Abstract
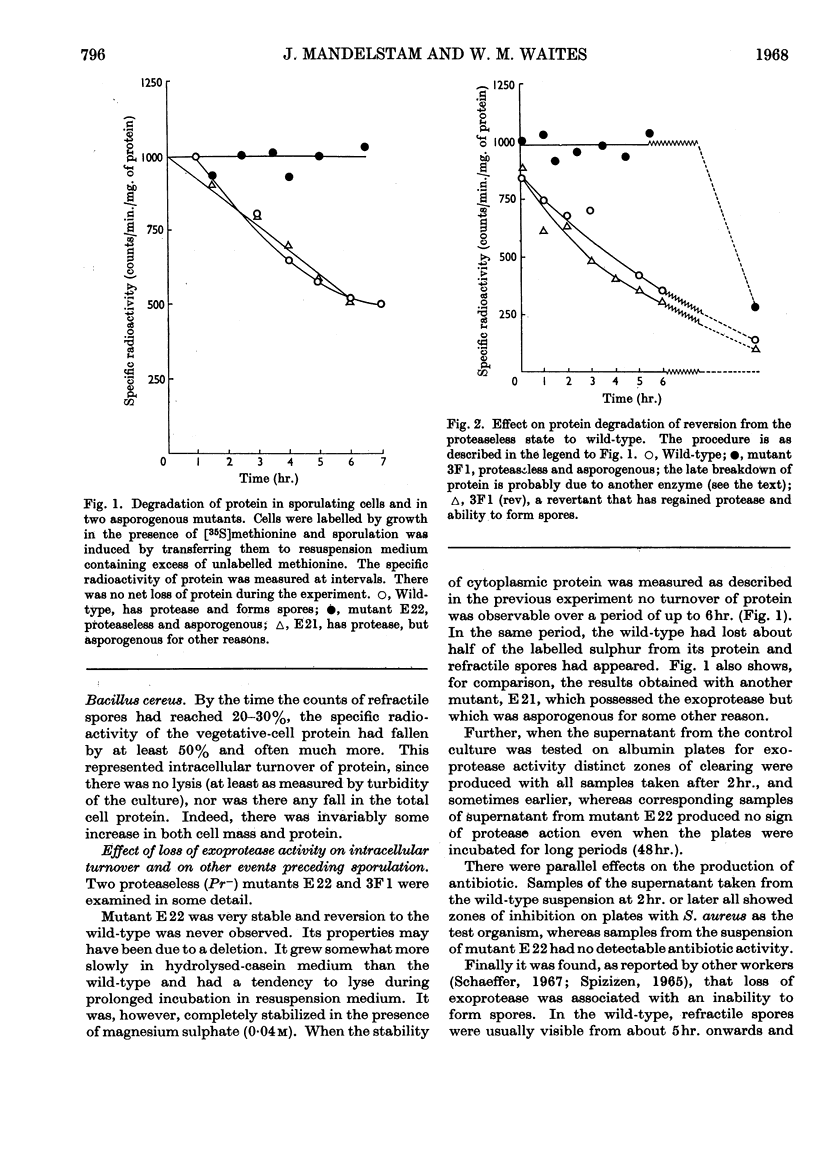
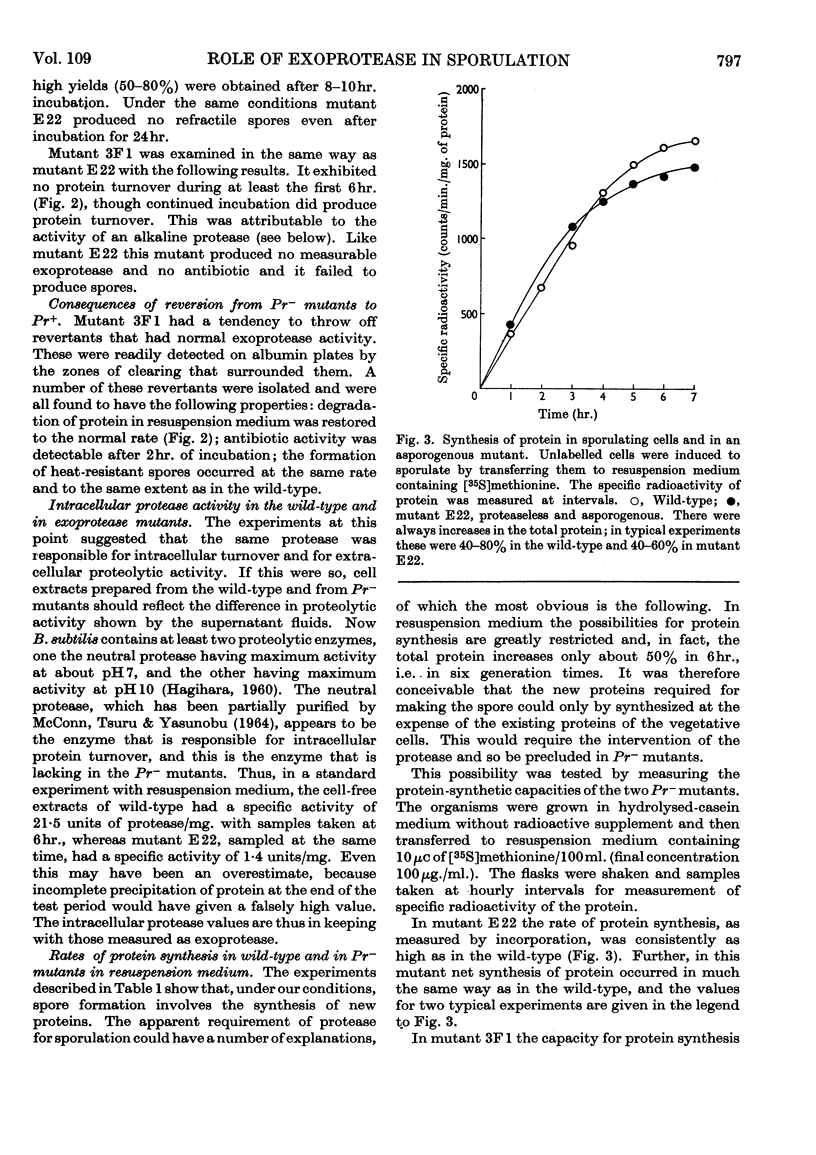
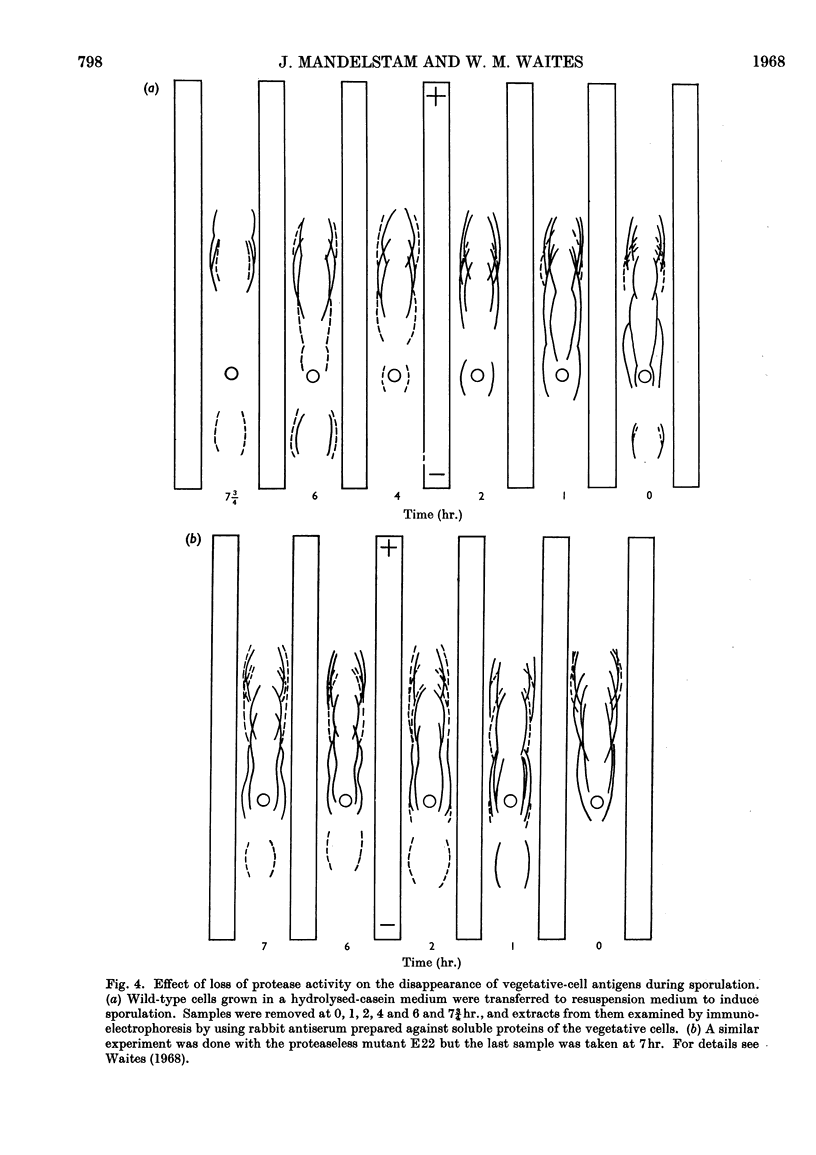
1. Intracellular turnover of protein was measured in wild-type Bacillus subtilis, which produces exoprotease at stage I in the sporulation process. Protein is degraded at a rate of 8–10%/hr. 2. As a result of this turnover, the proteins of the mother cell are extensively degraded and resynthesized by about 6hr., so that the later stages of spore formation occur in a cytoplasm containing mainly `new' protein. 3. The same protease appears to be responsible both for the intracellular turnover of protein and for extracellular proteolytic activity. In mutants that have lost the exoenzyme the intracellular protein is stable for many hours. In addition, these mutants fail to produce antibiotic and are asporogenous. When the exoprotease is regained as a result of back-mutation all the lost capacities of the cell are restored together. 4. Protease activity also accounts for the change in antigenic pattern of extracts of cells sampled during sporulation. Immunoelectrophoresis shows that, in the wild-type, the antigens characteristic of the vegetative cell have largely disappeared after a few hours; in the proteaseless mutants the vegetative-cell pattern is conserved. Apart from changing the protein pattern of the cell the protease could also have the function of removing protein inhibitors of sporulation. Other possible interpretations of the results are discussed.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BALASSA G., IONESCO H., SCHAEFFER P. PREUVE G'EN'ETIQUE D'UNE RELATION ENTRE LA PRODUCTION D'UN ANTIBIOTIQUE PAR BACILLUS SUBTILIS ET SA SPORULATION. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1963 Jul 22;257:986–988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baillie A., Norris J. R. Antigen changes during spore formation in Bacillus cereus. J Bacteriol. 1964 May;87(5):1221–1226. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.5.1221-1226.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borek E., Ponticorvo L., Rittenberg D. PROTEIN TURNOVER IN MICRO-ORGANISMS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1958 May;44(5):369–374. doi: 10.1073/pnas.44.5.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CANFIELD R. E., SZULMAJSTER J. TIME OF SYNTHESIS OF DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID AND PROTEIN IN SPORES OF B. SUBTILIS. Nature. 1964 Aug 8;203:596–598. doi: 10.1038/203596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONNELLAN J. E., Jr, NAGS E. H., LEVINSON H. S. CHEMICALLY DEFINED, SYNTHETIC MEDIA FOR SPORULATION AND FOR GERMINATION AND GROWTH OF BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Feb;87:332–336. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.2.332-336.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOSTER J. W., PERRY J. J. Intracellular events occurring during endotrophic sporulation in Bacillus mycoides. J Bacteriol. 1954 Mar;67(3):295–302. doi: 10.1128/jb.67.3.295-302.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falaschi A., Kornberg A. Biochemical studies of bacterial sporulation. II. Deoxy- ribonucleic acid polymerase in spores of Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1966 Apr 10;241(7):1478–1482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner R., Kornberg A. Biochemical studies of bacterial sporulation and germination. V. Purine nucleoside phosphorylase of vegetative cells and spores of Bacillus cereus. J Biol Chem. 1967 May 25;242(10):2383–2388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay D., Warren S. C. Sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Morphological changes. Biochem J. 1968 Oct;109(5):819–824. doi: 10.1042/bj1090819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDELSTAM J. The intracellular turnover of protein and nucleic acids and its role in biochemical differentiation. Bacteriol Rev. 1960 Sep;24(3):289–308. doi: 10.1128/br.24.3.289-308.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDELSTAM J. Turnover of protein in growing and non-growing populations of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1958 May;69(1):110–119. doi: 10.1042/bj0690110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCONN J. D., TSURU D., YASUNOBU K. T. BACILLUS SUBTILIS NEUTRAL PROTEINASE. I. A ZINC ENZYME OF HIGH SPECIFIC ACTIVITY. J Biol Chem. 1964 Nov;239:3706–3715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONRO R. E. Protein turnover and the formation of protein inclusions during sporulation of Bacillus thuringiensis. Biochem J. 1961 Nov;81:225–232. doi: 10.1042/bj0810225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORRIS J. R., BAILLIE A. IMMUNOLOGICAL SPECIFICITIES OF SPORE AND VEGETATIVE CELL CATALASES OF BACILLUS CEREUS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jul;88:264–265. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.1.264-265.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryter A., Schaeffer P., Ionesco H. Classification cytologique, par leur stade de blocage, des mutants de sporulation de Bacillus subtilis Marburg. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1966 Mar;110(3):305–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryter A., Szulmajster J. Action du chloramphénicol sur la sporogenèse de B. subtilis. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1965 May;108(5):640–651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tono H., Kornberg A. Biochemical studies of bacterial sporulation. 3. Inorganic pyrophosphatase of vegetative cells and spores of Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1967 May 25;242(10):2375–2382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- URBA R. C. Protein breakdown in Bacillus cereus. Biochem J. 1959 Mar;71(3):513–518. doi: 10.1042/bj0710513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waites W. M. Sporulation in bacillus subtilis. Antigenic changes during spore formation. Biochem J. 1968 Oct;109(5):803–810. doi: 10.1042/bj1090803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren S. C. Sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Biochemical changes. Biochem J. 1968 Oct;109(5):811–818. doi: 10.1042/bj1090811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willetts N. S. Intracellular protein breakdown in non-growing cells of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1967 May;103(2):453–461. doi: 10.1042/bj1030453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUNG I. E., FITZ-JAMES P. C. Chemical and morphological studies of bacterial spore formation. II. Spore and parasporal protein formation in Bacillus cereus var. alesti. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1959 Dec;6:483–498. doi: 10.1083/jcb.6.3.483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


