Abstract
1. The β-glucosidase activity of pig kidney is located in the unsedimentable fraction of the cell and is not associated with the lysosomes. 2. The enzyme is active towards β-d-glucosides, β-d-galactosides, β-d-xylosides and α-l-arabinosides. 3. These activities could not be separated by gel electrophoresis, gel filtration or DEAE-cellulose chromatography. 4. Response to inhibitors, heat-denaturation and competitive substrates suggests that a single active site is responsible for all four activities. 5. Two forms of the enzyme were found to occur either separately or together in kidneys of pigs from several different breeds. 6. Electro-focusing experiments show these to have a small difference in isoelectric point (4·9 and 5·1), and gel filtration gives an approximate molecular weight of 50000 for both forms. 7. The characteristics of these two enzymes are compared.
Full text
PDF

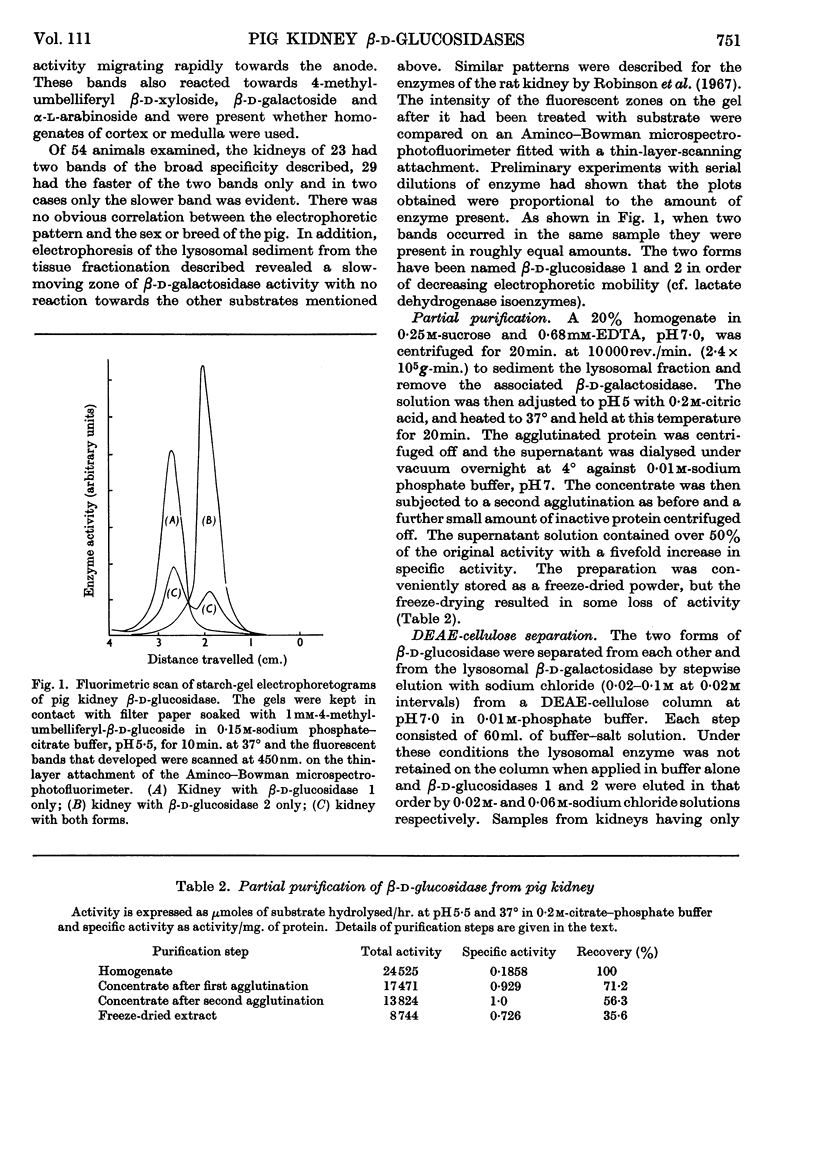
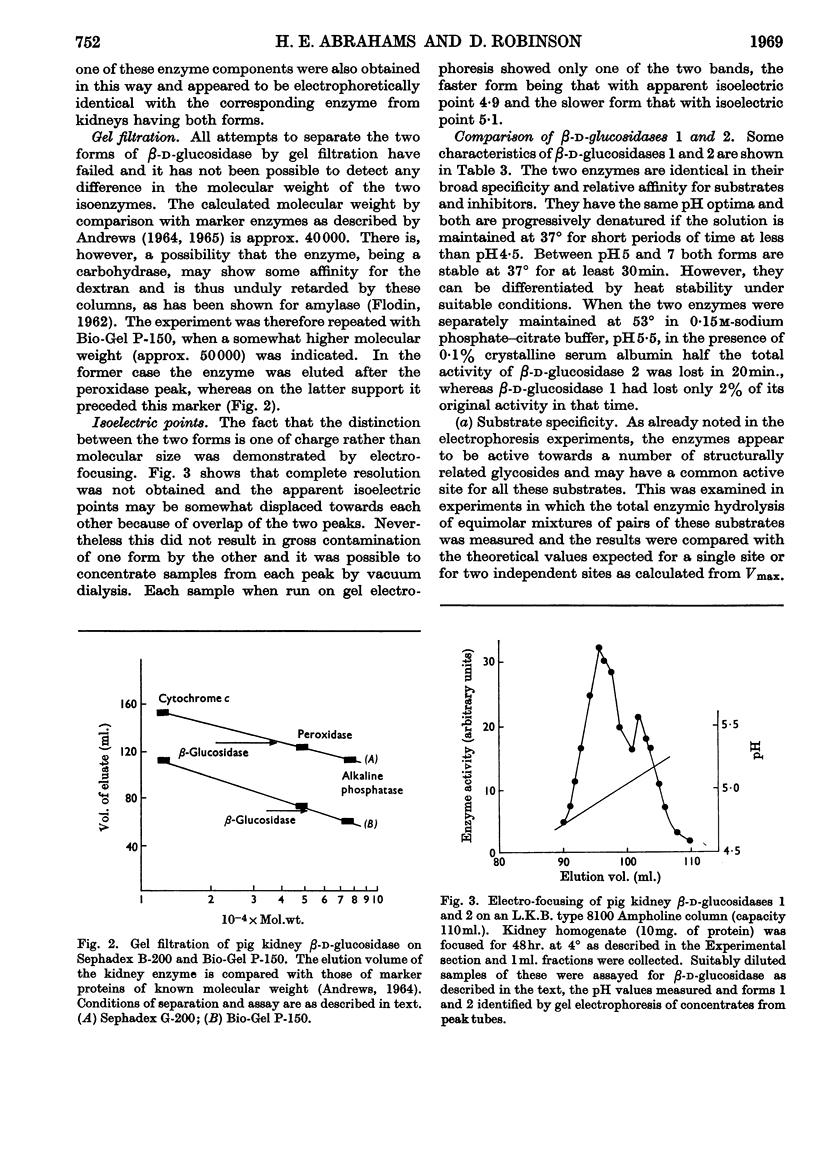
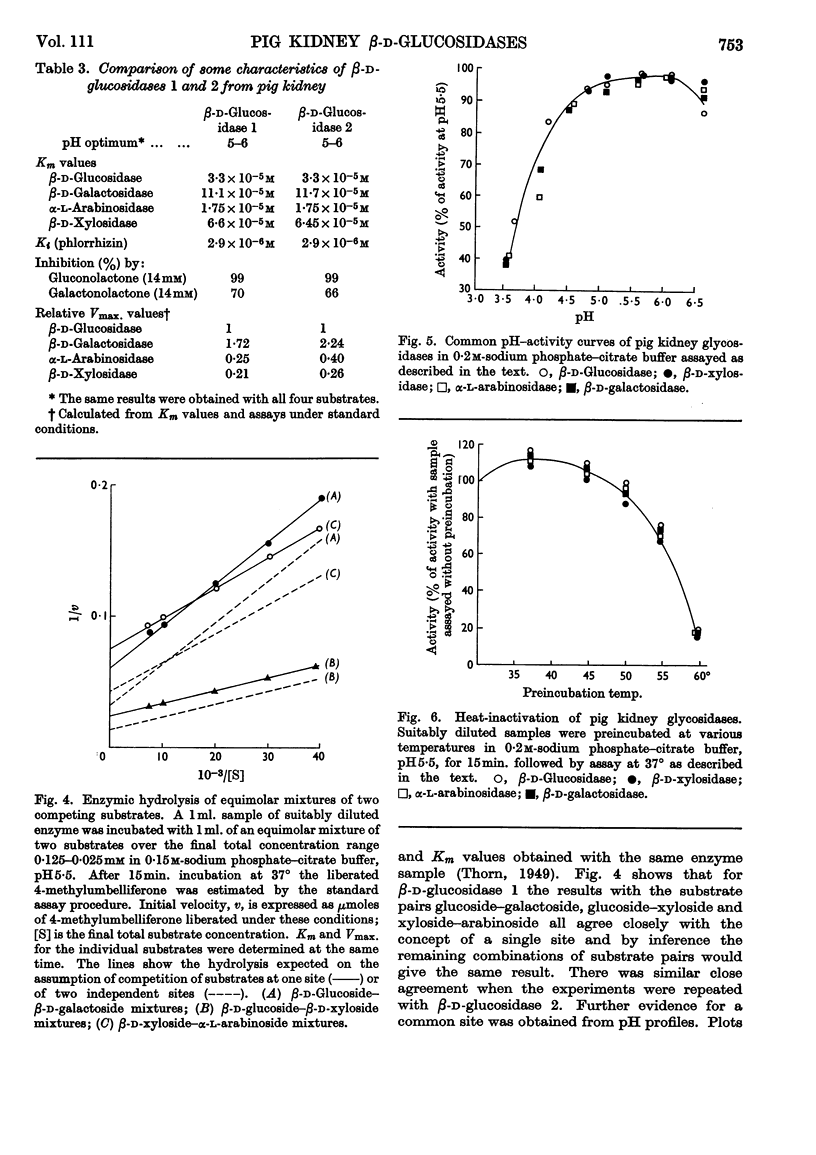
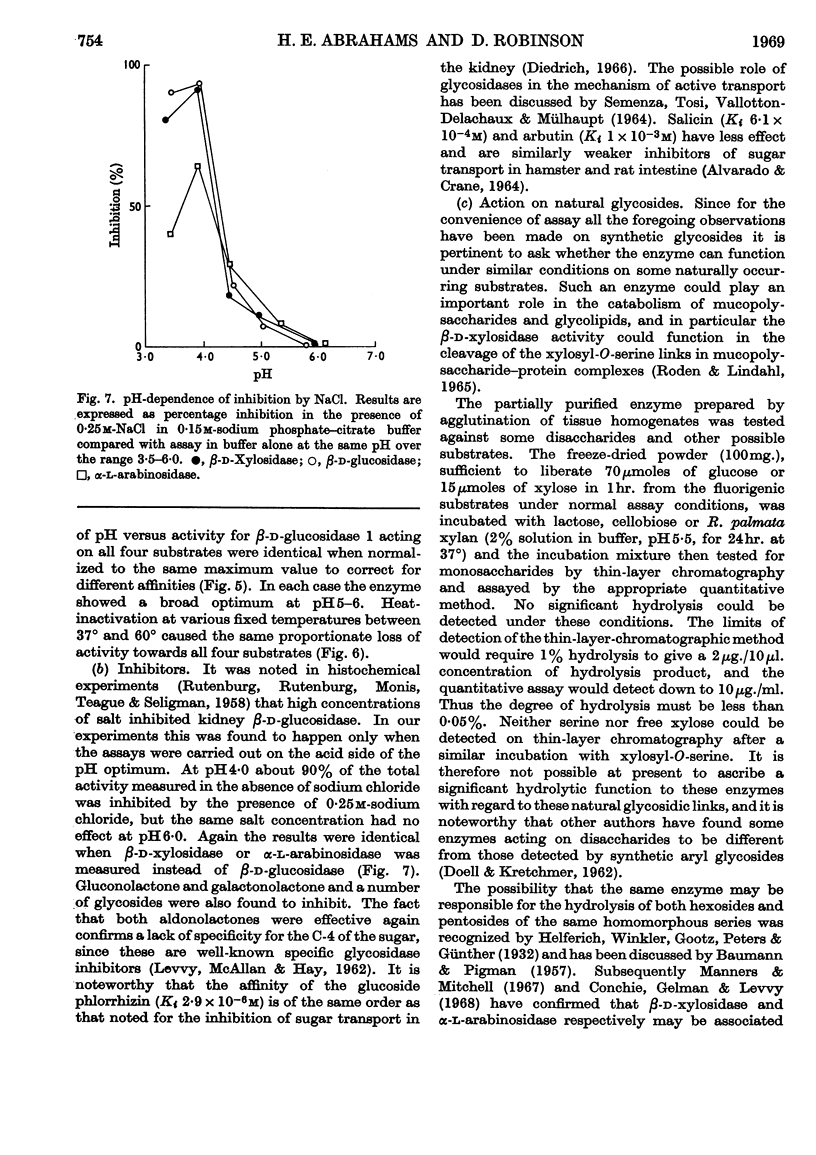

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALVARADO F., CRANE R. K. STUDIES ON THE MECHANISM OF INTESTINAL ABSORPTION OF SUGARS. VII. PHENYLGLYCOSIDE TRANSPORT AND ITS POSSIBLE RELATIONSHIP TO PHLORIZIN INHIBITION OF THE ACTIVE TRANSPORT OF SUGARS BY THE SMALL INTESTINE. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Oct 9;93:116–135. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90266-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. J. The estimation of phosphorus. Biochem J. 1940 Jun;34(6):858–865. doi: 10.1042/bj0340858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. Estimation of the molecular weights of proteins by Sephadex gel-filtration. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):222–233. doi: 10.1042/bj0910222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. The gel-filtration behaviour of proteins related to their molecular weights over a wide range. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):595–606. doi: 10.1042/bj0960595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck C., Tappel A. L. Rat-liver lysosomal beta-glucosidase: a membrane enzyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jan 8;151(1):159–164. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(68)90170-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN R. B., TSOU K-C, RUTENBURG S. H., SELIGMAN A. M. The colorimetric estimation and histochemical demonstration of beta-d-galactosidase. J Biol Chem. 1952 Mar;195(1):239–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chytil F. Mammalian beta-galactosidases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 May 18;19(5):630–636. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90386-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conchie J., Gelman A. L., Levvy G. A. Inhibition of glycosidases by aldonolactones of corresponding configuration. The specificity of alpha-L-arabinosidase. Biochem J. 1968 Jan;106(1):135–140. doi: 10.1042/bj1060135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOELL R. G., KRETCHMER N. Studies of small intestine during development. I. Distribution and activity of beta-galactosidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Aug 13;62:353–362. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90097-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D., Whitehouse M. W., Kent P. W. Beta-xylosidase and beta-galactosidase activities of mammalian connective tissues and other sources. Nature. 1967 Jan 14;213(5072):204–205. doi: 10.1038/213204a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furth A. J., Robinson D. Specificity and multiple forms of beta-galactosidase in the rat. Biochem J. 1965 Oct;97(1):59–66. doi: 10.1042/bj0970059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAREN A., LEVINTHAL C. A fine-structure genetic and chemical study of the enzyme alkaline phosphatase of E. coli. I. Purification and characterization of alkaline phosphatase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Mar 11;38:470–483. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVVY G. A., McALLAN A., HAY A. J. Inhibition of glycosidases by aldonolactones of corresponding configuration. 3. Inhibitors of beta-D-galactosidase. Biochem J. 1962 Feb;82:225–232. doi: 10.1042/bj0820225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEARSON B., ANDREWS M., GROSE F. Histochemical demonstration of mammalian glucosidase by means of 3-(5-bromoindolyl)-beta-D-glucopyranoside. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1961 Dec;108:619–623. doi: 10.3181/00379727-108-27014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price R. G., Robinson D. A comparison of the beta-D-glucosidase and beta-D-galactosidase activities from eleven enzyme sources. Comp Biochem Physiol. 1966 Jan;17(1):129–138. doi: 10.1016/0010-406x(66)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBINSON D. The fluorimetric determination of beta-glucosidase: its occurrence in the tissues of animals, including insects. Biochem J. 1956 May;63(1):39–44. doi: 10.1042/bj0630039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUTENBURG A. M., RUTENBURG S. H., MONIS B., TEAGUE R., SELIGMAN A. M. Histochemical demonstration of beta-D-galactosidase in the rat. J Histochem Cytochem. 1958 Mar;6(2):122–129. doi: 10.1177/6.2.122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson D., Abrahams H. E. Beta-D-xylosidase in pig kidney. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Jan 11;132(1):212–214. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(67)90215-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson D., Price R. G., Dance N. Separation and properties of beta-galactosidase, beta-glucosidase, beta-glucuronidase and N-acetyl-beta-glucosaminidase from rat kidney. Biochem J. 1967 Feb;102(2):525–532. doi: 10.1042/bj1020525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEMENZA G., TOSI R., VALLOTTON-DELACHAUX M. C., MUELHAUPT E. SODIUM ACTIVATION OF HUMAN INTESTINAL SUCRASE AND ITS POSSIBLE SIGNIFICANCE IN THE ENZYME ORGANIZATION OF BRUSH BORDERS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Jul 8;89:109–116. doi: 10.1016/0926-6569(64)90104-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHIBKO S., TAPPEL A. L. RAT-KIDNEY LYSOSOMES: ISOLATION AND PROPERTIES. Biochem J. 1965 Jun;95:731–741. doi: 10.1042/bj0950731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLATER T. F., PLANTEROSE D. N. An assay procedure for a succinate-neotetrazolium-reductase system. Biochem J. 1960 Mar;74:591–596. doi: 10.1042/bj0740591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J. B., Smith I. Sensitive location reagent for the simultaneous detection of sugars, amino sugars and sialic acids. Nature. 1967 Aug 5;215(5101):638–638. doi: 10.1038/215638a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


