Abstract
1. The work reported was designed to provide quantitative information about the capacity of the extrahepatic tissues of the rat to degrade injected VLD lipoproteins (very-low-density lipoproteins, d less than 1.006) to LD lipoproteins (low-density lipoproteins, d 1.006--1.063) and to study the fate of the different VLD-lipoprotein apoproteins during the degradative process. 2. Rat liver VLD lipoproteins, radioactively labelled in their protein moieties, were produced by the perfusion of the organ and were either injected into the circulation of the supradiaphragmatic rats or incubated in rat plasma at 37 degrees C. At a time (75 min) when approx. 90% of the triacylglycerol of the VLD lipoproteins had been hydrolysed the supradiaphragmatic rats were bled and VLD lipoproteins, LD lipoproteins and HD lipoproteins (high-density lipoproteins, d 1.063--1.21) were separated from their plasma and from the plasma incubated in vitro. The apoproteins of each of the lipoprotein classes were resolved by gel-filtration chromatography into three main fractions, designated peaks I, II and III. 3. Incubation of the liver VLD lipoproteins in plasma in vitro led to the transfer of about 30% of the total protein radioactivity to the HD lipoproteins. The transfer mainly involved the peak-II (arginine-rich and/or apo A-I) and peak-III (apo C) proteins. There was also a small transfer of radioactivity (about 5% of the total) to the LD lipoproteins. 4. Injection of the liver VLD lipoproteins into the circulation of the supradiaphragmatic rat resulted in the transfer of about 15% of the total VLD-lipoprotein radioactivity to the LD lipoproteins. The transfer involved mainly the peak-I (apo B) proteins and accounted for about 20% of the total apo B protein radioactivity of the injected VLD lipoproteins. When the endogenous plasma VLD lipoprotein was taken into account the transfer of apo B protein was about 35%. 5. The transfer of peak-II protein radioactivity from the VLD to the HD lipoproteins was greater in the plasma of the supradiaphragmatic rat than in the incubated plasma suggesting that there was a net transfer of peak-II apoproteins during the VLD lipoprotein degradation. The transfer of peak-III protein radioactivity was not greater in the plasma of the supradiaphragmatic rat, but there was a loss of this radioactivity from the circulation.
Full text
PDF



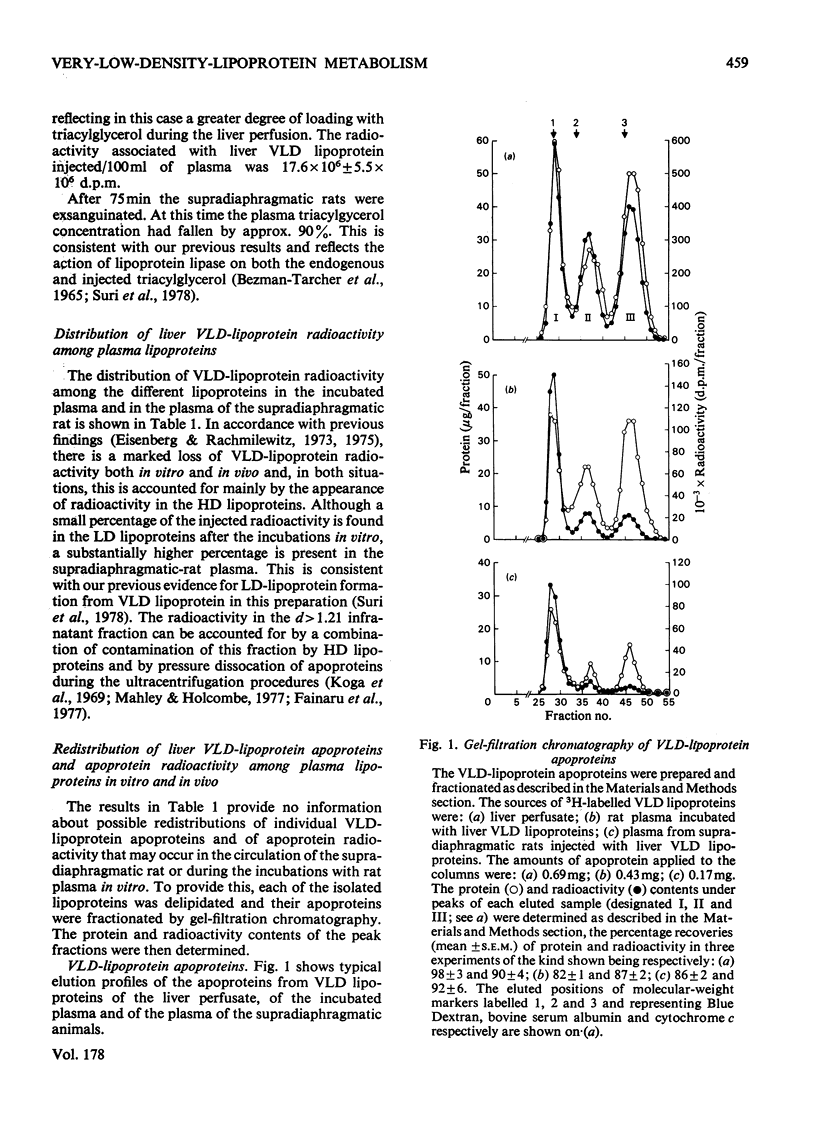

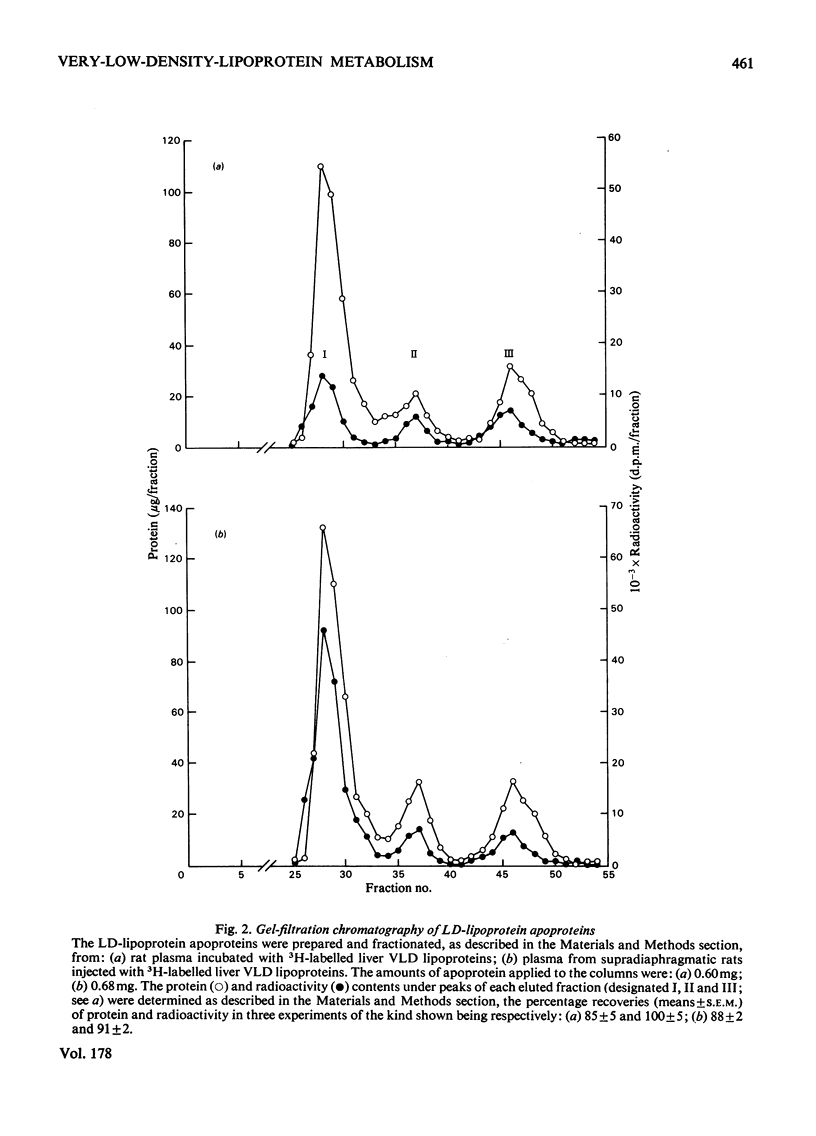
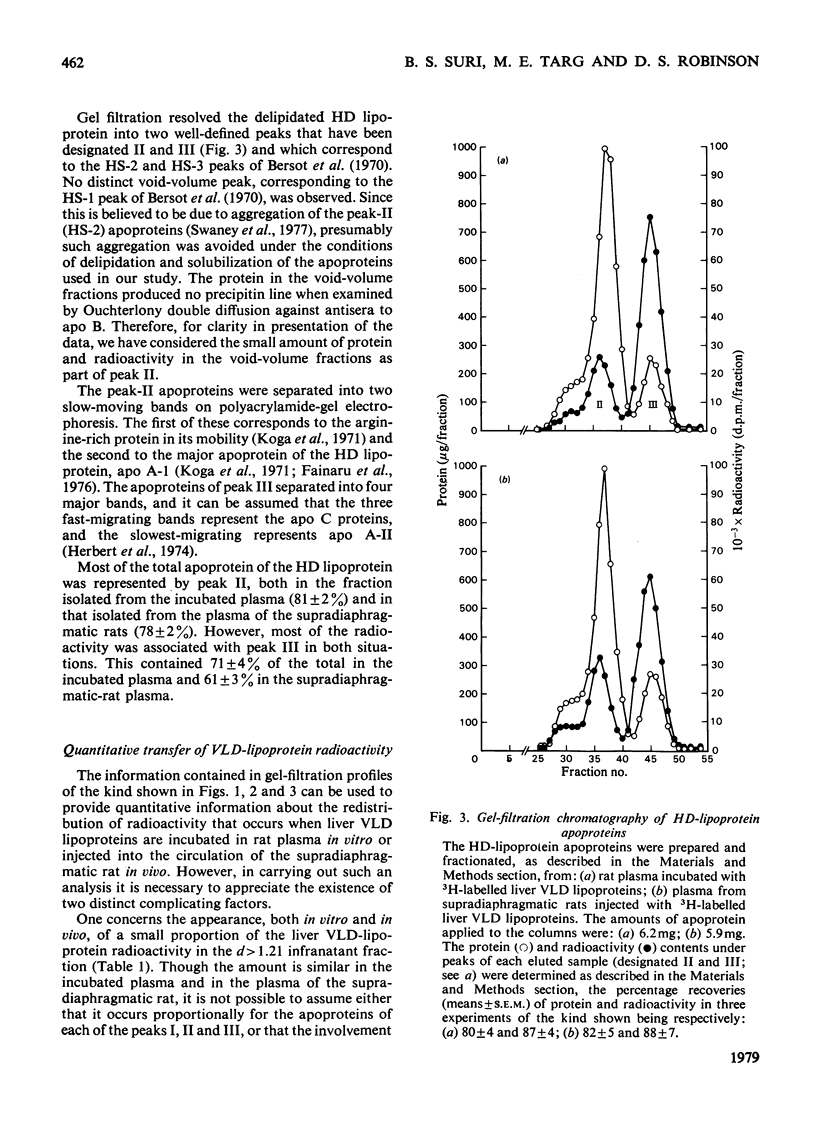




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berman M., Hall M., 3rd, Levy R. I., Eisenberg S., Bilheimer D. W., Phair R. D., Goebel R. H. Metabolsim of apoB and apoC lipoproteins in man: kinetic studies in normal and hyperlipoproteininemic subjects. J Lipid Res. 1978 Jan;19(1):38–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bersot T. P., Brown W. V., Levy R. I., Windmueller H. G., Fredrickson D. S., LeQuire V. S. Further characterization of the apolipoproteins of rat plasma lipoproteins. Biochemistry. 1970 Aug 18;9(17):3427–3433. doi: 10.1021/bi00819a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper A. D. The metabolism of chylomicron remnants by isolated perfused rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Sep 28;488(3):464–474. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(77)90204-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dory L., Pocock D., Rubinstein D. The catabolism of human and rat very low density lipoproteins by perfused rat hearts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Feb 27;528(2):161–175. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(78)90191-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein C., Lim C. T., Scanu A. M. On the subunit structure of the protein of human serum high density lipoprotein. I. A study of its major polypeptide component (Sephadex, fraction 3). J Biol Chem. 1972 Sep 25;247(18):5842–5849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S., Bilheimer D. W., Levy R. I., Lindgren F. T. On the metabolic conversion of human plasma very low density lipoprotein to low density lipoprotein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Dec 20;326(3):361–377. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(73)90138-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S., Bilheimer D. W., Levy R. I. The metabolism of very low density lipoprotein proteins. II. Studies on the transfer of apoproteins between plasma lipoproteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Sep 7;280(1):94–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S., Levy R. I. Lipoprotein metabolism. Adv Lipid Res. 1975;13:1–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S., Rachmilewitz D. Interaction of rat plasma very low density lipoprotein with lipoprotein lipase-rich (postheparin) plasma. J Lipid Res. 1975 Sep;16(5):341–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S., Rachmilewitz D. Metabolism of rat plasma very low density lipoprotein. I. Fate in circulation of the whole lipoprotein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Dec 20;326(3):378–390. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(73)90139-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faergeman O., Havel R. J. Metabolism of cholesteryl esters of rat very low density lipoproteins. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jun;55(6):1210–1218. doi: 10.1172/JCI108039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faergeman O., Sata T., Kane J. P., Havel R. J. Metabolism of apoprotein B of plasma very low density lipoproteins in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1975 Dec;56(6):1396–1403. doi: 10.1172/JCI108220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fainaru M., Havel R. J., Felker T. E. Radioimmunoassay of apolipoprotein A-I of rat serum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 28;446(1):56–68. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(76)90097-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fainaru M., Havel R. J., Imaizumi K. Apoprotein content of plasma lipoproteins of the rat separated by gel chromatography or ultracentrifugation. Biochem Med. 1977 Jun;17(3):347–355. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(77)90040-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felts J. M., Itakura H., Crane R. T. The mechanism of assimilation of constituents of chylomicrons, very low density lipoproteins and remnants - a new theory. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Oct 27;66(4):1467–1475. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90524-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidge N. H., Poulis P. Studies on the radioiodination of very low density lipoprotein obtained from different mammalian species. Clin Chim Acta. 1974 Mar;52(1):15–26. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(74)90383-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidge N., Poulis P. Studies on the metabolism of rat serum very low density apolipoprotein. J Lipid Res. 1975 Sep;16(5):367–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher M. J. A colorimetric method for estimating serum triglycerides. Clin Chim Acta. 1968 Nov;22(3):393–397. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(68)90041-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florén C. H., Nilsson A. Binding, interiorization and degradation of cholesteryl ester-labelled chylomicron-remmant particles by rat hepatocyte monolayers. Biochem J. 1977 Dec 15;168(3):483–494. doi: 10.1042/bj1680483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glangeaud M. C., Eisenberg S., Olivecrona T. Very low density lipoprotein. Dissociation of apolipoprotein C during lipoprotein lipase induced lipolysis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jan 18;486(1):23–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R. L., Williams M. C., Fielding C. J., Havel R. J. Discoidal bilayer structure of nascent high density lipoproteins from perfused rat liver. J Clin Invest. 1976 Sep;58(3):667–680. doi: 10.1172/JCI108513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hems R., Ross B. D., Berry M. N., Krebs H. A. Gluconeogenesis in the perfused rat liver. Biochem J. 1966 Nov;101(2):284–292. doi: 10.1042/bj1010284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert P. N., Windmueller H. G., Bersot T. P., Shulman R. S. Characterization of the rat apolipoproteins. I. The low molecular weight proteins of rat plasma high density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 25;249(18):5718–5724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koga S., Bolis L., Scanu A. M. Isolation and characterization of subunit polypeptides from apoproteins of rat serum lipoprotein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 May 25;236(2):416–430. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90222-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koga S., Horwitz D. L., Scanu A. M. Isolation and properties of lipoproteins from normal rat serum. J Lipid Res. 1969 Sep;10(5):577–588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushwaha R. S., Hazzard W. R. Catabolism of very low density lipoproteins in the rabbit. Effect of changing composition and pool size. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Feb 27;528(2):176–189. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(78)90192-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis B. Plasma-lipoprotein interrelationships. Biochem Soc Trans. 1977;5(2):589–601. doi: 10.1042/bst0050589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Holcombe K. S. Alterations of the plasma lipoproteins and apoproteins following cholesterol feeding in the rat. J Lipid Res. 1977 May;18(3):314–324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mjos O. D., Faergeman O., Hamilton R. L., Havel R. J. Characterization of remnants produced during the metabolism of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins of blood plasma and intestinal lymph in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1975 Sep;56(3):603–615. doi: 10.1172/JCI108130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noel S. P., Dolphin P. J., Rubinstein D. An in vitro model for the catabolism of rat chylomicrons. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Apr 7;63(3):764–772. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80449-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne J. C., Jr, Brewer H. B., Jr The plasma lipoproteins. Adv Protein Chem. 1977;31:253–337. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60220-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersburg S. J., Madeley A., Robinson D. S. A study of the interrelationship between the triacylglycerol and protein components of very-low-density lipoproteins using the perfused rat liver. Biochem J. 1975 Sep;150(3):315–321. doi: 10.1042/bj1500315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redgrave T. G. Formation of cholesteryl ester-rich particulate lipid during metabolism of chylomicrons. J Clin Invest. 1970 Mar;49(3):465–471. doi: 10.1172/JCI106255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanu A. M., Edelstein C. Solubility in aqueous solutions of ethanol of the small molecular weight peptides of the serum very low density and high density lipoproteins: relevance to the recovery problem during delipidation of serum lipoproteins. Anal Biochem. 1971 Dec;44(2):576–588. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90247-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen B. W., Scanu A. M., Kézdy F. J. Structure of human serum lipoproteins inferred from compositional analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):837–841. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd J., Bedford D. K., Morgan H. G. Radioiodination of human low density lipoprotein: a comparison of four methods. Clin Chim Acta. 1976 Jan 2;66(1):97–109. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(76)90376-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigurdsson G., Nicoll A., Lewis B. Conversion of very low density lipoprotein to low density lipoprotein. A metabolic study of apolipoprotein B kinetics in human subjects. J Clin Invest. 1975 Dec;56(6):1481–1490. doi: 10.1172/JCI108229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surgi B. S., Targ M. E., Robinson D. S. The degradation of very low density lipoprotein by the extrahepatic tissues of the rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 May 25;529(2):331–341. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(78)90076-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaney J. B., Braithwaite F., Eder H. A. Characterization of the apolipoproteins of rat plasma lipoproteins. Biochemistry. 1977 Jan 25;16(2):271–278. doi: 10.1021/bi00621a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolman E. L., Schworer C. M., Jefferson L. S. Effects of hypophysectomy on amino acid metabolism and gluconeogenesis in the perfused rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jul 10;248(13):4552–4560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udenfriend S., Stein S., Böhlen P., Dairman W., Leimgruber W., Weigele M. Fluorescamine: a reagent for assay of amino acids, peptides, proteins, and primary amines in the picomole range. Science. 1972 Nov 24;178(4063):871–872. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4063.871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Harken D. R., Dixon C. W., Heimberg M. Hepatic lipid metabolism in experimental diabetes. V. The effect of concentration of oleate on metabolism of triglycerides and on ketogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1969 May 10;244(9):2278–2285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanaman T. C., Wakil S. J., Hill R. L. The preparation of tryptic, peptic, thermolysin, and cyanogen bromide peptides from the acyl carrier protein of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1968 Dec 25;243(24):6409–6419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WANG L. Plasma volume, cell volume, total blood volume and F cells factor in the normal and splenectomized Sherman rat. Am J Physiol. 1959 Jan;196(1):188–192. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1958.196.1.188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W., Assmann G. The rat arginine-rich apoprotein and its redistribution following injection of iodinated lipoproteins into normal and hypercholesterolemic rats. Atherosclerosis. 1977 Oct;28(2):121–140. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(77)90150-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windmueller H. G., Herbert P. N., Levy R. I. Biosynthesis of lymph and plasma lipoprotein apoproteins by isolated perfused rat liver and intestine. J Lipid Res. 1973 Mar;14(2):215–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


