Abstract
1. The interactions of retinol and retinoic acid with two electron acceptors, 7,7,8,8-tetracyanoquinodimethane (TCNQ) and tetrachloro-1,4-benzoquinone (chloranil), were studied in an investigation on the ability of vitamin A to behave as a donor of electrons. 2. Retinol reacts with TCNQ in polar organic solvents with the formation, as judged by spectral studies, of the radical anion of TCNQ. 3. Addition of the products of this reaction to water is accompanied by a rapid consumption of OH− ions. 4. Consumption of OH− ions is also a feature of the reactions between retinol and chloranil, but the spectrum of the radical anion of chloranil is observed only when retinol and chloranil are suspended in aqueous salt solutions. 5. Retinoic acid behaves similarly to retinol in its reactions with TCNQ and chloranil, but it appears to be a weaker electron donor than retinol. 6. The reaction products that may be formed from retinol in its reactions with TCNQ and chloranil are discussed. 7. It is suggested that the ability of vitamin A to behave as a donor of electrons may be an important aspect of its biochemical mode of action.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BALL S., MORTON R. A. Vitamin A1 and retinene1 in relation to photopic vision. Biochem J. 1949;45(3):298–304. doi: 10.1042/bj0450298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
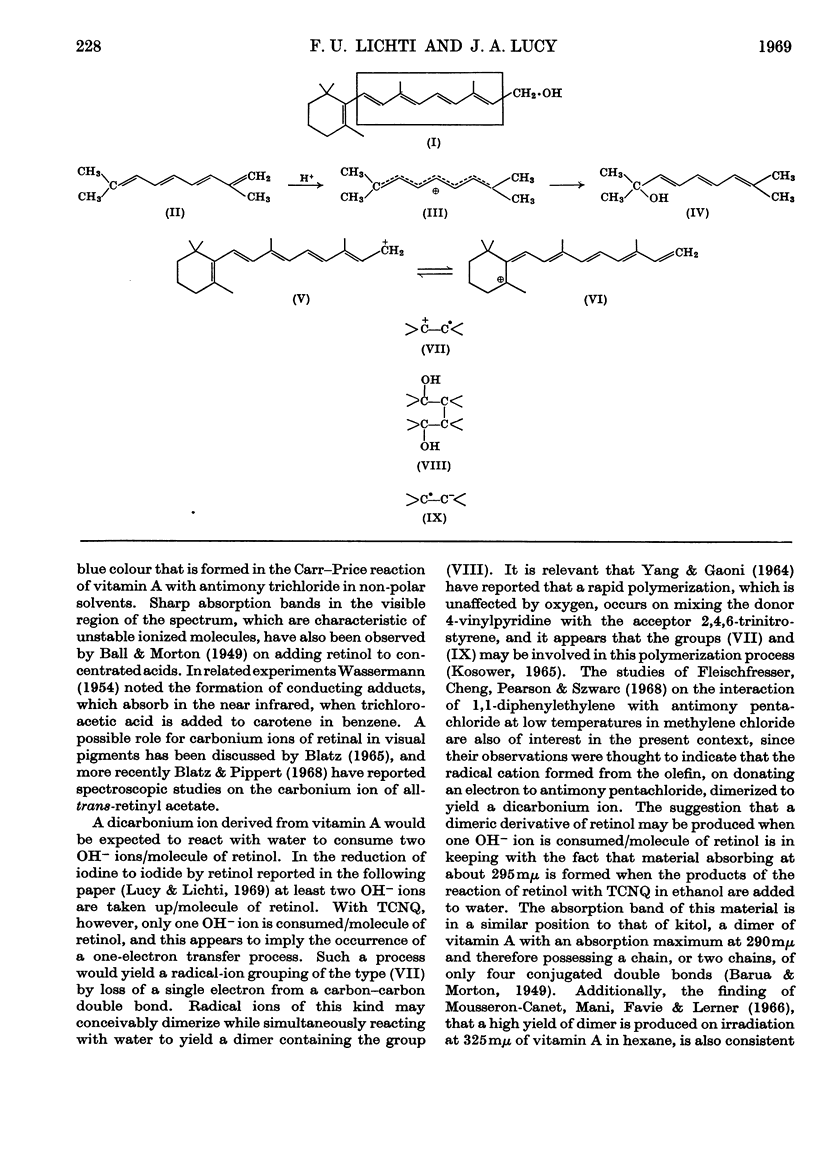
- BARUA R. K., MORTON R. A. Studies in vitamin A; whale-liver oil analysis; preparation of kitol esters. Biochem J. 1949;45(3):308–317. doi: 10.1042/bj0450308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLATZ P. E. THE ROLE OF CARBONIUM IONS IN COLOR RECEPTION. J Gen Physiol. 1965 May;48:753–760. doi: 10.1085/jgp.48.5.753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bangham A. D., Dingle J. T., Lucy J. A. Studies on the mode of action of excess of vitamin A. 9. Penetration of lipid monolayers by compounds in the vitamin A series. Biochem J. 1964 Jan;90(1):133–140. doi: 10.1042/bj0900133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DINGLE J. T., LUCY J. A. Studies on the mode of action of excess of vitamin A. 5. The effect of vitamin A on the stability of the erythrocyte membrane. Biochem J. 1962 Sep;84:611–621. doi: 10.1042/bj0840611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DINGLE J. T., LUCY J. A. VITAMIN A, CAROTENOIDS AND CELL FUNCTION. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 1965 Aug;40:422–461. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185x.1965.tb00809.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel M. R., Dingle J. T., Glauert A. M., Lucy J. A. The action of excess of vitamin A alcohol on the fine structure of rat dermal fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1966 Sep;30(3):465–475. doi: 10.1083/jcb.30.3.465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grady F. J., Borg D. C. Light-induced free radicals of retinal, retinol, and rhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1968 Feb;7(2):675–682. doi: 10.1021/bi00842a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucy J. A., Lichti F. U. Reactions of vitamin A with acceptors of electrons. Interactions with iodine and the formation of iodide. Biochem J. 1969 Apr;112(2):231–241. doi: 10.1042/bj1120231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTON R. A. Symposium on vitamin A and metabolism in honor of Professor P. Karrer: summary discussion. Vitam Horm. 1960;18:543–569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


