Abstract
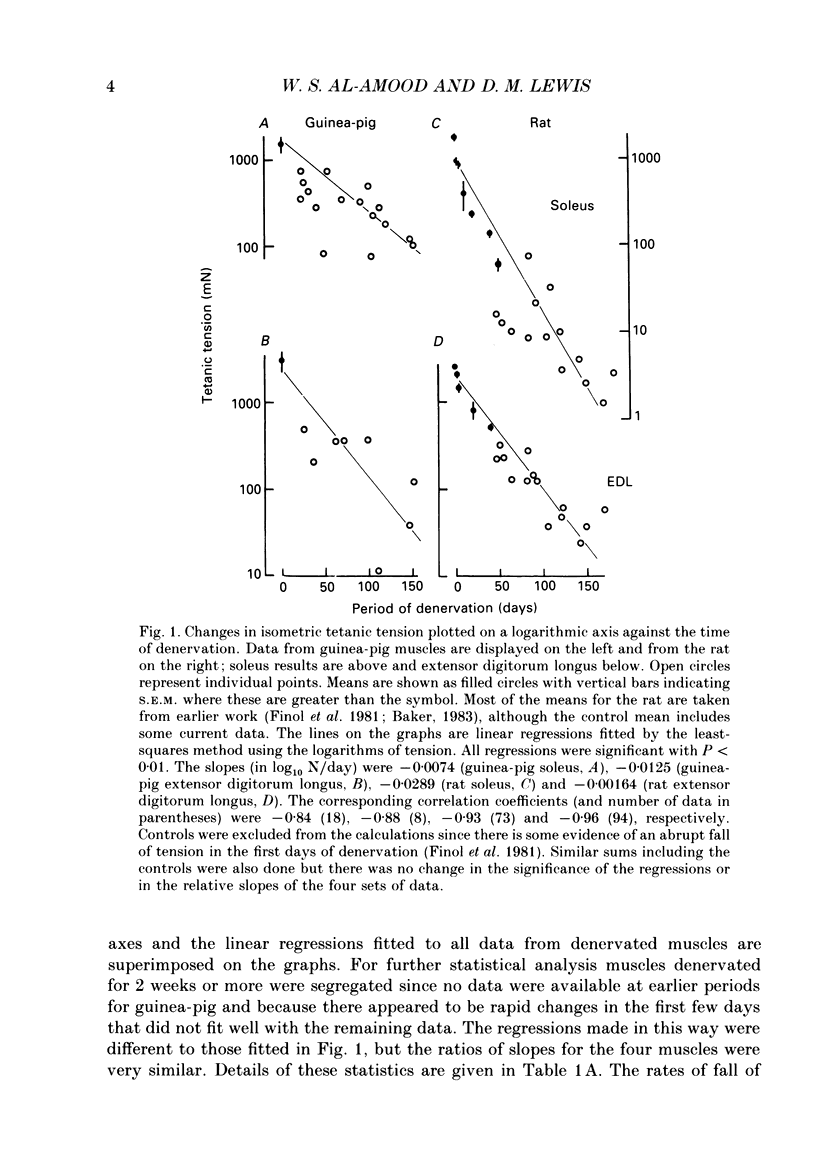
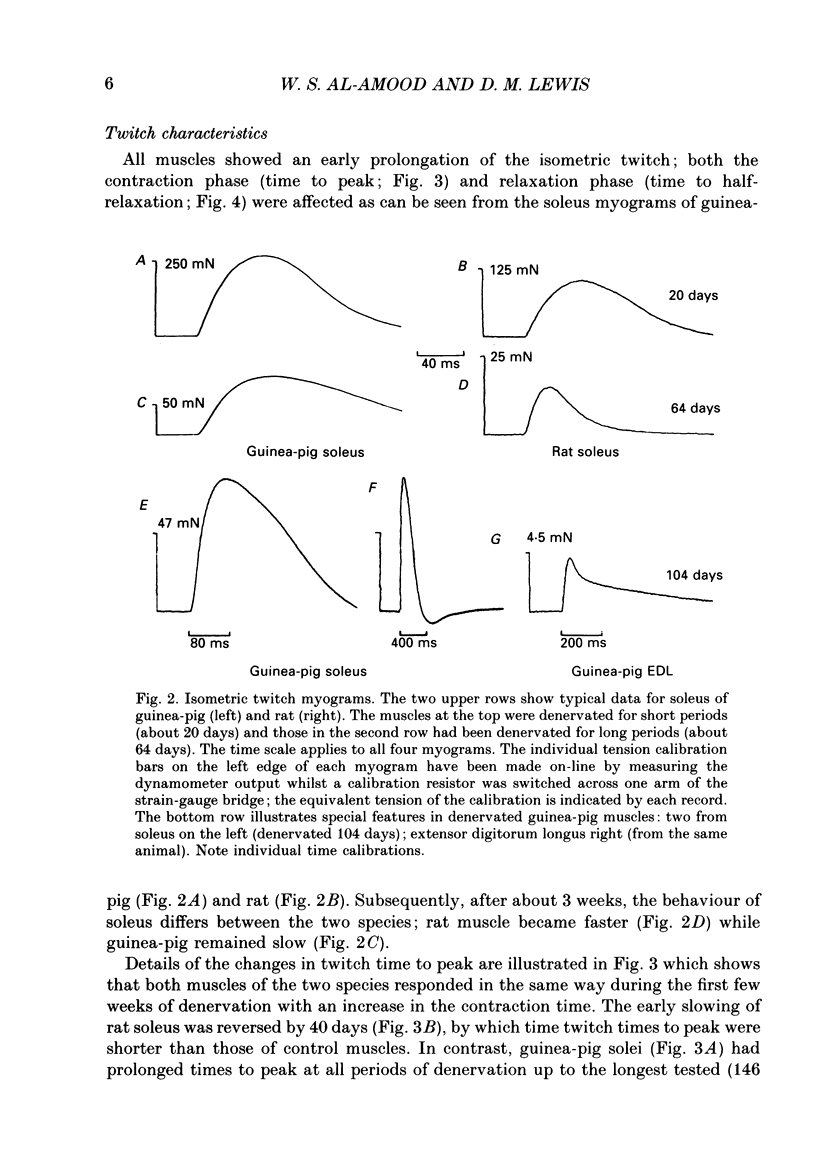
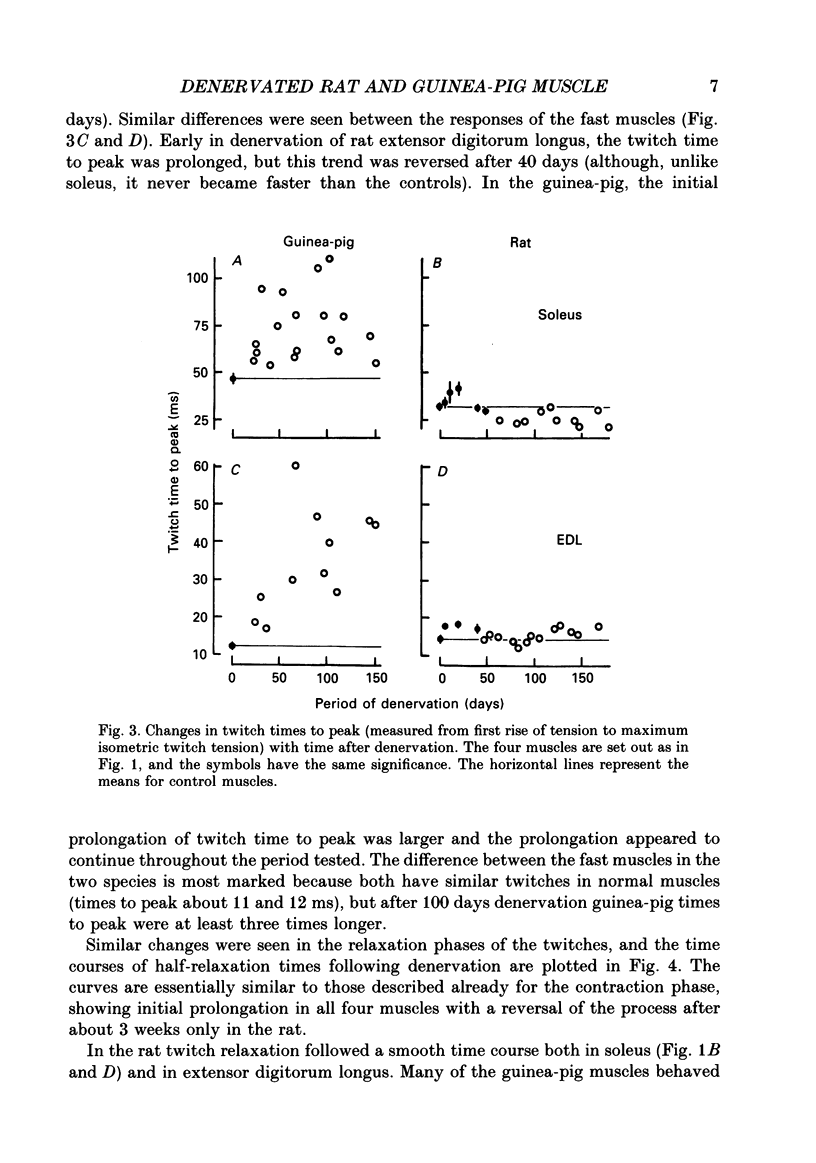
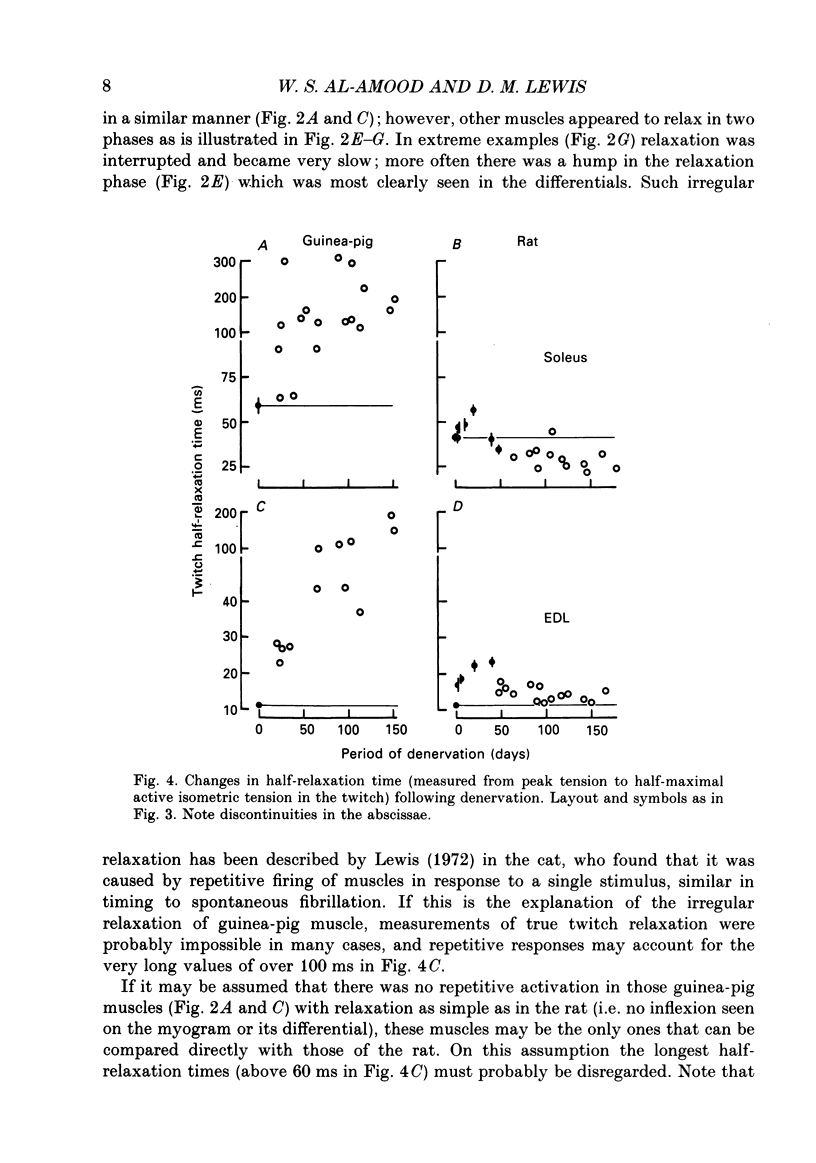
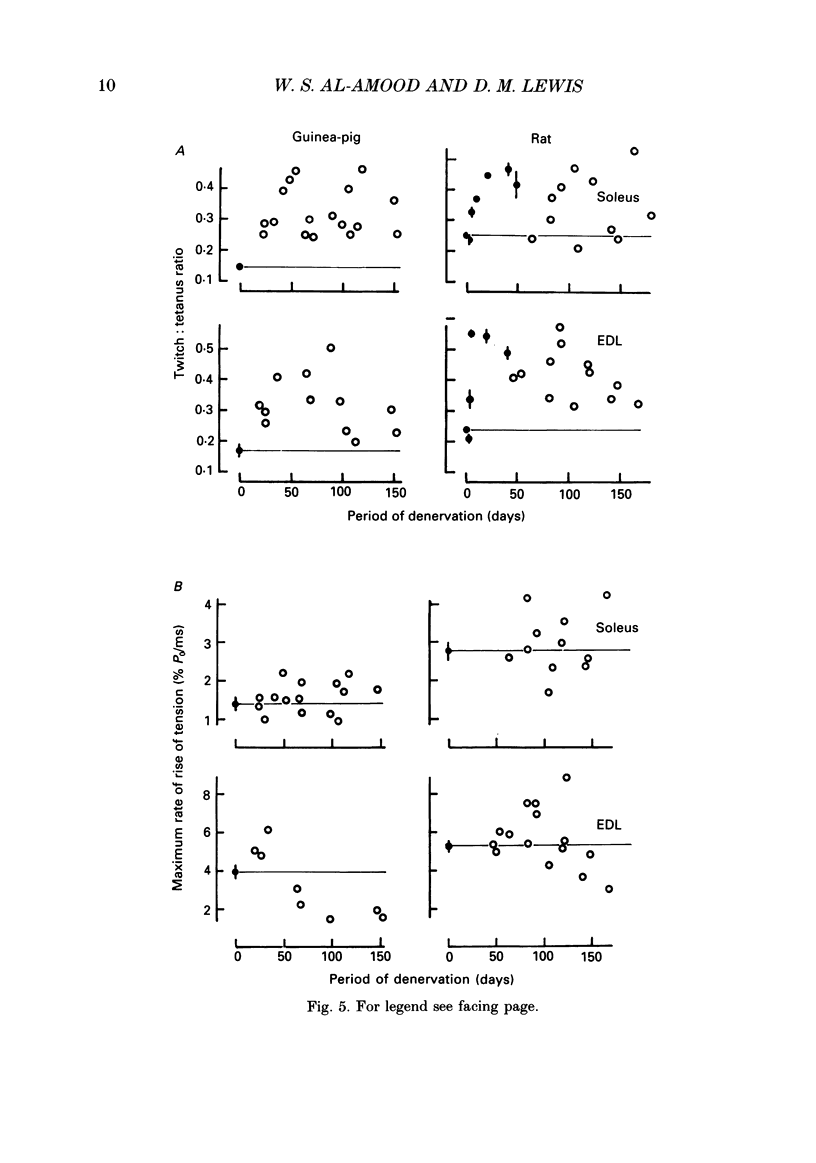
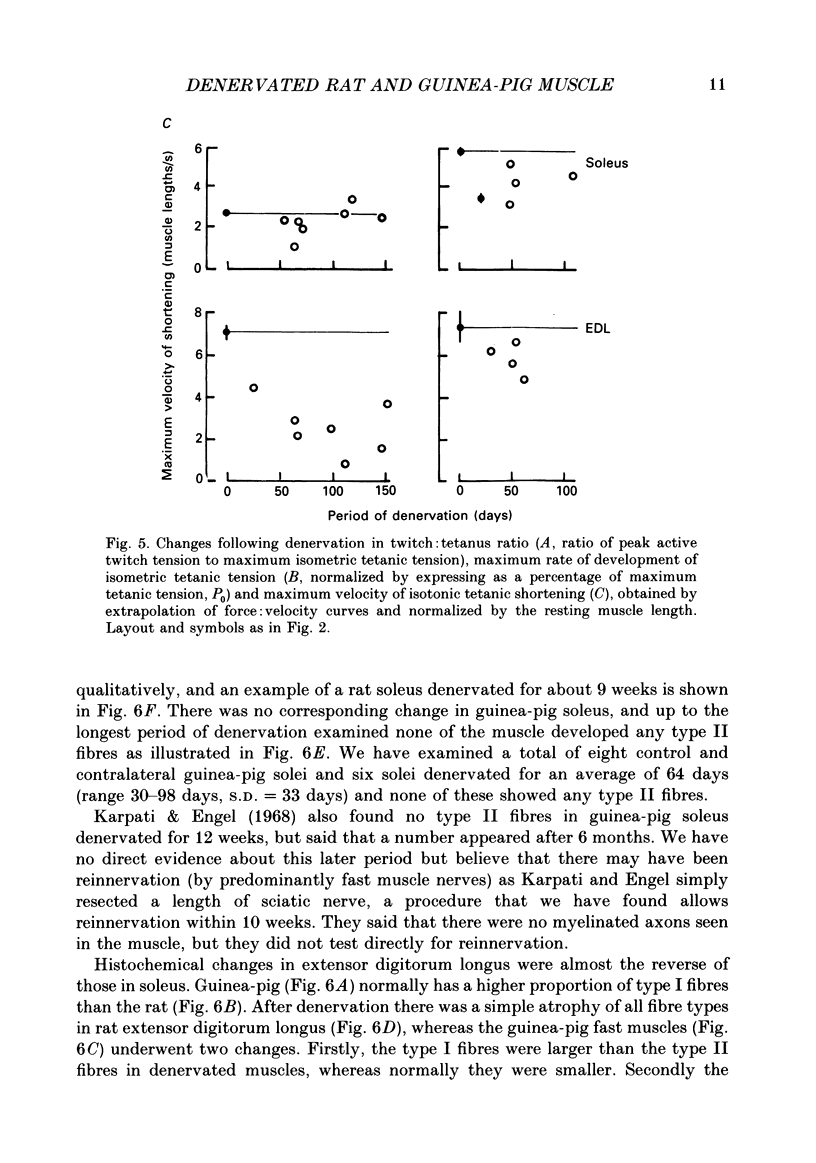
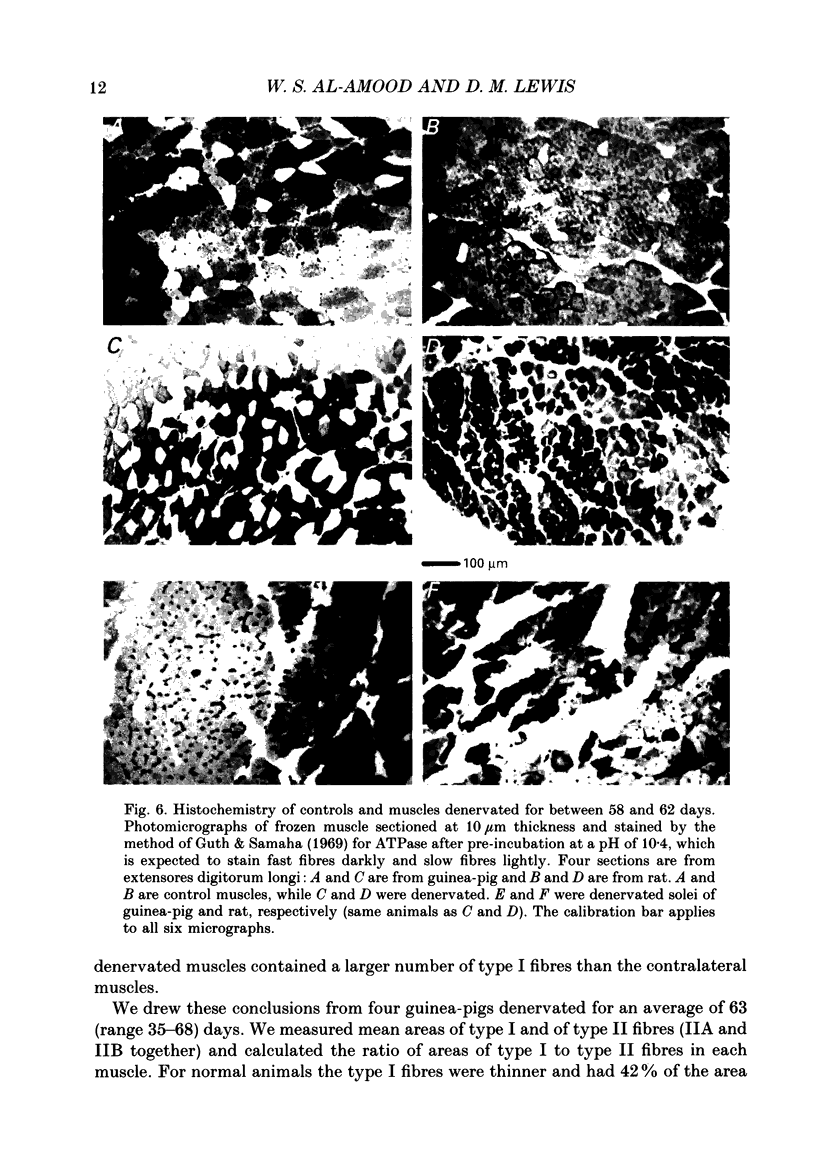
1. A fast (extensor digitorum longus) and slow (soleus) twitch muscle were denervated in rats and guinea-pigs and isometric and isotonic contractions were followed for periods of up to 6 months after. 2. The decay of tetanic tension with time could be described as exponential. The rate of decay of tension was greatest in rat soleus and least in guinea-pig soleus by a factor of more than three. The fast muscles atrophied at intermediate rates. 3. The contraction and relaxation times of soleus and extensor digitorum longus of rat, initially prolonged by denervation, became shorter after 3 weeks. There was no such reversal in either guinea-pig muscle, indeed extensor digitorum longus twitch became even more prolonged. Guinea-pig muscles often showed signs of repetitive response to a single stimulus, resulting in distortion of relaxation of the twitch. 4. There was a slowing of isotonic shortening velocity in the late stage of denervation of guinea-pig extensor digitorum longus, accompanied by a fall in the rate of development of isometric tetanic tension. There was a just-significant (P less than 0.1) increase in the shortening velocity of rat soleus. None of the other muscles showed any change in either rate characteristic. 5. In guinea-pig extensor digitorum longus the type I fibres atrophied less than type II fibres; in all other muscles the atrophy was more uniform, possibly faster in type II. Guinea-pig soleus remained pure type I contrasting with an increase in the numbers of type II fibres in rat soleus. There was a possible increase in the number of type I fibres in guinea-pig fast muscle and no change in the rat.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Al-Amood W. S., Finol H. J., Lewis D. M. Chronic stimulation modifies the isotonic shortening velocity of denervated rat slow-twitch muscle. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1986 Jun 23;228(1250):43–58. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1986.0039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulhunty A. F. Excitation-contraction coupling and contractile properties in denervated rat EDL and soleus muscles. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1985 Apr;6(2):207–225. doi: 10.1007/BF00713062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finol H. J., Lewis D. M., Owens R. The effects of denervation on contractile properties or rat skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1981;319:81–92. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guth L., Samaha F. J. Qualitative differences between actomyosin ATPase of slow and fast mammalian muscle. Exp Neurol. 1969 Sep;25(1):138–152. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(69)90077-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guth L., Wells J. B. Physiological and histochemical properties of the soleus muscle after denervation of its antagonists. Exp Neurol. 1972 Sep;36(3):463–471. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(72)90006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutmann E., Melichna J., Syrový I. Contraction properties and ATPase activity in fast and slow muscle of the rat during denervation. Exp Neurol. 1972 Sep;36(3):488–497. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(72)90008-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaweed M. M., Herbison G. J., Ditunno J. F. Denervation and reinnervation of fast and slow muscles. A histochemical study in rats. J Histochem Cytochem. 1975 Nov;23(11):808–827. doi: 10.1177/23.11.127809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpati G., Engel W. K. Histochemical investigation of fiber type ratios with the myofibrillar ATP-ase reaction in normal and denervated skeletal muscles of guinea pig. Am J Anat. 1968 Jan;122(1):145–155. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001220109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpati G., Engel W. K. Neuronal trophic function. A new aspect demonstrated histochemically in developing soleus muscle. Arch Neurol. 1967 Nov;17(5):542–545. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1967.00470290096012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kean C. J., Lewis D. M., McGarrick J. D. Dynamic properties of denervated fast and slow twitch muscle of the cat. J Physiol. 1974 Feb;237(1):103–113. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kugelberg E. Adaptive transformation of rat soleus motor units during growth. J Neurol Sci. 1976 Mar;27(3):269–289. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(76)90001-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. M., Pardoe M. J., Webb S. N. The effect of denervation on the mechanical and electrical properties of cat skeletal muscle [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1978 Apr;277:48P–49P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. M. The effect of denervation on the mechanical and electrical responses of fast and slow mammalian twitch muscle. J Physiol. 1972 Apr;222(1):51–75. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomo T., Westgaard R. H., Dahl H. A. Contractile properties of muscle: control by pattern of muscle activity in the rat. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1974 Aug 27;187(1086):99–103. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1974.0064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pachter B. R., Eberstein A., Goodgold J. Electrical stimulation effect on denervated skeletal myofibers in rats: a light and electron microscopic study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1982 Sep;63(9):427–430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmons S., Vrbová G. The influence of activity on some contractile characteristics of mammalian fast and slow muscles. J Physiol. 1969 May;201(3):535–549. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector S. A. Trophic effects on the contractile and histochemical properties of rat soleus muscle. J Neurosci. 1985 Aug;5(8):2189–2196. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-08-02189.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syrový I., Gutmann E., Melichna J. Differential response of myosin--ATPase activity and contraction properties of fast and slow rabbit muscles following denervation. Experientia. 1971 Dec 15;27(12):1426–1427. doi: 10.1007/BF02154269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]