Abstract
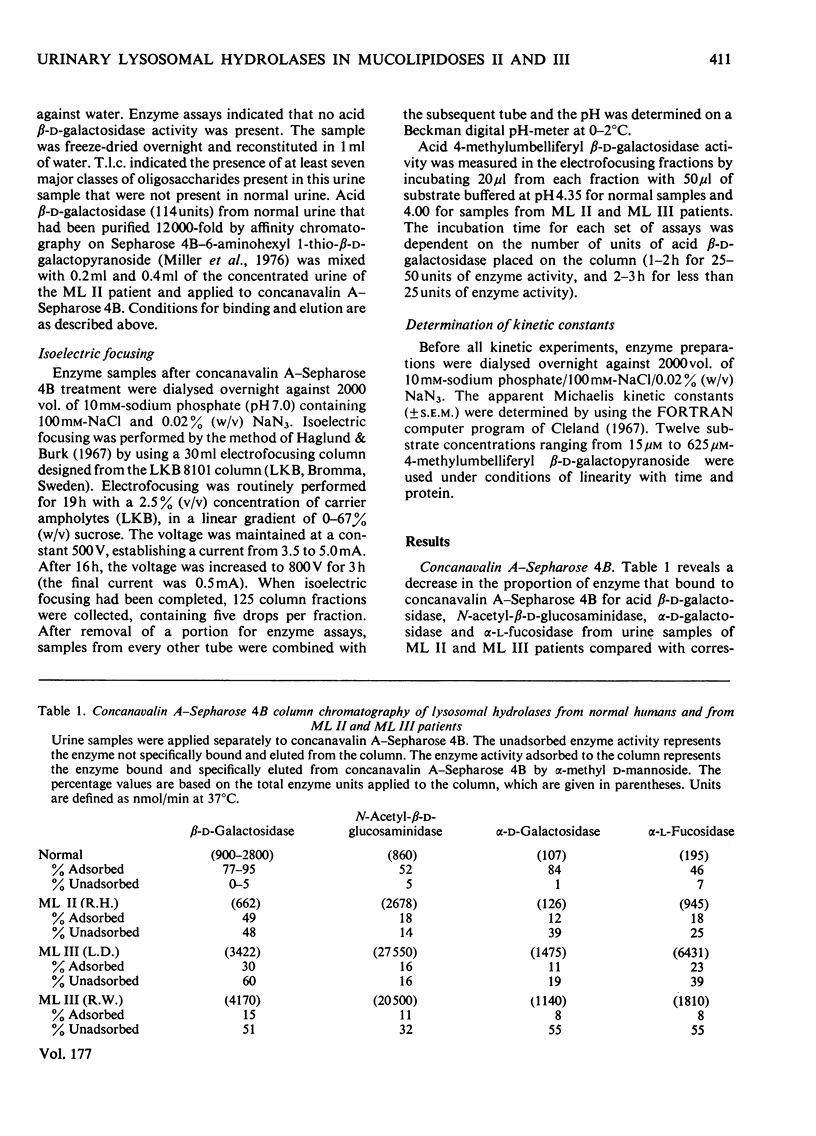
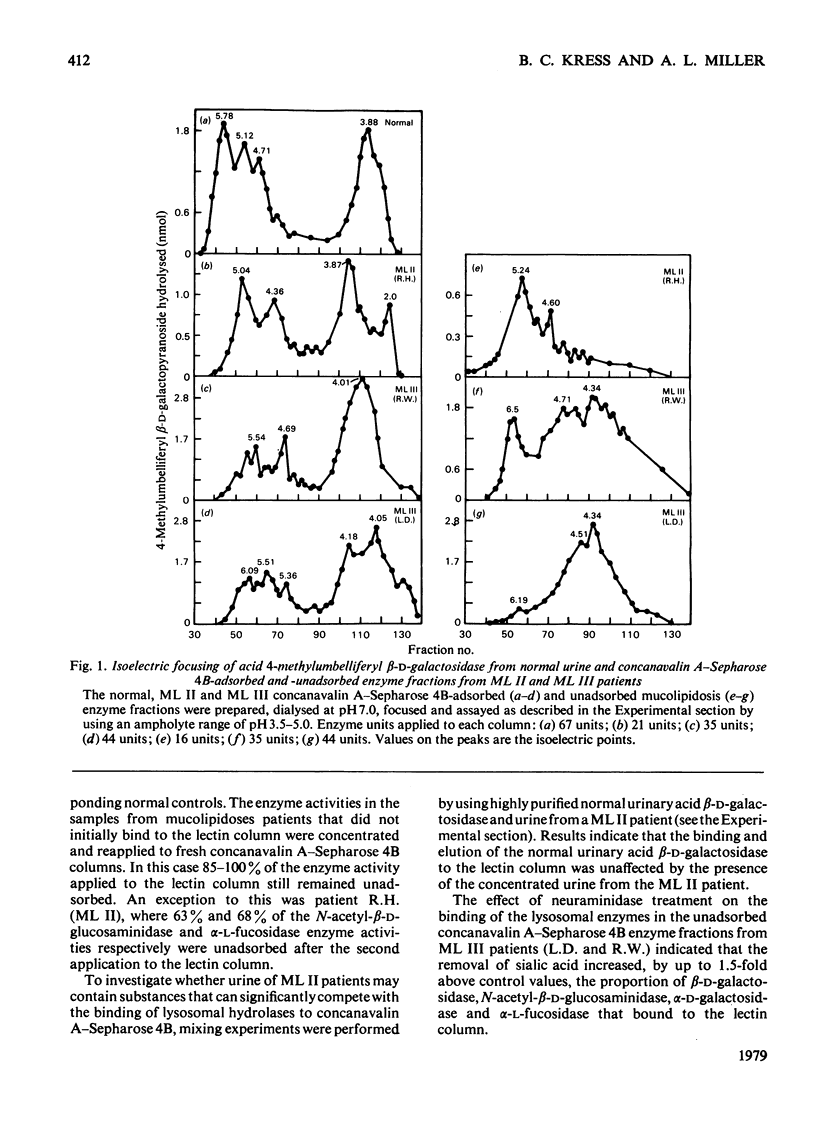
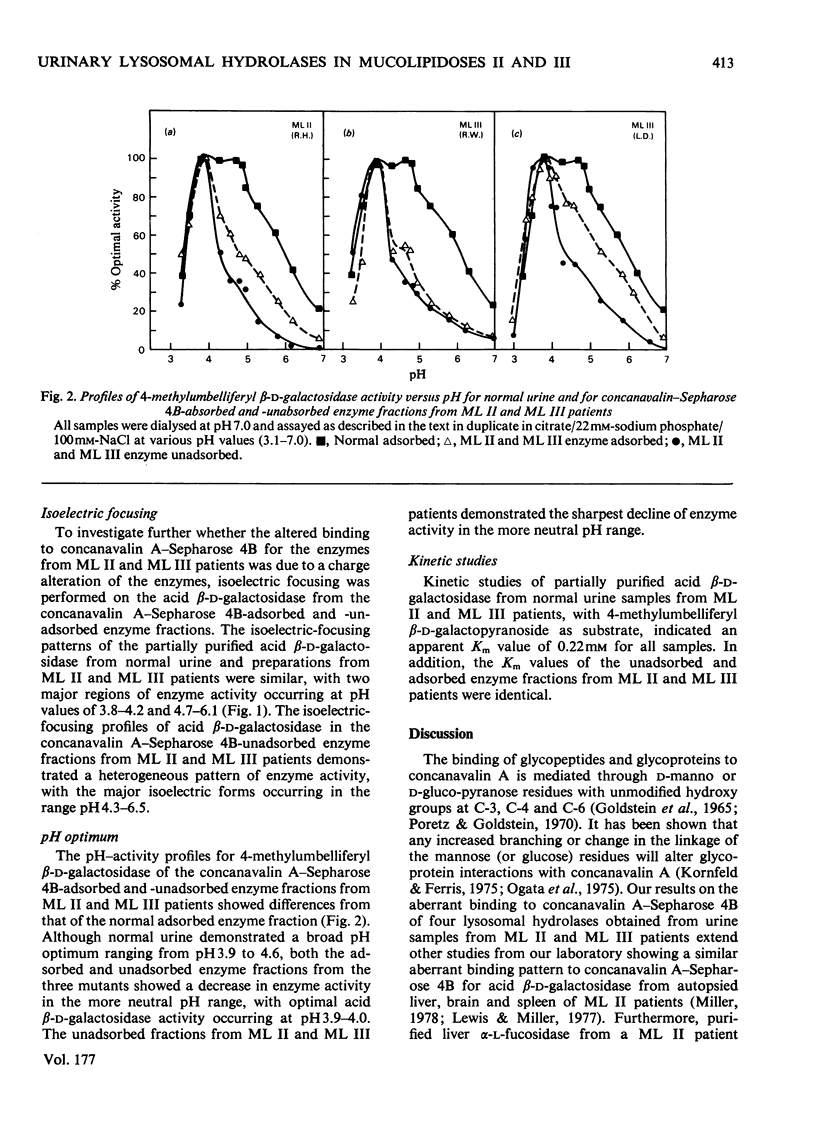
Investigation of the binding characteristics of acid beta-D-galactosidase, N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase, alpha-D-galactosidase and alpha-L-fucosidase from patients with mucolipidosis II and mucolipidosis III to concanavalin A--Sepharose 4B revealed a 2--10-fold decrease in the proportion of enzyme activities from patients with mucolipidoses II and III that adsorbed on the lectin. Neuraminidase treatment of the unadsorbed enzyme fraction did not significantly increased the proportion of enzyme activities that bound to the concanavalin A--Sepharose 4B. Characterization of acid beta-D-galactosidase from the adsorbed and unadsorbed enzyme fractions of mucolipidosis II and mucolipidosis III patients demonstrated identical apparent Km values of 0.22 mM with respect to 4-methylumbelliferyl beta-D-galactopyranoside, altered pH--activity profiles and heterogeneous isoelectric-focusing patterns. The results of this study support the suggestion of an alteration of a post-translational modification (possibly glycosylation) occurring in mucolipidosis II and mucolipidosis III common to the lysosomal hydrolases that affects the mannoserelated properties of these enzymes.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berman E. R., Kohn G., Yatziv S., Stein H. Acid hydrolase deficiencies and abnormal glycoproteins in mucolipidosis. 3 (pseudo-Hurler polydystrophy). Clin Chim Acta. 1974 Mar;52(1):115–124. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(74)90394-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champion M. J., Shows T. B. Electrophoretic abnormalities of lysosomal enzymes in mucolipidosis fibroblast lines. Am J Hum Genet. 1977 Mar;29(2):149–163. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleland W. W. The statistical analysis of enzyme kinetic data. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1967;29:1–32. doi: 10.1002/9780470122747.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDSTEIN I. J., HOLLERMAN C. E., SMITH E. E. PROTEIN-CARBOHYDRATE INTERACTION. II. INHIBITION STUDIES ON THE INTERACTION OF CONCANAVALIN A WITH POLYSACCHARIDES. Biochemistry. 1965 May;4:876–883. doi: 10.1021/bi00881a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser J. H., McAlister W. H., Sly W. S. Genetic heterogeneity in multiple lysosomal hydrolase deficiency. J Pediatr. 1974 Aug;85(2):192–198. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(74)80391-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman S., Neufeld E. F. A hypothesis for I-cell disease: defective hydrolases that do not enter lysosomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Nov 15;49(4):992–999. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90310-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman S., Shapiro L. J., Neufeld E. F. A recognition marker required for uptake of a lysosomal enzyme by cultured fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Mar 15;57(1):55–61. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80356-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hieber V., Distler J., Myerowitz R., Schmickel R. D., Jourdian G. W. The role of glycosidically bound mannose in the assimilation of beta-galactosidase by generalized gangliosidosis fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Dec 6;73(3):710–717. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90868-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes E. W., Miller A. L., Frost R. G., O'Brien J. S. Characterization of beta-D-galactosidase isolated from I-cell disease liver. Am J Hum Genet. 1975 Nov;27(6):719–727. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A., Achord D. T., Sly W. S. Phosphohexosyl components of a lysosomal enzyme are recognized by pinocytosis receptors on human fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2026–2030. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A., Fischer D., Achord D., Sly W. Phosphohexosyl recognition is a general characteristic of pinocytosis of lysosomal glycosidases by human fibroblasts. J Clin Invest. 1977 Nov;60(5):1088–1093. doi: 10.1172/JCI108860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld R., Ferris C. Interaction of immunoglobulin glycopeptides with concanavalin A. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 10;250(7):2614–2619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leroy J. G., Demars R. I. Mutant enzymatic and cytological phenotypes in cultured human fibroblasts. Science. 1967 Aug 18;157(3790):804–806. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3790.804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leroy J. G., Ho M. W., MacBrinn M. C., Zielke K., Jacob J., O'Brien J. S. I-cell disease: biochemical studies. Pediatr Res. 1972 Oct;6(10):752–757. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197210000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leroy J. G., Spranger J. W., Feingold M., Opitz J. M., Crocker A. C. I-cell disease: a clinical picture. J Pediatr. 1971 Sep;79(3):360–365. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(71)80142-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melhem R., Dorst J. P., Scott C. I., Jr, McKusick V. A. Roentgen findings in mucolipidosis III (Pseudo-Hurler polydystrophy). Radiology. 1973 Jan;106(1):153–160. doi: 10.1148/106.1.153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. L., Frost R. G., O'Brien J. Purification of human liver acid beta-D-galactosidases using affinity chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1976 Aug;74(2):537–545. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90236-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. L. I-Cell disease: isoelectric focusing, concanavalin A-Sepharose 4B binding and kinetic properties of human liver acid beta-D-galactosidases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jan 12;522(1):174–186. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90333-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neufeld E. F., Lim T. W., Shapiro L. J. Inherited disorders of lysosomal metabolism. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:357–376. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.002041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norden A. G., O'Brien J. S. Binding of human liver beta-galactosidases to plant lectins insolubilized on agarose. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Jan;56(1):193–198. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80333-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata S., Muramatsu T., Kobata A. Fractionation of glycopeptides by affinity column chromatography on concanavalin A-sepharose. J Biochem. 1975 Oct;78(4):687–696. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippart M., Sarlieve L., Manacorda A. Urinary glycolipids in Fabry's disease. Their examination in the detection of atypical variants and the pre-symptomatic state. Pediatrics. 1969 Feb;43(2):201–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poretz R. D., Goldstein I. J. An examination of the topography of the saccharide binding sites of concanavalin A and of the forces involved in complexation. Biochemistry. 1970 Jul 7;9(14):2890–2896. doi: 10.1021/bi00816a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sando G. N., Neufeld E. F. Recognition and receptor-mediated uptake of a lysosomal enzyme, alpha-l-iduronidase, by cultured human fibroblasts. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):619–627. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90262-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strecker G., Peers M. C., Michalski J. C., Hondi-Assah T., Fournet B., Spik G., Montreuil J., Farriaux J. P., Maroteaux P., Durand P. Structure of nine sialyl-oligosaccharides accumulated in urine of eleven patients with three different types of sialidosis. Mucolipidosis II and two new types of mucolipidosis. Eur J Biochem. 1977 May 16;75(2):391–403. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11540.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabas I., Schlesinger S., Kornfeld S. Processing of high mannose oligosaccharides to form complex type oligosaccharides on the newly synthesized polypeptides of the vesicular stomatitis virus G protein and the IgG heavy chain. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 10;253(3):716–722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. H., Taylor H. A., Reynolds L. W., Miller C. S. Mucolipidosis 3 (Pseudo-Hurler polydystrophy): multiple lysosomal enzyme abnormalities in serum and cultured fibroblast cells. Pediatr Res. 1973 Sep;7(9):751–756. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197309000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. H., Tiller G. E., Jr, Reynolds L. W., Miller C. S., Bace J. W. Increased levels of sialic acid associated with a sialidase deficiency in I-cell disease (mucolipidosis II) fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jul 12;71(1):188–195. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90267-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tondeur M., Vamos-Hurwitz E., Mockel-Pohl S., Dereume J. P., Cremer N., Loeb H. Clinical, biochemical, and ultrastructural studies in a case of chondrodystrophy presenting the I-cell phenotype in tissue culture. J Pediatr. 1971 Sep;79(3):366–378. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(71)80143-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vladutiu G. D., Rattazzi M. C. Abnormal lysosomal hydrolases excreted by cultured fibroblasts in I-cell disease (mucolipidosis II). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Dec 1;67(3):956–964. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90768-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vladutiu G. D., Rattazzi M. C. Cell disease: desialylation of beta-hexosaminidase and its effect on uptake by fibroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Feb 13;539(1):31–36. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90118-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiesmann U. N., Herschkowitz N. N. Studies on the pathogenetic mechanism of I-cell disease in cultured fibroblasts. Pediatr Res. 1974 Nov;8(11):865–869. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197411000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiesmann U. N., Lightbody J., Vassella F., Herschkowitz N. N. Multiple lysosomal deficiency due to enzyme leakage? N Engl J Med. 1971 Jan 14;284(2):109–110. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197101142840221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


