Abstract
1. α-Mannosidase from jack-bean meal was purified 150-fold. β-N-Acetyl-glucosaminidase and β-galactosidase were removed from the preparation by treatment with pyridine. Zn2+ was added during the purification to stabilize the α-mannosidase. 2. At pH values below neutrality, α-mannosidase undergoes reversible spontaneous inactivation at a rate dependent on the temperature, the degree of dilution and the extent of purification. The enzyme is also subject to irreversible inactivation, which is prevented by the addition of albumin. 3. Reversible inactivation of α-mannosidase is accelerated by EDTA and reversed or prevented by Zn2+. Other cations, such as Co2+, Cd2+ and Cu2+, accelerate inactivation; an excess of Zn2+ again exerts a protective action, and so does EDTA in suitable concentration. 4. Neither Zn2+ nor EDTA has any marked effect in the assay of untreated enzyme. In an EDTA-treated preparation, however, Zn2+ reactivates the enzyme during assay. 5. It is postulated that α-mannosidase is a dissociable Zn2+–protein complex in which Zn2+ is essential for enzyme activity.
Full text
PDF

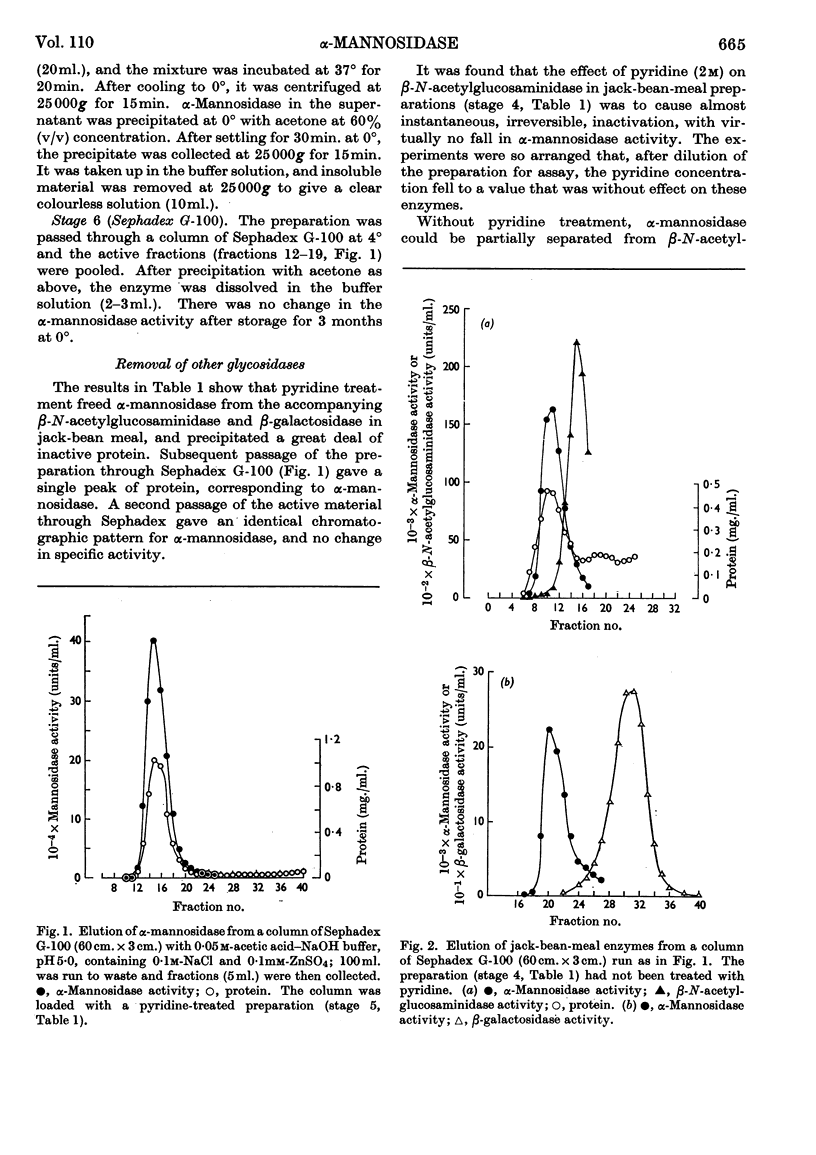

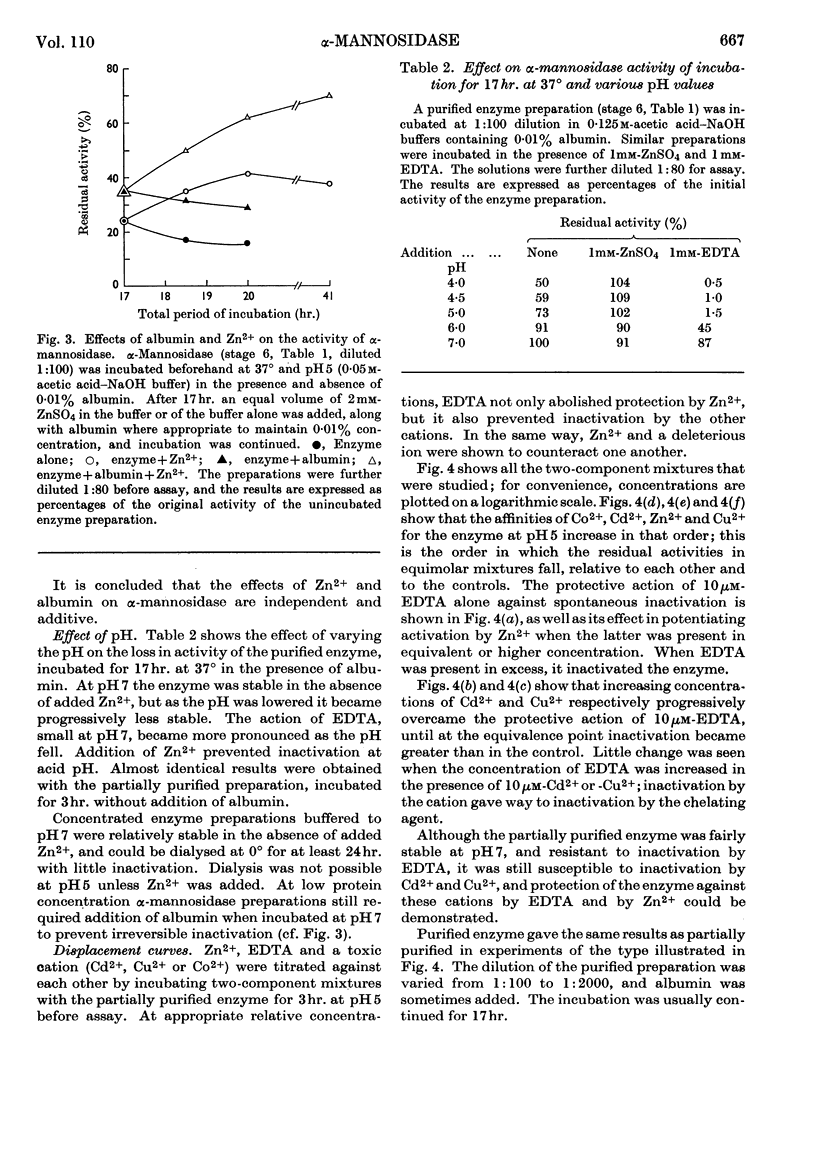
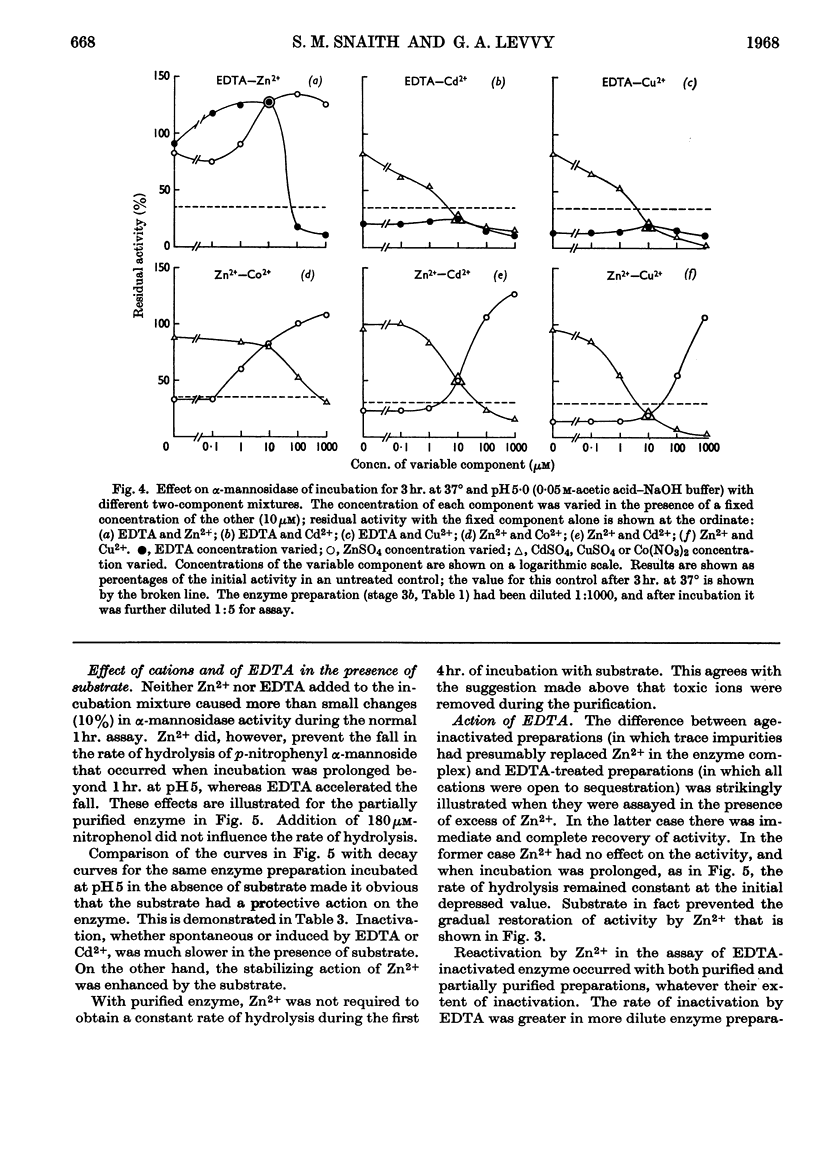
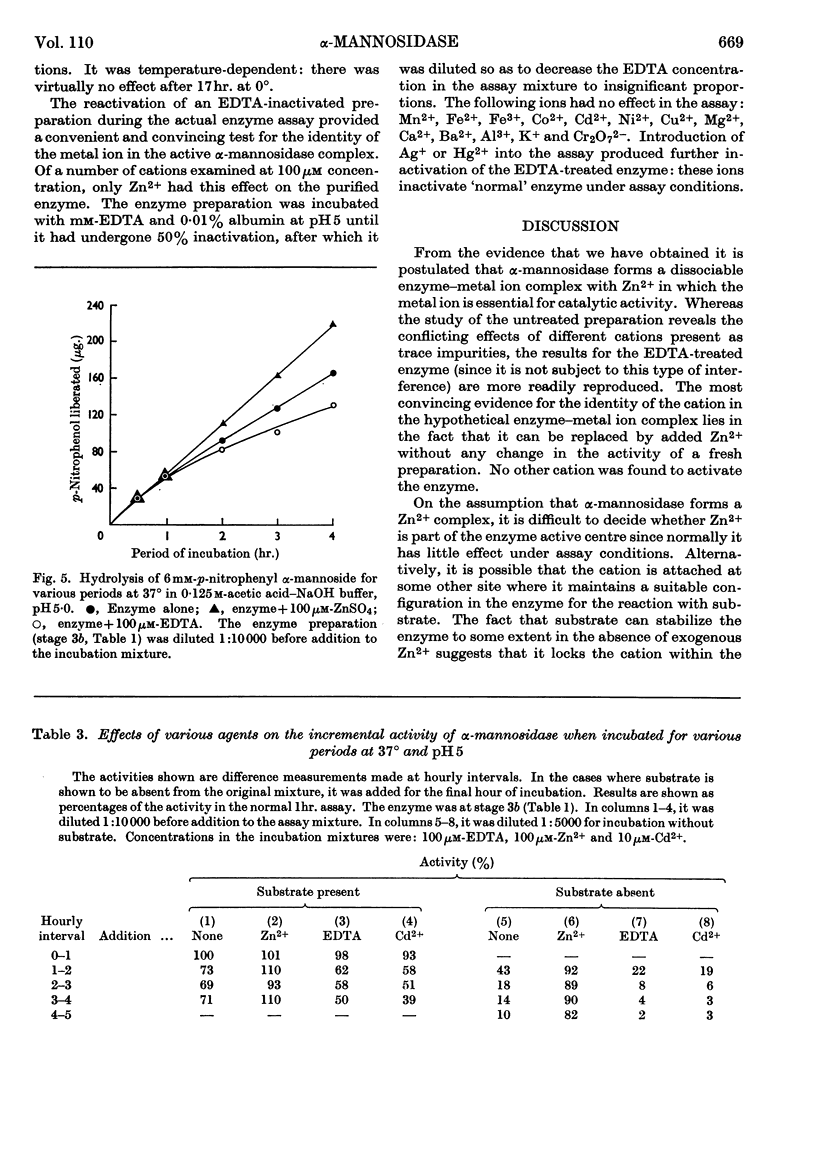

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CLAMP J. R., HOUGH L. STUDIES ON A GLYCOPEPTIDE FROM OVALBUMIN. Biochem J. 1965 Feb;94:502–508. doi: 10.1042/bj0940502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONCHIE J., FINDLAY J., LEVVY G. A. Mammalian glycosidases; distribution in the body. Biochem J. 1959 Feb;71(2):318–325. doi: 10.1042/bj0710318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONCHIE J., HAY A. J. Mammalian glycosidases. 2. Properties of alpha-mannosidase and beta-galactosidase from rat epididymis. Biochem J. 1959 Oct;73:327–334. doi: 10.1042/bj0730327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONCHIE J., LEVVY G. A. Inhibition of glycosidases by aldonolactones of corresponding configuration. Biochem J. 1957 Feb;65(2):389–395. doi: 10.1042/bj0650389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conchie J., Gelman A. L., Levvy G. A. Inhibition of glycosidases by aldonolactones of corresponding configuration. The C-4- and C-6-specificity of beta-glucosidase and beta-galactosidase. Biochem J. 1967 Jun;103(3):609–615. doi: 10.1042/bj1030609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conchie J., Gelman A. L., Levvy G. A. Inhibition of glycosidases by aldonolactones of corresponding configuration. The specificity of alpha-L-arabinosidase. Biochem J. 1968 Jan;106(1):135–140. doi: 10.1042/bj1060135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINDLAY J., LEVVY G. A., MARSH C. A. Inhibition of glycosidases by aldonolactones of corresponding configuration. 2. Inhibitors of beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase. Biochem J. 1958 Jul;69(3):467–476. doi: 10.1042/bj0690467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLETCHER A. P., MARKS G. S., MARSHALL R. D., NEUBERGER A. Carbohydrates in protein. 5. Procedures for the isolation of glycopeptides from hen's-egg albumin and their oxidation by periodate. Biochem J. 1963 May;87:265–273. doi: 10.1042/bj0870265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVVY G. A., McALLAN A. Some plant glycosidases. Nature. 1962 Jul 28;195:387–387. doi: 10.1038/195387a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levvy G. A., Hay A. J., Conchie J. Inhibition of glycosidases by aldonolactones of corresponding configuration. 4. Inhibitors of mannosidase and glucosidase. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):378–384. doi: 10.1042/bj0910378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y. T. Presence of alpha-D-mannosidic linkage in glycoproteins. Liberation of d-mannose from various glycoproteins by alpha-mannosidase isolated from jack bean meal. J Biol Chem. 1966 Feb 25;241(4):1010–1012. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y. T. Studies on the glycosidases in jack bean meal. I. Isolation and properties of alpha-mannosidase. J Biol Chem. 1967 Dec 10;242(23):5474–5480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu T. Purification and properties of alpha-mannosidase from the liver of Charonia lampas. J Biochem. 1967 Oct;62(4):487–491. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snaith S. M., Levvy G. A. Alpha-mannosidase as a zinc-dependent enzyme. Nature. 1968 Apr 6;218(5136):91–92. doi: 10.1038/218091a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


