Abstract
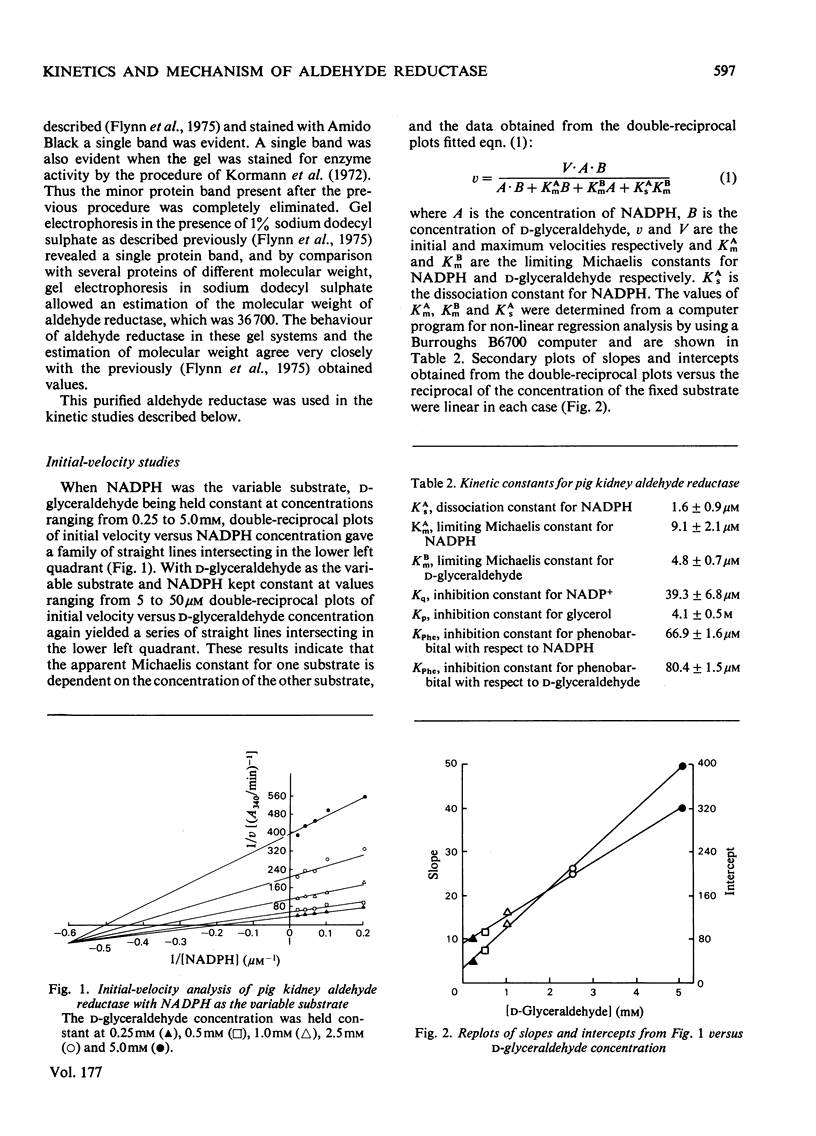
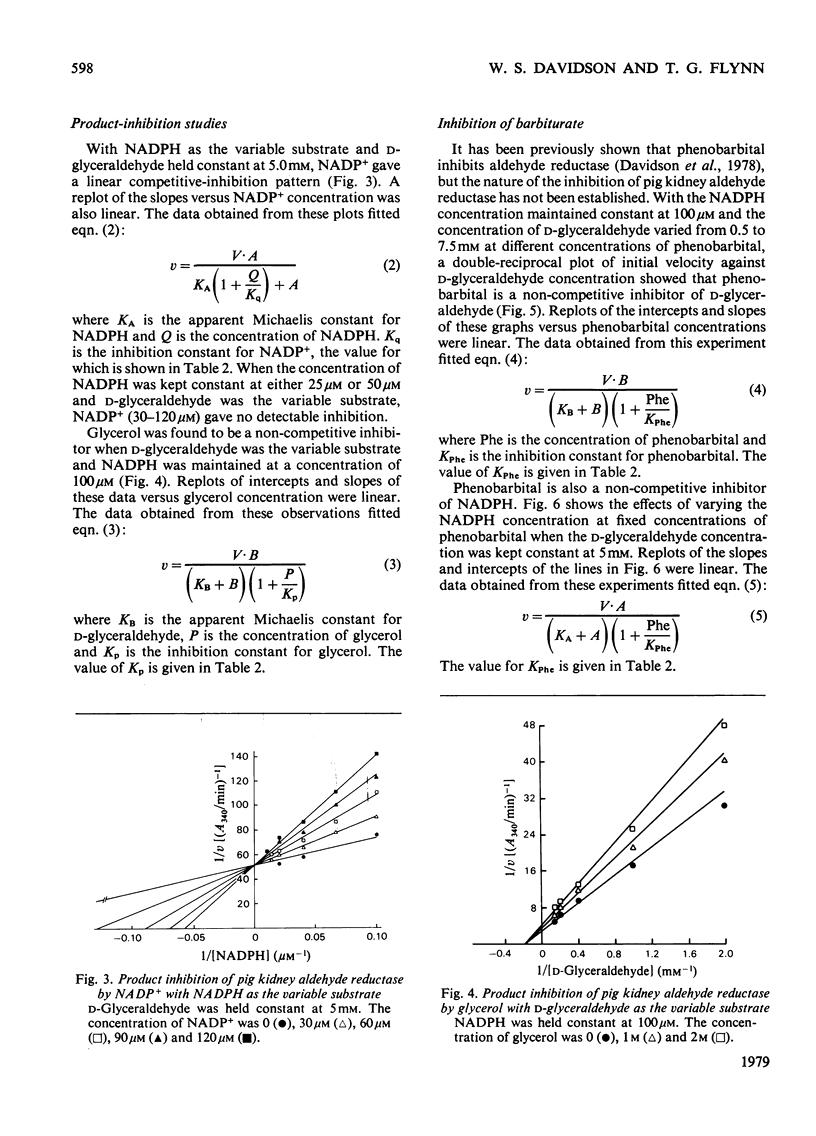
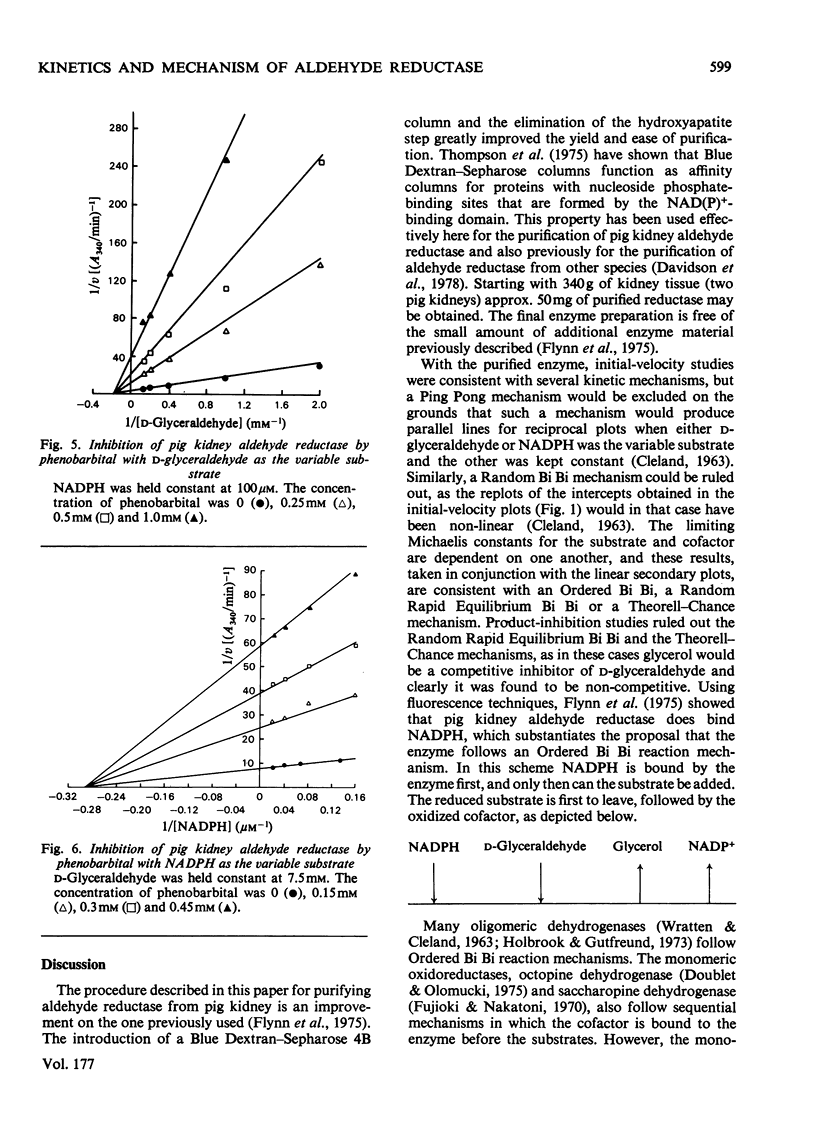
An improved procedure for purifying aldehyde reductase is described. Utilization of Blue Dextran--Sepharose 4B and elimination of hydroxyapatite chromatography greatly improves the yield and ease of purification. Starting with 340 g of kidney tissue (two pig kidneys) approx. 50 mg of purified reductase may be routinely and reproducibly obtained. The purified reductase was used to establish the kinetic reaction mechanism of the enzyme. Initial-velocity analysis and product-inhibition data revealed that pig kidney aldehyde reductase follows an Ordered Bi Bi reaction mechanism in which NADPH binds first before D-glyceraldehyde. The limiting Michaelis constants for D-glyceraldehyde and NADPH were 4.8 +/- 0.7 mM and 9.1 +/- 2.1 micrometer respectively. The mechanism is similar to that of another monomeric oxidoreductase, octopine dehydrogenase, towards which aldehyde reductase exhibits several similarities, but differs from that of other aldehyde reductases. Phenobarbital is a potent inhibitor of aldehyde reductase, inhibiting both substrate and cofactor non-competitively (Ki = 80.4 +/- 10.5 micrometer and 66.9 +/- 1.6 micrometer respectively). Barbiturate inhibition seems to be a common property of NADPH-dependent aldehyde reductases.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bosron W. F., Prairie R. L. Triphosphopyridine nucleotide-linked aldehyde reductase. I. Purification and properties of the enzyme from pig kidney cortex. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jul 25;247(14):4480–4485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breese G. R., Chase T. N., Kopin I. J. Metabolism of tyramine-3H and octopamine-3H by rat brain. Biochem Pharmacol. 1969 Apr;18(4):863–869. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(69)90057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bronaugh R. L., Erwin V. G. Further characterization of a reduced nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide phosphate-dependent aldehyde reductase from bovine brain. Inhibition by phenothiazine derivatives. Biochem Pharmacol. 1972 May 15;21(10):1457–1464. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(72)90370-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLELAND W. W. The kinetics of enzyme-catalyzed reactions with two or more substrates or products. I. Nomenclature and rate equations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Jan 8;67:104–137. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91800-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson W. S., Walton D. J., Flynn T. G. A comparative study of the tissue and species distribution of NADPH-dependent aldehyde reductase. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1978;60(3):309–315. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(78)90106-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doublet M. O., Olomucki A. Investigations on the kinetic mechanism of octopine dehydrogenase. 1. Steady-state kinetics. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Nov 1;59(1):175–183. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02439.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erwin V. G., Tabakoff B., Bronaugh R. L. Inhibition of a reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-linked aldehyde reductase from bovine brain by barbiturates. Mol Pharmacol. 1971 Mar;7(2):169–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn T. G., Shires J., Walton D. J. Properties of the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-dependent aldehyde reductase from pig kidney. Amino acid composition, reactivity of cysteinyl residues, and stereochemistry of D-glyceraldehyde reduction. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 25;250(8):2933–2940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujioka M., Nakatani Y. A kinetic study of saccharopine dehydrogenase reaction. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Sep;16(1):180–186. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01070.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbrook J. J., Gutfreund H. Approaches to the study of enzyme mechanisms lactate dehydrogenase. FEBS Lett. 1973 Apr 15;31(2):157–169. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80095-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kormann A. W., Hurst R. O., Flynn T. G. Purification and properties of an NADP + -dependent glycerol dehydrogenase from rabbit skeletal muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 20;258(1):40–55. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90965-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monneuse-Doublet M. O., Olomucki A., Buc J. Investigation on the kinetic mechanism of octopine dehydrogenase. A regulatory behavior. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Mar 15;84(2):441–448. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12185.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plapp B. V. Enhancement of the activity of horse liver alcohol dehydrogenase by modification of amino groups at the active sites. J Biol Chem. 1970 Apr 10;245(7):1727–1735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ris M. M., Deitrich R. A., Von Wartburg J. P. Inhibition of aldehyde reductase isoenzymes in human and rat brain. Biochem Pharmacol. 1975 Oct 15;24(20):1865–1869. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(75)90405-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ris M. M., von Wartburg J. P. Heterogeneity of NADPH-dependent aldehyde reductase from human and rat brain. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Aug 1;37(1):69–77. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02958.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan L. D., Vestling C. S. Rapid purification of lactate dehydrogenase from rat liver and hepatoma: a new approach. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Jan;160(1):279–284. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(74)80035-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. T., Cass K. H., Stellwagen E. Blue dextran-sepharose: an affinity column for the dinucleotide fold in proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):669–672. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toews C. J. The kinetics and reaction mechanism of the nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide phosphate-specific glycerol dehydrogenase of rat skeletal muscle. Biochem J. 1967 Dec;105(3):1067–1073. doi: 10.1042/bj1051067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner A. J., Hick P. E. Inhibition of aldehyde reductase by acidic metabolites of the biogenic amines. Biochem Pharmacol. 1975 Sep 15;24(18):1731–1733. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(75)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WRATTEN C. C., CLELAND W. W. PRODUCT INHIBITION STUDIES ON YEAST AND LIVER ALCOHOL DEHYDROGENASES. Biochemistry. 1963 Sep-Oct;2:935–941. doi: 10.1021/bi00905a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wermuth B., Münch J. D., von Wartburg J. P. Purification and properties of NADPH-dependent aldehyde reductase from human liver. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 10;252(11):3821–3828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


