Abstract
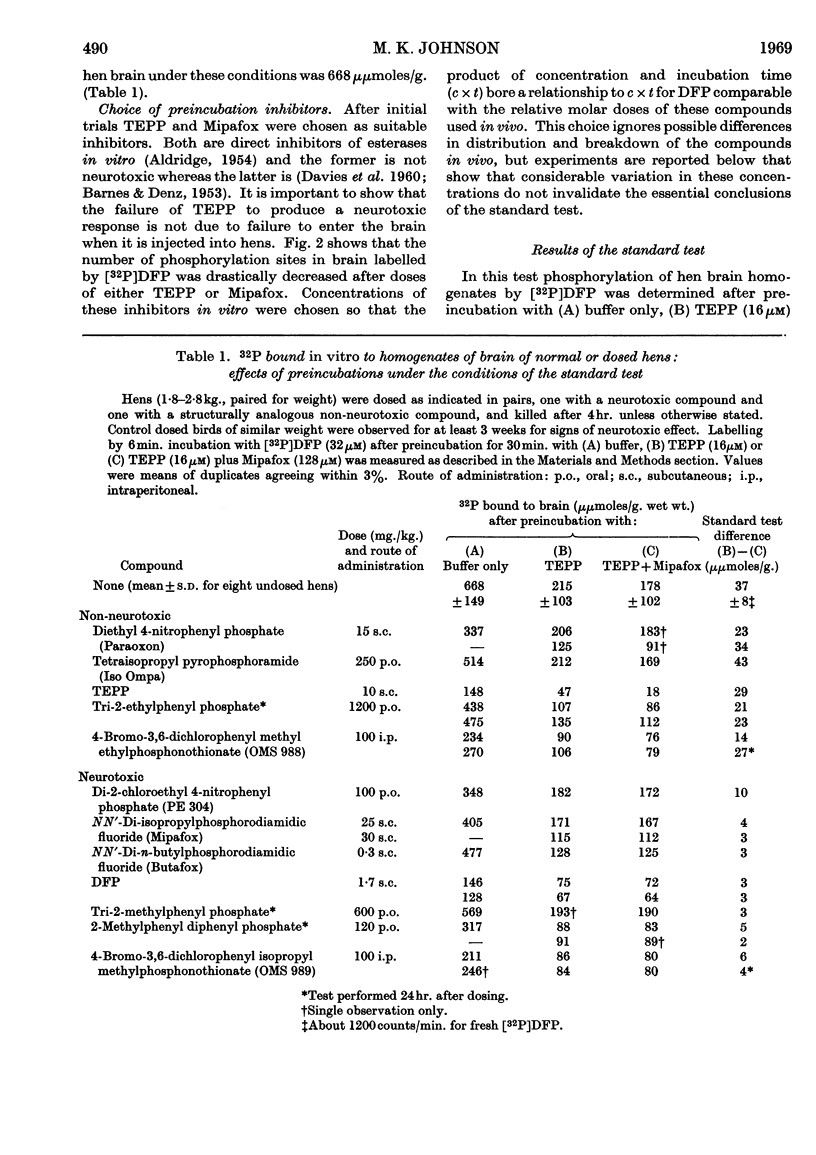
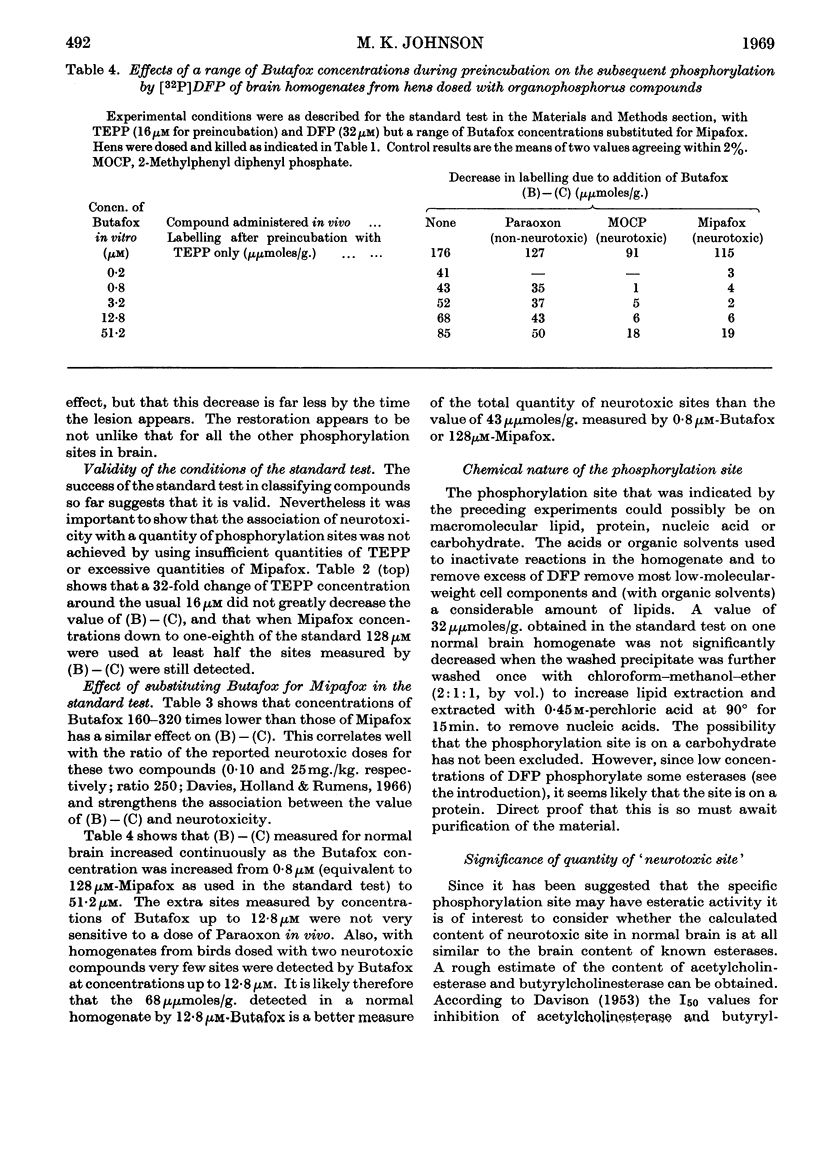
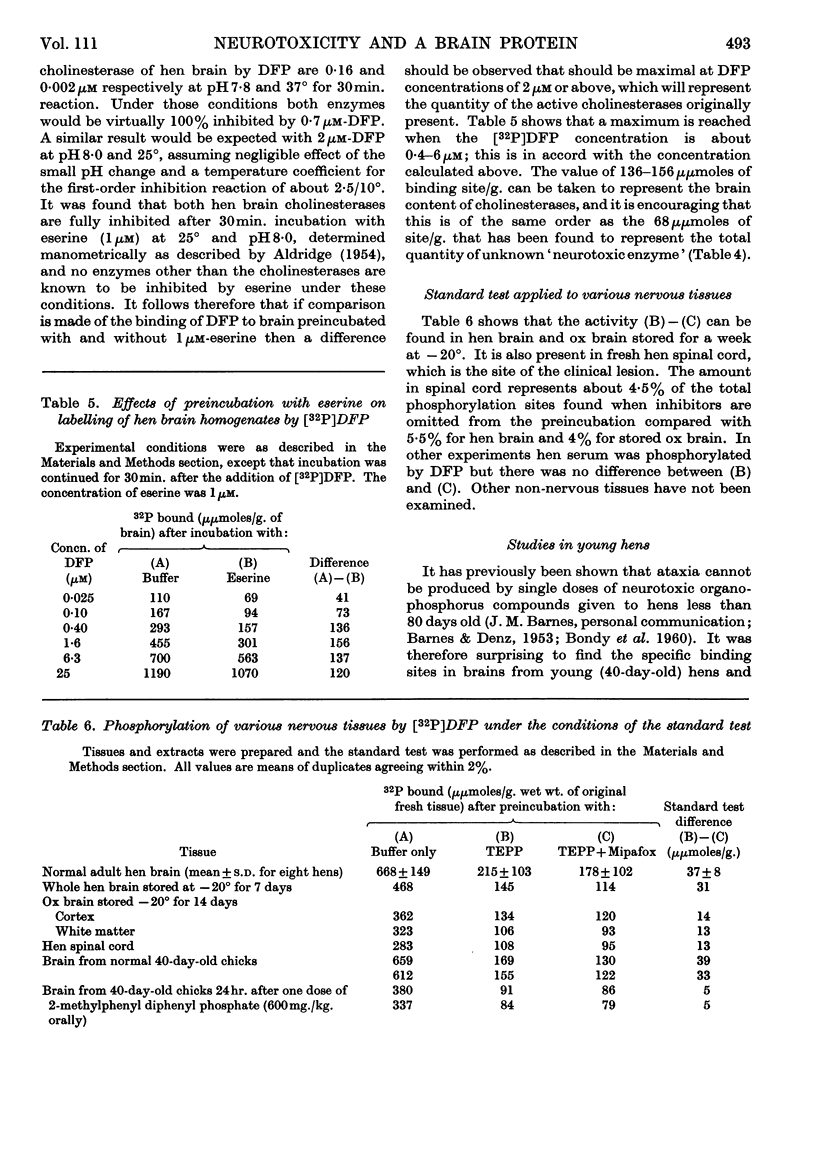
1. It is proposed that part of a neurotoxic dose of di-isopropyl phosphorofluoridate will be covalently bound in vivo to a specific component in the brain and spinal cord as the initial biochemical event in the genesis of the lesion. 2. A test system in vitro was devised that removes many di-isopropyl phosphorofluoridate-binding sites and indicates that the specific component may be a protein present in brain at a concentration comparable with that of the cholinesterases. 3. The site was found to be present and capable of binding di-isopropyl phosphorofluoridate in vitro in brain samples taken from either normal hens or those dosed with organophosphorus esterase inhibitors that are not neurotoxic. 4. Very little of the specific binding activity was found in brain samples from hens pre-dosed with a variety of neurotoxic organophosphorus compounds. 5. A solubilized preparation of the active brain component was obtained, suitable for further purification and study.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALDRIDGE W. N., BARNES J. M. Neurotoxic and biochemical properties of some triaryl phosphates. Biochem Pharmacol. 1961 May;6:177–188. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(61)90162-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALDRIDGE W. N., EMERY R. C., STREET B. W. A tissue homogenizer. Biochem J. 1960 Nov;77:326–327. doi: 10.1042/bj0770326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALDRIDGE W. N. Serum esterases. I. Two types of esterase (A and B) hydrolysing p-nitrophenyl acetate, propionate and butyrate, and a method for their determination. Biochem J. 1953 Jan;53(1):110–117. doi: 10.1042/bj0530110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALDRIDGE W. N. Serum esterases. II. An enzyme hydrolysing diethyl p-nitrophenyl phosphate (E600) and its identity with the A-esterase of mammalian sera. Biochem J. 1953 Jan;53(1):117–124. doi: 10.1042/bj0530117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALDRIDGE W. N. Some esterases of the rat. Biochem J. 1954 Aug;57(4):692–702. doi: 10.1042/bj0570692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aldridge W. N., Barnes J. M. Esterases and neurotoxicity of some organophosphorus compounds. Biochem Pharmacol. 1966 May;15(5):549–554. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(66)90021-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARNES J. M., DENZ F. A. Experimental demyelination with organo-phosphorus compounds. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1953 Apr;65(2):597–605. doi: 10.1002/path.1700650230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BONDY H. F., FIELD E. J., WORDEN A. N., HUGHES J. P. A study on the acute toxicity of the tri-aryl phosphates used as plasticizers. Br J Ind Med. 1960 Jul;17:190–200. doi: 10.1136/oem.17.3.190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavanagh J. B. The significance of the "dying back" process in experimental and human neurological disease. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1964;3:219–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIES D. R., HOLLAND P., RUMENS M. J. The relationship between the chemical structure and neurotoxicity of alkyl organophosphorus compounds. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1960 Jun;15:271–278. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1960.tb01243.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MYERS D. K. Studies on ali-esterases. 4. Differentiation of esterases in pancreas and brain by the use of organophosphorus inhibitors. Biochem J. 1956 Dec;64(4):740–747. doi: 10.1042/bj0640740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAMACHANDRAN B. V., ENGSTROM L., AGREN G. Fractionation of DF32P-binding proteins of rat-liver cell fractions by DEAE-cellulose chromatography. Distribution of esterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol. 1963 Feb;12:167–172. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(63)90181-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


