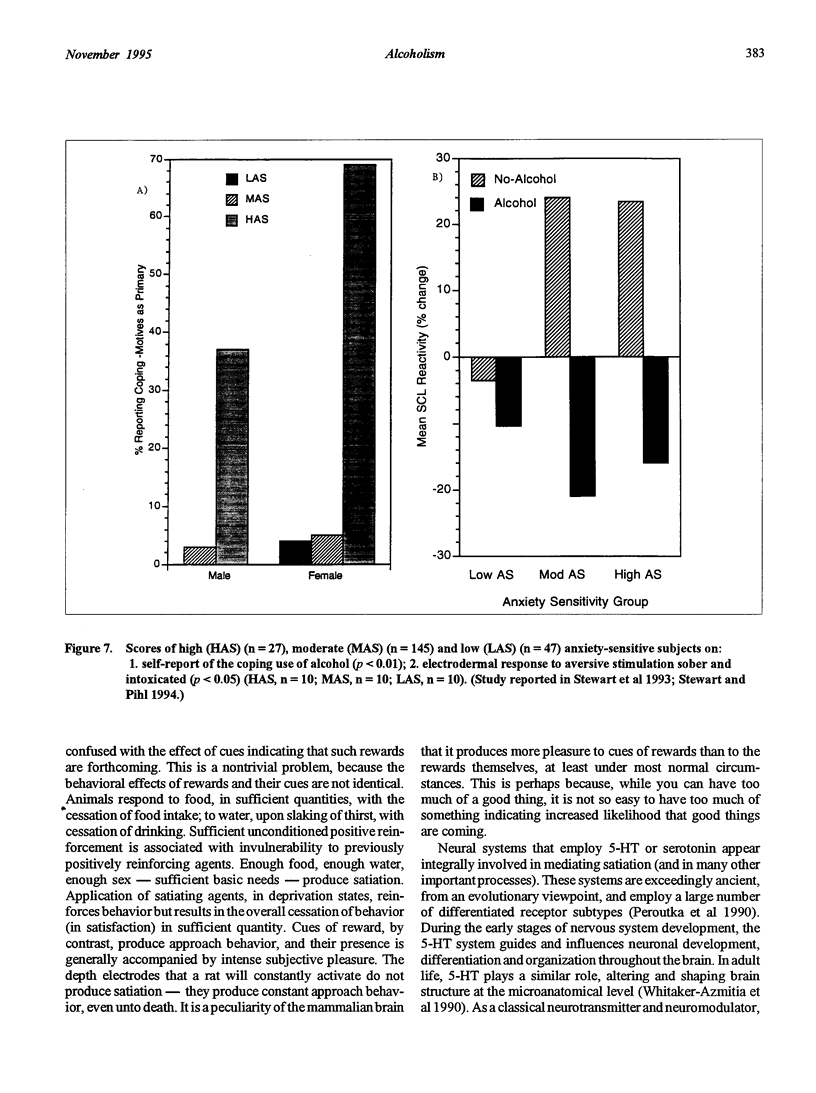
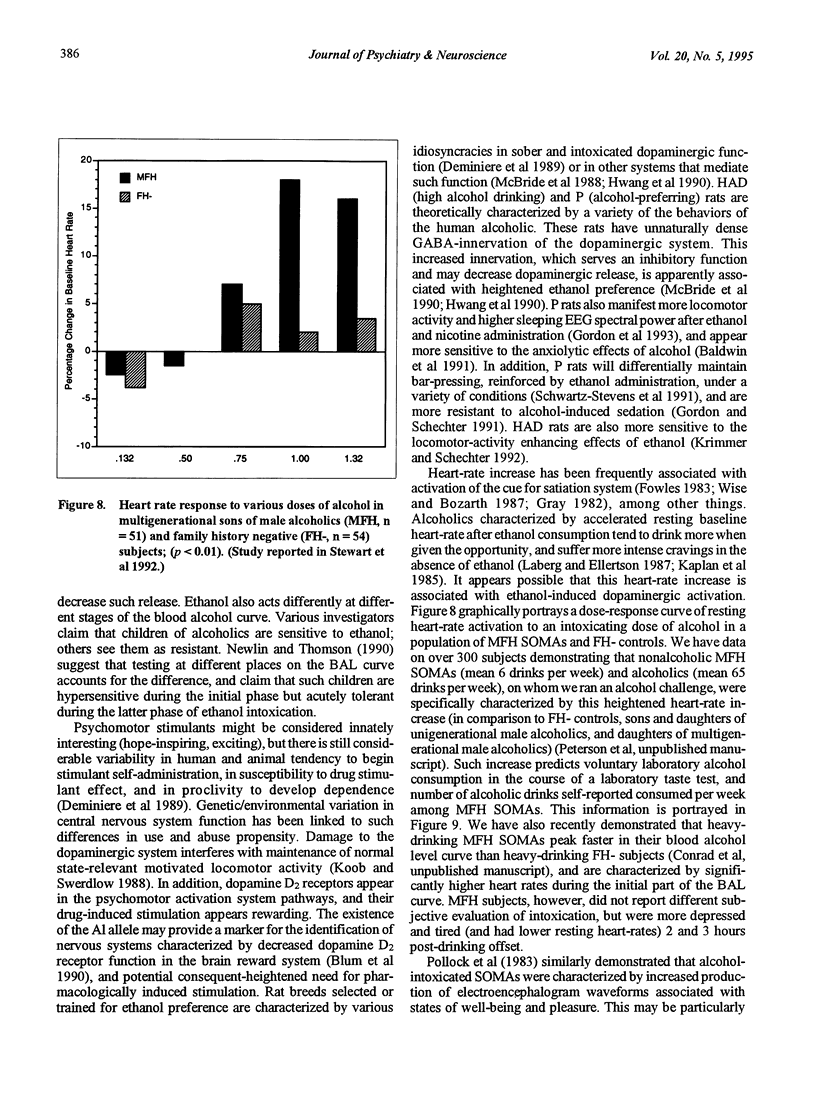
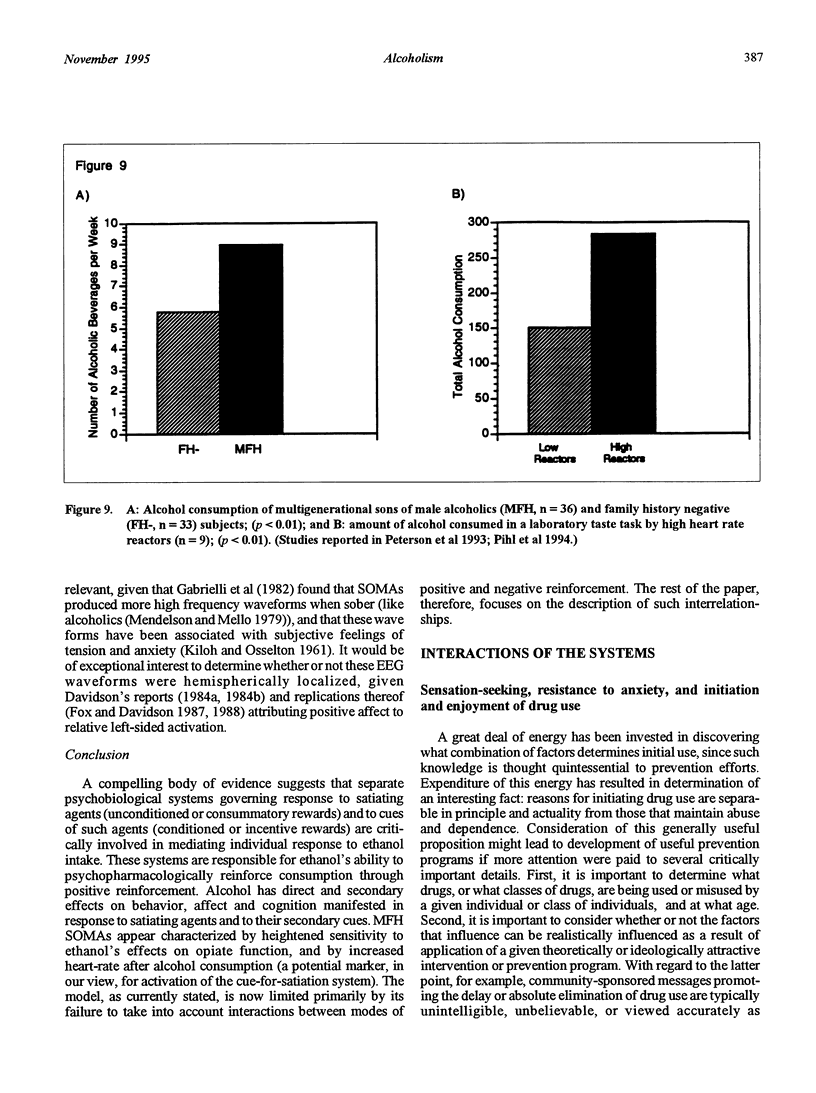
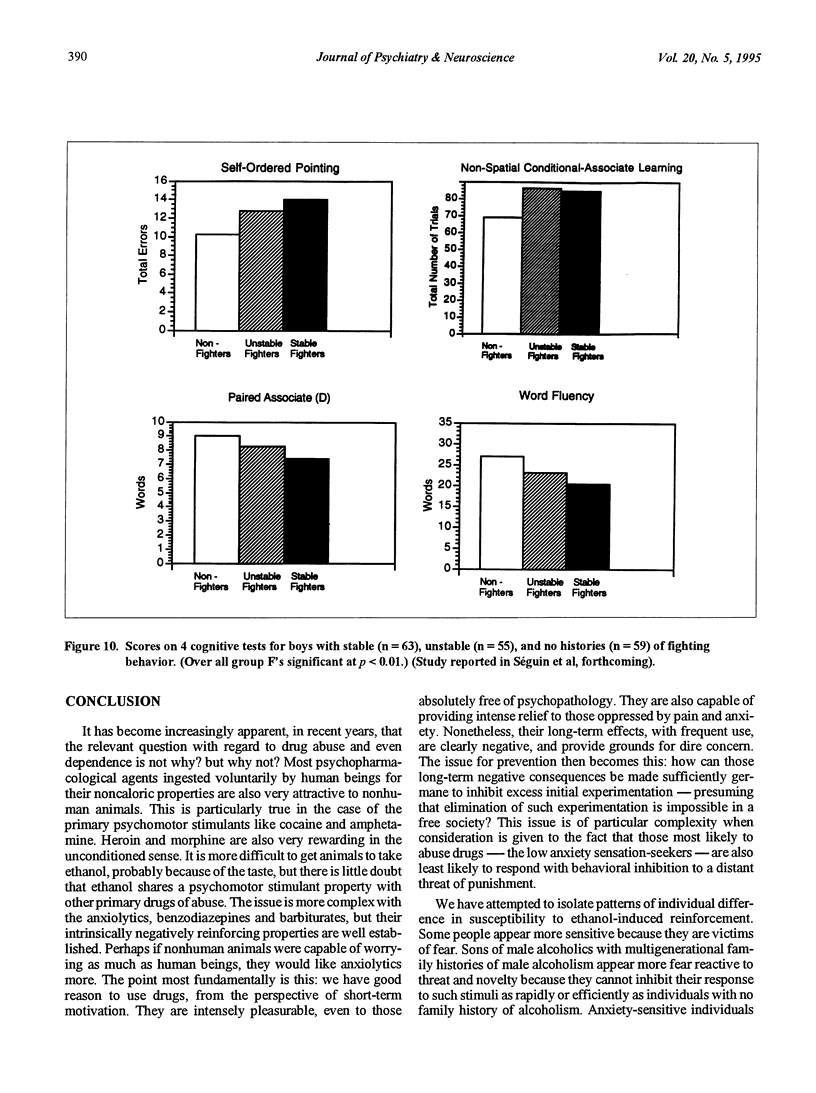
Abstract
Individuals use and misuse alcohol (and other drugs) because of the pharmacologically mediated effects these substances have on the operation of 4 psychobiological systems, mediating response to motivationally relevant unconditioned and conditioned stimuli. These 4 systems have unique neuroanatomical structure, biochemical modes of operation, association with affect, behavior and cognition, and responsiveness to drugs of abuse. Individual variation in the operation of these systems determines individual susceptibility to initiation and maintenance of drug use and abuse. Sources of such variation differ, in a vitally important fashion, in various specific populations of individuals at heightened risk for drug abuse. Nonalcoholic sons of male alcoholics, with multigenerational family histories of male alcoholism, appear to be at heightened risk for the development of alcohol abuse because alcohol eliminates their heightened response to threat, and because they are hypersensitive to ethanol's psychomotor stimulant effects. Anxiety-sensitive individuals also appear attracted to alcohol for its anxiolytic properties. Many other important sources of idiosyncratic variability exist. Detailed analysis of such sources may lead to the development of more effective prevention and treatment programs.
Full text
PDF
















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altshuler H. L., Phillips P. E., Feinhandler D. A. Alteration of ethanol self-administration by naltrexone. Life Sci. 1980 Mar 3;26(9):679–688. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90257-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrucci G. L., Archer R. P., Pancoast D. L., Gordon R. A. The relationship of MMPI and Sensation Seeking Scales to adolescent drug use. J Pers Assess. 1989 Summer;53(2):253–266. doi: 10.1207/s15327752jpa5302_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azrin N. H., Sisson R. W., Meyers R., Godley M. Alcoholism treatment by disulfiram and community reinforcement therapy. J Behav Ther Exp Psychiatry. 1982 Jun;13(2):105–112. doi: 10.1016/0005-7916(82)90050-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker R. C., Smolen A., Smolen T. N., Deitrich R. A. Relationship between acute ethanol-related responses in long-sleep and short-sleep mice. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1987 Dec;11(6):574–578. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1987.tb00177.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin H. A., Wall T. L., Schuckit M. A., Koob G. F. Differential effects of ethanol on punished responding in the P and NP rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1991 Aug;15(4):700–704. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1991.tb00582.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates M. E. Recent developments in alcoholism:psychology. Recent Dev Alcohol. 1993;11:45–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkowitz A., Perkins H. W. Personality characteristics of children of alcoholics. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1988 Apr;56(2):206–209. doi: 10.1037//0022-006x.56.2.206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibb J. L., Chambless D. L. Alcohol use and abuse among diagnosed agoraphobics. Behav Res Ther. 1986;24(1):49–58. doi: 10.1016/0005-7967(86)90149-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blass E. M., Fitzgerald E. Milk-induced analgesia and comforting in 10-day-old rats: opioid mediation. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1988 Jan;29(1):9–13. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(88)90266-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blass E. M., Hoffmeyer L. B. Sucrose as an analgesic for newborn infants. Pediatrics. 1991 Feb;87(2):215–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blass E., Fitzgerald E., Kehoe P. Interactions between sucrose, pain and isolation distress. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1987 Mar;26(3):483–489. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(87)90153-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum K., Noble E. P., Sheridan P. J., Montgomery A., Ritchie T., Jagadeeswaran P., Nogami H., Briggs A. H., Cohn J. B. Allelic association of human dopamine D2 receptor gene in alcoholism. JAMA. 1990 Apr 18;263(15):2055–2060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodnoff S. R., Suranyi-Cadotte B. E., Quirion R., Meaney M. J. Role of the central benzodiazepine receptor system in behavioral habituation to novelty. Behav Neurosci. 1989 Feb;103(1):209–212. doi: 10.1037//0735-7044.103.1.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucholz K. K. A review of correlates of alcohol use and alcohol problems in adolescence. Recent Dev Alcohol. 1990;8:111–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Centerwall B. S., Robinette C. D. Twin concordance for dishonorable discharge from the military: with a review of the genetics of antisocial behavior. Compr Psychiatry. 1989 Sep-Oct;30(5):442–446. doi: 10.1016/0010-440x(89)90010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chassin L., Rogosch F., Barrera M. Substance use and symptomatology among adolescent children of alcoholics. J Abnorm Psychol. 1991 Nov;100(4):449–463. doi: 10.1037//0021-843x.100.4.449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloninger C. R. Neurogenetic adaptive mechanisms in alcoholism. Science. 1987 Apr 24;236(4800):410–416. doi: 10.1126/science.2882604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox B. J., Norton G. R., Swinson R. P., Endler N. S. Substance abuse and panic-related anxiety: a critical review. Behav Res Ther. 1990;28(5):385–393. doi: 10.1016/0005-7967(90)90157-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox B. J., Swinson R. P., Shulman I. D., Kuch K., Reichman J. T. Gender effects and alcohol use in panic disorder with agoraphobia. Behav Res Ther. 1993 May;31(4):413–416. doi: 10.1016/0005-7967(93)90099-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabbe J. C., Belknap J. K., Buck K. J. Genetic animal models of alcohol and drug abuse. Science. 1994 Jun 17;264(5166):1715–1723. doi: 10.1126/science.8209252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabbe J. C. Genetic animal models in the study of alcoholism. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1989 Feb;13(1):120–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1989.tb00296.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson D. A., Harford T. C., Grant B. F. Family history as a predictor of alcohol dependence. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1992 Jun;16(3):572–575. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1992.tb01419.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deminiere J. M., Piazza P. V., Le Moal M., Simon H. Experimental approach to individual vulnerability to psychostimulant addiction. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 1989 Summer-Fall;13(2-3):141–147. doi: 10.1016/s0149-7634(89)80023-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depue R. A., Spoont M. R. Conceptualizing a serotonin trait. A behavioral dimension of constraint. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;487:47–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb27885.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditto B. Parental history of essential hypertension, active coping, and cardiovascular reactivity. Psychophysiology. 1986 Jan;23(1):62–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.1986.tb00596.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan-Johnson C. C., Donchin E. On quantifying surprise: the variation of event-related potentials with subjective probability. Psychophysiology. 1977 Sep;14(5):456–467. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.1977.tb01312.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmasian R., Neville H., Woods D., Schuckit M., Bloom F. Event-related brain potentials are different in individuals at high and low risk for developing alcoholism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7900–7903. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emrick C. D. Alcoholics Anonymous: membership characteristics and effectiveness as treatment. Recent Dev Alcohol. 1989;7:37–53. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4899-1678-5_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emrick C. D., Hansen J. Assertions regarding effectiveness of treatment for alcoholism. Fact or fantasy? Am Psychol. 1983 Oct;38(10):1078–1088. doi: 10.1037//0003-066x.38.10.1078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fibiger H. C., Phillips A. G. Mesocorticolimbic dopamine systems and reward. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;537:206–215. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb42107.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fillmore K. M., Midanik L. Chronicity of drinking problems among men: a longitudinal study. J Stud Alcohol. 1984 May;45(3):228–236. doi: 10.15288/jsa.1984.45.228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finn P. R., Earleywine M., Pihl R. O. Sensation seeking, stress reactivity, and alcohol dampening discriminate the density of a family history of alcoholism. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1992 Jun;16(3):585–590. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1992.tb01421.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finn P. R., Pihl R. O. Men at high risk for alcoholism: the effect of alcohol on cardiovascular response to unavoidable shock. J Abnorm Psychol. 1987 Aug;96(3):230–236. doi: 10.1037//0021-843x.96.3.230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finn P. R., Pihl R. O. Risk for alcoholism: a comparison between two different groups of sons of alcoholics on cardiovascular reactivity and sensitivity to alcohol. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1988 Dec;12(6):742–747. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1988.tb01338.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- France C., Ditto B., Adler P. Pain sensitivity in offspring of hypertensives at rest and during baroreflex stimulation. J Behav Med. 1991 Oct;14(5):513–525. doi: 10.1007/BF00845108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank S. J., Jacobson S., Tuer M. Psychological predictors of young adults' drinking behaviors. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1990 Oct;59(4):770–780. doi: 10.1037//0022-3514.59.4.770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frith C. D., Friston K. J., Liddle P. F., Frackowiak R. S. A PET study of word finding. Neuropsychologia. 1991;29(12):1137–1148. doi: 10.1016/0028-3932(91)90029-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabrielli W. F., Jr, Mednick S. A., Volavka J., Pollock V. E., Schulsinger F., Itil T. M. Electroencephalograms in children of alcoholic fathers. Psychophysiology. 1982 Jul;19(4):404–407. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.1982.tb02495.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George D. T., Nutt D. J., Dwyer B. A., Linnoila M. Alcoholism and panic disorder: is the comorbidity more than coincidence? Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1990 Feb;81(2):97–107. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1990.tb06460.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George F. R. Genetic approaches to studying drug abuse: correlates of drug self-administration. Alcohol. 1990 May-Jun;7(3):207–211. doi: 10.1016/0741-8329(90)90006-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George S. R., Roldan L., Lui A., Naranjo C. A. Endogenous opioids are involved in the genetically determined high preference for ethanol consumption. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1991 Aug;15(4):668–672. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1991.tb00576.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gessa G. L., Muntoni F., Collu M., Vargiu L., Mereu G. Low doses of ethanol activate dopaminergic neurons in the ventral tegmental area. Brain Res. 1985 Nov 25;348(1):201–203. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gianoulakis C., Béliveau D., Angelogianni P., Meaney M., Thavundayil J., Tawar V., Dumas M. Different pituitary beta-endorphin and adrenal cortisol response to ethanol in individuals with high and low risk for future development of alcoholism. Life Sci. 1989;45(12):1097–1109. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(89)90167-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gianoulakis C., Gupta A. Endorphins in inbred mice with variable sensitivity to ethanol: effect of acute ethanol treatment. Neuropeptides. 1985 Feb;5(4-6):579–582. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(85)90084-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman M. S., Brown S. A., Christiansen B. A., Smith G. T. Alcoholism and memory: broadening the scope of alcohol-expectancy research. Psychol Bull. 1991 Jul;110(1):137–146. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.110.1.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin D. W., Schulsinger F., Knop J., Mednick S., Guze S. B. Alcoholism and depression in adopted-out daughters of alcoholics. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1977 Jul;34(7):751–755. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1977.01770190013001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin D. W., Schulsinger F., Moller N., Hermansen L., Winokur G., Guze S. B. Drinking problems in adopted and nonadopted sons of alcoholics. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1974 Aug;31(2):164–169. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1974.01760140022003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon T. L., Meehan S. M., Schechter M. D. Differential effects of nicotine but not cathinone on motor activity of P and NP rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1993 Mar;44(3):657–659. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(93)90182-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorelick D. A., Paredes A. Effect of fluoxetine on alcohol consumption in male alcoholics. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1992 Apr;16(2):261–265. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1992.tb01373.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorenstein E. E., Newman J. P. Disinhibitory psychopathology: a new perspective and a model for research. Psychol Rev. 1980 May;87(3):301–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greer N. L., Bartolome J. V., Schanberg S. M. Further evidence for the hypothesis that beta-endorphin mediates maternal deprivation effects. Life Sci. 1991;48(7):643–648. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(91)90539-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harden P. W., Pihl R. O. Cognitive function, cardiovascular reactivity, and behavior in boys at high risk for alcoholism. J Abnorm Psychol. 1995 Feb;104(1):94–103. doi: 10.1037//0021-843x.104.1.94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R. A., Allan A. M. Alcohol intoxication: ion channels and genetics. FASEB J. 1989 Apr;3(6):1689–1695. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.6.2467834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartka E., Johnstone B., Leino E. V., Motoyoshi M., Temple M. T., Fillmore K. M. A meta-analysis of depressive symptomatology and alcohol consumption over time. Br J Addict. 1991 Oct;86(10):1283–1298. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.1991.tb01704.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasin D. S., Grant B. F., Harford T. C., Endicott J. The drug dependence syndrome and related disabilities. Br J Addict. 1988 Jan;83(1):45–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.1988.tb00452.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins J. D., Catalano R. F., Miller J. Y. Risk and protective factors for alcohol and other drug problems in adolescence and early adulthood: implications for substance abuse prevention. Psychol Bull. 1992 Jul;112(1):64–105. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.112.1.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helzer J. E., Pryzbeck T. R. The co-occurrence of alcoholism with other psychiatric disorders in the general population and its impact on treatment. J Stud Alcohol. 1988 May;49(3):219–224. doi: 10.15288/jsa.1988.49.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman B. H., Panksepp J. Effects of morphine and naloxone on separation distress and approach attachment: evidence for opiate mediation of social affect. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1978 Aug;9(2):213–220. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(78)90167-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill S. Y., Steinhauer S., Park J., Zubin J. Event-related potential characteristics in children of alcoholics from high density families. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1990 Feb;14(1):6–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1990.tb00438.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooks M. S., Jones G. H., Smith A. D., Neill D. B., Justice J. B., Jr Individual differences in locomotor activity and sensitization. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1991 Feb;38(2):467–470. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(91)90308-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadden R. M., Cooney N. L., Getter H., Litt M. D. Matching alcoholics to coping skills or interactional therapies: posttreatment results. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1989 Dec;57(6):698–704. doi: 10.1037//0022-006x.57.6.698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan R. F., Cooney N. L., Baker L. H., Gillespie R. A., Meyer R. E., Pomerleau O. F. Reactivity to alcohol-related cues: physiological and subjective responses in alcoholics and nonproblem drinkers. J Stud Alcohol. 1985 Jul;46(4):267–272. doi: 10.15288/jsa.1985.46.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehoe P., Blass E. M. Behaviorally functional opioid systems in infant rats: II. Evidence for pharmacological, physiological, and psychological mediation of pain and stress. Behav Neurosci. 1986 Oct;100(5):624–630. doi: 10.1037//0735-7044.100.5.624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendler K. S., Neale M. C., Kessler R. C., Heath A. C., Eaves L. J. A population-based twin study of major depression in women. The impact of varying definitions of illness. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1992 Apr;49(4):257–266. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1992.01820040009001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler R. C., McGonagle K. A., Zhao S., Nelson C. B., Hughes M., Eshleman S., Wittchen H. U., Kendler K. S. Lifetime and 12-month prevalence of DSM-III-R psychiatric disorders in the United States. Results from the National Comorbidity Survey. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1994 Jan;51(1):8–19. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1994.03950010008002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles P. A., Conner R. L., Panksepp J. Opiate effects on social behavior of juvenile dogs as a function of social deprivation. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1989 Jul;33(3):533–537. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(89)90382-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koob G. F., Bloom F. E. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of drug dependence. Science. 1988 Nov 4;242(4879):715–723. doi: 10.1126/science.2903550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koob G. F., Swerdlow N. R. The functional output of the mesolimbic dopamine system. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;537:216–227. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb42108.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krantz D. S., Manuck S. B. Acute psychophysiologic reactivity and risk of cardiovascular disease: a review and methodologic critique. Psychol Bull. 1984 Nov;96(3):435–464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krimmer E. C., Schechter M. D. HAD and LAD rats respond differently to stimulating effect but not discriminative effects of ethanol. Alcohol. 1992 Jan-Feb;9(1):71–74. doi: 10.1016/0741-8329(92)90012-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushner M. G., Sher K. J., Beitman B. D. The relation between alcohol problems and the anxiety disorders. Am J Psychiatry. 1990 Jun;147(6):685–695. doi: 10.1176/ajp.147.6.685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laberg J. C., Ellertsen B. Psychophysiological indicators of craving in alcoholics: effects of cue exposure. Br J Addict. 1987 Dec;82(12):1341–1348. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.1987.tb00437.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeMarquand D., Pihl R. O., Benkelfat C. Serotonin and alcohol intake, abuse, and dependence: clinical evidence. Biol Psychiatry. 1994 Sep 1;36(5):326–337. doi: 10.1016/0006-3223(94)90630-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeMarquand D., Pihl R. O., Benkelfat C. Serotonin and alcohol intake, abuse, and dependence: findings of animal studies. Biol Psychiatry. 1994 Sep 15;36(6):395–421. doi: 10.1016/0006-3223(94)91215-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovinger D. M., White G., Weight F. F. Ethanol inhibits NMDA-activated ion current in hippocampal neurons. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1721–1724. doi: 10.1126/science.2467382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin N. G., Eaves L. J., Fulker D. W. The genetical relationship of impulsiveness and sensation seeking to Eysenck's personality dimensions. Acta Genet Med Gemellol (Roma) 1979;28(3):197–210. doi: 10.1017/s0001566000009053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer J., Myerson D. J. Outpatient treatment of alcoholics. Effects of status, stability and nature of treatment. Q J Stud Alcohol. 1971 Sep;32(3):620–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride W. J., Murphy J. M., Lumeng L., Li T. K. Serotonin, dopamine and GABA involvement in alcohol drinking of selectively bred rats. Alcohol. 1990 May-Jun;7(3):199–205. doi: 10.1016/0741-8329(90)90005-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuffin P., Katz R. The genetics of depression and manic-depressive disorder. Br J Psychiatry. 1989 Sep;155:294–304. doi: 10.1192/bjp.155.3.294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLellan A. T., Luborsky L., Woody G. E., O'Brien C. P., Druley K. A. Predicting response to alcohol and drug abuse treatments. Role of psychiatric severity. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1983 Jun;40(6):620–625. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1983.04390010030004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNally R. J., Lorenz M. Anxiety sensitivity in agoraphobics. J Behav Ther Exp Psychiatry. 1987 Mar;18(1):3–11. doi: 10.1016/0005-7916(87)90065-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehta A. K., Ticku M. K. Ethanol potentiation of GABAergic transmission in cultured spinal cord neurons involves gamma-aminobutyric acidA-gated chloride channels. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Aug;246(2):558–564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelson J. H., Mello N. K. Medical progress. Biologic concomitants of alcoholism. N Engl J Med. 1979 Oct 25;301(17):912–921. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197910253011704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merikangas K. R., Gelernter C. S. Comorbidity for alcoholism and depression. Psychiatr Clin North Am. 1990 Dec;13(4):613–632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner B., Petrides M., Smith M. L. Frontal lobes and the temporal organization of memory. Hum Neurobiol. 1985;4(3):137–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. D., Bone L. R., Geller G., Mamon J. A., Stokes E. J., Levine D. M. Prevalence, detection, and treatment of alcoholism in hospitalized patients. JAMA. 1989 Jan 20;261(3):403–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murdoch D., Pihl R. O., Ross D. Alcohol and crimes of violence: present issues. Int J Addict. 1990 Sep;25(9):1065–1081. doi: 10.3109/10826089009058873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nace E. P. Recent developments in alcoholism: inpatient treatment. Recent Dev Alcohol. 1993;11:429–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadel L. The hippocampus and space revisited. Hippocampus. 1991 Jul;1(3):221–229. doi: 10.1002/hipo.450010302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Najam N., Panksepp J. Effect of chronic neonatal morphine and naloxone on sensorimotor and social development of young rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1989 Jul;33(3):539–544. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(89)90383-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naranjo C. A., Sullivan J. T., Kadlec K. E., Woodley-Remus D. V., Kennedy G., Sellers E. M. Differential effects of viqualine on alcohol intake and other consummatory behaviors. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1989 Sep;46(3):301–309. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1989.142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcomb M. D., Maddahian E., Bentler P. M. Risk factors for drug use among adolescents: concurrent and longitudinal analyses. Am J Public Health. 1986 May;76(5):525–531. doi: 10.2105/ajph.76.5.525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newlin D. B., Thomson J. B. Alcohol challenge with sons of alcoholics: a critical review and analysis. Psychol Bull. 1990 Nov;108(3):383–402. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.108.3.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton G. R., Rockman G. E., Luy B., Marion T. Suicide, chemical abuse, and panic attacks: a preliminary report. Behav Res Ther. 1993 Jan;31(1):37–40. doi: 10.1016/0005-7967(93)90040-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley S. S., Jaffe A. J., Chang G., Schottenfeld R. S., Meyer R. E., Rounsaville B. Naltrexone and coping skills therapy for alcohol dependence. A controlled study. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1992 Nov;49(11):881–887. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1992.01820110045007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada Y. C., Kaufman L., Williamson S. J. The hippocampal formation as a source of the slow endogenous potentials. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1983 Apr;55(4):417–426. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(83)90130-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olenick N. L., Chalmers D. K. Gender-specific drinking styles in alcoholics and nonalcoholics. J Stud Alcohol. 1991 Jul;52(4):325–330. doi: 10.15288/jsa.1991.52.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks R. W., Loewenstein D. A., Dodrill K. L., Barker W. W., Yoshii F., Chang J. Y., Emran A., Apicella A., Sheramata W. A., Duara R. Cerebral metabolic effects of a verbal fluency test: a PET scan study. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 1988 Oct;10(5):565–575. doi: 10.1080/01688638808402795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen W., Clausen S. E., Lavik N. J. Patterns of drug use and sensation-seeking among adolescents in Norway. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1989 Apr;79(4):386–390. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1989.tb10274.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen W. Mental health, sensation seeking and drug use patterns: a longitudinal study. Br J Addict. 1991 Feb;86(2):195–204. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.1991.tb01769.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peroutka S. J., Schmidt A. W., Sleight A. J., Harrington M. A. Serotonin receptor "families" in the central nervous system: an overview. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;600:104–113. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb16876.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson J. B., Pihl R. O. Information processing, neuropsychological function, and the inherited predisposition to alcoholism. Neuropsychol Rev. 1990 Dec;1(4):343–369. doi: 10.1007/BF01109029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson J. B., Pihl R. O., Séguin J. R., Finn P. R., Stewart S. H. Heart-rate reactivity and alcohol consumption among sons of male alcoholics and sons of non-alcoholics. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 1993 Jul;18(4):190–198. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson J. B., Rothfleisch J., Zelazo P. D., Pihl R. O. Acute alcohol intoxication and cognitive functioning. J Stud Alcohol. 1990 Mar;51(2):114–122. doi: 10.15288/jsa.1990.51.114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrides M., Alivisatos B., Evans A. C., Meyer E. Dissociation of human mid-dorsolateral from posterior dorsolateral frontal cortex in memory processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 1;90(3):873–877. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.3.873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrides M., Alivisatos B., Meyer E., Evans A. C. Functional activation of the human frontal cortex during the performance of verbal working memory tasks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 1;90(3):878–882. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.3.878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrides M. Nonspatial conditional learning impaired in patients with unilateral frontal but not unilateral temporal lobe excisions. Neuropsychologia. 1990;28(2):137–149. doi: 10.1016/0028-3932(90)90096-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piazza P. V., Deminière J. M., Le Moal M., Simon H. Factors that predict individual vulnerability to amphetamine self-administration. Science. 1989 Sep 29;245(4925):1511–1513. doi: 10.1126/science.2781295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pihl R. O., Giancola P. R., Peterson J. B. Cardiovascular reactivity as a predictor of alcohol consumption in a taste test situation. J Clin Psychol. 1994 Mar;50(2):280–286. doi: 10.1002/1097-4679(199403)50:2<280::aid-jclp2270500222>3.0.co;2-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pihl R. O., Peterson J., Finn P. Inherited predisposition to alcoholism: characteristics of sons of male alcoholics. J Abnorm Psychol. 1990 Aug;99(3):291–301. doi: 10.1037//0021-843x.99.3.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock V. E., Volavka J., Goodwin D. W., Mednick S. A., Gabrielli W. F., Knop J., Schulsinger F. The EEG after alcohol administration in men at risk for alcoholism. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1983 Aug;40(8):857–861. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1983.01790070047006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson J., Robertson J. Young children in brief separation. A fresh look. Psychoanal Study Child. 1971;26:264–315. doi: 10.1080/00797308.1971.11822274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rounsaville B. J., Kosten T. R., Weissman M. M., Prusoff B., Pauls D., Anton S. F., Merikangas K. Psychiatric disorders in relatives of probands with opiate addiction. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1991 Jan;48(1):33–42. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1991.01810250035004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sangameswaran L., Fales H. M., Friedrich P., De Blas A. L. Purification of a benzodiazepine from bovine brain and detection of benzodiazepine-like immunoreactivity in human brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9236–9240. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuckit M. A. Genetic and clinical implications of alcoholism and affective disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 1986 Feb;143(2):140–147. doi: 10.1176/ajp.143.2.140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz-Stevens K., Samson H. H., Tolliver G. A., Lumeng L., Li T. K. The effects of ethanol initiation procedures on ethanol reinforced behavior in the alcohol-preferring rat. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1991 Mar;15(2):277–285. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1991.tb01869.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shedler J., Block J. Adolescent drug use and psychological health. A longitudinal inquiry. Am Psychol. 1990 May;45(5):612–630. doi: 10.1037//0003-066x.45.5.612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shide D. J., Blass E. M. Opioidlike effects of intraoral infusions of corn oil and polycose on stress reactions in 10-day-old rats. Behav Neurosci. 1989 Dec;103(6):1168–1175. doi: 10.1037//0735-7044.103.6.1168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spoont M. R. Modulatory role of serotonin in neural information processing: implications for human psychopathology. Psychol Bull. 1992 Sep;112(2):330–350. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.112.2.330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart S. H., Finn P. R., Pihl R. O. The effects of alcohol on the cardiovascular stress response in men at high risk for alcoholism: a dose response study. J Stud Alcohol. 1992 Sep;53(5):499–506. doi: 10.15288/jsa.1992.53.499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarter R. E., Alterman A. I., Edwards K. L. Vulnerability to alcoholism in men: a behavior-genetic perspective. J Stud Alcohol. 1985 Jul;46(4):329–356. doi: 10.15288/jsa.1985.46.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarter R. E., Kabene M., Escallier E. A., Laird S. B., Jacob T. Temperament deviation and risk for alcoholism. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1990 Jun;14(3):380–382. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1990.tb00490.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Telch M. J., Lucas J. A., Schmidt N. B., Hanna H. H., LaNae Jaimez T., Lucas R. A. Group cognitive-behavioral treatment of panic disorder. Behav Res Ther. 1993 Mar;31(3):279–287. doi: 10.1016/0005-7967(93)90026-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokar J. T., Brunse A. J., Stefflre V. J., Sodergren J. A., Napior D. A. Determining what heroin means to heroin addicts. Dis Nerv Syst. 1975 Feb;36(2):77–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tremblay R. E., Loeber R., Gagnon C., Charlebois P., Larivée S., LeBlanc M. Disruptive boys with stable and unstable high fighting behavior patterns during junior elementary school. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 1991 Jun;19(3):285–300. doi: 10.1007/BF00911232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tremblay R. E., Pihl R. O., Vitaro F., Dobkin P. L. Predicting early onset of male antisocial behavior from preschool behavior. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1994 Sep;51(9):732–739. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1994.03950090064009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpicelli J. R., Alterman A. I., Hayashida M., O'Brien C. P. Naltrexone in the treatment of alcohol dependence. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1992 Nov;49(11):876–880. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1992.01820110040006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warneke L. B. Benzodiazepines: abuse and new use. Can J Psychiatry. 1991 Apr;36(3):194–205. doi: 10.1177/070674379103600308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker-Azmitia P. M., Shemer A. V., Caruso J., Molino L., Azmitia E. C. Role of high affinity serotonin receptors in neuronal growth. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;600:315–330. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb16892.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winokur G., Coryell W. Familial alcoholism in primary unipolar major depressive disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 1991 Feb;148(2):184–188. doi: 10.1176/ajp.148.2.184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winokur G. The development and validity of familial subtypes in primary unipolar depression. Pharmacopsychiatria. 1982 Jul;15(4):142–146. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1019527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R. A., Bozarth M. A. A psychomotor stimulant theory of addiction. Psychol Rev. 1987 Oct;94(4):469–492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R. A. Psychomotor stimulant properties of addictive drugs. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;537:228–234. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb42109.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zorumski C. F., Isenberg K. E. Insights into the structure and function of GABA-benzodiazepine receptors: ion channels and psychiatry. Am J Psychiatry. 1991 Feb;148(2):162–173. doi: 10.1176/ajp.148.2.162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



