Abstract
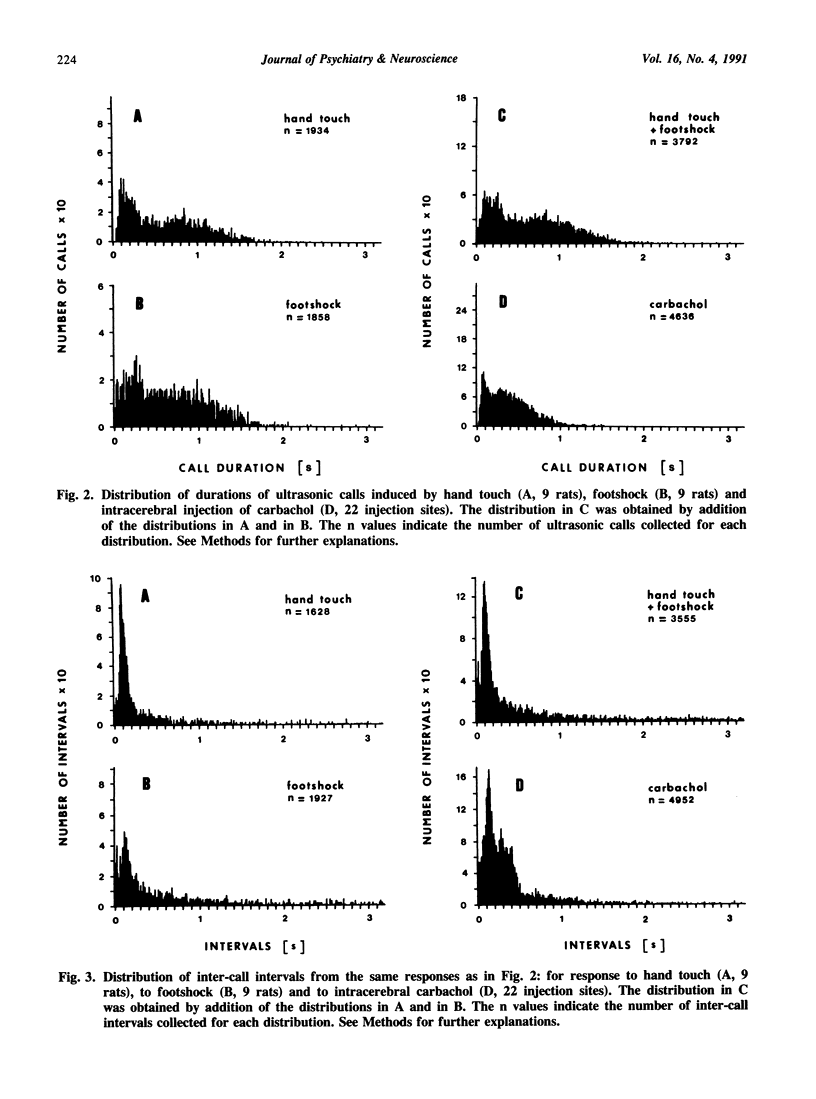
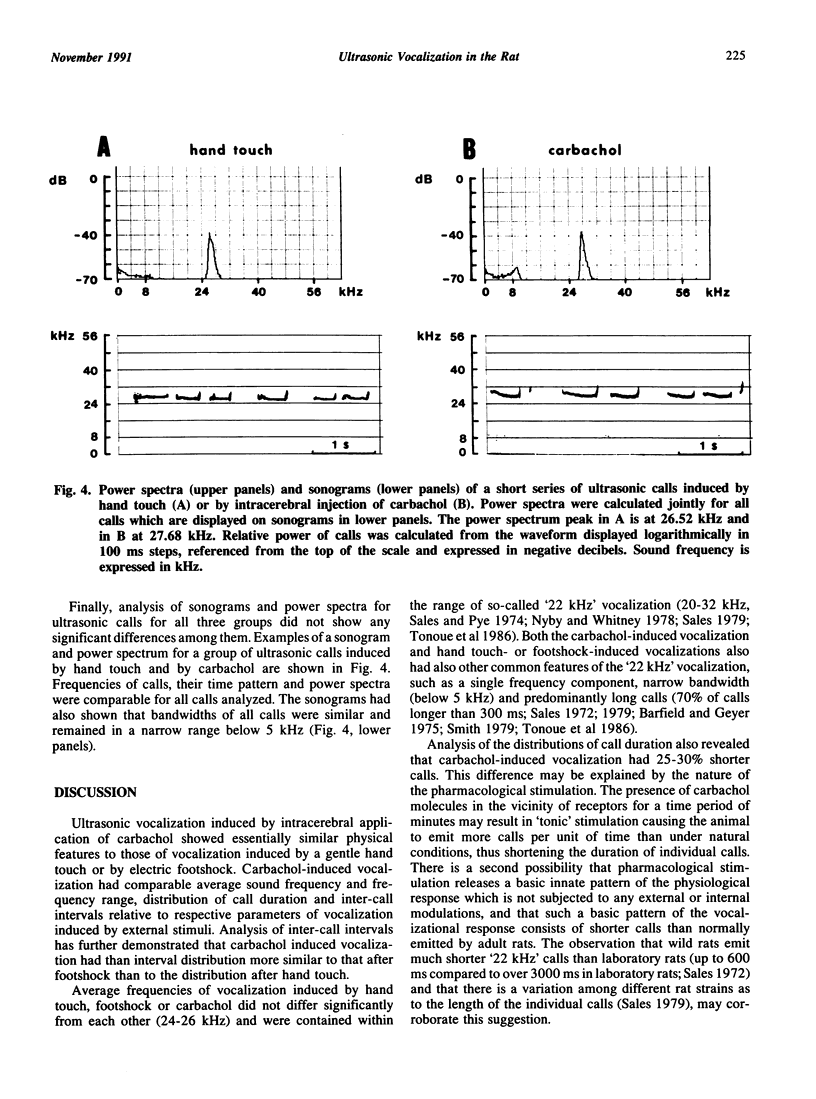
Ultrasonic vocalization in rats accompanying stressful situations or induced by direct brain stimulation may be used as a measure of emotionality and as a potential response model for testing anti-anxiety agents. The aim of the present study was to compare physical features of pharmacologically-induced ultrasonic vocalization with naturally triggered vocalization. Ultrasonic calls induced by hand touch, footshock, or by direct intracerebral injection of carbachol in adult rats were compared. Ultrasonic calls obtained in all these situations were described as '22 kHz' vocalization. Average frequencies of vocalization were 24.1 +/- 0.78 kHz, 26.0 +/- 2.64 kHz and 25.0 +/- 1.87 (SD) kHz for handled, footshocked and carbachol injected rats, respectively, and they did not differ significantly from each other. Histograms of single call duration showed similar distribution patterns for all groups with a predominance of long calls, although carbachol-induced calls were shorter than calls induced by touch or footshock. Histograms for inter-call intervals showed one major peak at 100-150 ms for all groups. Sonograms and power spectra showed similar characteristics both for calls induced by intracerebral carbachol and by hand touch or footshock. The results indicate that physical features of ultrasonic vocalization induced by intracerebral carbachol are comparable with those for naturally induced vocalization and fall into the category of '22 kHz' calls.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barfield R. J., Geyer L. A. The ultrasonic postejaculatory vocalization and the postejaculatory refractory period of the male rat. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1975 Feb;88(2):723–734. doi: 10.1037/h0076435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brudzynski S. M., Bihari F. Ultrasonic vocalization in rats produced by cholinergic stimulation of the brain. Neurosci Lett. 1990 Feb 5;109(1-2):222–226. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90567-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brudzynski S. M., McLachlan R. S., Girvin J. P. Cholinergically mediated reduction of locomotor activity from the basal forebrain of the rat. Exp Neurol. 1989 Aug;105(2):197–205. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(89)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brudzyński S. M., Kiełczykowska E., Romaniuk A. The effects of external stimuli on the emotional-aversive response evoked by intrahypothalamic carbachol injections. Behav Brain Res. 1982 Jan;4(1):33–43. doi: 10.1016/0166-4328(82)90162-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuomo V., Cagiano R., De Salvia M. A., Maselli M. A., Renna G., Racagni G. Ultrasonic vocalization in response to unavoidable aversive stimuli in rats: effects of benzodiazepines. Life Sci. 1988;43(6):485–491. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(88)90149-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eschalier A., Marty H., Trolese J. F., Moncharmont L., Fialip J. An automated method to analyze vocalization of unrestrained rats submitted to noxious electrical stimuli. J Pharmacol Methods. 1988 Apr;19(2):175–184. doi: 10.1016/0160-5402(88)90038-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner C. R. Distress vocalization in rat pups. A simple screening method for anxiolytic drugs. J Pharmacol Methods. 1985 Nov;14(3):181–187. doi: 10.1016/0160-5402(85)90031-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hård E., Engel J. Effects of 8-OH-DPAT on ultrasonic vocalization and audiogenic immobility reaction in pre-weanling rats. Neuropharmacology. 1988 Oct;27(10):981–986. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(88)90056-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaltwasser M. T. Startle-inducing acoustic stimuli evoke ultrasonic vocalization in the rat. Physiol Behav. 1990 Jul;48(1):13–17. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(90)90253-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sales G. D. Ultrasound and aggressive behaviour in rats and other small mammals. Anim Behav. 1972 Feb;20(1):88–100. doi: 10.1016/s0003-3472(72)80177-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonoue T., Ashida Y., Makino H., Hata H. Inhibition of shock-elicited ultrasonic vocalization by opioid peptides in the rat: a psychotropic effect. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 1986;11(2):177–184. doi: 10.1016/0306-4530(86)90052-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


