Abstract
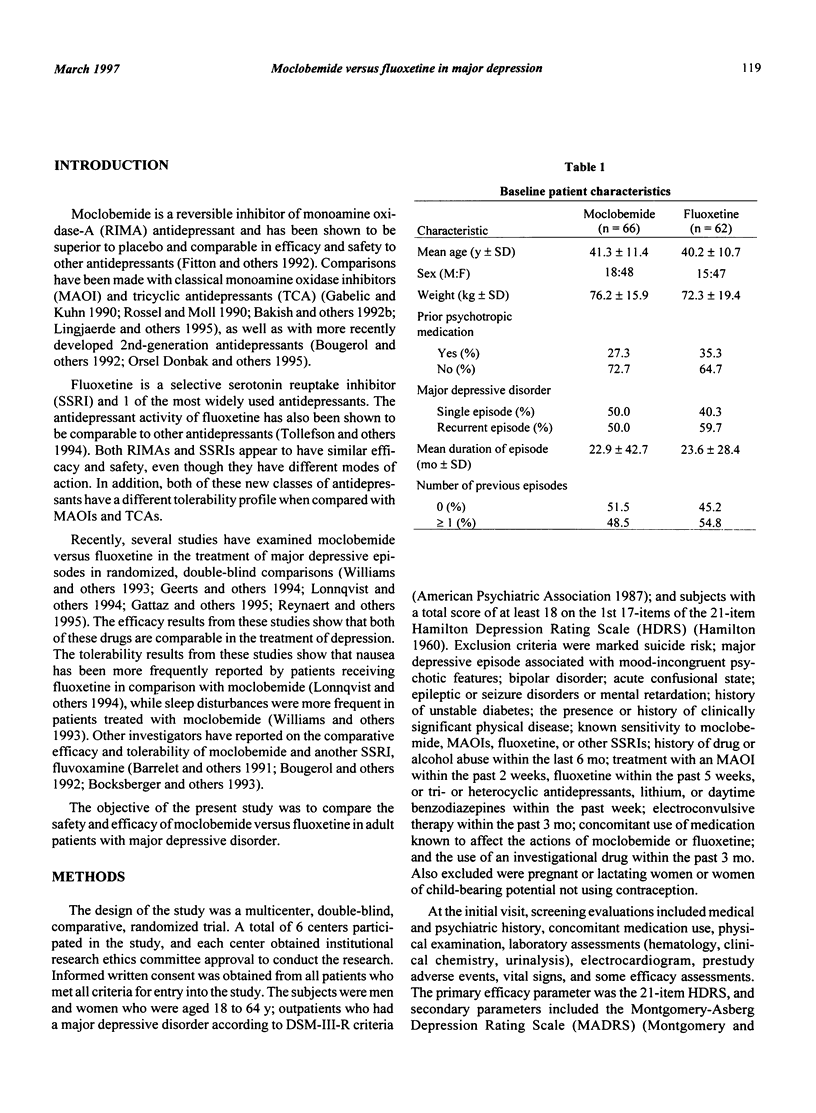
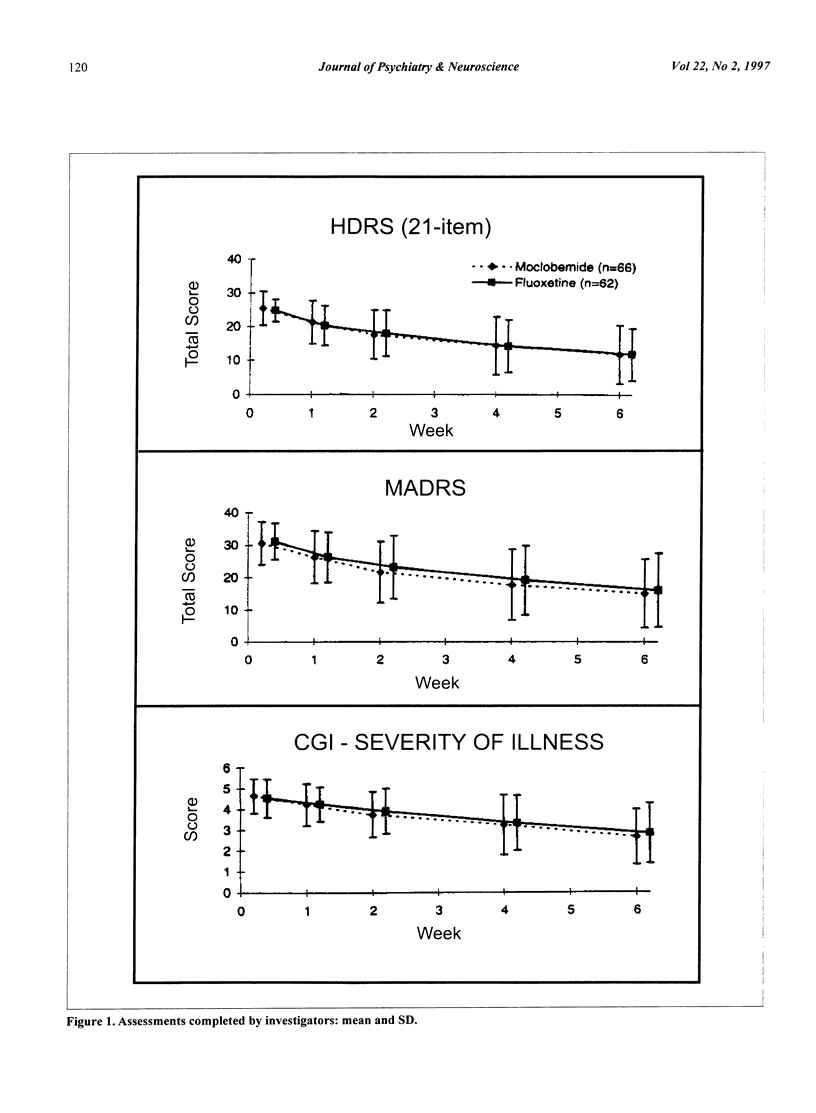
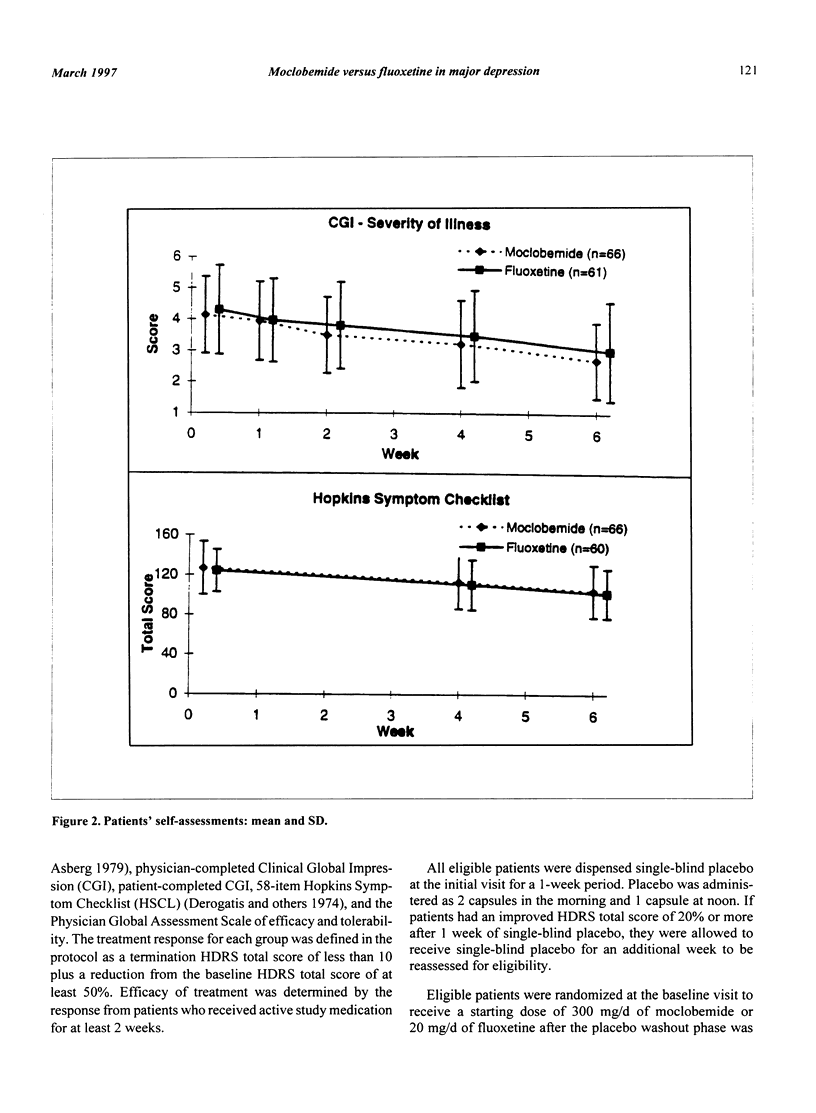
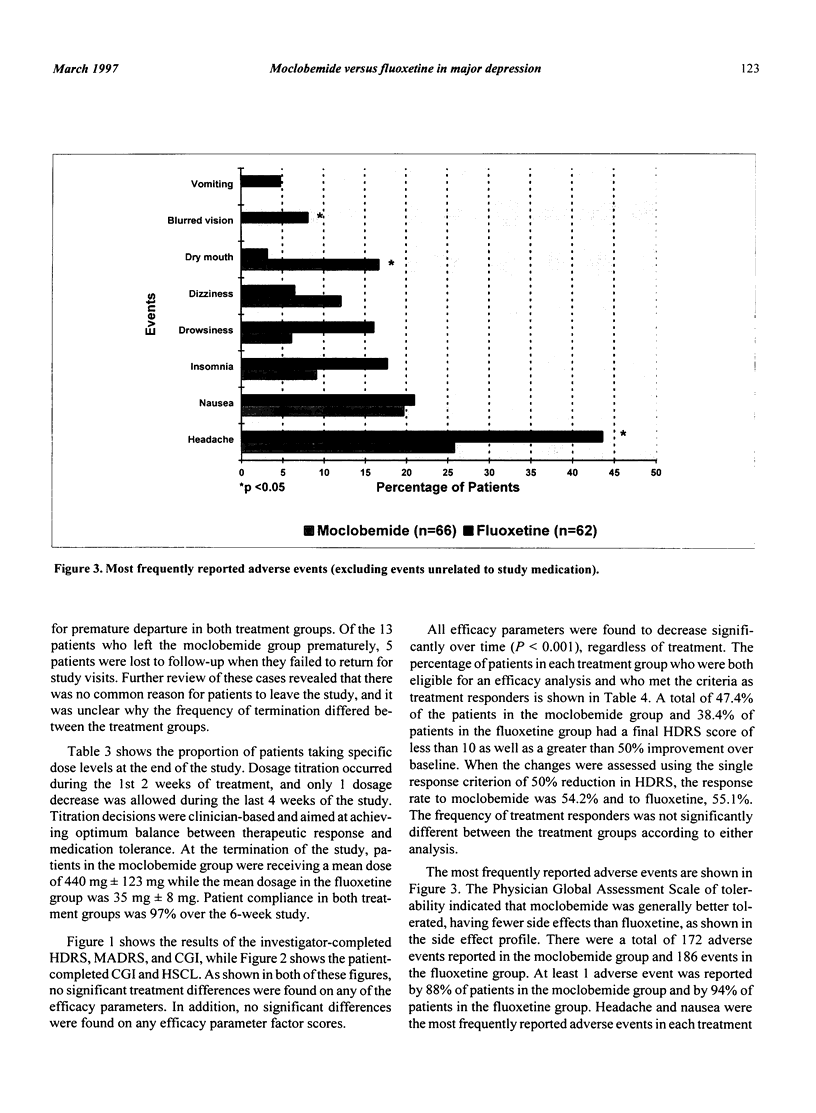
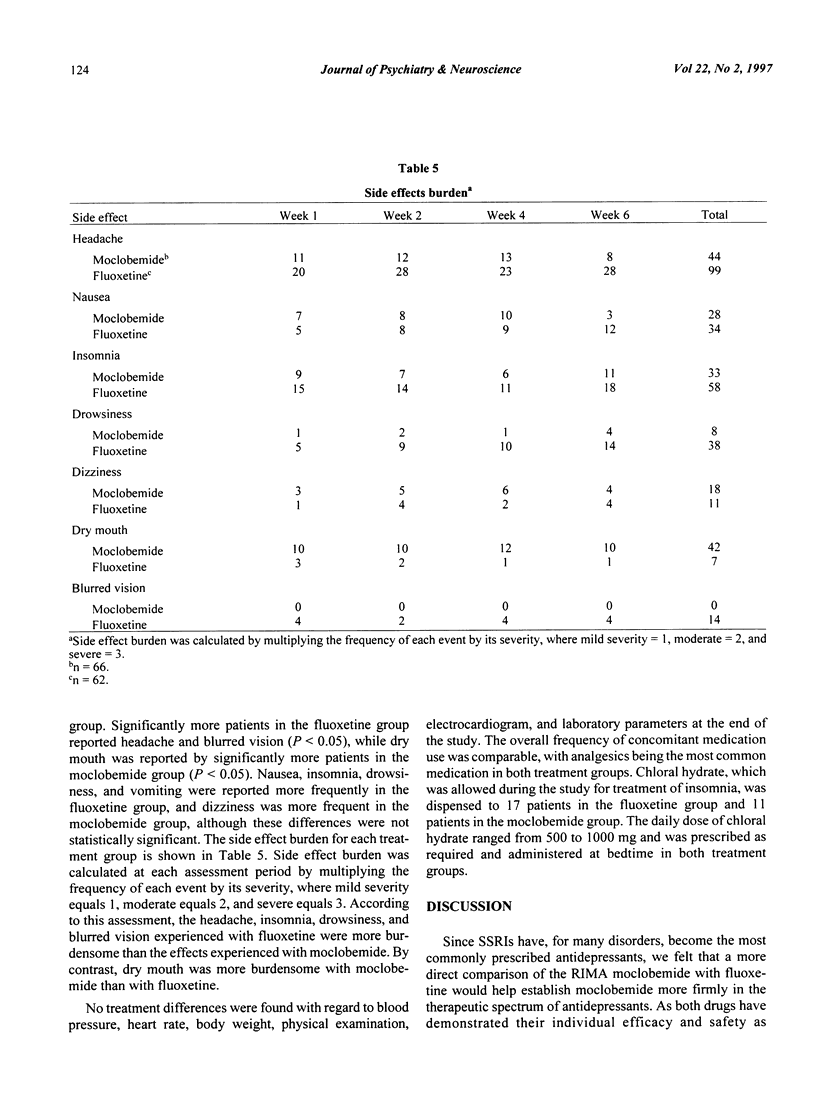
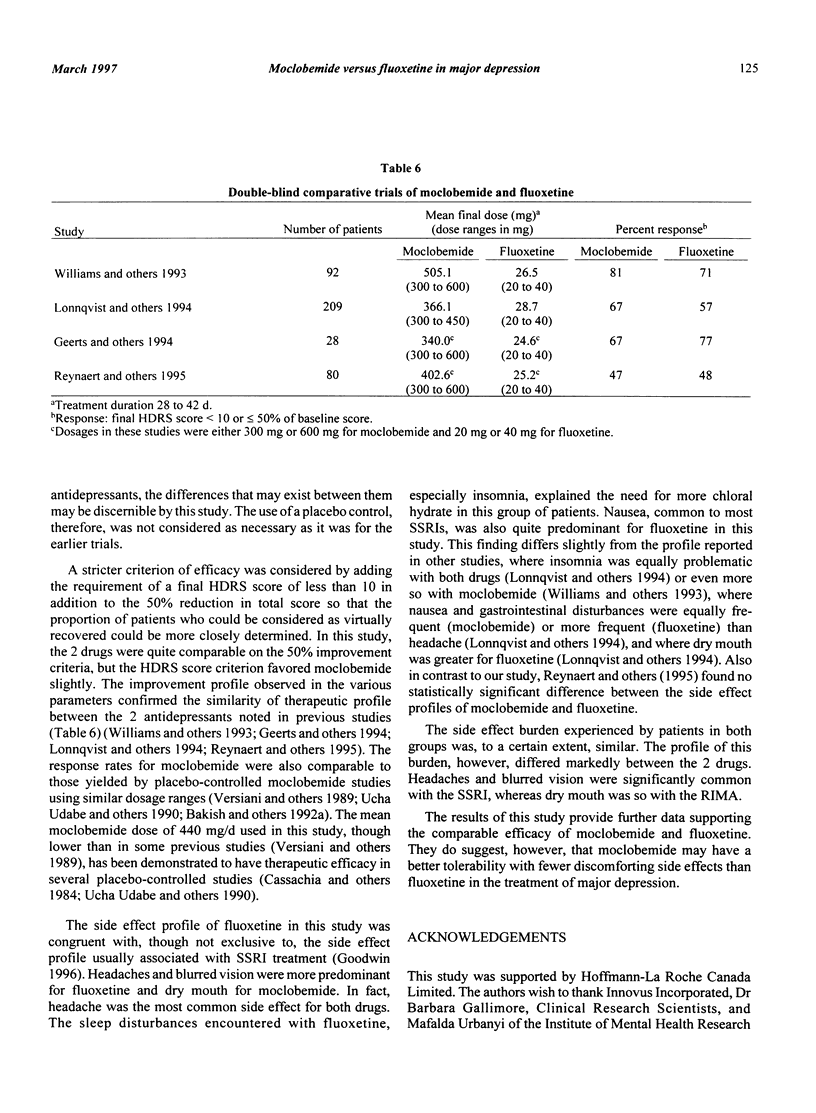
The objective of the present study was to compare the safety and efficacy of moclobemide versus fluoxetine in adult patients with major depressive disorder. The design of the study was a multicenter, double-blind, comparative, and randomized trial. A 1- to 2-week single-blind placebo washout phase was followed by 6 weeks of double-blind treatment with moclobemide or fluoxetine. A total of 150 patients were enrolled in the study. There were 128 patients eligible to be randomized, with 66 patients receiving moclobemide and 62 patients receiving fluoxetine. At the termination of the study, patients in the moclobemide group were receiving a mean dose of 440 mg +/- 123 mg, while the mean dose in the fluoxetine group was 35 mg +/- 8 mg. No significant treatment differences were found for any of the efficacy parameters. Headache and nausea were the most frequently reported adverse events in both treatment groups. Headache and blurred vision were reported significantly more often (P < 0.05) in the fluoxetine group, whereas significantly more dry mouth was reported (P < 0.05) in the moclobemide group. These results provide supporting evidence of the comparable efficacy of moclobemide and fluoxetine and the better tolerability of moclobemide when used in the treatment of major depressive disorder.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakish D., Bradwejn J., Nair N., McClure J., Remick R., Bulger L. A comparison of moclobemide, amitriptyline and placebo in depression: a Canadian multicentre study. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1992;106 (Suppl):S98–101. doi: 10.1007/BF02246248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrelet L., Blajev B., Bolzani L., de Saussure C., Kasas A., Van H., Gachoud J. P. Etude multicentrique comparant l'efficacité et la tolérance du moclobémide et de la fluvoxamine chez des patients hospitalisés et ambulatoires présentant un épisode dépressif majeur. Schweiz Rundsch Med Prax. 1991 May 7;80(19):524–528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll B. T. Complications of catatonia. J Clin Psychiatry. 1996 Feb;57(2):95–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casacchia M., Carolei A., Barba C., Frontoni M., Rossi A., Meco G., Zylberman M. R. A placebo-controlled study of the antidepressant activity of moclobemide, a new MAO-A inhibitor. Pharmacopsychiatry. 1984 Jul;17(4):122–125. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1017421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derogatis L. R., Lipman R. S., Rickels K., Uhlenhuth E. H., Covi L. The Hopkins Symptom Checklist (HSCL): a self-report symptom inventory. Behav Sci. 1974 Jan;19(1):1–15. doi: 10.1002/bs.3830190102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitton A., Faulds D., Goa K. L. Moclobemide. A review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic use in depressive illness. Drugs. 1992 Apr;43(4):561–596. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199243040-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gattaz W. F., Vogel P., Kick H., Kohnen R. Moclobemide versus fluoxetine in the treatment of inpatients with major depression. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1995 Aug;15(4 Suppl 2):35S–40S. doi: 10.1097/00004714-199508001-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMILTON M. A rating scale for depression. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1960 Feb;23:56–62. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.23.1.56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingjaerde O., Jørgensen J., Støren R., Thomle S., Wendt Raeder L., Ruud L. E., Schetelig E., Sveaas H. K., Leivestad O. A double-blind comparison of moclobemide and doxepin in depressed general practice patients. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1995 Aug;92(2):125–131. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1995.tb09555.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonnqvist J., Sintonen H., Syvälahti E., Appelberg B., Koskinen T., Mannikko T., Mehtonen O. P., Naarala M., Sihvo S., Auvinen J. Antidepressant efficacy and quality of life in depression: a double-blind study with moclobemide and fluoxetine. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1994 Jun;89(6):363–369. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1994.tb01530.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery S. A., Asberg M. A new depression scale designed to be sensitive to change. Br J Psychiatry. 1979 Apr;134:382–389. doi: 10.1192/bjp.134.4.382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orsel Donbak S., Turkçapar M. H., Ozturk Kiliç E. Z., Demirergi N., Akdemir A., Sirin A., Ozbay M. H. Moclobemide and sertraline in the treatment of depressive disorders: a comparative study. Acta Psychiatr Belg. 1995 May-Jun;95(3):139–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynaert C., Parent M., Mirel J., Janne P., Haazen L. Moclobemide versus fluoxetine for a major depressive episode. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1995 Mar;118(2):183–187. doi: 10.1007/BF02245838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollefson G. D., Holman S. L., Sayler M. E., Potvin J. H. Fluoxetine, placebo, and tricyclic antidepressants in major depression with and without anxious features. J Clin Psychiatry. 1994 Feb;55(2):50–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R., Edwards R. A., Newburn G. M., Mullen R., Menkes D. B., Segkar C. A double-blind comparison of moclobemide and fluoxetine in the treatment of depressive disorders. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 1993 Jan;7(3-4):155–158. doi: 10.1097/00004850-199300730-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



