Abstract
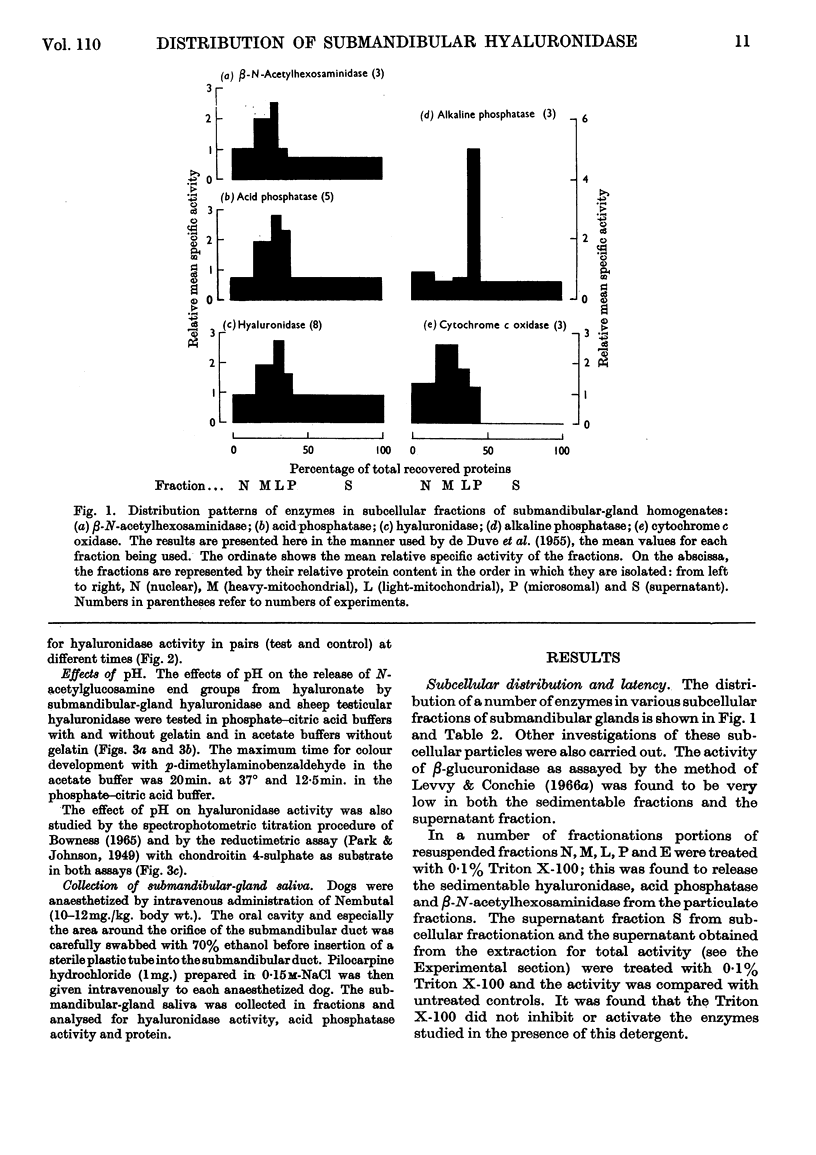
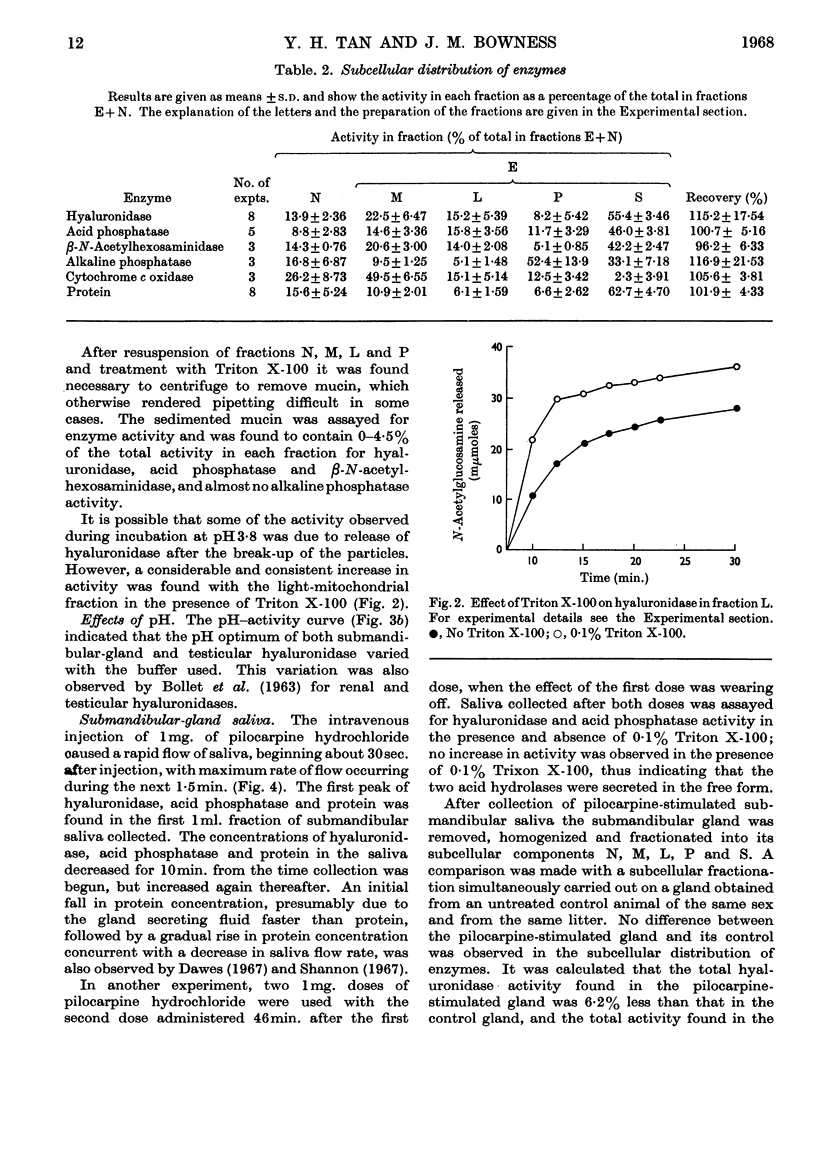
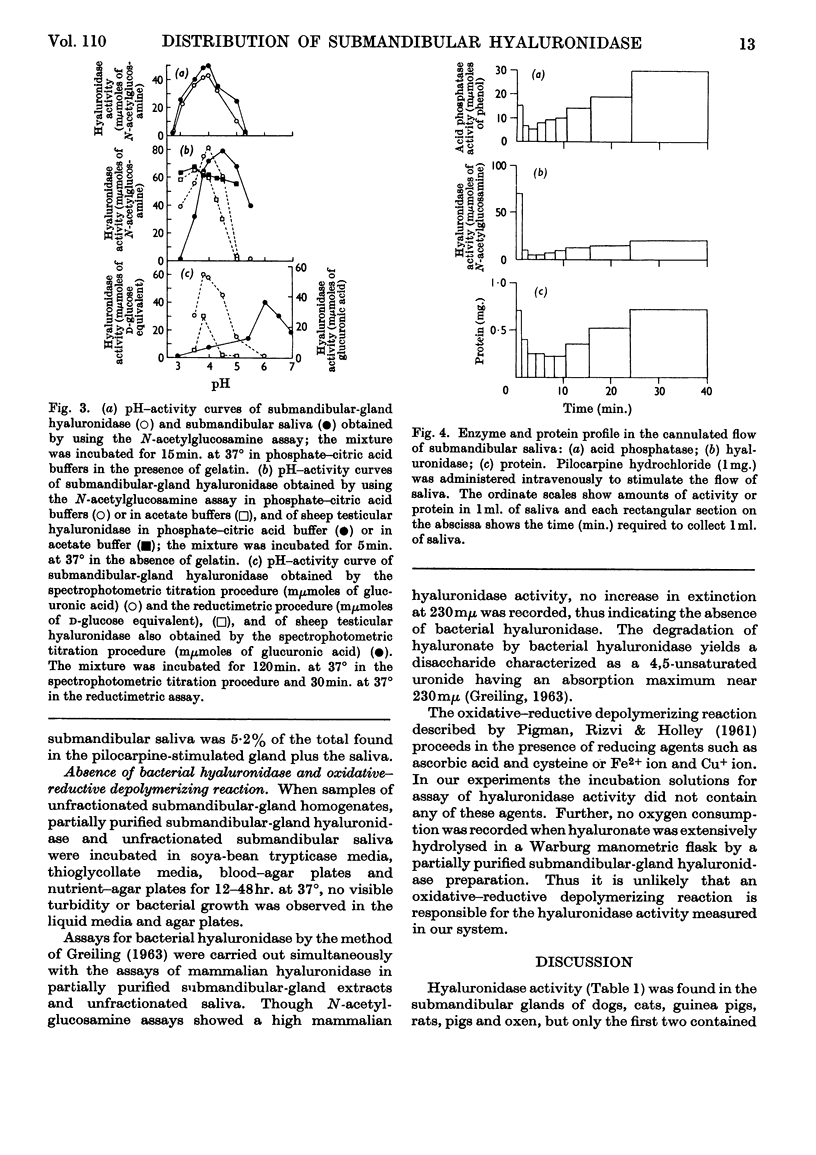
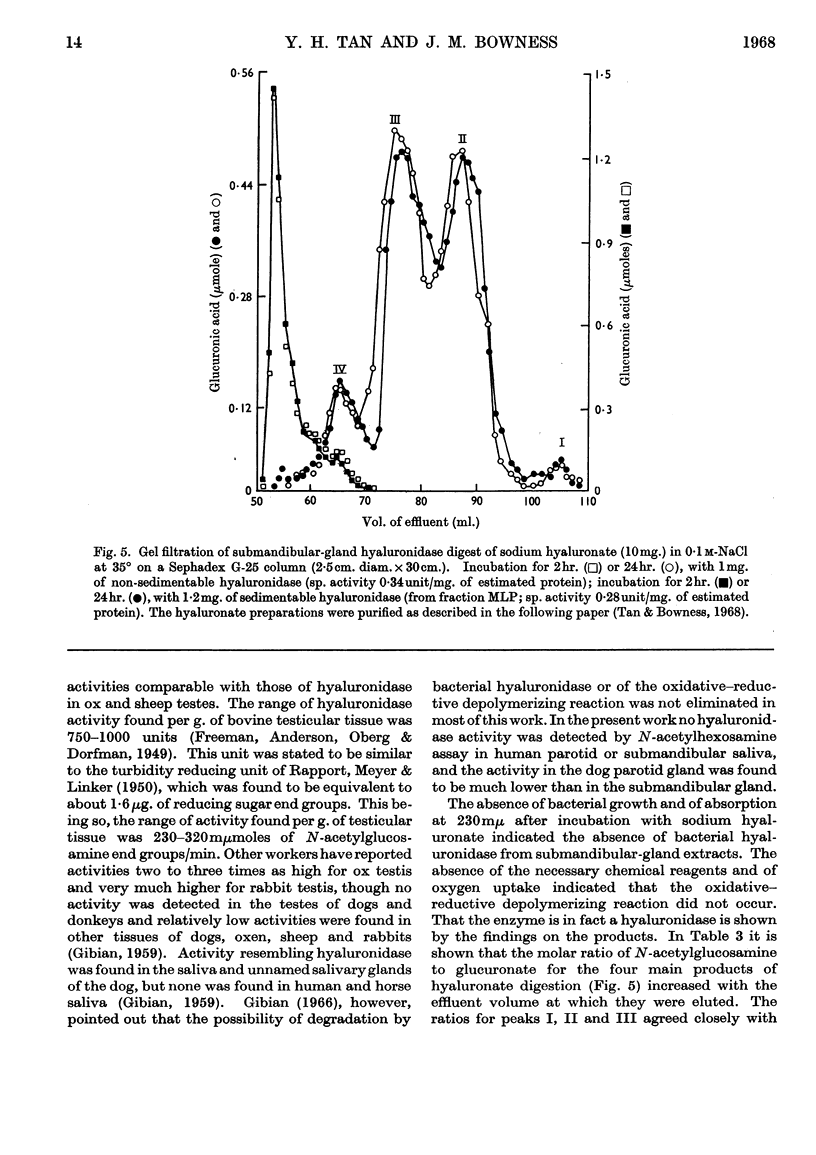
1. Submandibular glands from four species of mammal have been shown to contain a hyaluronidase active at acid pH; glands from dog and cat had a much higher content of this enzyme than has been found in other sources. 2. Product formation from hyaluronate after 24hr. incubation was almost the same as with testicular hyaluronidase, indicating that the enzyme is an endo-poly-β-hexosaminidase. 3. When submandibular-gland homogenates were fractionated by the scheme developed for liver by de Duve, Pressman, Gianetto, Wattiaux & Appelmans (1955), all the enzymes assayed, except cytochrome c oxidase, were found to occur partly in the soluble fraction and partly in the particulate fractions. Among the particular fractions, the highest specific activity was found in the heavy-mitochondrial fraction for cytochrome c oxidase, in the microsomal fraction for alkaline phosphatase and in the light-mitochondrial fraction for acid phosphatase, β-N-acetylhexosaminidase and acid-active hyaluronidase. 4. Release of the enzyme activity from the sedimentable fractions occurred in 0·1% Triton X-100 or after high-speed homogenization. 5. Stimulation of dogs by pilocarpine was found to decrease the hyaluronidase content of the submandibular gland by 5% and to cause the occurrence of a corresponding amount of acid-active hyaluronidase in the submandibular saliva. 6. The results are discussed in relation to the subcellular localization of hyaluronidase.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- APPELMANS F., DE DUVE C. Tissue fractionation studies. 3. Further observations on the binding of acid phosphatase by rat-liver particles. Biochem J. 1955 Mar;59(3):426–433. doi: 10.1042/bj0590426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ARONSON N. N., Jr, DAVIDSON E. A. LYSOSOMAL HYALURONIDASE. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jul;240:PC3222–PC3224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronson N. N., Jr, Davidson E. A. Lysosomal hyaluronidase from rat liver. I. Preparation. J Biol Chem. 1967 Feb 10;242(3):437–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOLLET A. J., BONNER W. M., Jr, NANCE J. L. THE PRESENCE OF HYALURONIDASE IN VARIOUS MAMMALIAN TISSUES. J Biol Chem. 1963 Nov;238:3522–3527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOWNESS J. M. Application of the carbazole reaction to the estimation of glucuronic acid and flucose in some acidic polysaccharides and in urine. Biochem J. 1957 Oct;67(2):295–300. doi: 10.1042/bj0670295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOWNESS J. M. HYALURONIDASE ASSAY USING A CHONDROITINSULPHATE SUBSTRATE. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Mar 1;101:26–36. doi: 10.1016/0926-6534(65)90027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Jr, Cantey E. Y. Colorimetric method for determination of serum hyaluronidase activity. Clin Chim Acta. 1966 Jun;13(6):746–752. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(66)90142-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowers W. E., Finkenstaedt J. T., de Duve C. Lysosomes in lymphoid tissue. I. The measurement of hydrolytic activities in whole homogenates. J Cell Biol. 1967 Feb;32(2):325–337. doi: 10.1083/jcb.32.2.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowness J. M., Harding G. Increase in serum hyaluronidase levels in rats given hydrocortisone or prednisolone. Can J Biochem. 1968 May;46(5):489–495. doi: 10.1139/o68-074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COBBIN L. B., DICKER S. E. Some characteristics of plasma and urine 'hyaluronidase'. J Physiol. 1962 Aug;163:168–174. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOPERSTEIN S. J., LAZAROW A. A microspectrophotometric method for the determination of cytochrome oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1951 Apr;189(2):665–670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE DUVE C., PRESSMAN B. C., GIANETTO R., WATTIAUX R., APPELMANS F. Tissue fractionation studies. 6. Intracellular distribution patterns of enzymes in rat-liver tissue. Biochem J. 1955 Aug;60(4):604–617. doi: 10.1042/bj0600604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawes C. The effect of flow rate and length of stimulation on the protein concentration in human parotid saliva. Arch Oral Biol. 1967 Jul;12(7):783–788. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(67)90101-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Duve C., Wattiaux R. Functions of lysosomes. Annu Rev Physiol. 1966;28:435–492. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.28.030166.002251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Salegui M., Pigman W. The existence of an acid-active hyaluronidase in serum. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1967 Apr;120(1):60–67. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(67)90598-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLODIN P., GREGORY J. D., RODEN L. SEPARATION OF ACIDIC OLIGOSACCHARIDES BY GEL FILTRATION. Anal Biochem. 1964 Aug;8:424–433. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(64)90240-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIANETTO R., DE DUVE C. Tissue fractionation studies. 4. Comparative study of the binding of acid phosphatase, beta-glucuronidase and cathepsin by rat-liver particles. Biochem J. 1955 Mar;59(3):433–438. doi: 10.1042/bj0590433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goggins J. F., Fullmer H. M., Steffek A. J. Hyaluronidase activity of human gingiva. Arch Pathol. 1968 Mar;85(3):272–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herveg J. P., Beckers C., De Visscher M. Lysosomal hydrolases in calf thyroid. Biochem J. 1966 Aug;100(2):540–547. doi: 10.1042/bj1000540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutterer F. Degradation of mucopolysaccharides by hepatic lysosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 28;115(2):312–319. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90430-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JEANLOZ R. W., FORCHIELLI E. Studies on hyaluronic acid and related substances. I. Preparation of hyaluronic acid and derivatives from human umbilical cord. J Biol Chem. 1950 Oct;186(2):495–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIND P. R., KING E. J. Estimation of plasma phosphatase by determination of hydrolysed phenol with amino-antipyrine. J Clin Pathol. 1954 Nov;7(4):322–326. doi: 10.1136/jcp.7.4.322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARK J. T., JOHNSON M. J. A submicrodetermination of glucose. J Biol Chem. 1949 Nov;181(1):149–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PIGMAN W., RIZVI S., HOLLEY H. L. Depolymerization of hyaluronic acid by the ORD reaction. Arthritis Rheum. 1961 Jun;4:240–252. doi: 10.1002/art.1780040303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPPORT M. M., MEYER K., LINKER A. Correlation of reductimetric and turbidimetric methods for hyaluronidase assay. J Biol Chem. 1950 Oct;186(2):615–623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan Y. H., Bowness J. M. Canine submandibular-gland hyaluronidase. Purification and properties. Biochem J. 1968 Nov;110(1):19–25. doi: 10.1042/bj1100019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaes G. Hyaluronidase activity in lysosomes of bone tissue. Biochem J. 1967 Jun;103(3):802–804. doi: 10.1042/bj1030802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaes G., Jacques P. Studies on bone enzymes. Distribution of acid hydrolases, alkaline phenylphosphatase, cytochrome oxidase and catalase in subcellular fraction of bone tissue homogenates. Biochem J. 1965 Nov;97(2):389–392. doi: 10.1042/bj0970389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaes G., Jacques P. Studies on bone enzymes. The assay of acid hydrolases and other enzymes in bone tissue. Biochem J. 1965 Nov;97(2):380–388. doi: 10.1042/bj0970380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaes G. Studies on bone enzymes. The activation and release of latent acid hydrolases and catalase in bone-tissue homogenates. Biochem J. 1965 Nov;97(2):393–402. doi: 10.1042/bj0970393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


