Abstract
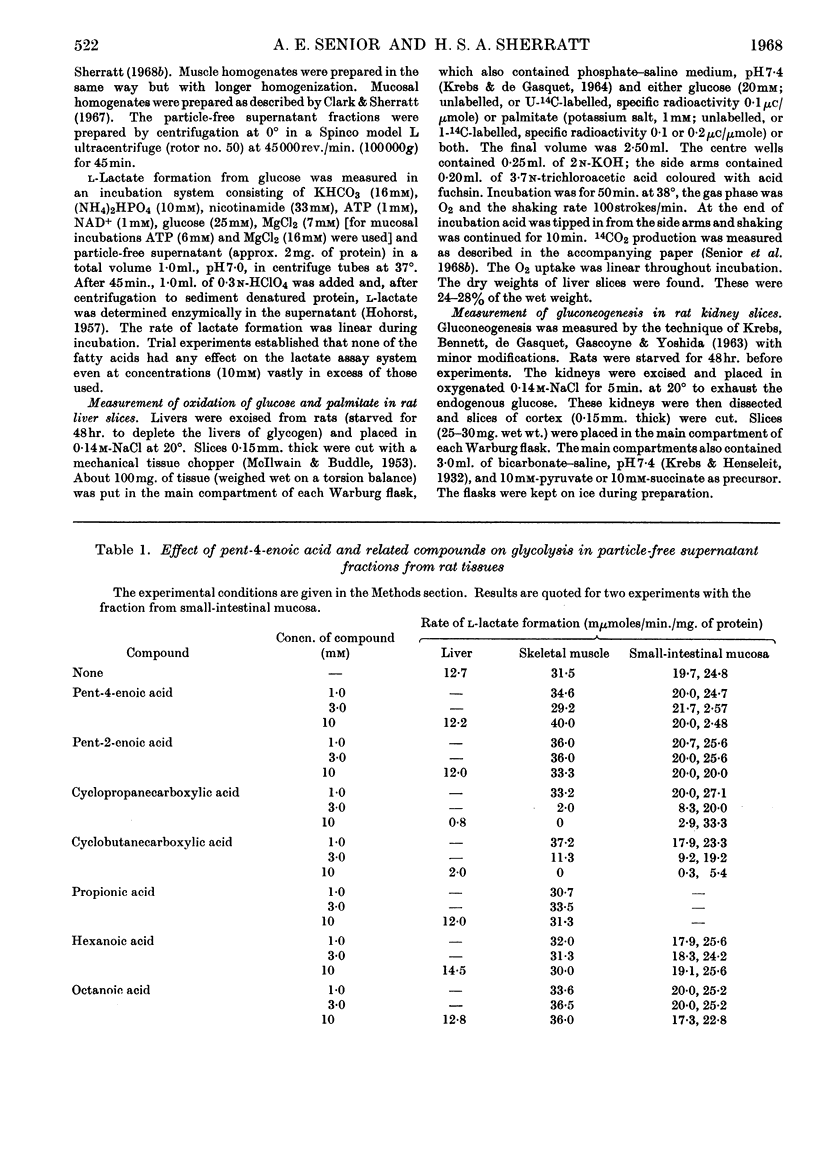
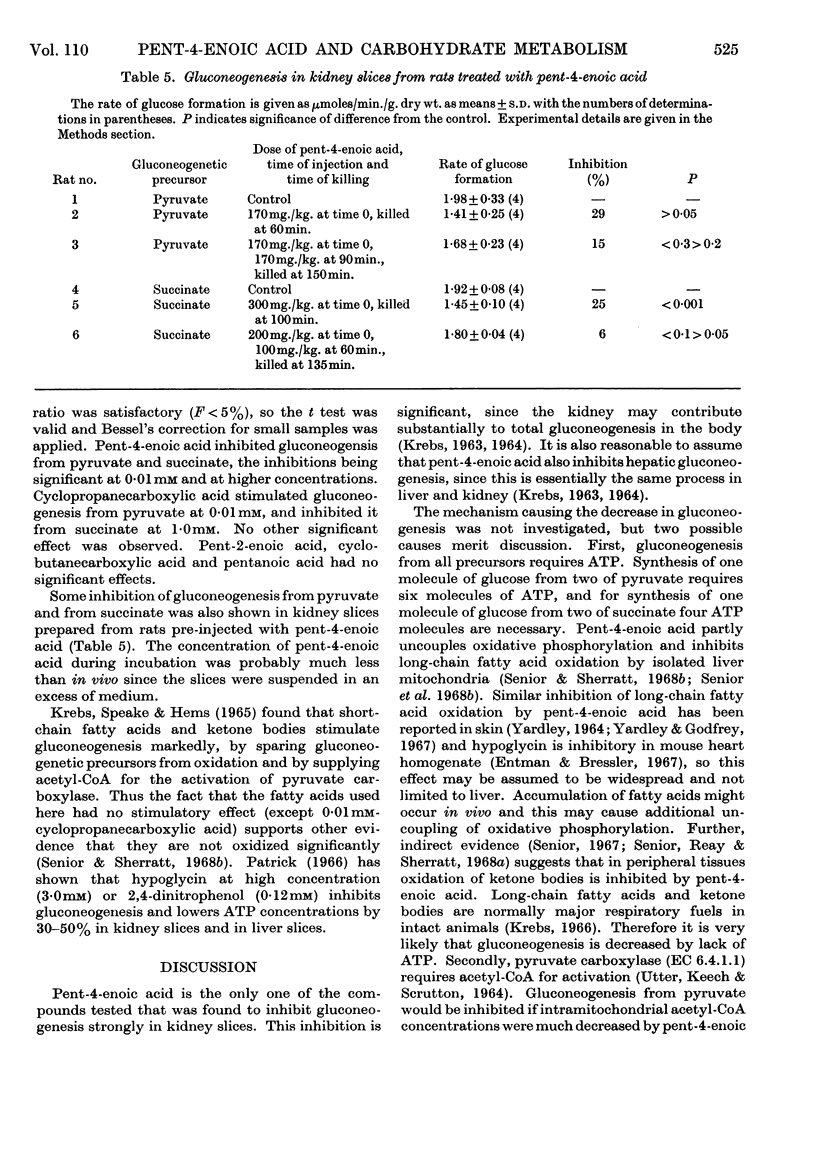
1. The effects of the hypoglycaemic compound, pent-4-enoic acid, and of four structurally related non-hypoglycaemic compounds (pent-2-enoic acid, pentanoic acid, cyclopropanecarboxylic acid and cyclobutanecarboxylic acid), on glycolysis, glucose oxidation and gluconeogenesis in some rat tissues were determined. 2. None of the compounds at low concentrations inhibited glycolysis by particle-free supernatant fractions from rat liver, skeletal muscle and intestinal mucosa, though there was inhibition by cyclopropanecarboxylic acid and cyclobutanecarboxylic acid at 3mm concentration. 3. Pent-4-enoic inhibited the oxidation of [1-14C]palmitate by rat liver slices, but did not increase the oxidation of [U-14C]glucose. 4. Pent-4-enoic acid (0·01mm) strongly inhibited gluconeogenesis by rat kidney slices from pyruvate or succinate, but none of the other compounds inhibited significantly at low concentrations. 5. There was also some inhibition of gluconeogenesis in kidney slices from rats injected with pent-4-enoic acid. 6. The mechanism of the hypoglycaemic effect of pent-4-enoic acid is discussed; it is suggested that there is an inhibition of fatty acid and ketone-body oxidation and of gluconeogenesis so that glucose reserves become exhausted, leading to hypoglycaemia. 7. The mechanism of the hypoglycaemic action of pent-4-enoic acid appears to be similar to that of hypoglycin.
Full text
PDF

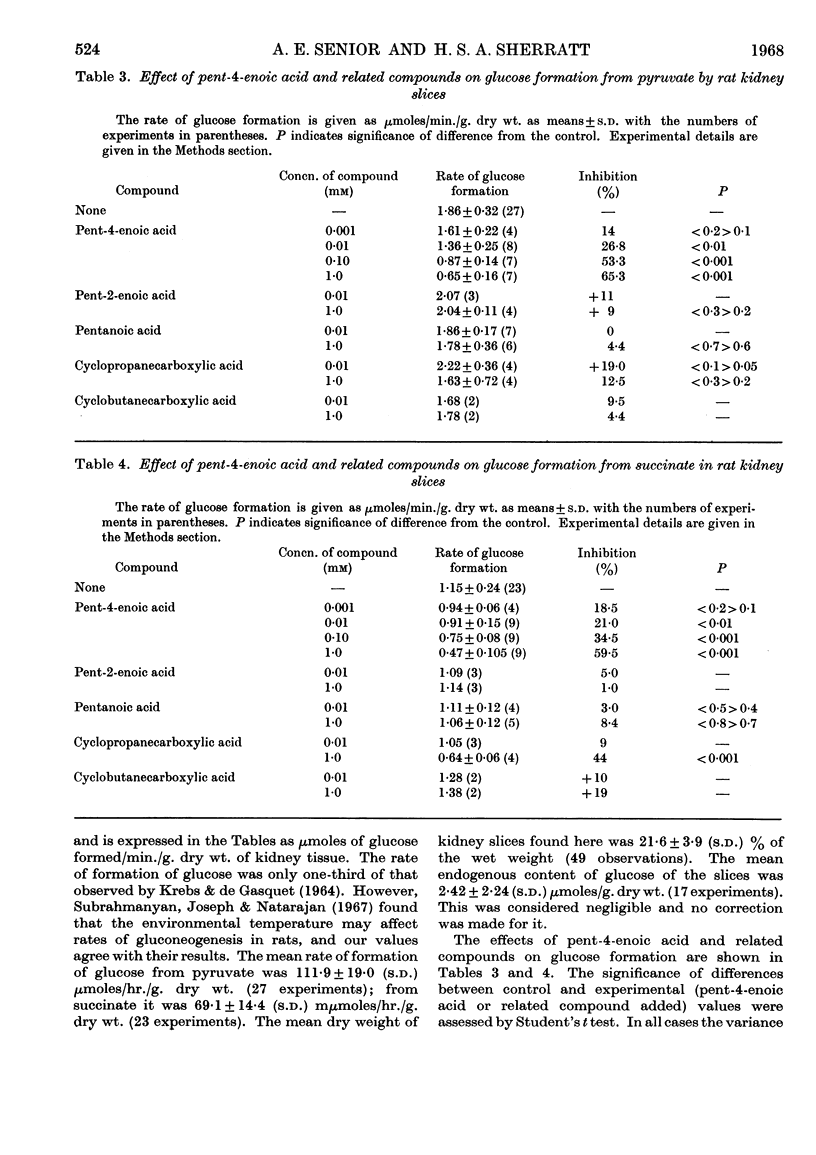


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Black J. A., Simpson K. Fructose tolerance. Br Med J. 1967 Oct 28;4(5572):138–141. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5572.138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANCE B., HOLLUNGER G. Inhibition of electron and energy transfer in mitochondria. II. The site and the mechanism of guanidine action. J Biol Chem. 1963 Jan;238:432–438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAPPELL J. B. The effect of alkylguanidines on mitochondrial metabolism. J Biol Chem. 1963 Jan;238:410–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corredor C., Brendel K., Bressler R. Studies of the mechanism of the hypoglycemic action of 4-pentenoic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Dec;58(6):2299–2306. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.6.2299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE MEUTTER R. C., SHREEVE W. W. Conversion of DL-lactate-2-C14 or -3-C14 or pyruvate-2-C14 to blood glucose in humans: effects of diabetes, insulin, tolbutamide, and glucose load. J Clin Invest. 1963 Apr;42:525–533. doi: 10.1172/JCI104741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUNCAN L. J., CLARKE B. F. PHARMACOLOGY AND MODE OF ACTION OF THE HYPOGLYCAEMIC SULPHONYLUREAS AND DIGUANIDES. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1965;5:151–162. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.05.040165.001055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Beer L., De Schepper P. J. Metabolic effects of hypoglycemic sulfonylureas. II. In vitro effect of sulfonylureas on cell-free protein synthesis and energy metabolism in rat tissues. Biochem Pharmacol. 1967 Dec;16(12):2355–2367. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(67)90221-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Schepper P. J. Metabolic effects of hypoglycemic sulfonylureas. I. In vitro effect of sulfonylureas on leucine incorporation and metabolism and on respiration of rat tissues. Biochem Pharmacol. 1967 Dec;16(12):2337–2353. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(67)90220-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Entman M., Bressler R. The mechanism of action of hypoglycin on long-chain fatty acid oxidation. Mol Pharmacol. 1967 Jul;3(4):333–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FENG P. C., PATRICK S. J. Studies of the action of hypoglycin-A, an hypoglycaemic substance. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1958 Jun;13(2):125–130. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1958.tb00206.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOTO Y., LUKENS F. D. Effects of tolbutamide, mesoxalate and phenformin in vitro on the liberation of nitrogen by rat liver slices. Diabetes. 1961 Jan-Feb;10:52–57. doi: 10.2337/diab.10.1.52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillory R. J., Slater E. C. The action of substituted guanidines on mitochondrial respiration and on the ADP-ATP exchange reaction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Aug 24;105(2):221–232. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(65)80147-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAAS D. PHOSPHORYLATION COUPLED TO THE OXIDATION OF NADH BY FUMARATE IN DIGITONIN FRAGMENTS OF BEEF-HEART MITOCHONDRIA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Dec 23;92:433–439. doi: 10.1016/0926-6569(64)90002-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASSALL C. H., REYLE K. Hypoglycin A,B: biologically active polypeptides from Blighia sapida. Nature. 1954 Feb 20;173(4399):356–357. doi: 10.1038/173356b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOHORST H. J. Enzymatische Bestimmung von L(+)-Milchsäure. Biochem Z. 1957;328(7):509–521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KREBS H. A., BENNETT D. A., DE GASQUET P., GASQUET P., GASCOYNE T., YOSHIDA T. Renal gluconeogenesis. The effect of diet on the gluconeogenic capacity of rat-kidney-cortex slices. Biochem J. 1963 Jan;86:22–27. doi: 10.1042/bj0860022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KREBS H. A. RENAL GLUCONEOGENESIS. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1963;1:385–400. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(63)90034-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KREBS H. A., SPEAKE R. N., HEMS R. ACCELERATION OF RENAL GLUCONEOGENESIS BY KETONE BODIES AND FATTY ACIDS. Biochem J. 1965 Mar;94:712–720. doi: 10.1042/bj0940712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KREBS H. THE CROONIAN LECTURE, 1963. GLUCONEOGENESIS. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1964 Mar 17;159:545–564. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1964.0019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs H. A., De Gasquet P. Inhibition of gluconeogenesis by alpha-oxo acids. Biochem J. 1964 Jan;90(1):149–154. doi: 10.1042/bj0900149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lochner A., Wulff J., Madison L. L. Ethanol-induced hypoglycemia. I. The acute effects of glucose output and peripheral glucose utilization in fasted dogs. Metabolism. 1967 Jan;16(1):1–18. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(67)90154-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCILWAIN H., BUDDLE H. L. Techniques in tissue metabolism. I. A mechanical chopper. Biochem J. 1953 Feb;53(3):412–420. doi: 10.1042/bj0530412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer F., Ipaktchi M., Clauser H. Specific inhibition of gluconeogenesis by biguanides. Nature. 1967 Jan 14;213(5072):203–204. doi: 10.1038/213203a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATRICK S. J. Effects of hypoglycin A on the metabolism of glucose by isolated tissues. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1962 Sep;40:1195–1201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrick S. J. Effects of phenfromin and hypoglycin on gluconeogenesis of rat tissues. Can J Biochem. 1966 Jan;44(1):27–33. doi: 10.1139/o66-004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posner B. I., Raben M. S. Inhibition of the oxidation of leucine by hypoglycin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Feb 7;136(1):179–181. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(67)90341-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANTI R. Potassium atractylate, a new inhibitor of the tricarboxylic acid cycle. Nature. 1958 Jul 26;182(4630):257–257. doi: 10.1038/182257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAEFER G. SITE-SPECIFIC UNCOUPLING AND INHIBITION OF ENERGY TRANSFER BY BIGUANIDES. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Nov 8;93:279–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior A. E., Robson B., Sherratt H. S. Biochemical effects of the hypoglycaemic compound pent--4-enoic acid and related non-hypoglycaemic fatty acids. Biochem J. 1968 Dec;110(3):511–519. doi: 10.1042/bj1100511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior A. E., Sherratt H. S. Biochemical effects of the hypoglycaemic compound pent-4-enoic acid and related non-hypoglycaemic fatty acids. Oxidative phosphorylation and mitochondrial oxidation of pyruvate, 3-hydroxybutyrate and tricarboxylic acid-cycle intermediates. Biochem J. 1968 Dec;110(3):499–509. doi: 10.1042/bj1100499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherratt H. S. The metabolism of the small intestine. Oxygen uptake and L-lactate production along the length of the small intestine of the rat and guinea pig. Comp Biochem Physiol. 1968 Mar;24(3):745–761. doi: 10.1016/0010-406x(68)90787-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subrahmanyam K., Joseph P. K., Natarajan P. Effect of environmental temperature and adrenalectomy on renal gluconeogenesis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1967 Jul;121(1):246–248. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(67)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Holt C., Von Holt M., Böhm H. Metabolic effects of hypoglycin and methylenecyclopropaneacetic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Aug 3;125(1):11–21. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(66)90139-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber G., Convery H. J., Lea M. A., Stamm N. B. Feedback inhibition of key glycolytic enzymes in liver: action of free fatty acids. Science. 1966 Dec 9;154(3754):1357–1360. doi: 10.1126/science.154.3754.1357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson J. R., Kreisberg R. A., Felts P. W. Mechanism for the stimulation of gluconeogenesis by fatty acids in perfused rat liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jul;56(1):247–254. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.1.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yardley H. J., Godfrey G. Some in vitro effects of hypoglycin on skin. Arch Dermatol. 1967 Jul;96(1):89–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalitis J., Oliver I. T. Inhibition of glucose phosphate isomerase by metabolic intermediates of fructose. Biochem J. 1967 Mar;102(3):753–759. doi: 10.1042/bj1020753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


