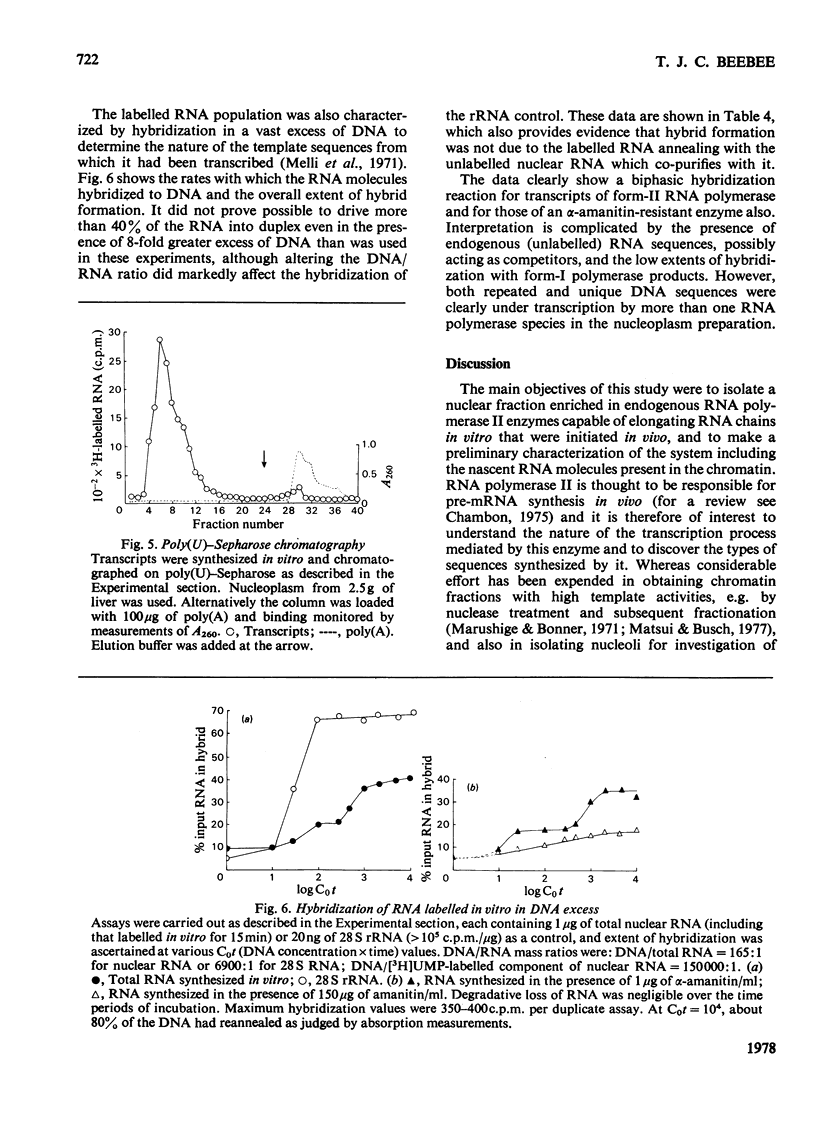
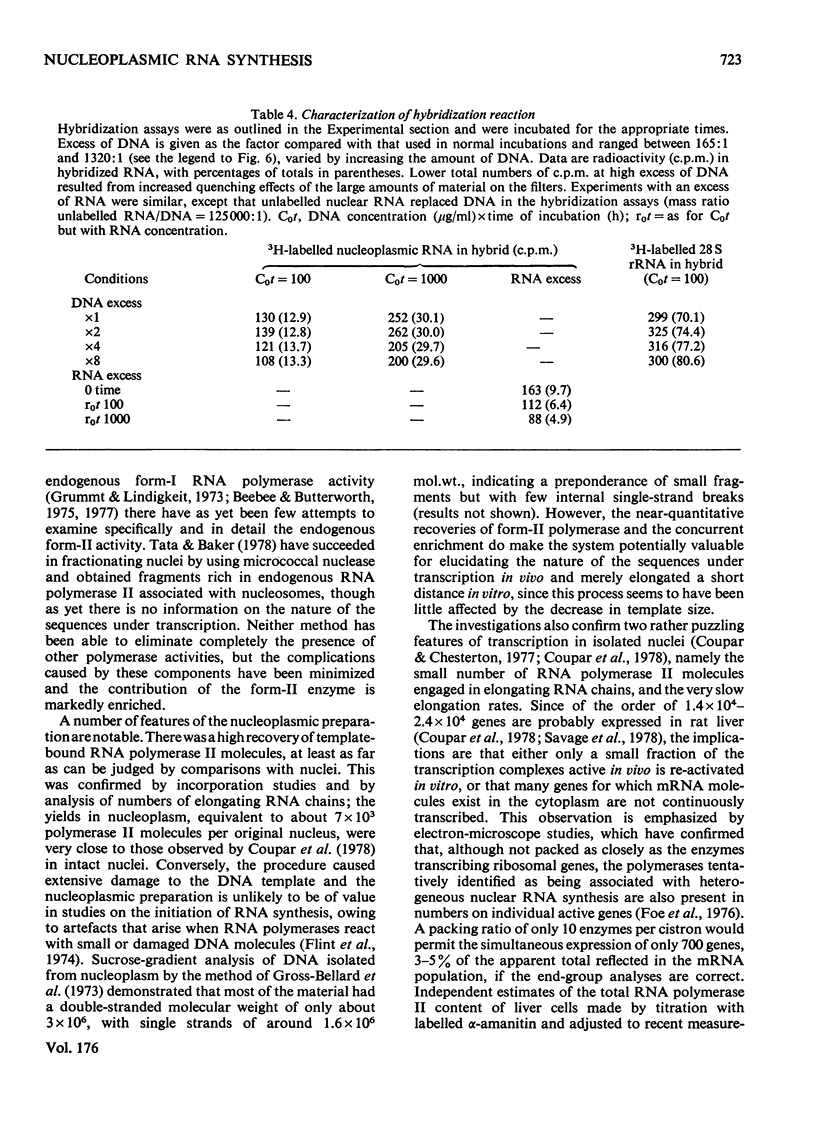


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atikkan E. E., Furth J. J. RNA synthesized in vitro by calf thymus RNA polymerase III (C), as well as by E. coli RNA polymerase, is restricted to a subset of calf thymus DNA. Cell Differ. 1977 Oct;6(3-4):253–262. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(77)90020-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacheler L. T., Smith K. D. Transcription of isolated mouse liver chromatin. Biochemistry. 1976 Jul 27;15(15):3281–3290. doi: 10.1021/bi00660a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beebee T. J., Butterworth P. H. The use of mercurated nucleoside triphosphate as a probe in transcription studies in vitro. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jul 15;66(3):543–550. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10580.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beebee T. J., Butterworth P. H. Transcription fidelity and structural integrity of isolated nucleoli. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jul 15;77(2):341–348. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11673.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beebee T. J., Butterworth P. H. Transcription of isolated nuclei and nucleoli by exogenous RNA polymerase A and B. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Feb 21;51(2):537–545. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb03954.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benecke B. J., Penman S. A new class of small nuclear RNA molecules synthesized by a type I RNA polymerase in HeLa cells. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):939–946. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90158-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biessmann H., Levy B., McCarthy B. J. In vitro transcription of heat-shock-specific RNA from chromatin of Drosophila melanogaster cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):759–763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambon P. Eukaryotic nuclear RNA polymerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:613–638. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.003145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan J. Y., Loor R. M., Wang T. Y. Transcription in vitro of Ehrlich ascites tumor DNA and chromatin by purified homologous RNA polymerase II (or B). Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Apr;173(2):564–576. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90293-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesterton C. J., Butterworth P. H. Selective extraction of form I DNA dependent RNA polymerase from rat liver nuclei and its separation into two species. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Mar 11;19(2):232–241. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01309.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chikaraishi D. M., Deeb S. S., Sueoka N. Sequence complexity of nuclear RNAs in adult rat tissues. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):111–120. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90142-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochet-Meilhac M., Nuret P., Courvalin J. C., Chambon P. Animal DNA-dependent RNA polymerases. 12. Determination of the cellular number of RNA polymerase B molecules. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jun 27;353(2):185–192. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(74)90183-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coupar B. E., Chesterton C. J. The mechanism by which heparin stimulates transcription in isolated rat liver nuclei. Polyribonucleotide elongation rates and the number of transcribing RNA polymerase molecules present. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Oct 3;79(2):525–533. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11837.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coupar B. E., Davies J. A., Chesterton C. J. Quantification of hepatic transcribing RNA polymerase molecules, polyribonucleotide elongation rates and messenger RNA complexity in fed and fasted rats. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Mar 15;84(2):611–623. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12204.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedoroff N., Wellauer P. K., Wall R. Intermolecular duplexes in heterogeneous nuclear RNA from HeLa cells. Cell. 1977 Apr;10(4):597–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90092-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flint S. J., De Pomerai D. I., Chesterton C. J., Butterworth P. H. Template specificity of eucaryotic DNA-dependent RNA polymerases. Effect of DNA structure and integrity. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Mar 1;42(2):567–579. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03372.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foe V. E., Wilkinson L. E., Laird C. D. Comparative organization of active transcription units in Oncopeltus fasciatus. Cell. 1976 Sep;9(1):131–146. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franze-Fernández M. T., Fontanive-Sanguesa A. V. Control of rRNA synthesis: effect of protein synthesis inhibition. FEBS Lett. 1975 Jun 1;54(1):26–29. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)81060-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg J. R. Isolation of messenger ribonucleoproteins in cesium sulfate density gradients: evidence that polyadenylated and non-polyadenylated messenger RNAs are associated with protein. J Mol Biol. 1976 Dec;108(2):403–416. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80127-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross-Bellard M., Oudet P., Chambon P. Isolation of high-molecular-weight DNA from mammalian cells. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jul 2;36(1):32–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02881.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Lindigkeit R. Pre-ribosomal RNA synthesis in isolated rat-liver nucleoli. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jul 2;36(1):244–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02906.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. D., Jant B. A., Kaufman S., Sokoloff L. Effects of ionic strength on the RNA polymerase activities of isolated nuclei and nucleoli of rat liver. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Feb;142(2):489–500. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90512-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellas B. L., Austoker J. L., Beebee T. J., Butterworth P. H. Forms AI and AII DNA-dependent RNA polymerases as components of two defined pools of polymerase activity in mammalian cells. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Feb;72(3):583–594. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11281.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis R., Penman S. The metabolism of poly (A)+ and poly(A)-hnRNA in cultured Drosophila cells studied with a rapid uridine pulse-chase. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):105–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90321-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewin B. Units of transcription and translation: sequence components of heterogeneous nuclear RNA and messenger RNA. Cell. 1975 Feb;4(2):77–93. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90113-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindell T. J., Weinberg F., Morris P. W., Roeder R. G., Rutter W. J. Specific inhibition of nuclear RNA polymerase II by alpha-amanitin. Science. 1970 Oct 23;170(3956):447–449. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3956.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marushige K., Bonner J. Fractionation of liver chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):2941–2944. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.2941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui S., Busch H. Isolation and characterization of rDNA-containing chromatin from nucleoli. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Oct 1;109(1):151–161. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90054-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meilhac M., Tysper Z., Chambon P. Animal DNA-dependent RNA polymerases. 4. Studies on inhibition by rifamycin derivatives. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jul 13;28(2):291–300. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01913.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melli M., Whitfield C., Rao K. V., Richardson M., Bishop J. O. DNA-RNA hybridization in vast DNA excess. Nat New Biol. 1971 May 5;231(18):8–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muto M. Estimation of gene reiteration from hybridization kinetics in moderate deoxyribonucleic acid excess. Biochem J. 1977 Jul 1;165(1):19–25. doi: 10.1042/bj1650019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul J., Gilmour R. S. Organ-specific restriction of transcription in mammalian chromatin. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jul 14;34(2):305–316. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90255-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder R. G., Rutter W. J. Specific nucleolar and nucleoplasmic RNA polymerases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Mar;65(3):675–682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.3.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage M. J., Sala-Trepat J. M., Bonner J. Measurement of the complexity and diversity of poly(adenylic acid) containing messenger RNA from rat liver. Biochemistry. 1978 Feb 7;17(3):462–467. doi: 10.1021/bi00596a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. B., Roeder R. G. Purification and subunit structure of deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase I from the mouse myeloma, MOPC 315. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 25;249(18):5898–5906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. B., Sklar V. E., Jaehning J. A., Weinmann R., Roeder R. G. Isolation and partial characterization of the multiple forms of deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase in the mouse myeloma, MOPC 315. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 25;249(18):5889–5897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifart K. H., Benecke B. J., Juhasz P. P. Multiple RNA polymerase species from rat liver tissue: possible existence of a cytoplasmic enzyme. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Aug;151(2):519–532. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90529-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tata J. R., Baker B. Enzymatic fractionation of nuclei: polynucleosomes and RNA polymerase II as endogenous transcriptional complexes. J Mol Biol. 1978 Jan 25;118(3):249–272. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90227-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widnell C. C., Tata J. R. Studies on the stimulation by ammonium sulphate of the DNA-dependent RNA polymerase of isolated rat-liver nuclei. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Sep;123(3):478–492. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90216-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


