Abstract
Galanin is a 29-amino-acid neuropeptide that is widely distributed in the mammalian central nervous system. Galanin-immunoreactive cell bodies, fibres and terminals, and galanin binding sites, are located in the basal forebrain of rats, monkeys and humans. Galanin fibres hyperinnervate the surviving cholinergic cell bodies in patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD). In rats, galanin inhibits acetylcholine release and produces deficits in learning and memory. These findings suggest that overexpressed galanin may contribute to the cognitive impairments exhibited by patients with AD. This paper reviews the literature on galanin distribution and function in light of its putative role in the mnemonic deficits in patients with AD, the effects of galanin on tests of learning and memory, and preliminary experiments with galanin antagonists in animal models of AD.
Full text
PDF













Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abas M. A., Sahakian B. J., Levy R. Neuropsychological deficits and CT scan changes in elderly depressives. Psychol Med. 1990 Aug;20(3):507–520. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700017025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agoston D. V., Komoly S., Palkovits M. Selective up-regulation of neuropeptide synthesis by blocking the neuronal activity: galanin expression in septohippocampal neurons. Exp Neurol. 1994 Apr;126(2):247–255. doi: 10.1006/exnr.1994.1062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahrén B., Böttcher G., Kowalyk S., Dunning B. E., Sundler F., Taborsky G. J., Jr Galanin is co-localized with noradrenaline and neuropeptide Y in dog pancreas and celiac ganglion. Cell Tissue Res. 1990 Jul;261(1):49–58. doi: 10.1007/BF00329437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akabayashi A., Koenig J. I., Watanabe Y., Alexander J. T., Leibowitz S. F. Galanin-containing neurons in the paraventricular nucleus: a neurochemical marker for fat ingestion and body weight gain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Oct 25;91(22):10375–10379. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.22.10375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amoroso D., Girotti P., Fisone G., Bartfai T., Consolo S. Mechanism of the galanin induced increase in acetylcholine release in vivo from striata of freely moving rats. Brain Res. 1992 Aug 28;589(1):33–38. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)91158-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amoroso D., Girotti P., Fisone G., Bartfai T., Consolo S. Mechanism of the galanin induced increase in acetylcholine release in vivo from striata of freely moving rats. Brain Res. 1992 Aug 28;589(1):33–38. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)91158-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arvat E., Gianotti L., Ramunni J., Grottoli S., Brossa P. C., Bertagna A., Camanni F., Ghigo E. Effect of galanin on basal and stimulated secretion of prolactin, gonadotropins, thyrotropin, adrenocorticotropin and cortisol in humans. Eur J Endocrinol. 1995 Sep;133(3):300–304. doi: 10.1530/eje.0.1330300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arvidsson K., Land T., Langel U., Bartfai T., Ehrenberg A. Solution structure by 2D 1H-NMR of a chimeric peptide recognized by galanin and neuropeptide Y receptors. Biochemistry. 1993 Aug 3;32(30):7787–7798. doi: 10.1021/bi00081a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arvidsson K., Langel U., Ehrenberg A. Comparison of the solution structures of the chimeric peptides galanin(1-12)-Ala-neuropeptide Y(25-36)amide and galanin(1-12)-Pro-neuropeptide Y(25-36)amide. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Jun 1;222(2):573–581. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb18899.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball M. J. Topographic distribution of neurofibrillary tangles and granulovacuolar degeneration in hippocampal cortex of aging and demented patients. A quantitative study. Acta Neuropathol. 1978 May 24;42(2):73–80. doi: 10.1007/BF00690970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartfai T., Bedecs K., Land T., Langel U., Bertorelli R., Girotti P., Consolo S., Xu X. J., Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z., Nilsson S. M-15: high-affinity chimeric peptide that blocks the neuronal actions of galanin in the hippocampus, locus coeruleus, and spinal cord. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10961–10965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartfai T., Fisone G., Langel U. Galanin and galanin antagonists: molecular and biochemical perspectives. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Aug;13(8):312–317. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90098-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartfai T., Hökfelt T., Langel U. Galanin--a neuroendocrine peptide. Crit Rev Neurobiol. 1993;7(3-4):229–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartfai T., Langel U., Bedecs K., Andell S., Land T., Gregersen S., Ahrén B., Girotti P., Consolo S., Corwin R. Galanin-receptor ligand M40 peptide distinguishes between putative galanin-receptor subtypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):11287–11291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.11287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartus R. T., Dean R. L., 3rd, Beer B., Lippa A. S. The cholinergic hypothesis of geriatric memory dysfunction. Science. 1982 Jul 30;217(4558):408–414. doi: 10.1126/science.7046051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer F. E., Adrian T. E., Christofides N. D., Ferri G. L., Yanaihara N., Polak J. M., Bloom S. R. Distribution and molecular heterogeneity of galanin in human, pig, guinea pig, and rat gastrointestinal tracts. Gastroenterology. 1986 Oct;91(4):877–883. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90689-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer F. E., Ginsberg L., Venetikou M., MacKay D. J., Burrin J. M., Bloom S. R. Growth hormone release in man induced by galanin, a new hypothalamic peptide. Lancet. 1986 Jul 26;2(8500):192–195. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92490-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beal M. F., Gabriel S. M., Swartz K. J., MacGarvey U. M. Distribution of galanin-like immunoreactivity in baboon brain. Peptides. 1988 Jul-Aug;9(4):847–851. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(88)90132-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beal M. F., MacGarvey U., Swartz K. J. Galanin immunoreactivity is increased in the nucleus basalis of Meynert in Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol. 1990 Aug;28(2):157–161. doi: 10.1002/ana.410280207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedecs K., Berthold M., Bartfai T. Galanin--10 years with a neuroendocrine peptide. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1995 Apr;27(4):337–349. doi: 10.1016/1357-2725(95)00008-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benelli A., Arletti R., Bertolini A., Menozzi B., Basaglia R., Poggioli R. Galantide stimulates sexual behaviour in male rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Aug 1;260(2-3):279–282. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(94)90352-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benzing W. C., Kordower J. H., Mufson E. J. Galanin immunoreactivity within the primate basal forebrain: evolutionary change between monkeys and apes. J Comp Neurol. 1993 Oct 1;336(1):31–39. doi: 10.1002/cne.903360103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloch G. J., Butler P. C., Kohlert J. G., Bloch D. A. Microinjection of galanin into the medial preoptic nucleus facilitates copulatory behavior in the male rat. Physiol Behav. 1993 Oct;54(4):615–624. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(93)90068-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloch G. J., Butler P. C., Kohlert J. G. Galanin microinjected into the medial preoptic nucleus facilitates female- and male-typical sexual behaviors in the female rat. Physiol Behav. 1996 Jun;59(6):1147–1154. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(95)02087-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnefond C., Palacios J. M., Probst A., Mengod G. Distribution of Galanin mRNA Containing Cells and Galanin Receptor Binding Sites in Human and Rat Hypothalamus. Eur J Neurosci. 1990;2(7):629–637. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1990.tb00452.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowser R., Kordower J. H., Mufson E. J. A confocal microscopic analysis of galaninergic hyperinnervation of cholinergic basal forebrain neurons in Alzheimer's disease. Brain Pathol. 1997 Apr;7(2):723–730. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.1997.tb01058.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braak H., Braak E. Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol. 1991;82(4):239–259. doi: 10.1007/BF00308809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray G. A. Peptides affect the intake of specific nutrients and the sympathetic nervous system. Am J Clin Nutr. 1992 Jan;55(1 Suppl):265S–271S. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/55.1.265s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray G. A. The nutrient balance hypothesis: peptides, sympathetic activity, and food intake. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1993 Mar 15;676:223–241. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1993.tb38737.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgevin M. C., Loquet I., Quarteronet D., Habert-Ortoli E. Cloning, pharmacological characterization, and anatomical distribution of a rat cDNA encoding for a galanin receptor. J Mol Neurosci. 1995;6(1):33–41. doi: 10.1007/BF02736757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey D. G., Iismaa T. P., Ho K. Y., Rajkovic I. A., Kelly J., Kraegen E. W., Ferguson J., Inglis A. S., Shine J., Chisholm D. J. Potent effects of human galanin in man: growth hormone secretion and vagal blockade. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1993 Jul;77(1):90–93. doi: 10.1210/jcem.77.1.7686918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ch'ng J. L., Christofides N. D., Anand P., Gibson S. J., Allen Y. S., Su H. C., Tatemoto K., Morrison J. F., Polak J. M., Bloom S. R. Distribution of galanin immunoreactivity in the central nervous system and the responses of galanin-containing neuronal pathways to injury. Neuroscience. 1985 Oct;16(2):343–354. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan-Palay V. Galanin hyperinnervates surviving neurons of the human basal nucleus of Meynert in dementias of Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease: a hypothesis for the role of galanin in accentuating cholinergic dysfunction in dementia. J Comp Neurol. 1988 Jul 22;273(4):543–557. doi: 10.1002/cne.902730409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan-Palay V. Hyperinnervation of surviving neurons of the human basal nucleus of meynert by galanin in dementias of Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease. Adv Neurol. 1990;51:253–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan-Palay V. Neurons with galanin innervate cholinergic cells in the human basal forebrain and galanin and acetylcholine coexist. Brain Res Bull. 1988 Sep;21(3):465–472. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(88)90160-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung A., Polak J. M., Bauer F. E., Cadieux A., Christofides N. D., Springall D. R., Bloom S. R. Distribution of galanin immunoreactivity in the respiratory tract of pig, guinea pig, rat, and dog. Thorax. 1985 Dec;40(12):889–896. doi: 10.1136/thx.40.12.889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Consolo S., Baldi G., Russi G., Civenni G., Bartfai T., Vezzani A. Impulse flow dependency of galanin release in vivo in the rat ventral hippocampus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 16;91(17):8047–8051. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.17.8047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Consolo S., Bertorelli R., Girotti P., La Porta C., Bartfai T., Parenti M., Zambelli M. Pertussis toxin-sensitive G-protein mediates galanin's inhibition of scopolamine-evoked acetylcholine release in vivo and carbachol-stimulated phosphoinositide turnover in rat ventral hippocampus. Neurosci Lett. 1991 May 13;126(1):29–32. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90363-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortés R., Villar M. J., Verhofstad A., Hökfelt T. Effects of central nervous system lesions on the expression of galanin: a comparative in situ hybridization and immunohistochemical study. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7742–7746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corwin R. L., Robinson J. K., Crawley J. N. Galanin antagonists block galanin-induced feeding in the hypothalamus and amygdala of the rat. Eur J Neurosci. 1993 Nov 1;5(11):1528–1533. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1993.tb00221.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corwin R. L., Rowe P. M., Crawley J. N. Galanin and the galanin antagonist M40 do not change fat intake in a fat-chow choice paradigm in rats. Am J Physiol. 1995 Sep;269(3 Pt 2):R511–R518. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1995.269.3.R511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyle J. T., Price D. L., DeLong M. R. Alzheimer's disease: a disorder of cortical cholinergic innervation. Science. 1983 Mar 11;219(4589):1184–1190. doi: 10.1126/science.6338589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawley J. N., Austin M. C., Fiske S. M., Martin B., Consolo S., Berthold M., Langel U., Fisone G., Bartfai T. Activity of centrally administered galanin fragments on stimulation of feeding behavior and on galanin receptor binding in the rat hypothalamus. J Neurosci. 1990 Nov;10(11):3695–3700. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-11-03695.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawley J. N. Functional interactions of galanin and acetylcholine: relevance to memory and Alzheimer's disease. Behav Brain Res. 1993 Nov 30;57(2):133–141. doi: 10.1016/0166-4328(93)90129-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawley J. N. Minireview. Galanin-acetylcholine interactions: relevance to memory and Alzheimer's disease. Life Sci. 1996;58(24):2185–2199. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(96)00093-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawley J. N., Robinson J. K., Langel U., Bartfai T. Galanin receptor antagonists M40 and C7 block galanin-induced feeding. Brain Res. 1993 Jan 15;600(2):268–272. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)91382-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawley J. N., Wenk G. L. Co-existence of galanin and acetylcholine: is galanin involved in memory processes and dementia? Trends Neurosci. 1989 Aug;12(8):278–282. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(89)90003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson M., Stern R. G., Bierer L. M., Horvath T. B., Zemishlani Z., Markofsky R., Mohs R. C. Cholinergic strategies in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl. 1991;366:47–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1991.tb03109.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B. M., Mohs R. C., Greenwald B. S., Mathé A. A., Johns C. A., Horvath T. B., Davis K. L. Clinical studies of the cholinergic deficit in Alzheimer's disease. I. Neurochemical and neuroendocrine studies. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1985 Nov;33(11):741–748. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1985.tb04184.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker M. W. Animal models of cognitive function. Crit Rev Neurobiol. 1995;9(4):321–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deecher D. C., Odusan O. O., Mufson E. J. Galanin receptors in human basal forebrain differ from receptors in the hypothalamus: characterization using [125I]galanin (porcine) and [125I]galantide. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1995 Nov;275(2):720–727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dournaud P., Delaere P., Hauw J. J., Epelbaum J. Differential correlation between neurochemical deficits, neuropathology, and cognitive status in Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging. 1995 Sep-Oct;16(5):817–823. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(95)00086-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunnett S. B., Everitt B. J., Robbins T. W. The basal forebrain-cortical cholinergic system: interpreting the functional consequences of excitotoxic lesions. Trends Neurosci. 1991 Nov;14(11):494–501. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(91)90061-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutar P., Lamour Y., Nicoll R. A. Galanin blocks the slow cholinergic EPSP in CA1 pyramidal neurons from ventral hippocampus. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 May 19;164(2):355–360. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90477-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekblad E., Håkanson R., Sundler F., Wahlestedt C. Galanin: neuromodulatory and direct contractile effects on smooth muscle preparations. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Sep;86(1):241–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb09455.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elfvin L. G., Hökfelt T., Bartfai T., Bedecs K. Immunohistochemical demonstration of galanin-, and galanin message-associated peptide-like immunoreactivities in sympathetic ganglia and adrenal gland of the guinea pig. Microsc Res Tech. 1994 Oct 1;29(2):131–142. doi: 10.1002/jemt.1070290210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisone G., Bartfai T., Nilsson S., Hökfelt T. Galanin inhibits the potassium-evoked release of acetylcholine and the muscarinic receptor-mediated stimulation of phosphoinositide turnover in slices of monkey hippocampus. Brain Res. 1991 Dec 24;568(1-2):279–284. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91409-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisone G., Berthold M., Bedecs K., Undén A., Bartfai T., Bertorelli R., Consolo S., Crawley J., Martin B., Nilsson S. N-terminal galanin-(1-16) fragment is an agonist at the hippocampal galanin receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9588–9591. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisone G., Wu C. F., Consolo S., Nordström O., Brynne N., Bartfai T., Melander T., Hökfelt T. Galanin inhibits acetylcholine release in the ventral hippocampus of the rat: histochemical, autoradiographic, in vivo, and in vitro studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7339–7343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flicker C., Bartus R. T., Crook T. H., Ferris S. H. Effects of aging and dementia upon recent visuospatial memory. Neurobiol Aging. 1984 Winter;5(4):275–283. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(84)90003-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flicker C., Dean R., Bartus R. T., Ferris S. H., Crook T. Animal and human memory dysfunctions associated with aging, cholinergic lesions, and senile dementia. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1985;444:515–517. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb37630.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flicker C., Ferris S. H., Kalkstein D., Serby M. A double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover study of ganglioside GM1 treatment for Alzheimer's disease. Am J Psychiatry. 1994 Jan;151(1):126–129. doi: 10.1176/ajp.151.1.126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flicker C., Ferris S. H., Reisberg B. A two-year longitudinal study of cognitive function in normal aging and Alzheimer's disease. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol. 1993 Apr-Jun;6(2):84–96. doi: 10.1177/089198879300600205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flicker C., Ferris S. H., Reisberg B. Mild cognitive impairment in the elderly: predictors of dementia. Neurology. 1991 Jul;41(7):1006–1009. doi: 10.1212/wnl.41.7.1006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. E., McDonald T. J., Kostolanska F., Tatemoto K. Galanin: an inhibitory neural peptide of the canine small intestine. Life Sci. 1986 Jul 14;39(2):103–110. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(86)90443-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridolf T., Ahrén B. Dual action of the neuropeptide galanin on the cytoplasmic free calcium concentration in RIN m5F cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Mar 31;191(3):1224–1229. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabriel S. M., Bierer L. M., Davidson M., Purohit D. P., Perl D. P., Harotunian V. Galanin-like immunoreactivity is increased in the postmortem cerebral cortex from patients with Alzheimer's disease. J Neurochem. 1994 Apr;62(4):1516–1523. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1994.62041516.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gai W. P., Geffen L. B., Blessing W. W. Galanin immunoreactive neurons in the human hypothalamus: colocalization with vasopressin-containing neurons. J Comp Neurol. 1990 Aug 15;298(3):265–280. doi: 10.1002/cne.902980302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentleman S. M., Falkai P., Bogerts B., Herrero M. T., Polak J. M., Roberts G. W. Distribution of galanin-like immunoreactivity in the human brain. Brain Res. 1989 Dec 29;505(2):311–315. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)91458-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghatei M. A., Springall D. R., Richards I. M., Oostveen J. A., Griffin R. L., Cadieux A., Polak J. M., Bloom S. R. Regulatory peptides in the respiratory tract of Macaca fascicularis. Thorax. 1987 Jun;42(6):431–439. doi: 10.1136/thx.42.6.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girotti P., Bertorelli R., Fisone G., Land T., Langel U., Consolo S., Bartfai T. N-terminal galanin fragments inhibit the hippocampal release of acetylcholine in vivo. Brain Res. 1993 May 28;612(1-2):258–262. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)91670-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Givens B. S., Olton D. S., Crawley J. N. Galanin in the medial septal area impairs working memory. Brain Res. 1992 Jun 5;582(1):71–77. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)90318-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodnick P., Gershon S. Chemotherapy of cognitive disorders in geriatric subjects. J Clin Psychiatry. 1984 May;45(5):196–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregersen S., Lindskog S., Land T., Langel U., Bartfai T., Ahrén B. Blockade of galanin-induced inhibition of insulin secretion from isolated mouse islets by the non-methionine containing antagonist M35. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Feb 23;232(1):35–39. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90725-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregg D. W., Galkin M., Gorski J. Effect of estrogen on the expression of galanin mRNA in pituitary tumor-sensitive and tumor-resistant rat strains. Steroids. 1996 Aug;61(8):468–472. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(96)00076-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu Z. F., Rossowski W. J., Coy D. H., Pradhan T. K., Jensen R. T. Chimeric galanin analogs that function as antagonists in the CNS are full agonists in gastrointestinal smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Aug;266(2):912–918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson E. L., Smith K. E., Durkin M. M., Gerald C., Branchek T. A. Distribution of a rat galanin receptor mRNA in rat brain. Neuroreport. 1996 Mar 22;7(4):953–957. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199603220-00025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington C. A., Mobley S. L., Wenk G. L. Nitric oxide formation does not underlie the memory deficits produced by ibotenate injections into the nucleus basalis of rats. Behav Neurosci. 1994 Apr;108(2):277–283. doi: 10.1037//0735-7044.108.2.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedlund P. B., Finnman U. B., Yanaihara N., Fuxe K. Galanin-(1-15), but not galanin-(1-29), modulates 5-HT1A receptors in the dorsal hippocampus of the rat brain: possible existence of galanin receptor subtypes. Brain Res. 1994 Jan 14;634(1):163–167. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(94)90271-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedlund P. B., Yanaihara N., Fuxe K. Evidence for specific N-terminal galanin fragment binding sites in the rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Dec 2;224(2-3):203–205. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90806-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuillet E., Bouaiche Z., Ménager J., Dugay P., Munoz N., Dubois H., Amiranoff B., Crespo A., Lavayre J., Blanchard J. C. The human galanin receptor: ligand-binding and functional characteristics in the Bowes melanoma cell line. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Oct 14;269(2):139–147. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(94)90080-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holets V. R., Hökfelt T., Rökaeus A., Terenius L., Goldstein M. Locus coeruleus neurons in the rat containing neuropeptide Y, tyrosine hydroxylase or galanin and their efferent projections to the spinal cord, cerebral cortex and hypothalamus. Neuroscience. 1988 Mar;24(3):893–906. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90076-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holst J. J., Bersani M., Hvidberg A., Knigge U., Christiansen E., Madsbad S., Harling H., Kofod H. On the effects of human galanin in man. Diabetologia. 1993 Jul;36(7):653–657. doi: 10.1007/BF00404076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard A. D., Tan C., Shiao L. L., Palyha O. C., McKee K. K., Weinberg D. H., Feighner S. D., Cascieri M. A., Smith R. G., Van Der Ploeg L. H. Molecular cloning and characterization of a new receptor for galanin. FEBS Lett. 1997 Apr 1;405(3):285–290. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(97)00196-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulting A. L., Land T., Berthold M., Langel U., Hökfelt T., Bartfai T. Galanin receptors from human pituitary tumors assayed with human galanin as ligand. Brain Res. 1993 Oct 15;625(1):173–176. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)90152-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulting A. L., Meister B., Carlsson L., Hilding A., Isaksson O. On the role of the peptide galanin in regulation of growth hormone secretion. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1991 Nov;125(5):518–525. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1250518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde J. F., Howard G. Regulation of galanin gene expression in the rat anterior pituitary gland by the somatostatin analog SMS 201-995. Endocrinology. 1992 Nov;131(5):2097–2102. doi: 10.1210/endo.131.5.1385097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde J. F., Keller B. K. Galanin secretion from anterior pituitary cells in vitro is regulated by dopamine, somatostatin, and thyrotropin-releasing hormone. Endocrinology. 1991 Feb;128(2):917–922. doi: 10.1210/endo-128-2-917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde J. F., Morrison D. G., Moore J. P., Jr, Howard G. MtTW-10 pituitary tumor cells: galanin gene expression and peptide secretion. Endocrinology. 1993 Dec;133(6):2588–2593. doi: 10.1210/endo.133.6.7694842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman B. T., Van Hoesen G. W., Damasio A. R., Barnes C. L. Alzheimer's disease: cell-specific pathology isolates the hippocampal formation. Science. 1984 Sep 14;225(4667):1168–1170. doi: 10.1126/science.6474172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Millhorn D., Seroogy K., Tsuruo Y., Ceccatelli S., Lindh B., Meister B., Melander T., Schalling M., Bartfai T. Coexistence of peptides with classical neurotransmitters. Experientia. 1987 Jul 15;43(7):768–780. doi: 10.1007/BF01945354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iishi H., Tatsuta M., Baba M., Uehara H., Yano H., Nakaizumi A. Chemoprevention by galanin against colon carcinogenesis induced by azoxymethane in Wistar rats. Int J Cancer. 1995 Jun 9;61(6):861–863. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910610619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda M., Dewar D., McCulloch J. Galanin receptor binding sites in the temporal and occipital cortex are minimally affected in Alzheimer's disease. Neurosci Lett. 1995 Jun 2;192(1):37–40. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(95)11602-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda M., Dewar D., McCulloch J. Preservation of [125I]galanin binding sites despite loss of cholinergic neurones to the hippocampus in Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res. 1991 Dec 24;568(1-2):303–306. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91414-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrard L. E. On the role of the hippocampus in learning and memory in the rat. Behav Neural Biol. 1993 Jul;60(1):9–26. doi: 10.1016/0163-1047(93)90664-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kameyama T., Ukai M., Miura M. Dynorphin A-(1-13) potently improves galanin-induced impairment of memory processes in mice. Neuropharmacology. 1994 Oct;33(10):1167–1169. doi: 10.1016/s0028-3908(05)80006-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kask K., Berthold M., Bartfai T. Galanin receptors: involvement in feeding, pain, depression and Alzheimer's disease. Life Sci. 1997;60(18):1523–1533. doi: 10.1016/s0024-3205(96)00624-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kask K., Berthold M., Bourne J., Andell S., Langel U., Bartfai T. Binding and agonist/antagonist actions of M35, galanin(1-13)-bradykinin(2-9)amide chimeric peptide, in Rin m 5F insulinoma cells. Regul Pept. 1995 Nov 10;59(3):341–348. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(95)00089-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kask K., Langel U., Bartfai T. Galanin--a neuropeptide with inhibitory actions. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 1995 Dec;15(6):653–673. doi: 10.1007/BF02071130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King S. C., Slater P., Turnberg L. A. Autoradiographic localization of binding sites for galanin and VIP in small intestine. Peptides. 1989 Mar-Apr;10(2):313–317. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(89)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konopka L. M., McKeon T. W., Parsons R. L. Galanin-induced hyperpolarization and decreased membrane excitability of neurones in mudpuppy cardiac ganglia. J Physiol. 1989 Mar;410:107–122. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konopka L. M., Merriam L. A., Hardwick J. C., Parsons R. L. Aminergic and peptidergic elements and actions in a cardiac parasympathetic ganglion. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1992;70 (Suppl):S32–S43. doi: 10.1139/y92-241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kordower J. H., Le H. K., Mufson E. J. Galanin immunoreactivity in the primate central nervous system. J Comp Neurol. 1992 May 22;319(4):479–500. doi: 10.1002/cne.903190403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kordower J. H., Mufson E. J. Galanin-like immunoreactivity within the primate basal forebrain: differential staining patterns between humans and monkeys. J Comp Neurol. 1990 Apr 8;294(2):281–292. doi: 10.1002/cne.902940211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowall N. W., Beal M. F. Galanin-like immunoreactivity is present in human substantia innominata and in senile plaques in Alzheimer's disease. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Mar 13;98(1):118–123. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90384-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krzywkowski P., Lagny-Pourmir I., Jazat F., Lamour Y., Epelbaum J. The age-related increase in galanin binding sites in the rat brain correlates with behavioral impairment. Neuroscience. 1994 Apr;59(3):599–607. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(94)90180-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyrkouli S. E., Stanley B. G., Seirafi R. D., Leibowitz S. F. Stimulation of feeding by galanin: anatomical localization and behavioral specificity of this peptide's effects in the brain. Peptides. 1990 Sep-Oct;11(5):995–1001. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(90)90023-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler C., Chan-Palay V. Galanin receptors in the post-mortem human brain. Regional distribution of 125I-galanin binding sites using the method of in vitro receptor autoradiography. Neurosci Lett. 1990 Dec 11;120(2):179–182. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90032-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler C., Hallman H., Melander T., Hökfelt T., Norheim E. Autoradiographic mapping of galanin receptors in the monkey brain. J Chem Neuroanat. 1989 Sep-Oct;2(5):269–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler C., Persson A., Melander T., Theodorsson E., Sedvall G., Hökfelt T. Distribution of galanin-binding sites in the monkey and human telencephalon: preliminary observations. Exp Brain Res. 1989;75(2):375–380. doi: 10.1007/BF00247944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langel U., Land T., Bartfai T. Design of chimeric peptide ligands to galanin receptors and substance P receptors. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1992 Jun;39(6):516–522. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1992.tb00282.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibowitz S. F. Brain peptides and obesity: pharmacologic treatment. Obes Res. 1995 Nov;3 (Suppl 4):573S–589S. doi: 10.1002/j.1550-8528.1995.tb00230.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibowitz S. F., Kim T. Impact of a galanin antagonist on exogenous galanin and natural patterns of fat ingestion. Brain Res. 1992 Dec 18;599(1):148–152. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)90863-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibowitz S. F. Specificity of hypothalamic peptides in the control of behavioral and physiological processes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1994 Oct 31;739:12–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1994.tb19804.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin M. C., Sawchenko P. E., Howe P. R., Bloom S. R., Polak J. M. Organization of galanin-immunoreactive inputs to the paraventricular nucleus with special reference to their relationship to catecholaminergic afferents. J Comp Neurol. 1987 Jul 22;261(4):562–582. doi: 10.1002/cne.902610408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindskog S., Ahrén B. Effects of galanin and norepinephrine on insulin secretion in the mouse. Pancreas. 1992;7(6):636–641. doi: 10.1097/00006676-199211000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindskog S., Ahrén B., Land T., Langel U., Bartfai T. The novel high-affinity antagonist, galantide, blocks the galanin-mediated inhibition of glucose-induced insulin secretion. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Jan 14;210(2):183–188. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90669-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindskog S., Gregersen S., Hermansen K., Ahrén B. Effects of galanin on proinsulin mRNA and insulin biosynthesis in normal islets. Regul Pept. 1995 Aug 22;58(3):135–139. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(95)00061-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S., Lyeth B. G., Hamm R. J. Protective effect of galanin on behavioral deficits in experimental traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma. 1994 Feb;11(1):73–82. doi: 10.1089/neu.1994.11.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longley C. D., Weaver L. C. Proportions of renal and splenic postganglionic sympathetic populations containing galanin and dopamine beta hydroxylase. Neuroscience. 1993 Jul;55(1):253–261. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(93)90470-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorinet A. M., Javoy-Agid F., Laburthe M., Amiranoff B. Galanin receptors in human hypothalamus: biochemical and structural analysis. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Sep 15;269(1):59–64. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(94)90026-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malin D. H., Novy B. J., Lett-Brown A. E., Plotner R. E., May B. T., Radulescu S. J., Crothers M. K., Osgood L. D., Lake J. R. Galanin attenuates retention of one-trial reward learning. Life Sci. 1992;50(13):939–944. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(92)90171-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastropaolo J., Nadi N. S., Ostrowski N. L., Crawley J. N. Galanin antagonizes acetylcholine on a memory task in basal forebrain-lesioned rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9841–9845. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazarati A. M., Halászi E., Telegdy G. Anticonvulsive effects of galanin administered into the central nervous system upon the picrotoxin-kindled seizure syndrome in rats. Brain Res. 1992 Aug 28;589(1):164–166. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)91179-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
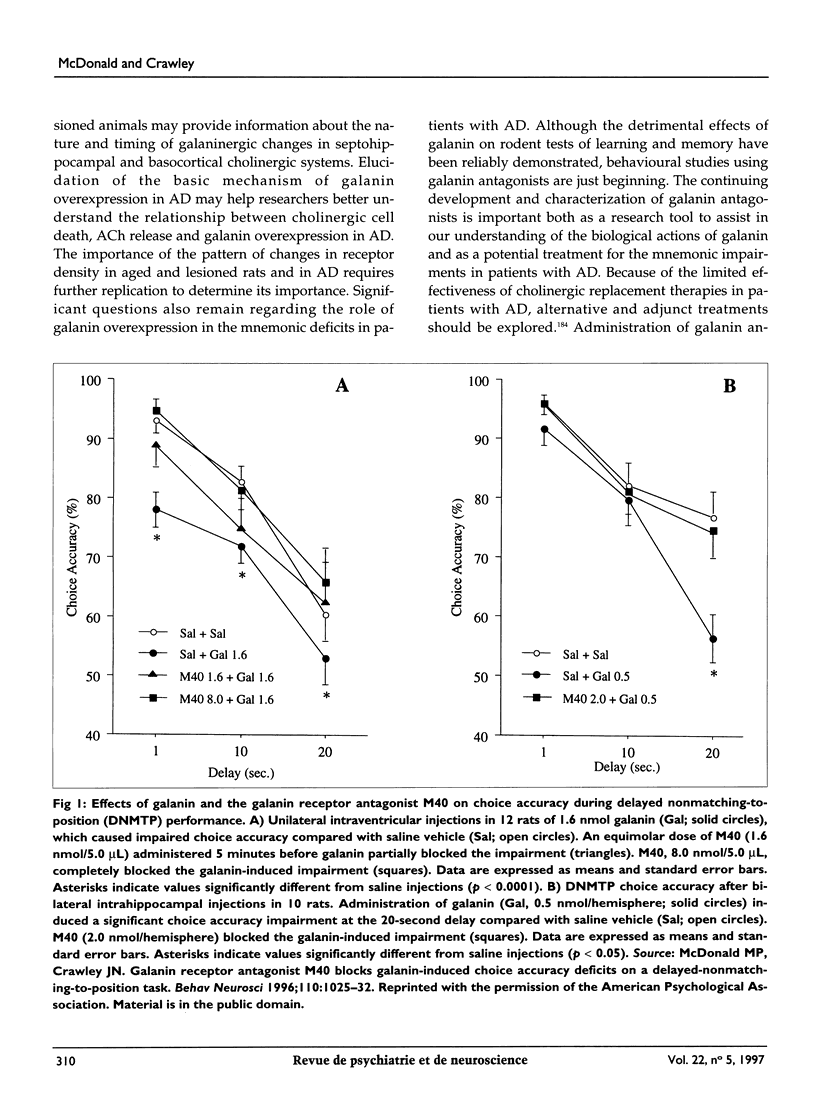
- McDonald M. P., Crawley J. N. Galanin receptor antagonist M40 blocks galanin-induced choice accuracy deficits on a delayed-nonmatching-to-position task. Behav Neurosci. 1996 Oct;110(5):1025–1032. doi: 10.1037//0735-7044.110.5.1025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald M. P., Crawley J. N. Galanin receptor antagonist M40 blocks galanin-induced choice accuracy deficits on a delayed-nonmatching-to-position task. Behav Neurosci. 1996 Oct;110(5):1025–1032. doi: 10.1037//0735-7044.110.5.1025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeon T. W., Parsons R. L. Galanin immunoreactivity in the mudpuppy cardiac ganglion. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1990 Nov;31(2):135–140. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(90)90070-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meister B., Scanlon M. F., Hökfelt T. Occurrence of galanin-like immunoreactivity in growth hormone-releasing factor (GRF)-containing neurons of the monkey (Macaca fascicularis) infundibular nucleus and median eminence. Neurosci Lett. 1990 Oct 30;119(1):136–139. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90775-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melander T., Bartfai T., Brynne N., Consolo S., Fisone G., Hökfelt T., Köhler C., Nordström O., Norheim-Theodorsson E., Persson A. Galanin in the cholinergic basal forebrain: histochemical, autoradiographic and in vivo studies. Prog Brain Res. 1989;79:85–91. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)62467-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melander T., Fuxe K., Härfstrand A., Eneroth P., Hökfelt T. Effects of intraventricular injections of galanin on neuroendocrine functions in the male rat. Possible involvement of hypothalamic catecholamine neuronal systems. Acta Physiol Scand. 1987 Sep;131(1):25–32. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1987.tb08201.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melander T., Hökfelt T., Nilsson S., Brodin E. Visualization of galanin binding sites in the rat central nervous system. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 May 27;124(3):381–382. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90247-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melander T., Hökfelt T., Rökaeus A., Cuello A. C., Oertel W. H., Verhofstad A., Goldstein M. Coexistence of galanin-like immunoreactivity with catecholamines, 5-hydroxytryptamine, GABA and neuropeptides in the rat CNS. J Neurosci. 1986 Dec;6(12):3640–3654. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-12-03640.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melander T., Hökfelt T., Rökaeus A. Distribution of galaninlike immunoreactivity in the rat central nervous system. J Comp Neurol. 1986 Jun 22;248(4):475–517. doi: 10.1002/cne.902480404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melander T., Hökfelt T., Rökaeus A., Fahrenkrug J., Tatemoto K., Mutt V. Distribution of galanin-like immunoreactivity in the gastro-intestinal tract of several mammalian species. Cell Tissue Res. 1985;239(2):253–270. doi: 10.1007/BF00218003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melander T., Köhler C., Nilsson S., Hökfelt T., Brodin E., Theodorsson E., Bartfai T. Autoradiographic quantitation and anatomical mapping of 125I-galanin binding sites in the rat central nervous system. J Chem Neuroanat. 1988 Jul-Aug;1(4):213–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melander T., Staines W. A. A galanin-like peptide coexists in putative cholinergic somata of the septum-basal forebrain complex and in acetylcholinesterase-containing fibers and varicosities within the hippocampus in the owl monkey (Aotus trivirgatus). Neurosci Lett. 1986 Jul 11;68(1):17–22. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90222-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melander T., Staines W. A., Hökfelt T., Rökaeus A., Eckenstein F., Salvaterra P. M., Wainer B. H. Galanin-like immunoreactivity in cholinergic neurons of the septum-basal forebrain complex projecting to the hippocampus of the rat. Brain Res. 1985 Dec 23;360(1-2):130–138. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91228-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melander T., Staines W. A., Rökaeus A. Galanin-like immunoreactivity in hippocampal afferents in the rat, with special reference to cholinergic and noradrenergic inputs. Neuroscience. 1986 Sep;19(1):223–240. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merchenthaler I., López F. J., Negro-Vilar A. Anatomy and physiology of central galanin-containing pathways. Prog Neurobiol. 1993 Jun;40(6):711–769. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(93)90012-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minami M., Makino Y., Arai H., Iizuka R. A disorganized increase of galanin-like immunoreactivity in cerebral cortex of Alzheimer-type dementia brains. J Neural Transm Park Dis Dement Sect. 1991;3(4):285–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Money E. A., Kirk R. C., McNaughton N. Alzheimer's dementia produces a loss of discrimination but no increase in rate of memory decay in delayed matching to sample. Neuropsychologia. 1992 Feb;30(2):133–143. doi: 10.1016/0028-3932(92)90023-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. Y., Gustafson E. L. The distribution of dopamine-beta-hydroxylase, neuropeptide Y and galanin in locus coeruleus neurons. J Chem Neuroanat. 1989 Mar-Apr;2(2):95–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mufson E. J., Benzing W. C., Kordower J. H. Dissociation of galaninergic and neurotrophic plasticity in Down syndrome and Alzheimer disease. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1995;393:105–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mufson E. J., Cochran E., Benzing W., Kordower J. H. Galaninergic innervation of the cholinergic vertical limb of the diagonal band (Ch2) and bed nucleus of the stria terminalis in aging, Alzheimer's disease and Down's syndrome. Dementia. 1993 Sep-Oct;4(5):237–250. doi: 10.1159/000107329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami Y., Kato Y., Koshiyama H., Inoue T., Yanaihara N., Imura H. Galanin stimulates growth hormone (GH) secretion via GH-releasing factor (GRF) in conscious rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Apr 29;136(3):415–418. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90316-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami Y., Ohshima K., Mochizuki T., Yanaihara N. Effect of human galanin on growth hormone prolactin, and antidiuretic hormone secretion in normal men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1993 Nov;77(5):1436–1438. doi: 10.1210/jcem.77.5.7521348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niimi M., Murao K., Takahara J., Kawanishi K. Identification of galanin-immunoreactive cells in the anterior pituitary of male monkeys (Macaca fascicularis). Endocr J. 1993 Apr;40(2):231–235. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.40.231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordström O., Melander T., Hökfelt T., Bartfai T., Goldstein M. Evidence for an inhibitory effect of the peptide galanin on dopamine release from the rat median eminence. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Jan 2;73(1):21–26. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90024-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Halloran D. J., Jones P. M., Bloom S. R. Neuropeptides synthesised in the anterior pituitary: possible paracrine role. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1991 Jan;75(1):C7–12. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(91)90237-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogren S. O., Hökfelt T., Kask K., Langel U., Bartfai T. Evidence for a role of the neuropeptide galanin in spatial learning. Neuroscience. 1992 Nov;51(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90463-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogren S. O., Pramanik A. Galanin stimulates acetylcholine release in the rat striatum. Neurosci Lett. 1991 Jul 22;128(2):253–256. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90273-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogren S. O., Pramanik A., Land T., Langel U. Differential effects of the putative galanin receptor antagonists M15 and M35 on striatal acetylcholine release. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Sep 21;242(1):59–64. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90010-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohman A., Lycksell P. O., Andell S., Langel U., Bartfai T., Gräslund A. Solvent stabilized solution structures of galanin and galanin analogs, studied by circular dichroism spectroscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995 Jun 14;1236(2):259–265. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(95)00056-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palazzi E., Felinska S., Zambelli M., Fisone G., Bartfai T., Consolo S. Galanin reduces carbachol stimulation of phosphoinositide turnover in rat ventral hippocampus by lowering Ca2+ influx through voltage-sensitive Ca2+ channels. J Neurochem. 1991 Mar;56(3):739–747. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb01986.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palazzi E., Fisone G., Hökfelt T., Bartfai T., Consolo S. Galanin inhibits the muscarinic stimulation of phosphoinositide turnover in rat ventral hippocampus. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Apr 13;148(3):479–480. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90133-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker E. M., Izzarelli D. G., Nowak H. P., Mahle C. D., Iben L. G., Wang J., Goldstein M. E. Cloning and characterization of the rat GALR1 galanin receptor from Rin14B insulinoma cells. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1995 Dec 28;34(2):179–189. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(95)00159-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons R. L., Konopka L. M. Analysis of the galanin-induced decrease in membrane excitability in mudpuppy parasympathetic neurons. Neuroscience. 1991;43(2-3):647–660. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(91)90323-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons R. L., Merriam L. A. Galanin and bethanechol appear to activate the same inwardly rectifying potassium current in mudpuppy parasympathetic neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1992 Jun 8;140(1):33–36. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(92)90675-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons R. L., Neel D. S., Konopka L. M., McKeon T. W. The presence and possible role of a galanin-like peptide in the mudpuppy heart. Neuroscience. 1989;29(3):749–759. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90146-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel S., Hutson P. H. Hypothermia induced by cholinomimetic drugs is blocked by galanin: possible involvement of ATP-sensitive K+ channels. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Apr 1;255(1-3):25–32. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(94)90078-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry E. K., Blessed G., Tomlinson B. E., Perry R. H., Crow T. J., Cross A. J., Dockray G. J., Dimaline R., Arregui A. Neurochemical activities in human temporal lobe related to aging and Alzheimer-type changes. Neurobiol Aging. 1981 Winter;2(4):251–256. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(81)90032-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry E. K., Perry R. H., Tomlinson B. E. Dietary lecithin supplements in dementia of Alzheimer type. Lancet. 1977 Jul 30;2(8031):242–243. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)92852-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry E. K. The cholinergic system in old age and Alzheimer's disease. Age Ageing. 1980 Feb;9(1):1–8. doi: 10.1093/ageing/9.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry E. K., Tomlinson B. E., Blessed G., Bergmann K., Gibson P. H., Perry R. H. Correlation of cholinergic abnormalities with senile plaques and mental test scores in senile dementia. Br Med J. 1978 Nov 25;2(6150):1457–1459. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6150.1457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Planas B., Kolb P. E., Raskind M. A., Miller M. A. Vasopressin and galanin mRNAs coexist in the nucleus of the horizontal diagonal band: a novel site of vasopressin gene expression. J Comp Neurol. 1995 Oct 9;361(1):48–56. doi: 10.1002/cne.903610105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polak J. M., Bloom S. R. Regulatory peptides of the gastrointestinal and respiratory tracts. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1986 Apr;280(2 Suppl):16–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post C., Alari L., Hökfelt T. Intrathecal galanin increases the latency in the tail-flick and hot-plate test in mouse. Acta Physiol Scand. 1988 Apr;132(4):583–584. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1988.tb08369.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pramanik A., Ogren S. O. Galanin stimulates striatal acetylcholine release via a mechanism unrelated to cholinergic receptor stimulation. Regul Pept. 1993 Jun 11;45(3):353–362. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(93)90361-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pramanik A., Ogren S. O. Galanin-evoked acetylcholine release in the rat striatum is blocked by the putative galanin antagonist M15. Brain Res. 1992 Mar 6;574(1-2):317–319. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)90832-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter J. A., Perry E. K., Tomlinson B. E. Acetylcholine and choline levels in post-mortem human brain tissue: preliminary observations in Alzheimer's disease. Life Sci. 1980 May 19;26(20):1683–1689. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90176-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. K., Crawley J. N. Analysis of anatomical sites at which galanin impairs delayed nonmatching to sample in rats. Behav Neurosci. 1994 Oct;108(5):941–950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. K., Crawley J. N. Intraseptal galanin potentiates scopolamine impairment of delayed nonmatching to sample. J Neurosci. 1993 Dec;13(12):5119–5125. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-12-05119.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. K., Crawley J. N. Intraventricular galanin impairs delayed nonmatching-to-sample performance in rats. Behav Neurosci. 1993 Jun;107(3):458–467. doi: 10.1037//0735-7044.107.3.458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. K., Crawley J. N. The role of galanin in cholinergically-mediated memory processes. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 1993 Jan;17(1):71–85. doi: 10.1016/0278-5846(93)90033-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Puertas R., Nilsson S., Pascual J., Pazos A., Hökfelt T. 125I-galanin binding sites in Alzheimer's disease: increases in hippocampal subfields and a decrease in the caudate nucleus. J Neurochem. 1997 Mar;68(3):1106–1113. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1997.68031106.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosier A. M., Vandesande F., Orban G. A. Laminar and regional distribution of galanin binding sites in cat and monkey visual cortex determined by in vitro receptor autoradiography. J Comp Neurol. 1991 Mar 8;305(2):264–272. doi: 10.1002/cne.903050207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rökaeus A., Melander T., Hökfelt T., Lundberg J. M., Tatemoto K., Carlquist M., Mutt V. A galanin-like peptide in the central nervous system and intestine of the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1984 Jun 15;47(2):161–166. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(84)90423-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rökaeus A., Young W. S., 3rd, Mezey E. Galanin coexists with vasopressin in the normal rat hypothalamus and galanin's synthesis is increased in the Brattleboro (diabetes insipidus) rat. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Jul 19;90(1-2):45–50. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90784-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahakian B. J., Morris R. G., Evenden J. L., Heald A., Levy R., Philpot M., Robbins T. W. A comparative study of visuospatial memory and learning in Alzheimer-type dementia and Parkinson's disease. Brain. 1988 Jun;111(Pt 3):695–718. doi: 10.1093/brain/111.3.695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahgal A., Keith A. B. Combined serotonergic-cholinergic lesions do not disrupt memory in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1993 Aug;45(4):995–1001. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(93)90155-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarter M., Bruno J. P., Dudchenko P. Activating the damaged basal forebrain cholinergic system: tonic stimulation versus signal amplification. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1990;101(1):1–17. doi: 10.1007/BF02253710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senut M. C., de Bilbao F., Lamour Y. Age-related loss of galanin-immunoreactive cells in the rat septal area. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Nov 6;105(3):257–262. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90630-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethi T., Rozengurt E. Galanin stimulates Ca2+ mobilization, inositol phosphate accumulation, and clonal growth in small cell lung cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1991 Mar 15;51(6):1674–1679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethi T., Rozengurt E. Multiple neuropeptides stimulate clonal growth of small cell lung cancer: effects of bradykinin, vasopressin, cholecystokinin, galanin, and neurotensin. Cancer Res. 1991 Jul 1;51(13):3621–3623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seutin V., Verbanck P., Massotte L., Dresse A. Galanin decreases the activity of locus coeruleus neurons in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 May 19;164(2):373–376. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90481-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sevcik J., Finta E. P., Illes P. Galanin receptors inhibit the spontaneous firing of locus coeruleus neurones and interact with mu-opioid receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Jan 12;230(2):223–230. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90806-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skofitsch G., Jacobowitz D. M., Amann R., Lembeck F. Galanin and vasopressin coexist in the rat hypothalamo-neurohypophyseal system. Neuroendocrinology. 1989 Apr;49(4):419–427. doi: 10.1159/000125147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skofitsch G., Jacobowitz D. M. Galanin-like immunoreactivity in capsaicin sensitive sensory neurons and ganglia. Brain Res Bull. 1985 Aug;15(2):191–195. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(85)90135-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skofitsch G., Jacobowitz D. M. Immunohistochemical mapping of galanin-like neurons in the rat central nervous system. Peptides. 1985 May-Jun;6(3):509–546. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(85)90118-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skofitsch G., Jacobowitz D. M. Quantitative distribution of galanin-like immunoreactivity in the rat central nervous system. Peptides. 1986 Jul-Aug;7(4):609–613. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(86)90035-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skofitsch G., Sills M. A., Jacobowitz D. M. Autoradiographic distribution of 125I-galanin binding sites in the rat central nervous system. Peptides. 1986 Nov-Dec;7(6):1029–1042. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(86)90133-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. K., York D. A., Bray G. A. Chronic cerebroventricular galanin does not induce sustained hyperphagia or obesity. Peptides. 1994;15(7):1267–1272. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(94)90152-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. M., Swash M. Possible biochemical basis of memory disorder in Alzheimer disease. Ann Neurol. 1978 Jun;3(6):471–473. doi: 10.1002/ana.410030602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steel J. H., Gon G., O'Halloran D. J., Jones P. M., Yanaihara N., Ishikawa H., Bloom S. R., Polak J. M. Galanin and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide are colocalised with classical pituitary hormones and show plasticity of expression. Histochemistry. 1989;93(2):183–189. doi: 10.1007/BF00315973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan K. A., Shiao L. L., Cascieri M. A. Pharmacological characterization and tissue distribution of the human and rat GALR1 receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1997 Apr 28;233(3):823–828. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1997.6542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundström E., Archer T., Melander T., Hökfelt T. Galanin impairs acquisition but not retrieval of spatial memory in rats studied in the Morris swim maze. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Jun 7;88(3):331–335. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanoh T., Shimatsu A., Ishikawa Y., Ihara C., Yanaihara N., Imura H. Galanin-induced growth hormone secretion in conscious rats: evidence for a possible involvement of somatostatin. J Neuroendocrinol. 1993 Apr;5(2):183–187. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2826.1993.tb00379.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K., Rökaeus A., Jörnvall H., McDonald T. J., Mutt V. Galanin - a novel biologically active peptide from porcine intestine. FEBS Lett. 1983 Nov 28;164(1):124–128. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempel D. L., Leibowitz K. J., Leibowitz S. F. Effects of PVN galanin on macronutrient selection. Peptides. 1988 Mar-Apr;9(2):309–314. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(88)90265-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson B. E., Kitchener D. Granulovacuolar degeneration of hippocampal pyramidal cells. J Pathol. 1972 Mar;106(3):165–185. doi: 10.1002/path.1711060305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda K., Tsuda S., Nishio I., Masuyama Y., Goldstein M. Modulation of norepinephrine release by galanin in rat medulla oblongata. Hypertension. 1992 Sep;20(3):361–366. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.20.3.361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ukai M., Miura M., Kameyama T. Effects of galanin on passive avoidance response, elevated plus-maze learning, and spontaneous alternation performance in mice. Peptides. 1995;16(7):1283–1286. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(95)02009-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulman L. G., Moriarty M., Potter E. K., McCloskey D. I. Galanin antagonist effects on cardiac vagal inhibitory actions of sympathetic stimulation in anaesthetized cats and dogs. J Physiol. 1993 May;464:491–499. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulman L. G., Potter E. K., McCloskey D. I. Effects of sympathetic activity and galanin on cardiac vagal action in anaesthetized cats. J Physiol. 1992 Mar;448:225–235. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulman L. G., Potter E. K., McCloskey D. I. Functional effects of a family of galanin antagonists on the cardiovascular system in anaesthetised cats. Regul Pept. 1994 Apr 14;51(1):17–23. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(94)90130-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger J. W., Schmidt Y. Galanin-immunoreactivity in the nucleus basalis of Meynert in the rat: age-related changes and differential response to lesion-induced cholinergic cell loss. Neurosci Lett. 1993 Apr 30;153(2):140–143. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(93)90307-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Hoesen G. W., Hyman B. T. Hippocampal formation: anatomy and the patterns of pathology in Alzheimer's disease. Prog Brain Res. 1990;83:445–457. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)61268-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villar M. J., Cortés R., Theodorsson E., Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z., Schalling M., Fahrenkrug J., Emson P. C., Hökfelt T. Neuropeptide expression in rat dorsal root ganglion cells and spinal cord after peripheral nerve injury with special reference to galanin. Neuroscience. 1989;33(3):587–604. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90411-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker L. C., Koliatsos V. E., Kitt C. A., Richardson R. T., Rökaeus A., Price D. L. Peptidergic neurons in the basal forebrain magnocellular complex of the rhesus monkey. J Comp Neurol. 1989 Feb 8;280(2):272–282. doi: 10.1002/cne.902800208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y. F., Mao Y. K., McDonald T. J., Daniel E. E. Distribution of galanin-immunoreactive nerves in the canine gastrointestinal tract. Peptides. 1995;16(2):237–247. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(94)00170-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenk G. L., Rökaeus A. Basal forebrain lesions differentially alter galanin levels and acetylcholinergic receptors in the hippocampus and neocortex. Brain Res. 1988 Sep 13;460(1):17–21. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90425-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenk G. L., Stoehr J. D., Quintana G., Mobley S., Wiley R. G. Behavioral, biochemical, histological, and electrophysiological effects of 192 IgG-saporin injections into the basal forebrain of rats. J Neurosci. 1994 Oct;14(10):5986–5995. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-10-05986.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wester P., Eriksson S., Forsell A., Puu G., Adolfsson R. Monoamine metabolite concentrations and cholinesterase activities in cerebrospinal fluid of progressive dementia patients: relation to clinical parameters. Acta Neurol Scand. 1988 Jan;77(1):12–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1988.tb06967.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehouse P. J., Price D. L., Struble R. G., Clark A. W., Coyle J. T., Delon M. R. Alzheimer's disease and senile dementia: loss of neurons in the basal forebrain. Science. 1982 Mar 5;215(4537):1237–1239. doi: 10.1126/science.7058341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z., Bartfai T., Hökfelt T. Galanin in sensory neurons in the spinal cord. Front Neuroendocrinol. 1992 Oct;13(4):319–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z., Xu X. J., Hao J. X., Hökfelt T. The behavioural effects of intrathecal galanin on tests of thermal and mechanical nociception in the rat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1993 Apr;147(4):457–458. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1993.tb09521.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z., Xu X. J., Hughes J., Horwell D. C., Hökfelt T. PD134308, a selective antagonist of cholecystokinin type B receptor, enhances the analgesic effect of morphine and synergistically interacts with intrathecal galanin to depress spinal nociceptive reflexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7105–7109. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z., Xu X. J., Hughes J., Horwell D. C., Hökfelt T. Studies on the effect of systemic PD134308 (CAM 958) in spinal reflex and pain models with special reference to interaction with morphine and intrathecal galanin. Neuropeptides. 1991 Jul;19 (Suppl):79–84. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(91)90086-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z., Xu X. J., Villar M. J., Hökfelt T. Intrathecal galanin potentiates the spinal analgesic effect of morphine: electrophysiological and behavioural studies. Neurosci Lett. 1990 Feb 5;109(1-2):217–221. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90566-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wynick D., Smith D. M., Ghatei M., Akinsanya K., Bhogal R., Purkiss P., Byfield P., Yanaihara N., Bloom S. R. Characterization of a high-affinity galanin receptor in the rat anterior pituitary: absence of biological effect and reduced membrane binding of the antagonist M15 differentiate it from the brain/gut receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):4231–4235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.4231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu X. J., Andell S., Hao J. X., Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z., Bartfai T. The effects of intrathecal galanin message-associated peptide (GMAP) on the flexor reflex in rats. Regul Pept. 1995 Jul 21;58(1-2):19–24. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(95)00054-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu X. J., Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z., Fisone G., Bartfai T., Hökfelt T. The N-terminal 1-16, but not C-terminal 17-29, galanin fragment affects the flexor reflex in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Jun 21;182(1):137–141. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90502-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu X. J., Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z., Langel U., Bedecs K., Bartfai T. New high affinity peptide antagonists to the spinal galanin receptor. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 Oct;116(3):2076–2080. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb16414.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu W., Dey R. D. Distribution of the neuropeptide galanin in the cat heart and coexistence with vasoactive intestinal peptide, substance P and neuropeptide Y. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1992 Jan;24(1):35–41. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(92)91157-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bilbao F., Jazat F., Lamour Y., Senut M. C. Age-related changes in galanin-immunoreactive cells of the rat medial septal area. J Comp Neurol. 1991 Nov 22;313(4):613–624. doi: 10.1002/cne.903130407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lacalle S., Kulkarni S., Mufson E. J. Plasticity of galaninergic fibers following neurotoxic damage within the rat basal forebrain: initial observations. Exp Neurol. 1997 Aug;146(2):361–366. doi: 10.1006/exnr.1997.6532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Pedro N., Céspedes M. V., Delgado M. J., Alonso-Bedate M. The galanin-induced feeding stimulation is mediated via alpha 2-adrenergic receptors in goldfish. Regul Pept. 1995 May 4;57(1):77–84. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(95)91255-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Salhy M., Stenling R., Grimelius L. Peptidergic innervation and endocrine cells in the human liver. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1993 Sep;28(9):809–815. doi: 10.3109/00365529309104014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


