Abstract
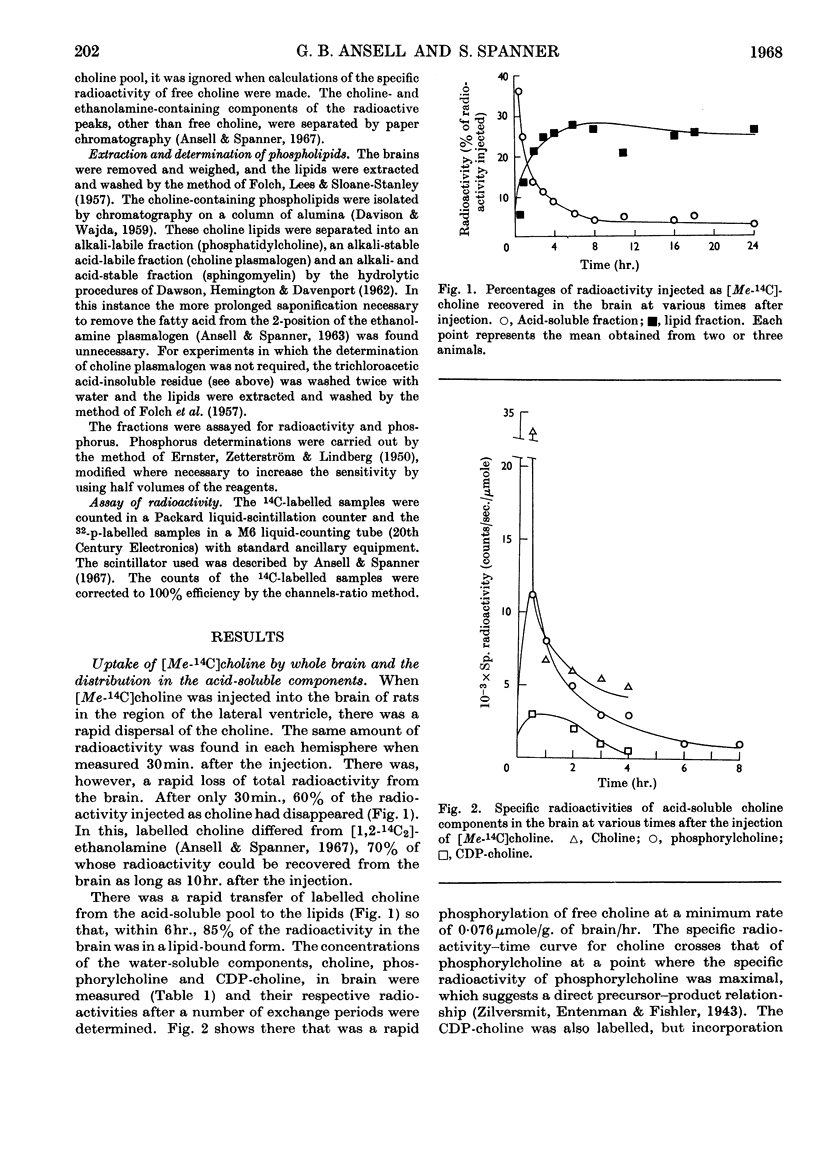
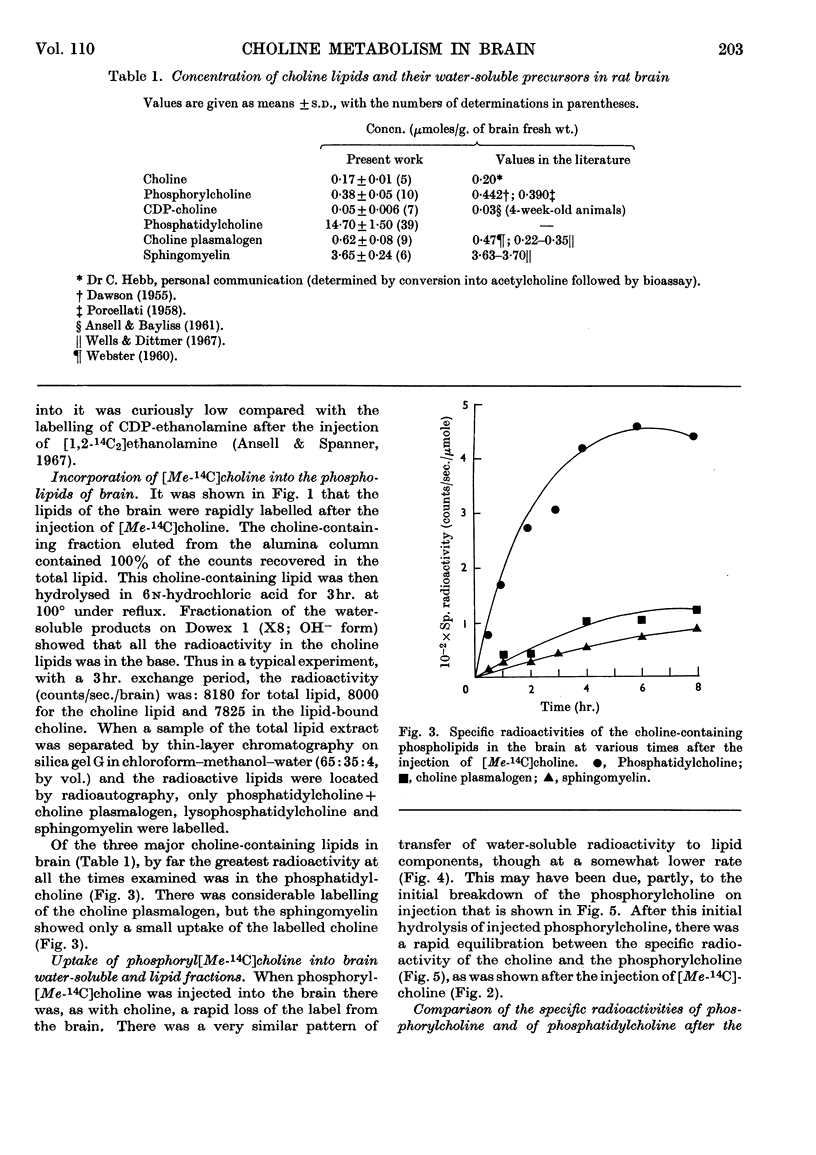
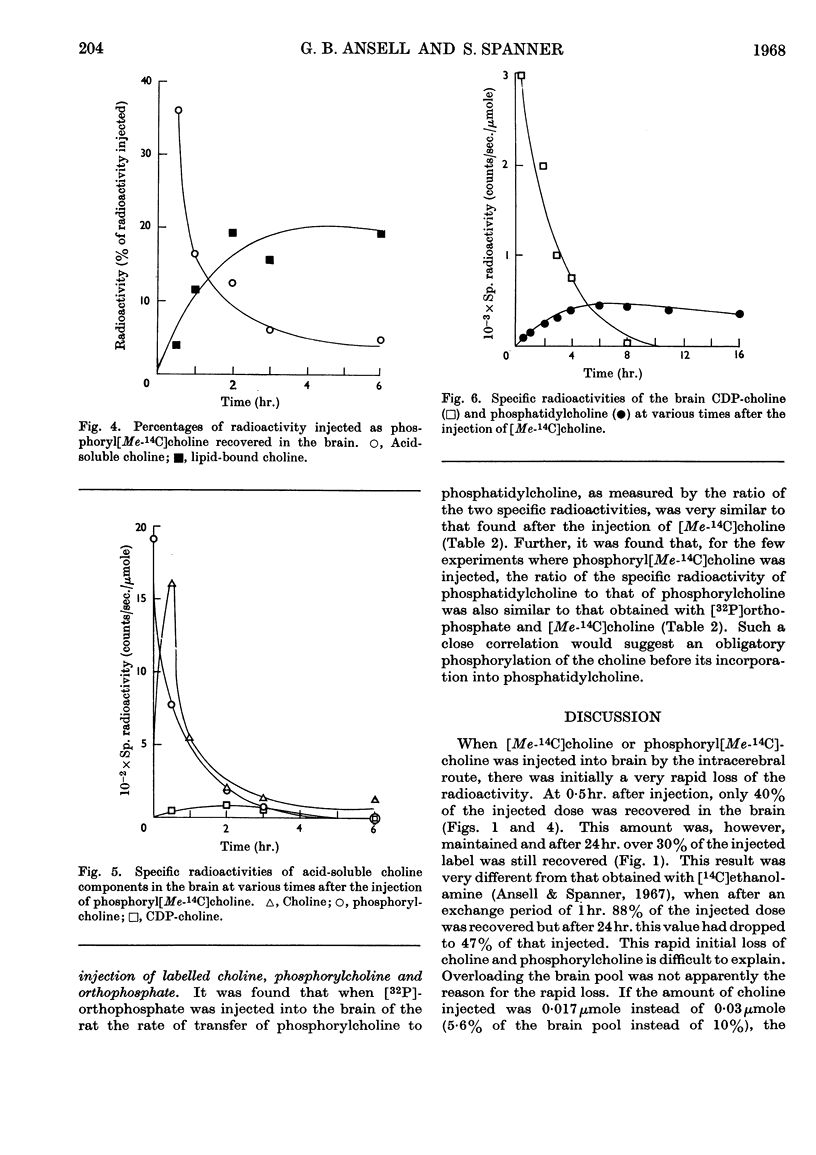
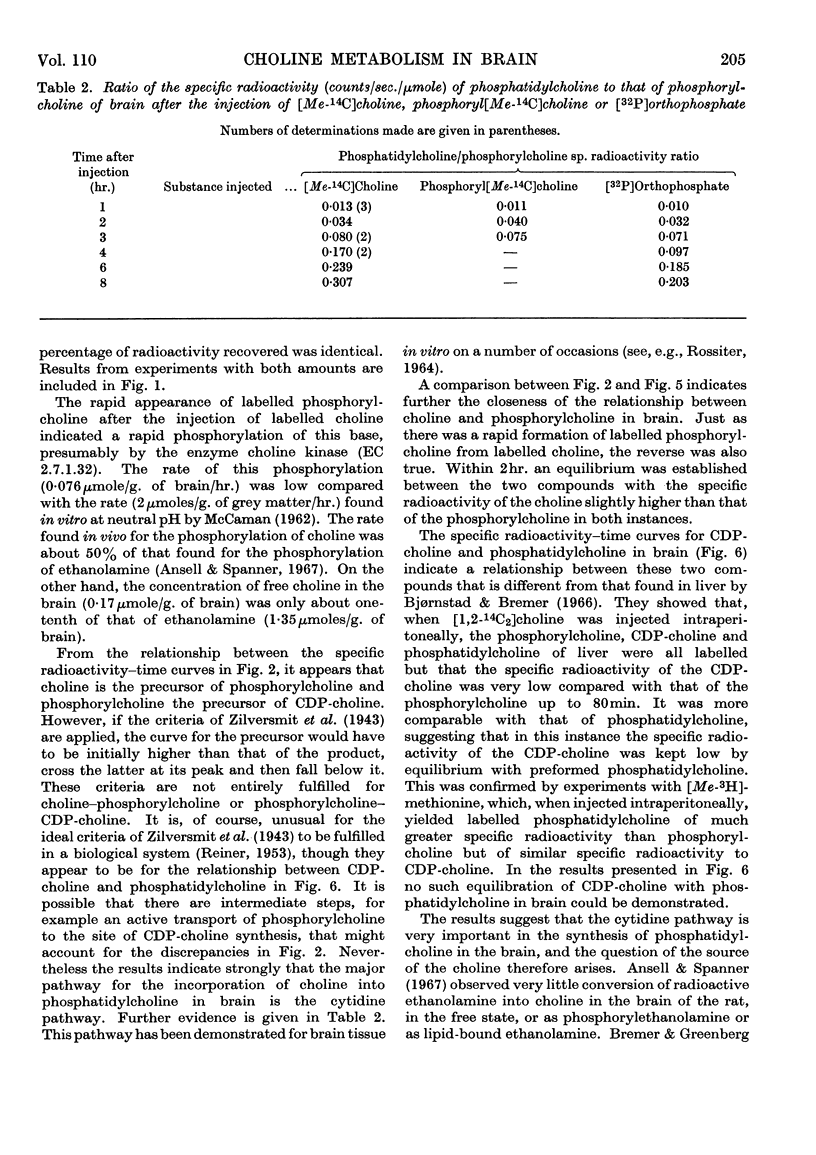
[Me-14C]Choline was injected intracerebrally into the adult rat, and its uptake into the lipids and their water-soluble precursors in brain was studied. The radioactivity could be detected only in the choline-containing lipids and was confined to the base choline. The results indicated that initial phosphorylation of the free choline followed by the formation of CDP-choline and the subsequent transfer of the phosphorylcholine to a diglyceride is one of the principal routes by which choline lipids in brain are formed. Further evidence for this was obtained in experiments in which either phosphoryl[Me-14C]choline or [32P]orthophosphate was injected and the radioactivity in the choline-containing water-soluble and lipidbound components studied.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANSELL G. B., BAYLISS B. J. The cytidine diphosphate choline content of rat brain. Biochem J. 1961 Jan;78:209–213. doi: 10.1042/bj0780209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANSELL G. B., SPANNER S. THE ALKALINE HYDROLYSIS OF THE ETHANOLAMINE PLASMALOGEN OF BRAIN TISSUE. J Neurochem. 1963 Dec;10:941–945. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1963.tb11921.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Latif A. A., Abood L. G. In vivo incorporation of l-[14C]serine into phospholipids and proteins of the subcellular fractions of developing rat brain. J Neurochem. 1966 Nov;13(11):1189–1196. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1966.tb04276.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ansell G. B., Chojnacki T. The incorporation of the phosphate esters of N-substituted aminoethanols into the phospholipids of brain and liver. Biochem J. 1966 Jan;98(1):303–310. doi: 10.1042/bj0980303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ansell G. B., Spanner S. The metabolism of labelled ethanolamine in the brain of the rat in vivo. J Neurochem. 1967 Sep;14(9):873–885. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1967.tb09576.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bickerstaffe R., Mead J. F. Metabolism of palmitaldehyde-1-14C in the rat brain. Biochemistry. 1967 Mar;6(3):655–662. doi: 10.1021/bi00855a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjørnstad P., Bremer J. In vivo studies on pathways for the biosynthesis of lecithin in the rat. J Lipid Res. 1966 Jan;7(1):38–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVISON A. N., WAJDA M. Metabolism of myelin lipids: estimation and separation of brain lipids in the developing rabbit. J Neurochem. 1959 Oct;4:353–359. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1959.tb13217.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON R. M., HEMINGTON N., DAVENPORT J. B. Improvements in the method of determining individual phospholipids in a complex mixture by successive chemical hydrolyses. Biochem J. 1962 Sep;84:497–501. doi: 10.1042/bj0840497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON R. M. Phosphorylcholine in rat tissues. Biochem J. 1955 Jun;60(2):325–328. doi: 10.1042/bj0600325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. N., Gregson N. A. Metabolism of cellular membrane sulpholipids in the rat brain. Biochem J. 1966 Mar;98(3):915–922. doi: 10.1042/bj0980915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROTH D. P., BAIN J. A., PFEIFFER C. C. The comparative distribution of C14-labeled 2-dimethylaminoethanol and choline in the mouse. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1958 Dec;124(4):290–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOPACZYK K. C., RADIN N. S. IN VIVO CONVERSIONS OF CEREBROSIDE AND CERAMIDE IN RAT BRAIN. J Lipid Res. 1965 Jan;6:140–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long C., Odavić R., Sargent E. J. The action of cabbage-leaf phospholipase D upon lysolecithin. Biochem J. 1967 Jan;102(1):216–220. doi: 10.1042/bj1020216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson B. H., Peacocke A. R. The inhibition of ribonucleic acid polymerase by acridines. Biochem J. 1966 Jul;100(1):50–58. doi: 10.1042/bj1000050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORCELLATI G. The levels of some free nitrogen-containing phosphate esters in nervous tissue. J Neurochem. 1958;2(2-3):128–137. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1958.tb12358.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REINER J. M. The study of metabolic turnover rates by means of isotopic tracers. I. Fundamental relations. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1953 Sep;46(1):53–79. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(53)90170-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHTER D., CROSSLAND J. Variation in acetylcholine content of the brain with physiological state. Am J Physiol. 1949 Nov;159(2):247–255. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1949.159.2.247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitzer H. L., Morrison K., Norman J. R. The incorporation of L-[Me-14C]methionine and [Me-3H]choline into lung phosphatides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 May 1;152(3):552–558. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(68)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBSTER G. R. Studies on the plasmalogens of nervous tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Oct 21;44:109–116. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91529-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells M. A., Dittmer J. C. A comprehensive study of the postnatal changes in the concentration of the lipids of developing rat brain. Biochemistry. 1967 Oct;6(10):3169–3175. doi: 10.1021/bi00862a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


