Abstract
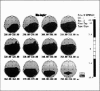
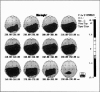
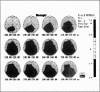
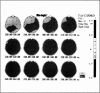
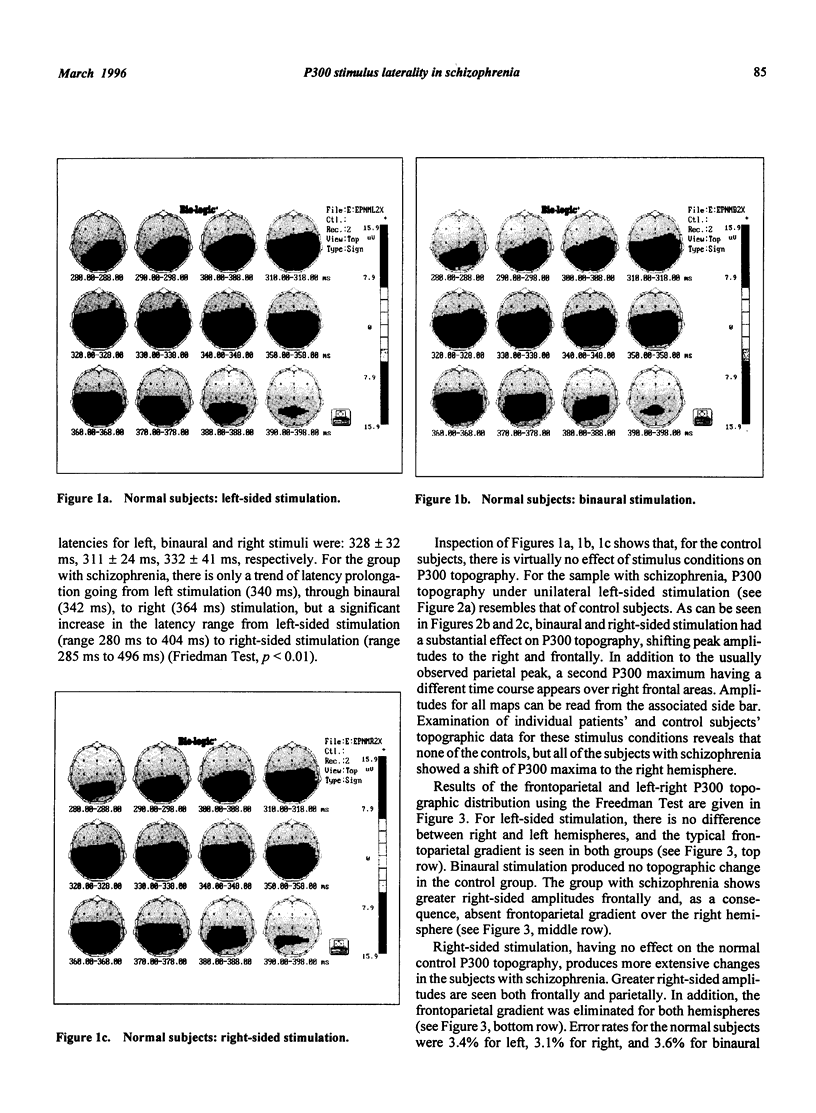
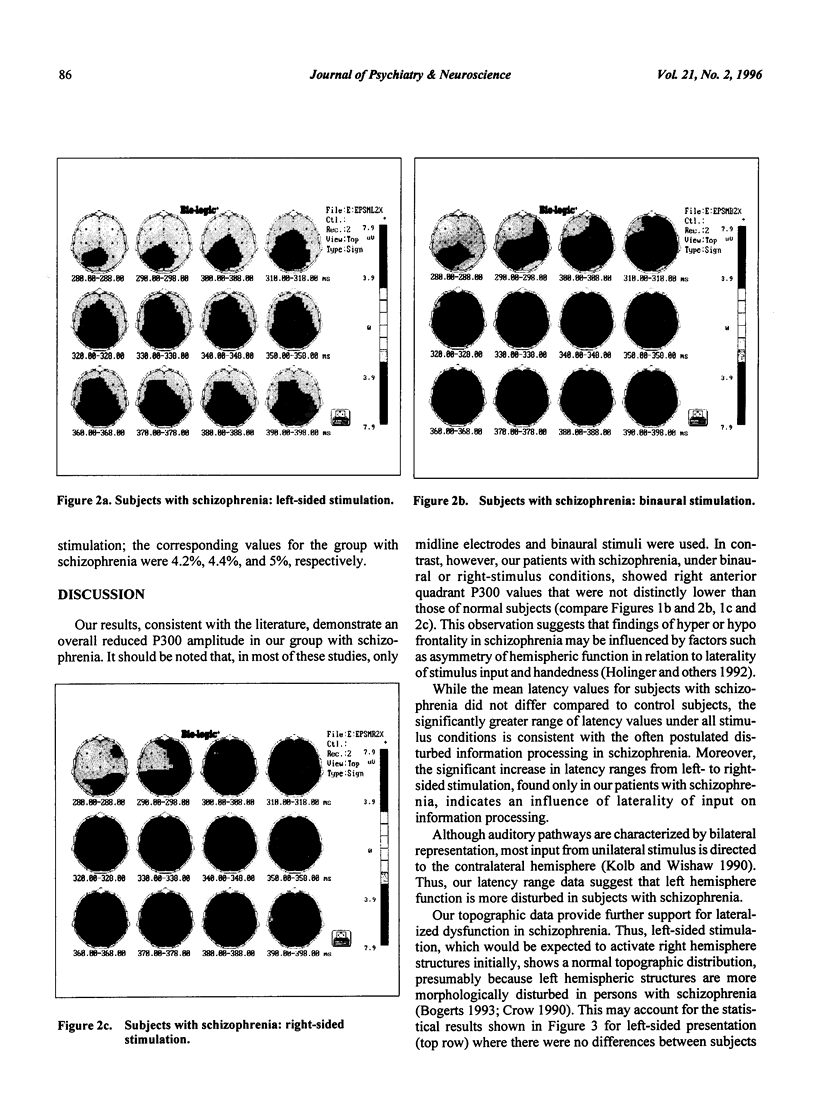
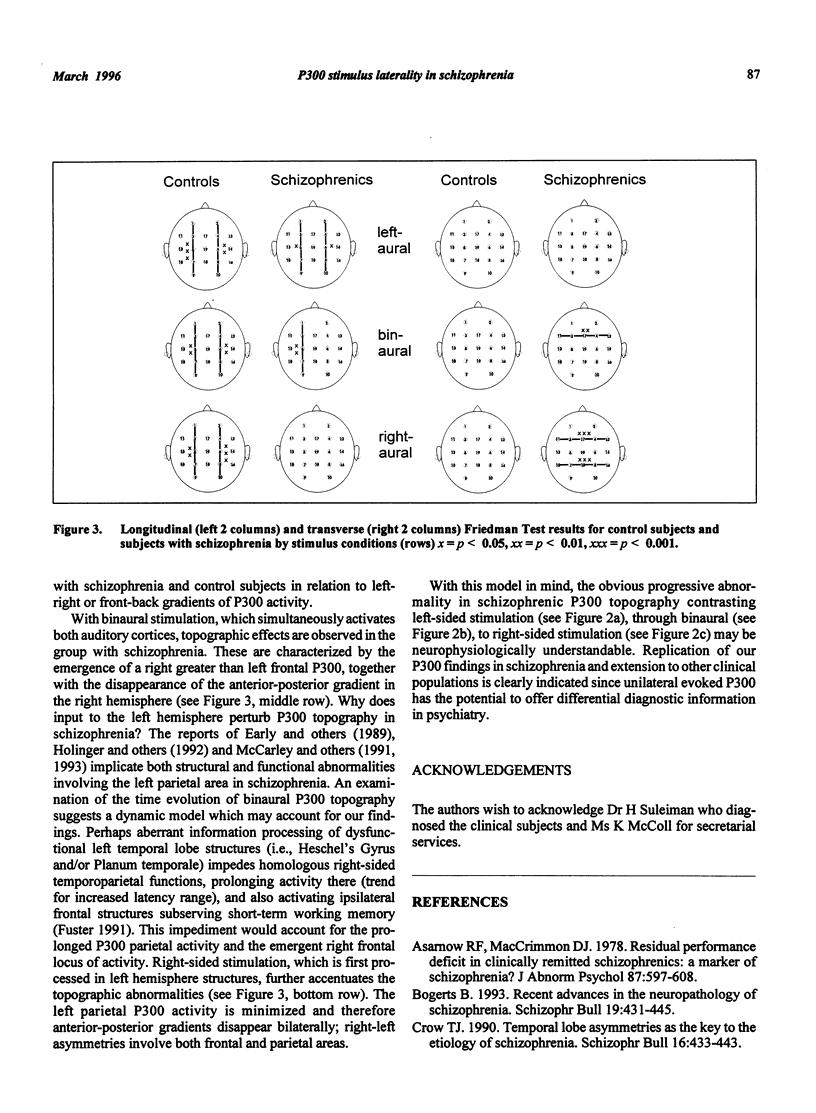
Reduced P300 amplitude in schizophrenia has been a consistent finding. Recent studies have raised the question of characteristic topographic distribution. This study reports the effects of binaural and unilateral stimuli on the P300 topography in schizophrenia. An auditory "oddball" paradigm was repeated 3 times with left, right and binaural stimulation. Data were recorded using a 19-electrode montage with linked ear reference. Subjects were 18 untreated, hallucinating, paranoid patients with schizophrenia and 24 healthy matched volunteers. For the control subjects, stimulus conditions had no effect on P300 topography. For the sample with schizophrenia, topography under unilateral left stimulation resembled that of control subjects. Binaural and right-sided stimulation shifted peak amplitudes to the right and frontally. In addition to the usually observed parietal peak, a second P300 maximum having a different time course appeared over right frontal areas. The data provide further support for lateralized dysfunction in schizophrenia.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asarnow R. F., MacCrimmon D. J. Residual performance deficit in clinically remitted schizophrenics: a marker of schizophrenia? J Abnorm Psychol. 1978 Dec;87(6):597–608. doi: 10.1037//0021-843x.87.6.597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogerts B. Recent advances in the neuropathology of schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. 1993;19(2):431–445. doi: 10.1093/schbul/19.2.431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crow T. J. Temporal lobe asymmetries as the key to the etiology of schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. 1990;16(3):433–443. doi: 10.1093/schbul/16.3.433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Early T. S., Posner M. I., Reiman E. M., Raichle M. E. Hyperactivity of the left striato-pallidal projection. Part I: Lower level theory. Psychiatr Dev. 1989 Summer;7(2):85–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faux S. F., Torello M. W., McCarley R. W., Shenton M. E., Duffy F. H. P300 in schizophrenia: confirmation and statistical validation of temporal region deficit in P300 topography. Biol Psychiatry. 1988 Apr 15;23(8):776–790. doi: 10.1016/0006-3223(88)90066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D., Squires-Wheeler E. Event-related potentials (ERPs) as indicators of risk for schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. 1994;20(1):63–74. doi: 10.1093/schbul/20.1.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuster J. M. The prefrontal cortex and its relation to behavior. Prog Brain Res. 1991;87:201–211. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)63053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holinger D. P., Faux S. F., Shenton M. E., Sokol N. S., Seidman L. J., Green A. I., McCarley R. W. Reversed temporal region asymmetries of P300 topography in left- and right-handed schizophrenic subjects. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1992 Nov-Dec;84(6):532–537. doi: 10.1016/0168-5597(92)90042-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer K., Dierks T., Strik W. K., Frölich L. P3 topography in psychiatry and psychopharmacology. Brain Topogr. 1990 Fall;3(1):79–84. doi: 10.1007/BF01128864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer K., Dierks T. Topographie der P300 in der Psychiatrie--I. Kognitive P300-Felder bei Psychosen. EEG EMG Z Elektroenzephalogr Elektromyogr Verwandte Geb. 1988 Mar;19(1):21–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarley R. W., Faux S. F., Shenton M. E., Nestor P. G., Adams J. Event-related potentials in schizophrenia: their biological and clinical correlates and a new model of schizophrenic pathophysiology. Schizophr Res. 1991 Mar-Apr;4(2):209–231. doi: 10.1016/0920-9964(91)90034-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarley R. W., Shenton M. E., O'Donnell B. F., Faux S. F., Kikinis R., Nestor P. G., Jolesz F. A. Auditory P300 abnormalities and left posterior superior temporal gyrus volume reduction in schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1993 Mar;50(3):190–197. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1993.01820150036003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfefferbaum A., Ford J. M., White P. M., Roth W. T. P3 in schizophrenia is affected by stimulus modality, response requirements, medication status, and negative symptoms. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1989 Nov;46(11):1035–1044. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1989.01810110077011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strik W. K., Dierks T., Franzek E., Stöber G., Maurer K. P300 asymmetries in schizophrenia revisited with reference-independent methods. Psychiatry Res. 1994 Sep;55(3):153–166. doi: 10.1016/0925-4927(94)90023-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]