Abstract
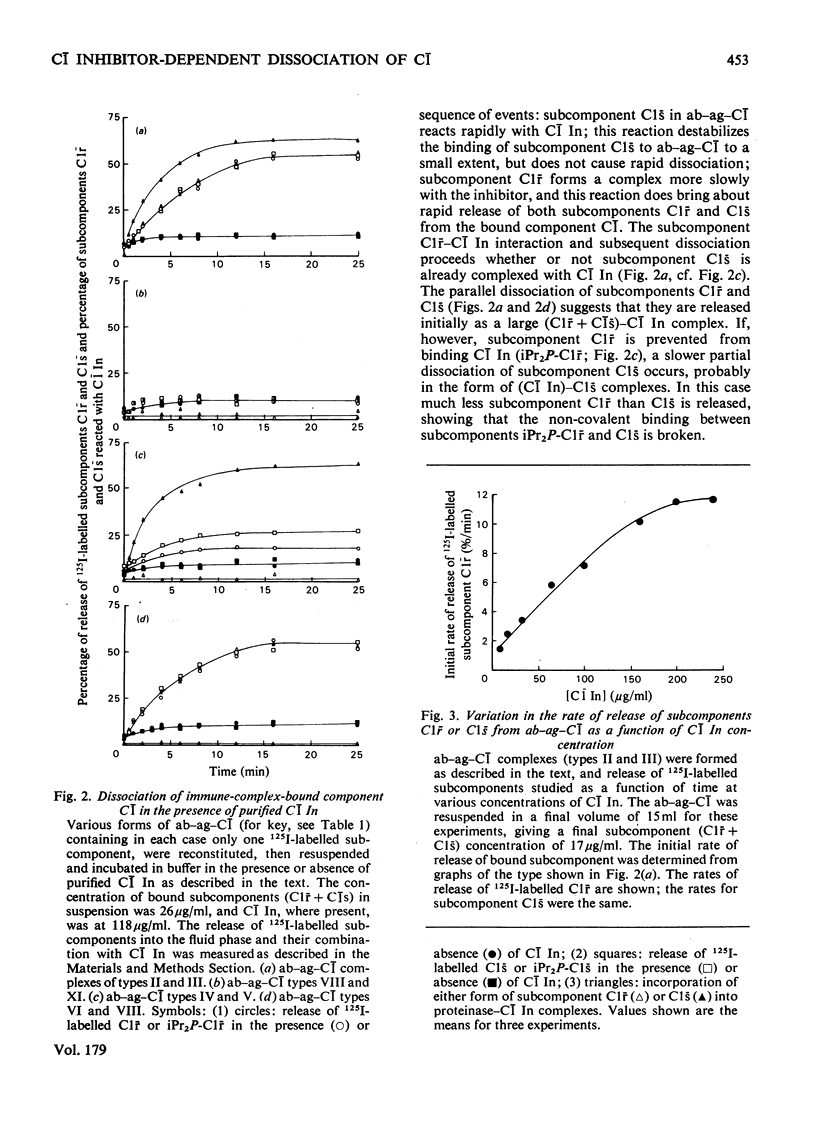
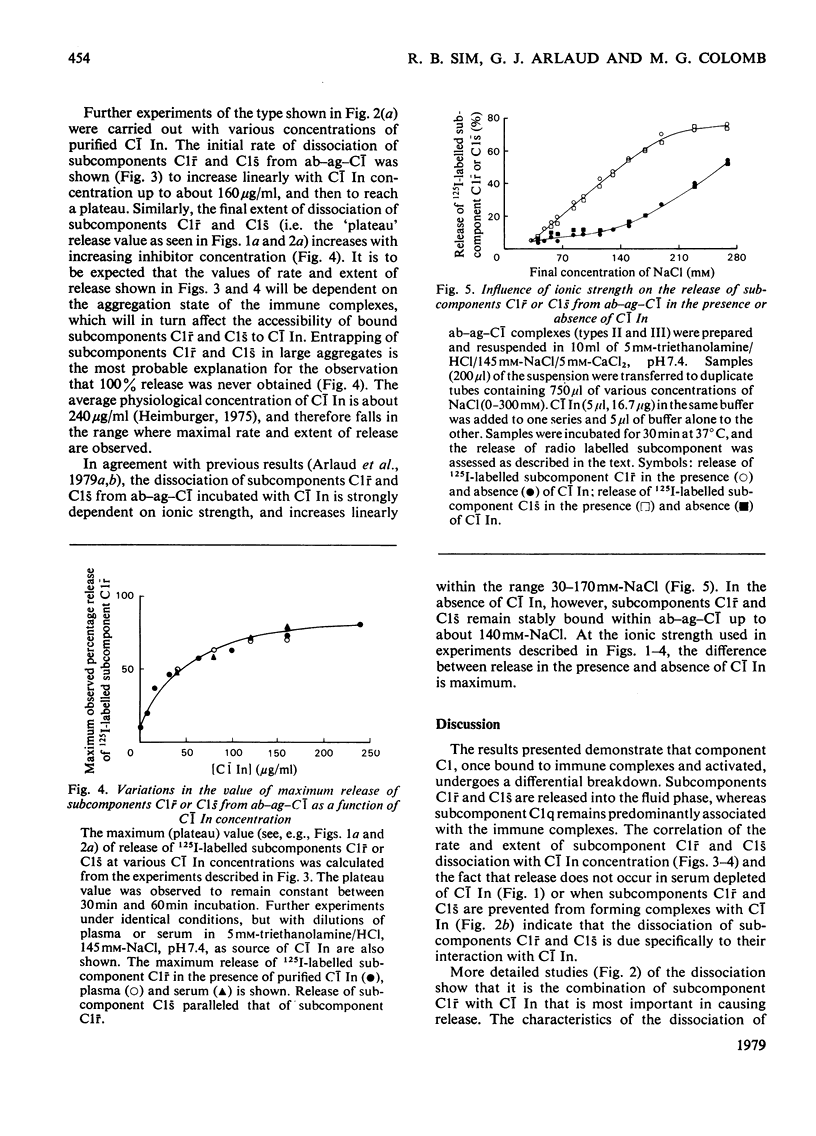
The interaction of C1 inhibitor with complement component C1 bound to immune complexes was examined by using 125I-labelled C1 subcomponents. The inhibitor binds rapidly to subcomponent C1s, and more slowly to subcomponent C1r. Formation of the C1r-C1 inhibitor complex causes rapid dissociation of subcomponents C1r and C1s from the antibody-antigen-component C1 aggregate. The rate and extent of this release are proportional to C1 Inhibitor concentration and are also dependent on ionic strength. Results obtained with purified C1 Inhibitor, plasma or serum as source of C1 Inhibitor are all closely comparable. Only slight dissociation of subcomponent C1q is observed under the same range of conditions. The implications of the release phenomenon are discussed in relation to the structure of component C1 and the possibility of differential turnover of C1 subcomponents.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan R., Isliker H. Studies on the complement-binding site of rabbit immunoglobulin G-11. The reaction of rabbit IgG and its fragments with Clq. Immunochemistry. 1974 May;11(5):243–248. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(74)90202-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arlaud G. J., Meyer C. M., Colomb M. G. Use of an IgG fragment prepared with particulate plasmin to study the C1 binding and activation. FEBS Lett. 1976 Jul 1;66(1):132–136. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80602-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arlaud G. J., Reboul A., Sim R. B., Colomb M. G. Interaction of C1-inhibitor with the C1r and C1s subcomponents in human C1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jan 25;576(1):151–162. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(79)90494-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assimeh S. N., Bing D. H., Painter R. H. A simple method for the isolation of the subcomponents of the first component of complement by affinity chromatography. J Immunol. 1974 Jul;113(1):225–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conradie J. D., Volanakis J. E., Stroud R. M. Evidence for a serum inhibitor of Clq. Immunochemistry. 1975 Dec;12(12):967–971. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(75)90260-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodds A. W., Sim R. B., Porter R. R., Kerr M. A. Activation of the first component of human complement (C1) by antibody-antigen aggregates. Biochem J. 1978 Nov 1;175(2):383–390. doi: 10.1042/bj1750383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghebrehiwet B., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Lysis of C1Q-coated chicken erythrocytes by human lymphoblastoid cell lines. J Immunol. 1978 Jan;120(1):27–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigli I., Porter R. R., Sim R. B. The unactivated form of the first component of human complement, C1. Biochem J. 1976 Sep 1;157(3):541–548. doi: 10.1042/bj1570541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAINES A. L., LEPOW I. H. STUDIES ON HUMAN C'1-ESTERASE. III. EFFECT OF RABBIT ANTI-C'1-ESTERASE ON ENZYMATIC AND COMPLEMENT ACTIVITIES. J Immunol. 1964 Mar;92:479–490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpel P. C. C1 inactivator. Methods Enzymol. 1976;45:751–750. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(76)45068-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpel P. C., Cooper N. R. Studies on human plasma C1 inactivator-enzyme interactions. I. Mechanisms of interaction with C1s, plasmin, and trypsin. J Clin Invest. 1975 Mar;55(3):593–604. doi: 10.1172/JCI107967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heusser C., Boesman M., Nordin J. H., Isliker H. Effect of chemical and enzymatic radioiodination on in vitro human Clq activities. J Immunol. 1973 Mar;110(3):820–828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland N. H., de Bracco M. M., Christian C. L. Pathways of complement activation in glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 1972 Feb;1(2):106–114. doi: 10.1038/ki.1972.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson U., Kamme C., Laurell A. B., Nilsson N. I. C1 subcomponents in acute pneumococcal otitis media in children. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1977 Feb;85(1):10–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1977.tb03604.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kluft C. Elimination of inhibition in euglobulin fibrinolysis by use of flufenamate: involvement of C1-inactivator. Haemostasis. 1977;6(6):351–369. doi: 10.1159/000214202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVY L. R., LEPOW I. H. Assay and properties of serum inhibitor of C'l-esterase. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Aug-Sep;101:608–611. doi: 10.3181/00379727-101-25034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell A. B., Mårtensson U. Interaction between C1q, C1r and C1s from human serum. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1974 Aug;82(4):585–589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell A. B., Mårtensson U., Sjöholm A. G. C1 subcomponent conplexes in normal and pathological sera studied by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1976 Dec;84C(6):455–464. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1976.tb00055.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagasawa S., Takahashi K., Koyama J. Isolation of a complex of the subcomponents of the activated first component of complement, Clr--Cls, from ACD-human plasma. FEBS Lett. 1974 May 1;41(2):280–282. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)81229-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfueller S. L., Lüscher E. F. The effects of immune complexes on blood platelets and their relationship to complement activation. Immunochemistry. 1972 Nov;9(11):1151–1165. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(72)90085-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickering R. J., Naff G. B., Stroud R. M., Good R. A., Gewurz H. Deficiency of C1r in human serum. Effects on the structure and function of macromolecular C1. J Exp Med. 1970 Apr 1;131(4):803–815. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.4.803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter R. R. The eleventh Hopkins Memorial Lecture: The biochemistry of complement. Biochem Soc Trans. 1977;5(6):1659–1674. doi: 10.1042/bst0051659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratnoff O. D., Pensky J., Ogston D., Naff G. B. The inhibition of plasmin, plasma kallikrein, plasma permeability factor, and the C'1r subcomponent of the first component of complement by serum C'1 esterase inhibitor. J Exp Med. 1969 Feb 1;129(2):315–331. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.2.315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reboul A., Arlaud G. J., Sim R. B., Colomb M. G. A simplified procedure for the purification of C1-inactivator from human plasma. Interaction with complement subcomponents C1r and C1s. FEBS Lett. 1977 Jul 1;79(1):45–50. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80347-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid K. B., Lowe D. M., Porter R. R. Isolation and characterization of C1q, a subcomponent of the first component of complement, from human and rabbit sera. Biochem J. 1972 Dec;130(3):749–763. doi: 10.1042/bj1300749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid K. B., Sim R. B., Faiers A. P. Inhibition of the reconstitution of the haemolytic activity of the first component of human complement by a pepsin-derived fragment of subcomponent C1q. Biochem J. 1977 Feb 1;161(2):239–245. doi: 10.1042/bj1610239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sim R. B., Porter R. R. Isolation and comparison of the proenzyme and activated forms of the human serum complement subcomponents C1r and C1s. Biochem Soc Trans. 1976;4(1):127–129. doi: 10.1042/bst0040127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sim R. B., Porter R. R., Reid K. B., Gigli I. The structure and enzymic activities of the C1r and C1s subcomponents of C1, the first component of human serum complement. Biochem J. 1977 May 1;163(2):219–227. doi: 10.1042/bj1630219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sim R. B., Reboul A., Arlaud G. J., Villiers C. L., Colomb M. G. Interaction of 125I-labelled complement subcomponents C-1r and C-1s with protease inhibitors in plasma. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jan 1;97(1):111–115. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80063-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stroud R. M., Nagaki K., Pickering R. J., Gewurz H., Good R. A., Cooper M. D. Sub-units of the first complement component in immunologic deficiency syndromes: independence of Cls and Clq. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Aug;7(2):133–137. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziccardi R. J., Cooper N. R. Physicochemical and functional characterization of the C1r subunit of the first complement component. J Immunol. 1976 Feb;116(2):496–503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziccardi R. J., Cooper N. R. The subunit composition and sedimentation properties of human C1. J Immunol. 1977 Jun;118(6):2047–2052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bracco M. M., Windhorst D., Stroud R. M., Moncada B. The autosomal recessive mode of inheritance of C1r deficiency in a large Puerto Rican family. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Feb;16(2):183–188. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


