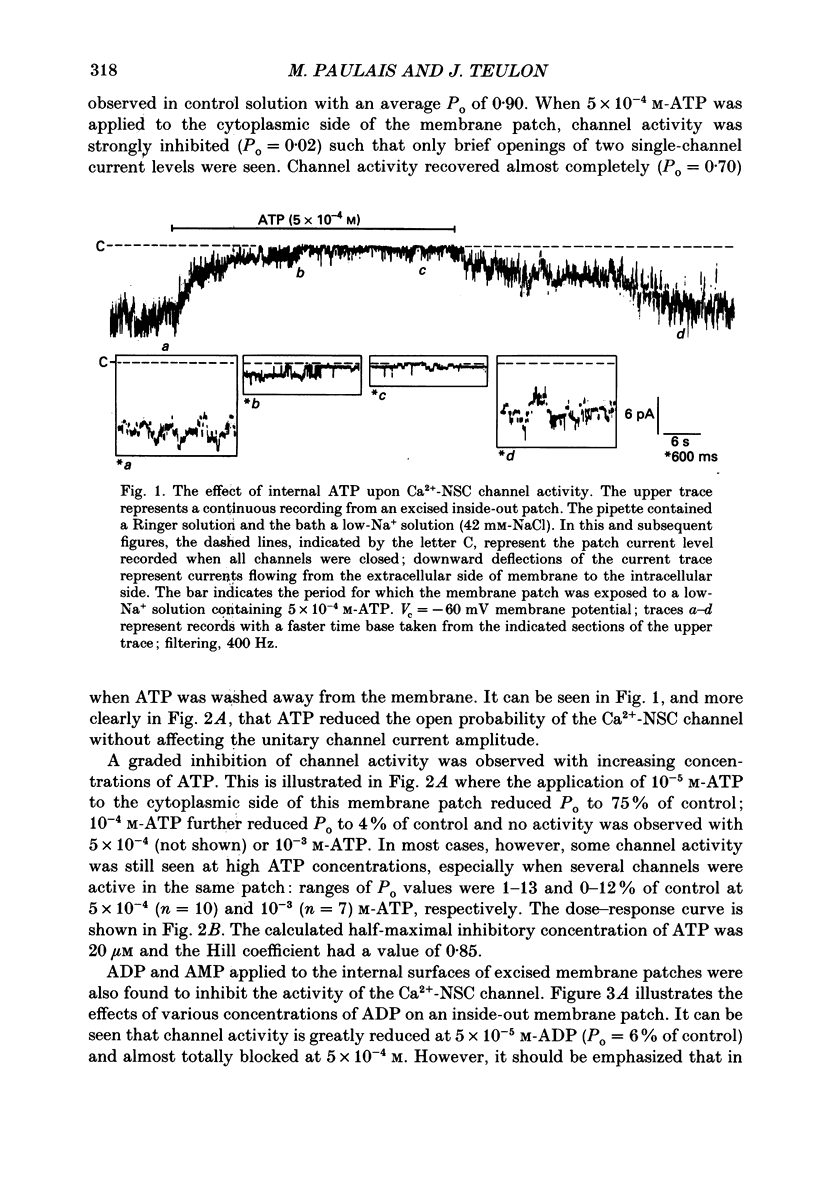
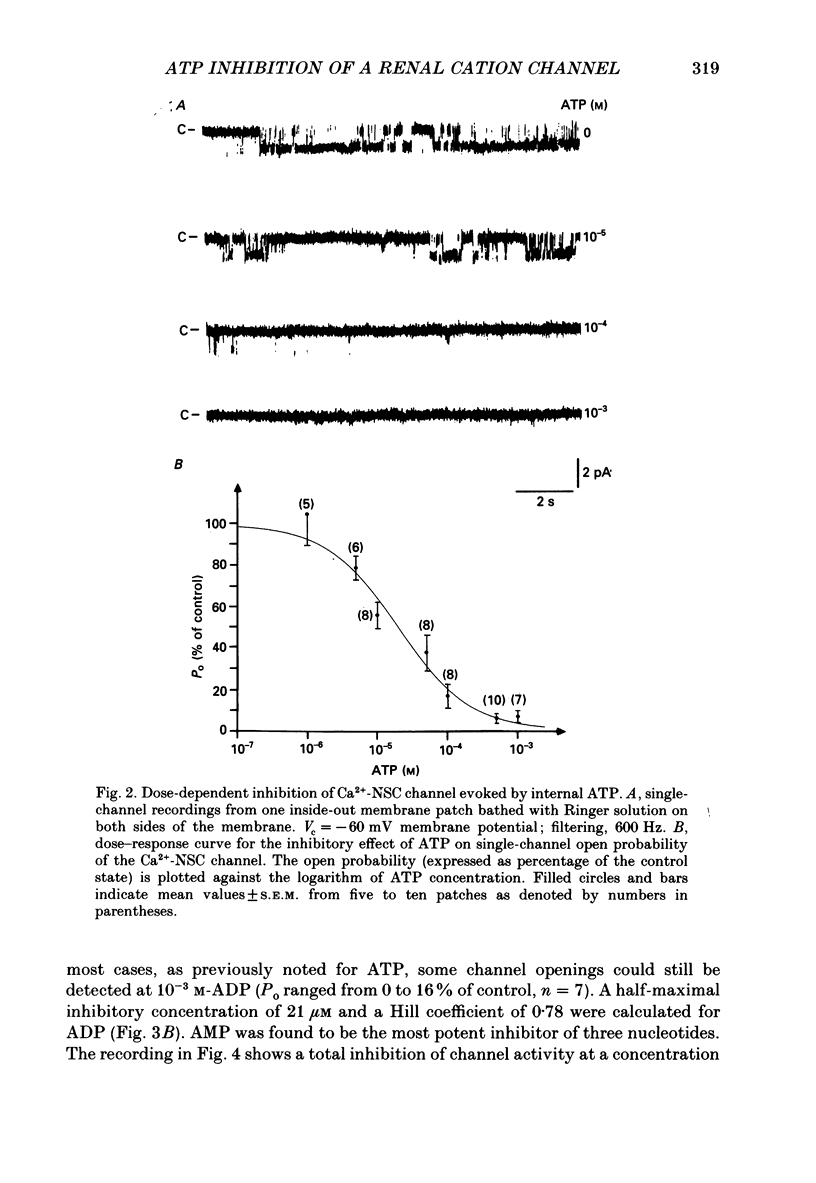
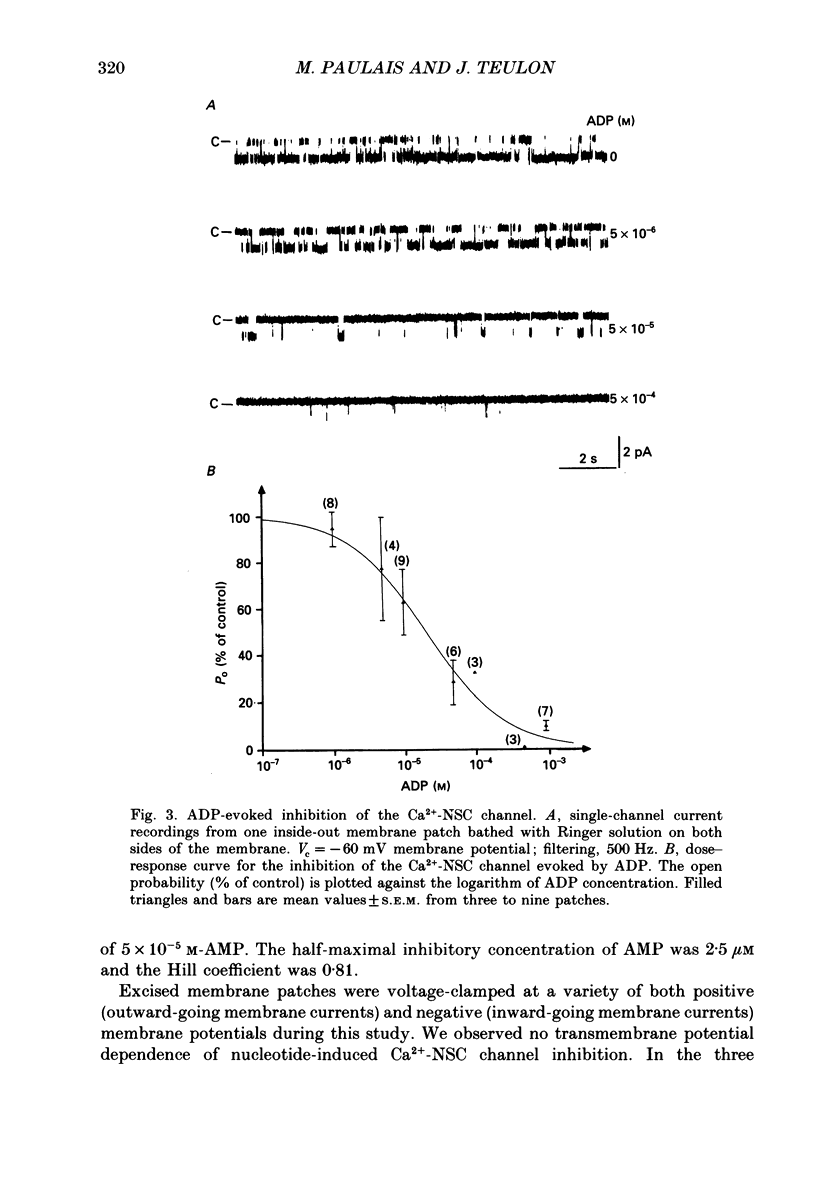
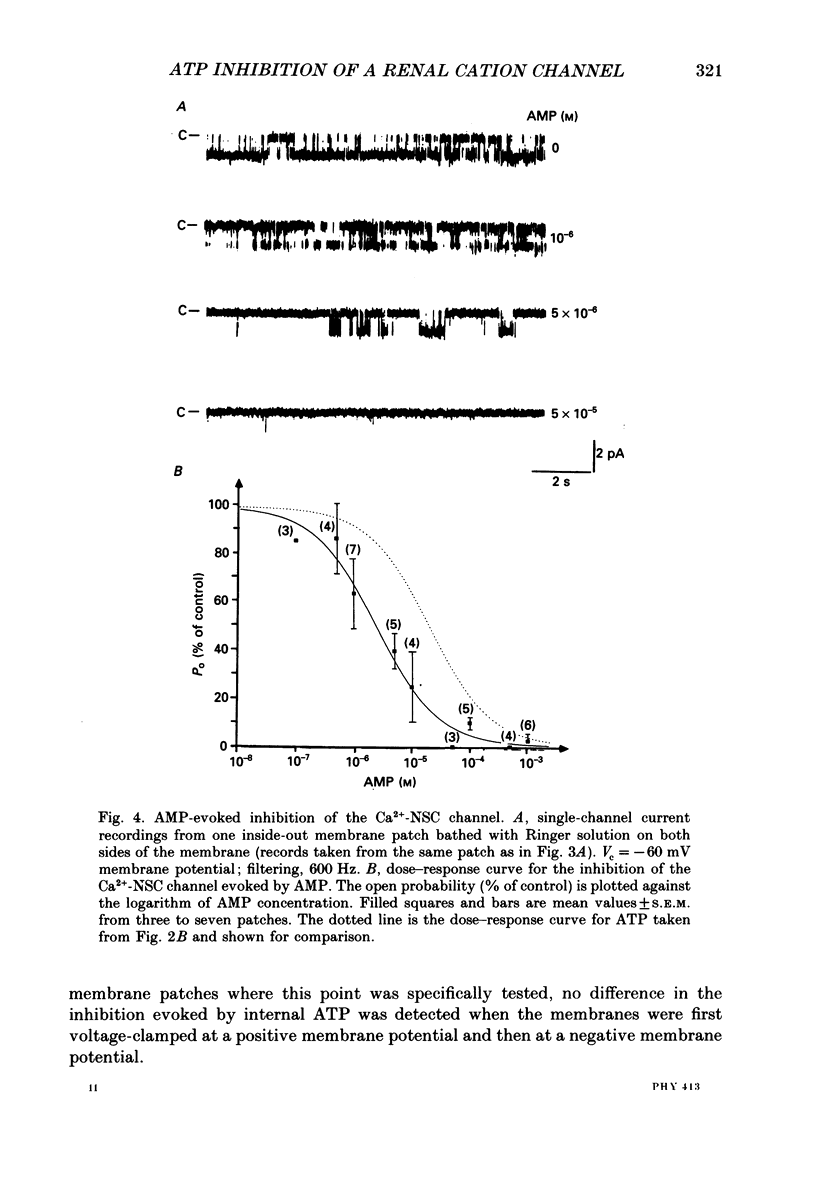
Abstract
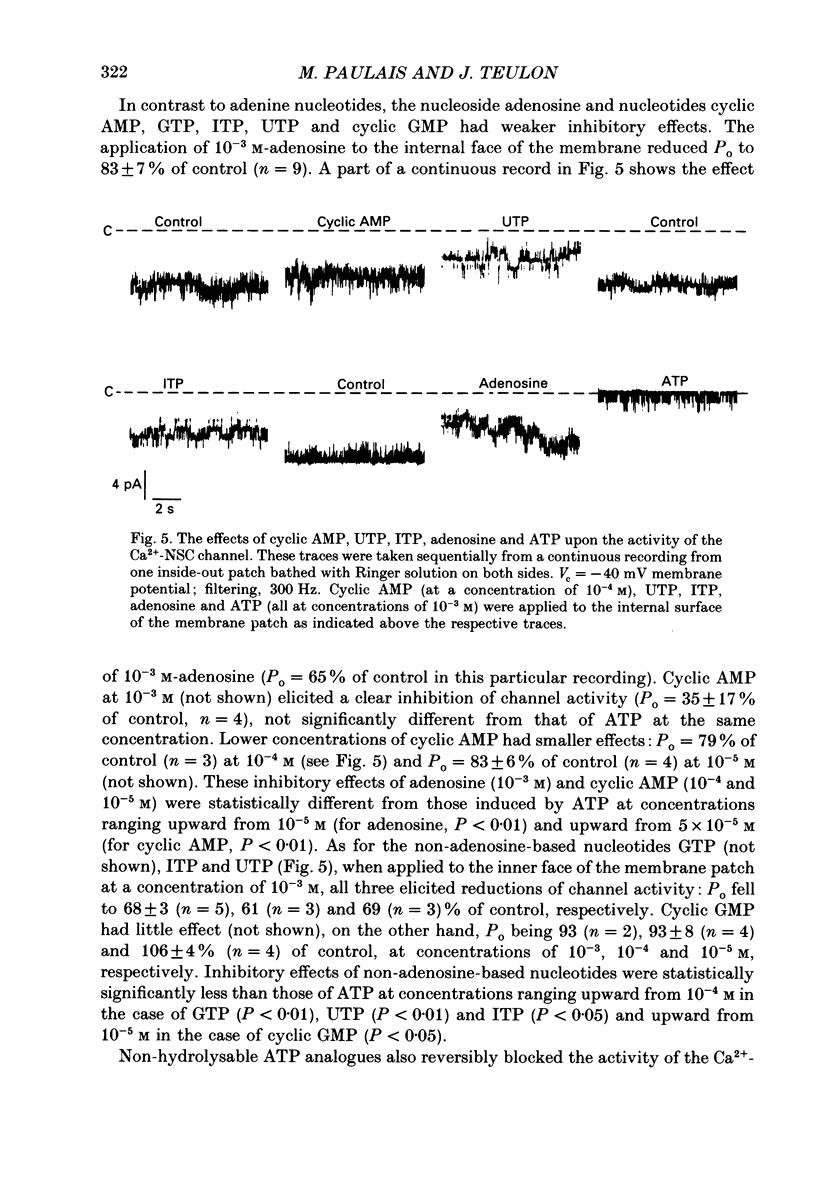
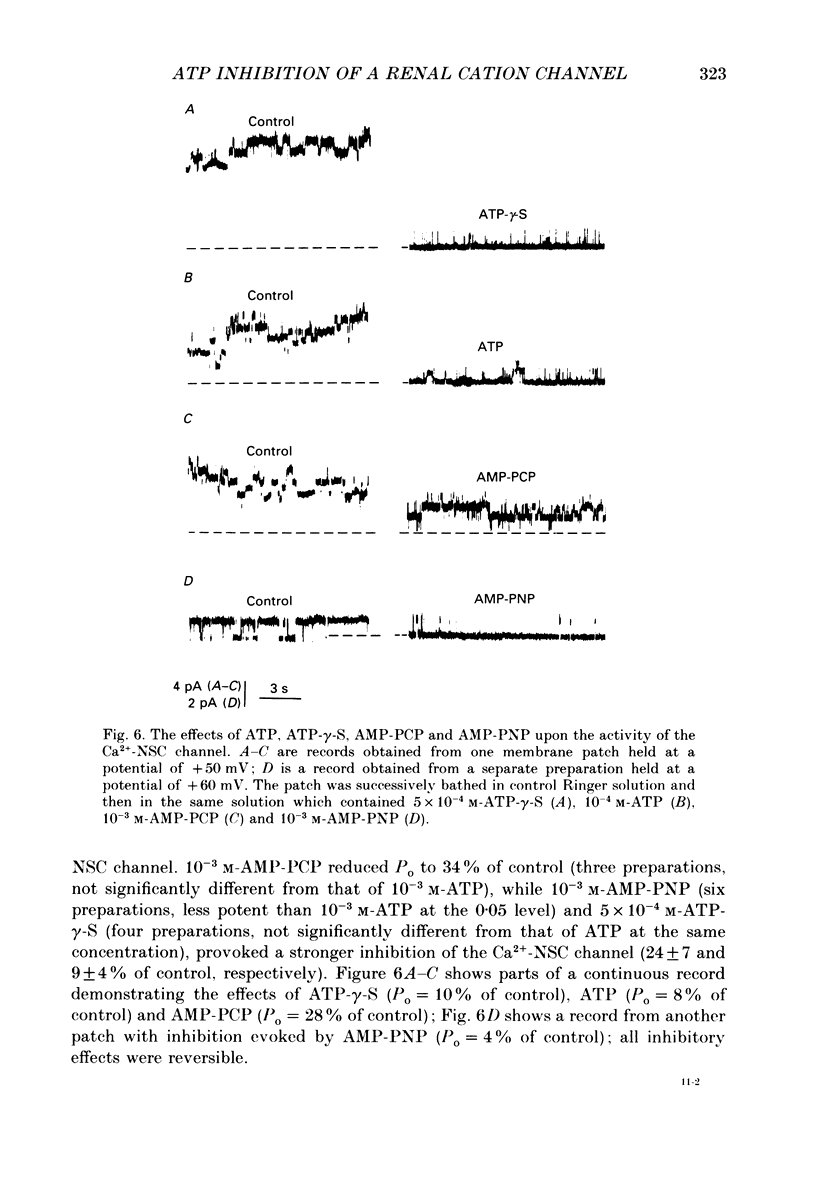
1. Patch-clamp single-channel current recordings were used to study the inhibition of Ca2+-activated non-selective cation channels by internal nucleotides in patches excised from basolateral membranes of the thick ascending limb of Henle's loop of the mouse kidney. 2. The application of ATP, ADP or AMP to the cytoplasmic face of excised inside-out membrane patches reduced the open-state probability of the channels (Po) in a dose-dependent way without effect upon the unitary current amplitude. Dose-response curves gave half-maximal inhibitory concentrations of 20, 21 and 2.5 microM for ATP, ADP and AMP, respectively, while the Hill coefficient was close to one in all three cases. 3. Cyclic AMP partially inhibited channel activity (Po = 35 +/- 17% of control) only at high, unphysiological concentrations (10(-3) M) while adenosine (10(-3) M) had very little effect (Po = 83 +/- 7% of control). 4. Replacement of adenine with other purines (guanine, hypoxanthine) or pyrimidine (uridine) bases very largely reduced inhibitory activity. Cyclic GMP had no effect. 5. Non-hydrolysable analogues of ATP, AMP-PNP (10(-3) M) and ATP-gamma-S (5 x 10(-4) M), were effective inhibitors of the channel (Po = 24 +/- 7 and 9 +/- 4% of control, respectively.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashcroft F. M. Adenosine 5'-triphosphate-sensitive potassium channels. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1988;11:97–118. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.11.030188.000525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevan S., Gray P. T., Ritchie J. M. A calcium-activated cation-selective channel in rat cultured Schwann cells. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1984 Sep 22;222(1228):349–355. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1984.0068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Neher E., Reuter H., Stevens C. F. Inward current channels activated by intracellular Ca in cultured cardiac cells. Nature. 1981 Dec 24;294(5843):752–754. doi: 10.1038/294752a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A. Myoplasmic free calcium concentration reached during the twitch of an intact isolated cardiac cell and during calcium-induced release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum of a skinned cardiac cell from the adult rat or rabbit ventricle. J Gen Physiol. 1981 Nov;78(5):457–497. doi: 10.1085/jgp.78.5.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greger R., Velázquez H. The cortical thick ascending limb and early distal convoluted tubule in the urinary concentrating mechanism. Kidney Int. 1987 Feb;31(2):590–596. doi: 10.1038/ki.1987.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakei M., Noma A., Shibasaki T. Properties of adenosine-triphosphate-regulated potassium channels in guinea-pig ventricular cells. J Physiol. 1985 Jun;363:441–462. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Light D. B., McCann F. V., Keller T. M., Stanton B. A. Amiloride-sensitive cation channel in apical membrane of inner medullary collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1988 Aug;255(2 Pt 2):F278–F286. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.255.2.F278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marty A., Tan Y. P., Trautmann A. Three types of calcium-dependent channel in rat lacrimal glands. J Physiol. 1984 Dec;357:293–325. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama Y., Petersen O. H. Cholecystokinin activation of single-channel currents is mediated by internal messenger in pancreatic acinar cells. Nature. 1982 Nov 4;300(5887):61–63. doi: 10.1038/300061a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama Y., Petersen O. H. Single calcium-dependent cation channels in mouse pancreatic acinar cells. J Membr Biol. 1984;81(1):83–87. doi: 10.1007/BF01868812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama Y., Peterson O. H. Single-channel currents in isolated patches of plasma membrane from basal surface of pancreatic acini. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):159–161. doi: 10.1038/299159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy E., Chamberlin M. E., Mandel L. J. Effects of calcitonin on cytosolic Ca in a suspension of rabbit medullary thick ascending limb tubules. Am J Physiol. 1986 Oct;251(4 Pt 1):C491–C495. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.251.4.C491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noma A. ATP-regulated K+ channels in cardiac muscle. Nature. 1983 Sep 8;305(5930):147–148. doi: 10.1038/305147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partridge L. D., Swandulla D. Calcium-activated non-specific cation channels. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Feb;11(2):69–72. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90167-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen O. H., Findlay I. Electrophysiology of the pancreas. Physiol Rev. 1987 Jul;67(3):1054–1116. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1987.67.3.1054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs F., Neil J., Barkakati N. The automated analysis of data from single ionic channels. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Dec;395(4):331–340. doi: 10.1007/BF00580798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soltoff S. P. ATP and the regulation of renal cell function. Annu Rev Physiol. 1986;48:9–31. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.48.030186.000301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgess N. C., Hales C. N., Ashford M. L. Calcium and ATP regulate the activity of a non-selective cation channel in a rat insulinoma cell line. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Aug;409(6):607–615. doi: 10.1007/BF00584661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgess N. C., Hales C. N., Ashford M. L. Inhibition of a calcium-activated, non-selective cation channel, in a rat insulinoma cell line, by adenine derivatives. FEBS Lett. 1986 Nov 24;208(2):397–400. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81056-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teulon J., Paulais M., Bouthier M. A Ca2-activated cation-selective channel in the basolateral membrane of the cortical thick ascending limb of Henle's loop of the mouse. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Nov 27;905(1):125–132. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90016-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yellen G. Single Ca2+-activated nonselective cation channels in neuroblastoma. Nature. 1982 Mar 25;296(5855):357–359. doi: 10.1038/296357a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


