Abstract
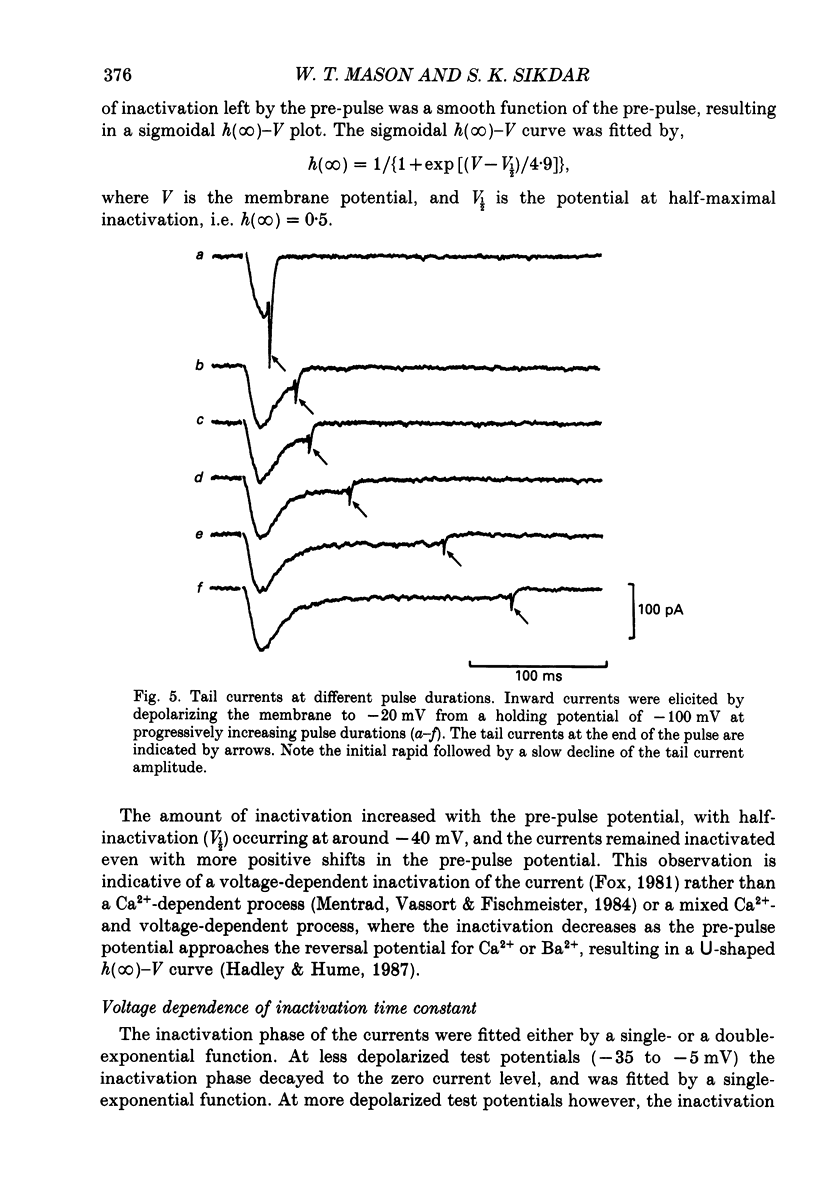
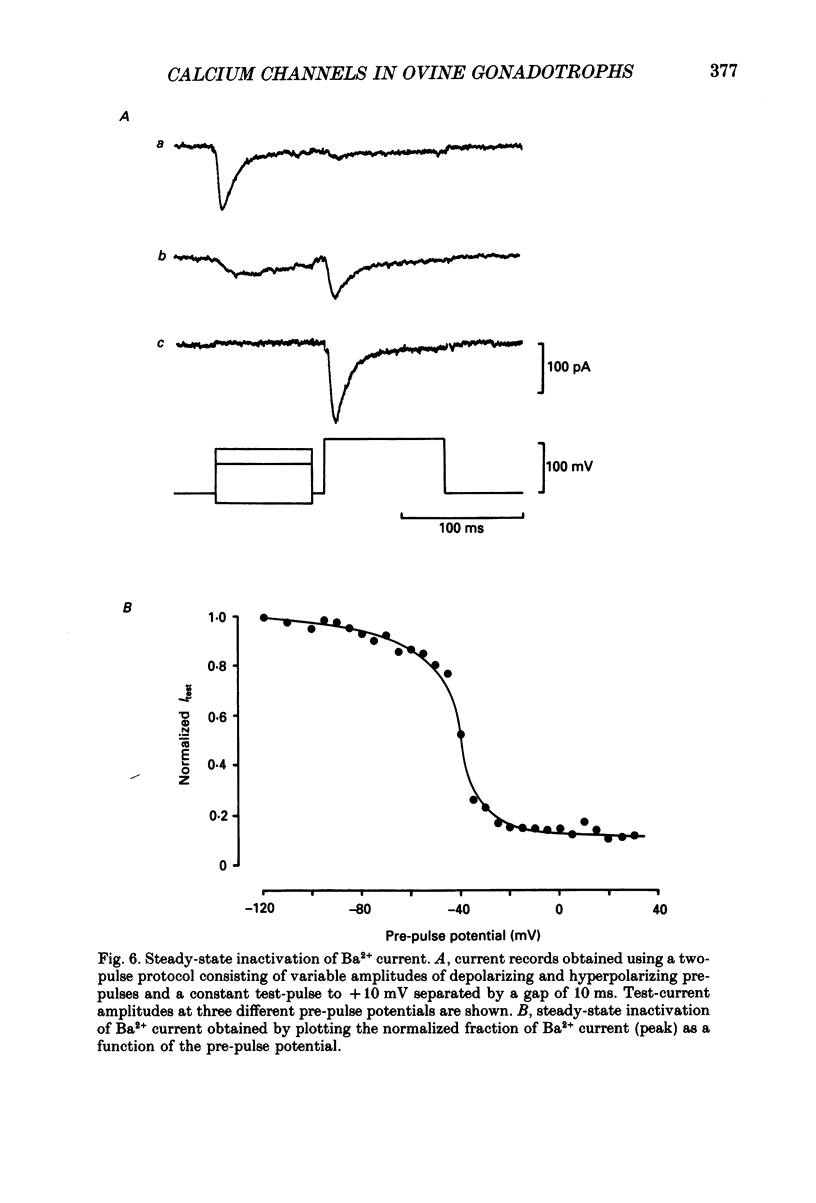
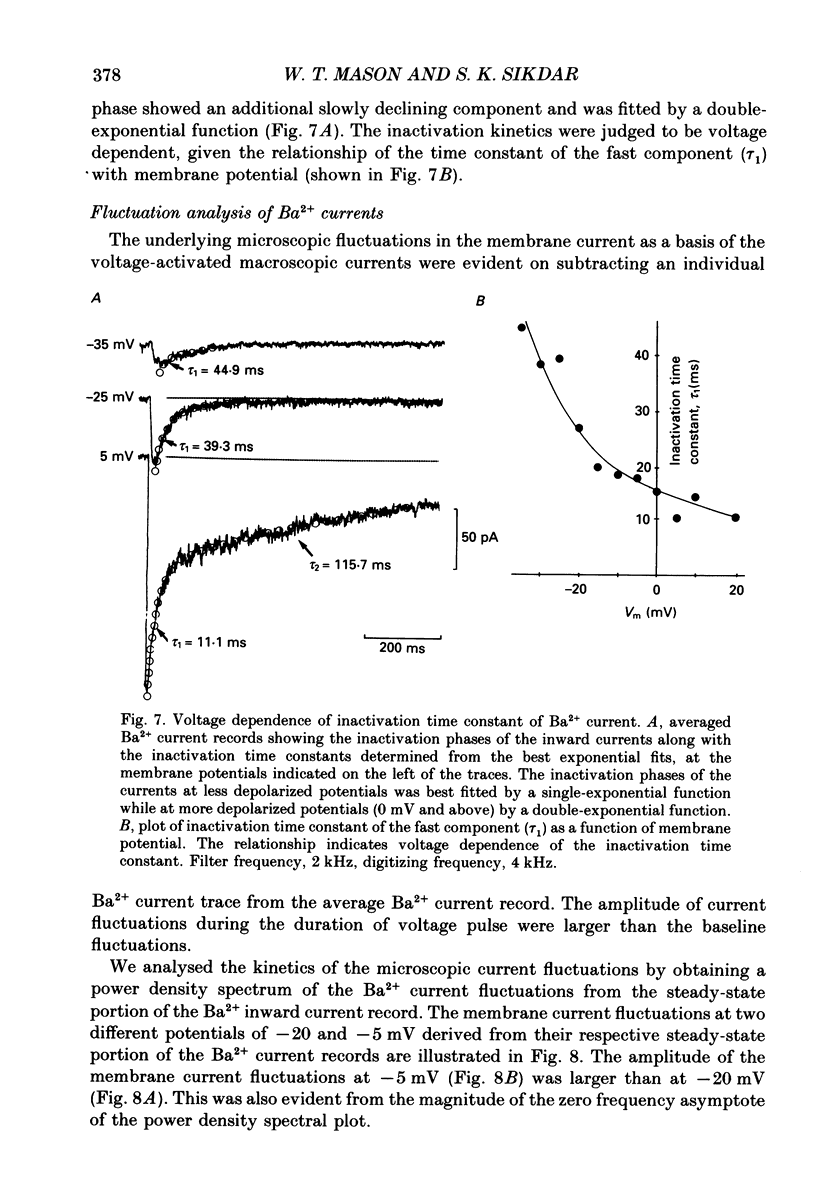
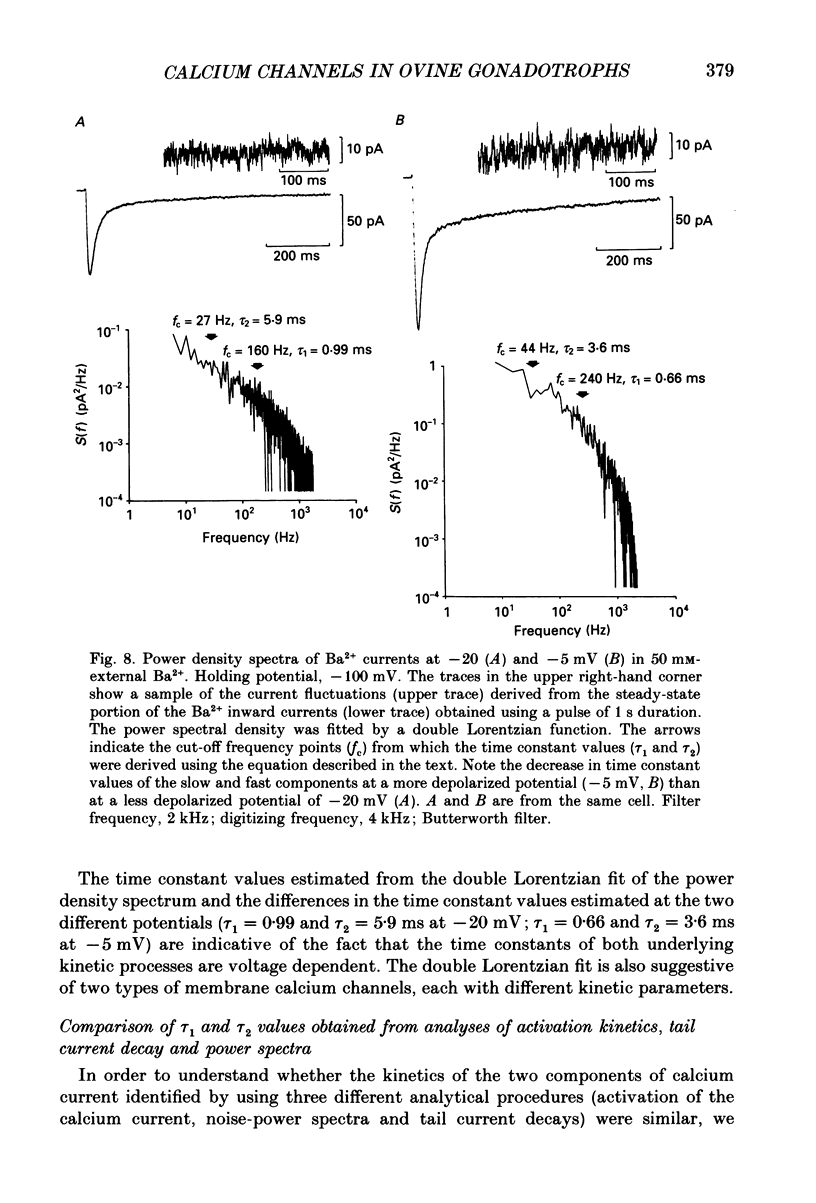
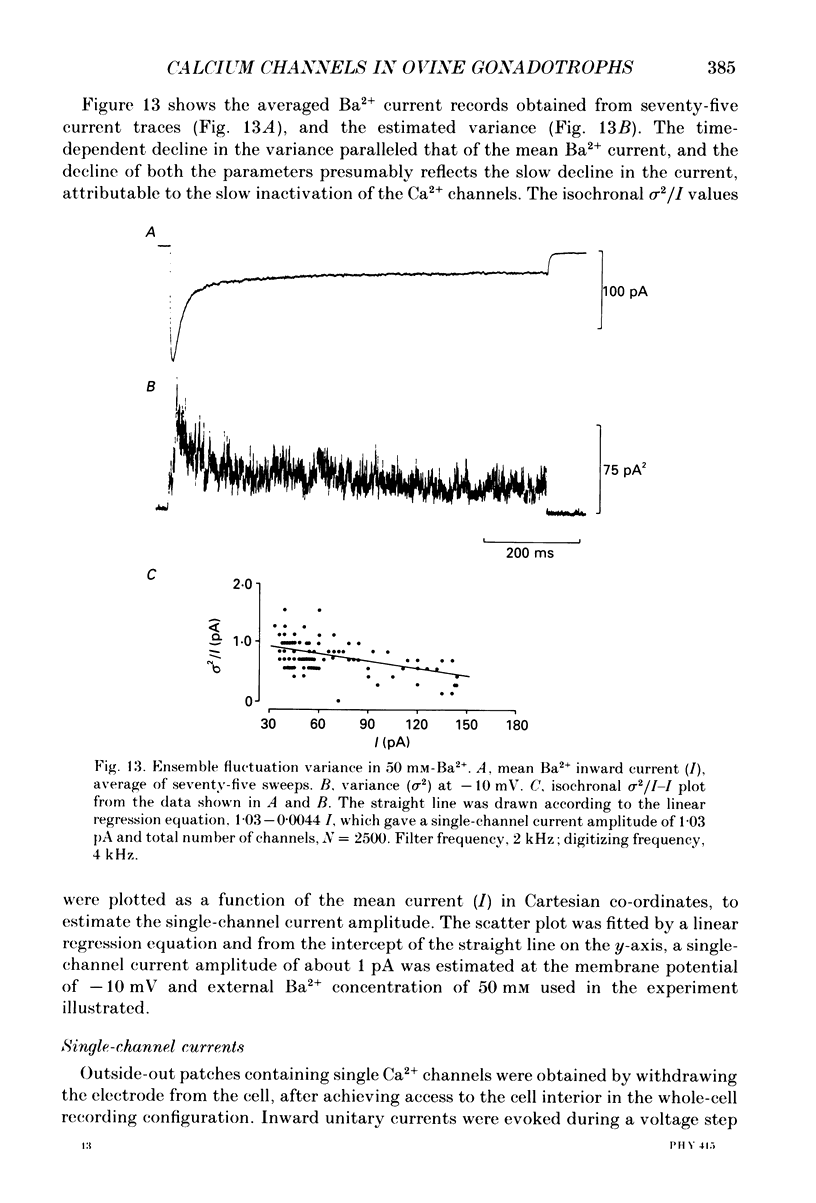
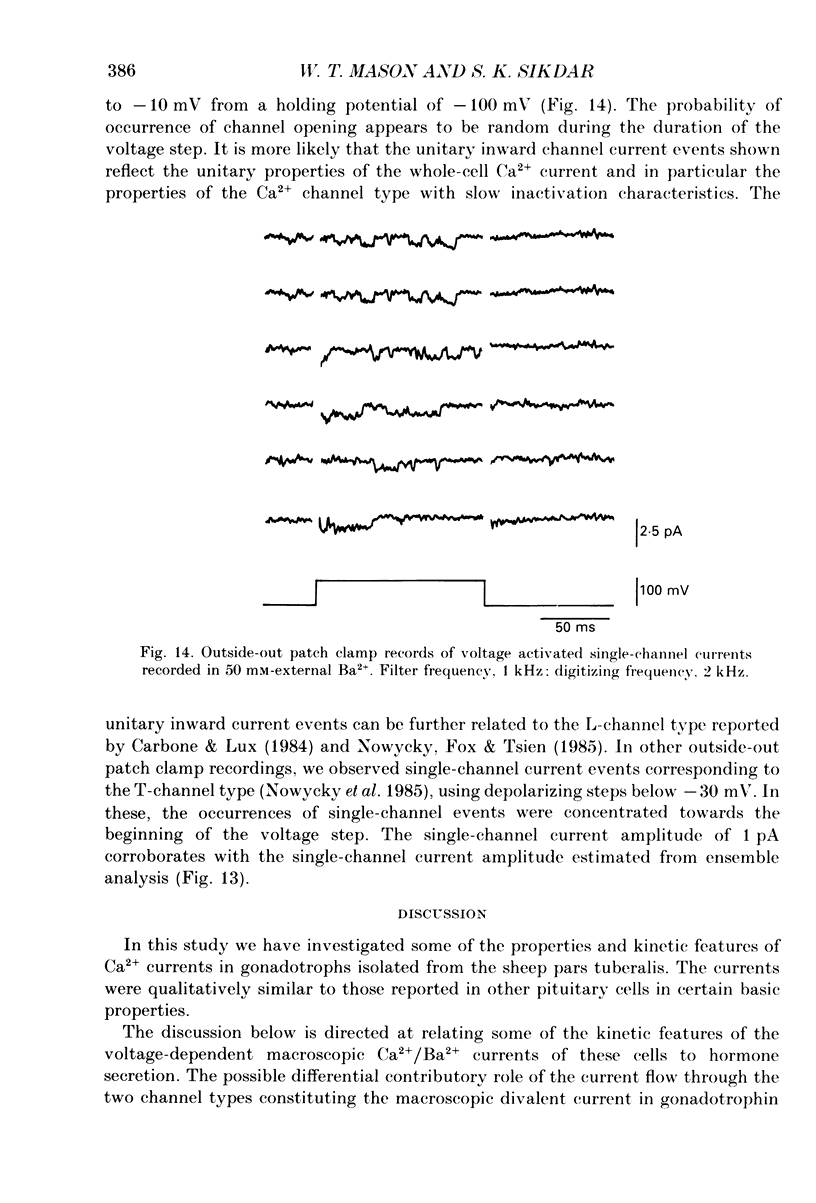
1. Voltage-clamp recordings were obtained from gonadotrophs of the ovine pars tuberalis in dissociated cell culture, utilizing the whole-cell recording mode of the patch-clamp technique. 2. The amplitudes of Ca2+ and Ba2+ currents were dependent on the extracellular concentration of divalent cation. 3. Ba2+ tail currents were observed on termination of depolarizing voltage steps. The extrapolated amplitudes of 'instantaneous' tail currents increased with membrane depolarization and showed saturation beyond +15 mV. 4. True inactivation of currents occurred in the presence of both external Ca2+ and Ba2+, judged from decrease in tail current amplitudes with progressive increases in duration of the activating voltage pulse. The inactivation process was fitted by a single-exponential function at membrane potentials below -25 mV, while at more depolarized potentials the inactivation was better described by a double-exponential function. The inactivation time constants decreased with positive shifts in membrane potential favouring a voltage-dependent inactivation. 5. The half-value of steady-state inactivation was observed at -40 mV using a two-pulse protocol. 6. Power spectral analysis of Ba2+ current noise from the steady-state portion of inward current showed a double Lorentzian fit of the power spectrum. 7. Two types of voltage-activated Ca2+ currents were identified based on their kinetics, voltage dependence, dependence on activation frequency, differential sensitivity to intracellular ATP and cyclic AMP, and to extracellular application of nifedipine. The channels with faster kinetics had a lower activation threshold (-50 mV) and the amplitude of the current was sensitive to clamping frequency. 8. From ensemble noise analysis of mean maximal inward current, single-channel amplitude of about 1 pA was estimated in 50 mM-Ba2+.
Full text
PDF




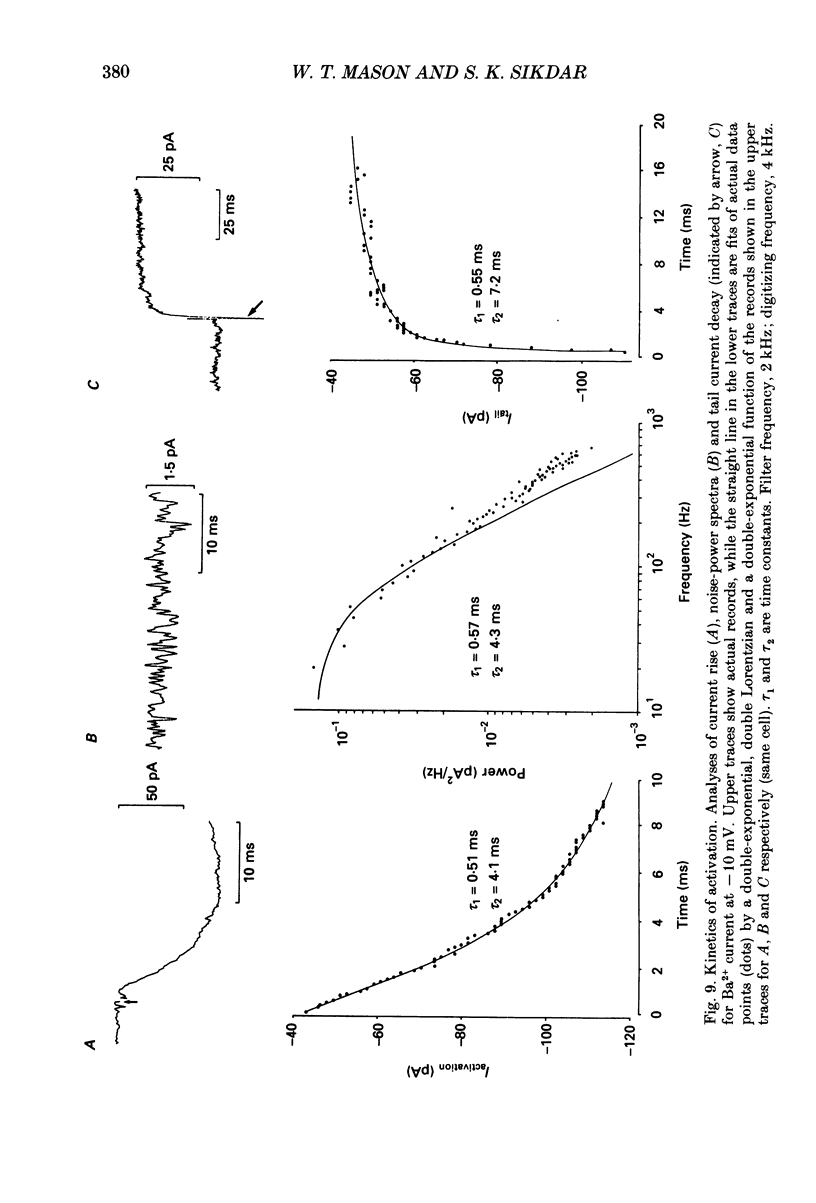

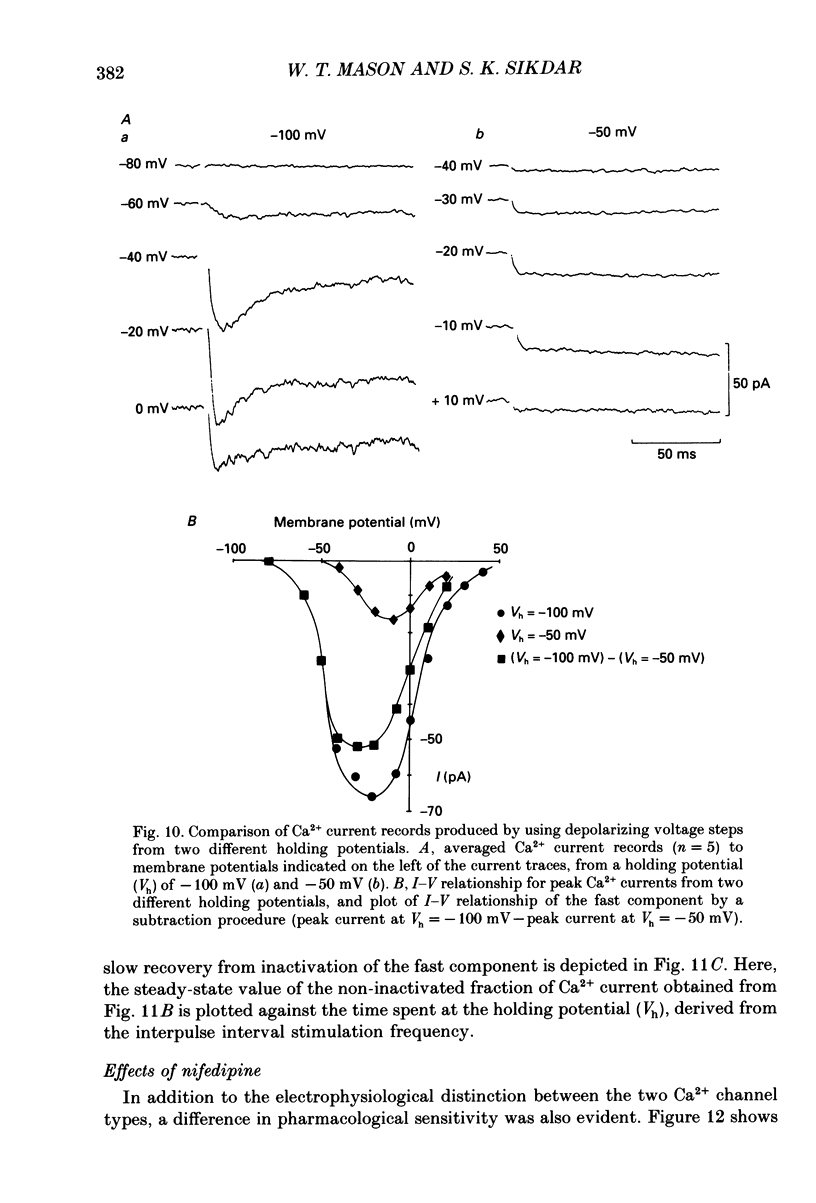
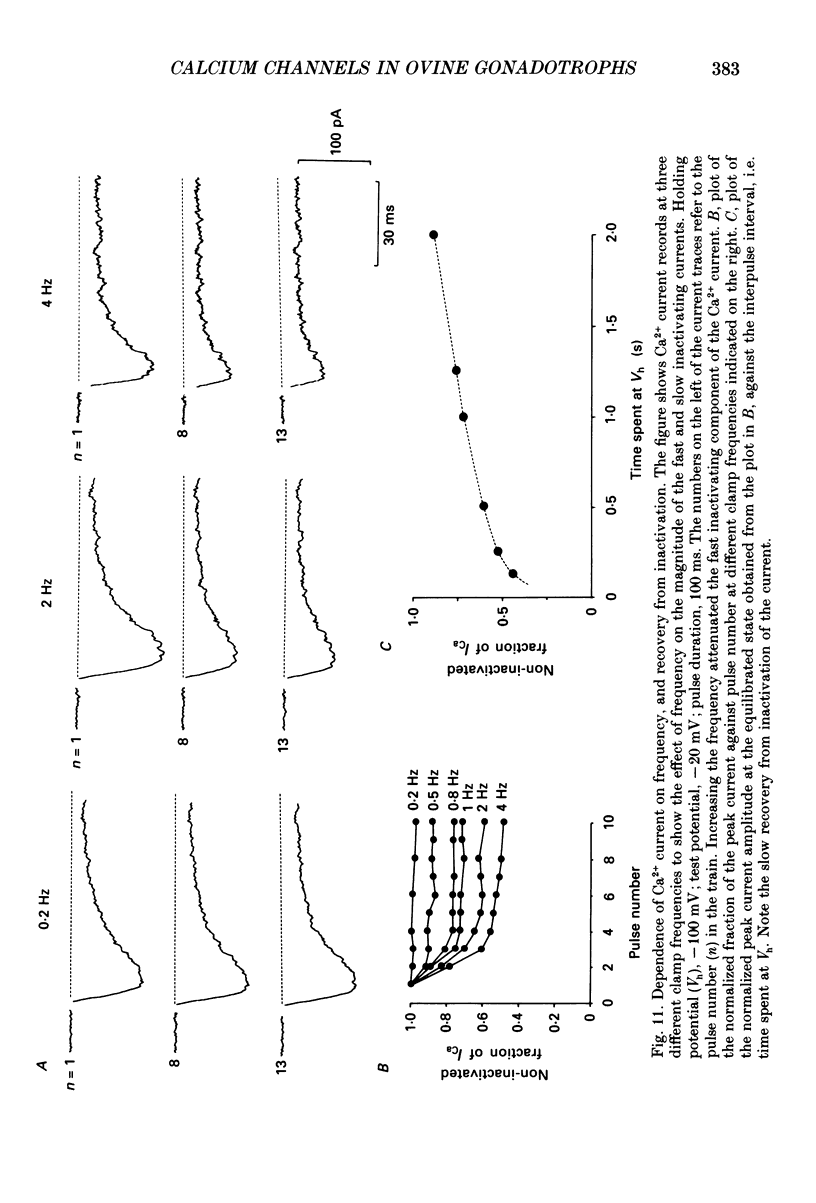
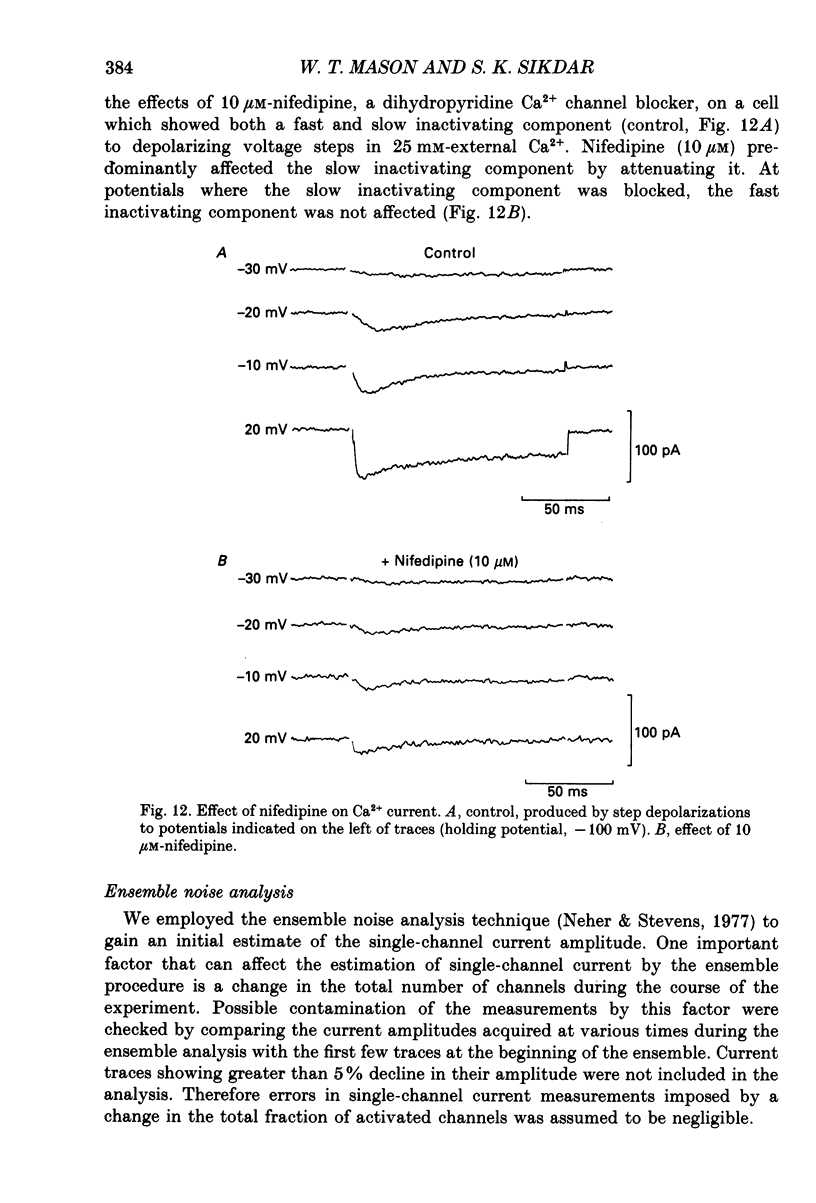





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akaike N., Lee K. S., Brown A. M. The calcium current of Helix neuron. J Gen Physiol. 1978 May;71(5):509–531. doi: 10.1085/jgp.71.5.509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belluzzi O., Sacchi O., Wanke E. Identification of delayed potassium and calcium currents in the rat sympathetic neurone under voltage clamp. J Physiol. 1985 Jan;358:109–129. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. M., Tsuda Y., Wilson D. L. A description of activation and conduction in calcium channels based on tail and turn-on current measurements in the snail. J Physiol. 1983 Nov;344:549–583. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbone E., Lux H. D. A low voltage-activated, fully inactivating Ca channel in vertebrate sensory neurones. Nature. 1984 Aug 9;310(5977):501–502. doi: 10.1038/310501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobbett P., Ingram C. D., Mason W. T. Voltage-activated currents through calcium channels in normal bovine lactotrophs. Neuroscience. 1987 Nov;23(2):661–677. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90084-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conn P. M., Rogers D. C., Seay S. G. Structure-function relationship of calcium ion channel antagonists at the pituitary gonadotrope. Endocrinology. 1983 Nov;113(5):1592–1595. doi: 10.1210/endo-113-5-1592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubinsky J. M., Oxford G. S. Ionic currents in two strains of rat anterior pituitary tumor cells. J Gen Physiol. 1984 Mar;83(3):309–339. doi: 10.1085/jgp.83.3.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert R., Chad J. E. Inactivation of Ca channels. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1984;44(3):215–267. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(84)90009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedulova S. A., Kostyuk P. G., Veselovsky N. S. Two types of calcium channels in the somatic membrane of new-born rat dorsal root ganglion neurones. J Physiol. 1985 Feb;359:431–446. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick E. M., Marty A., Neher E. Sodium and calcium channels in bovine chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:599–635. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox A. P. Voltage-dependent inactivation of a calcium channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):953–956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman M. E., Suarez-Kurtz G., Kaczorowski G. J., Katz G. M., Reuben J. P. Two calcium currents in a smooth muscle cell line. Am J Physiol. 1986 Apr;250(4 Pt 2):H699–H703. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1986.250.4.H699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross D. S., Turgeon J. L., Waring D. W. The ovine pars tuberalis: a naturally occurring source of partially purified gonadotropes which secrete luteinizing hormone in vitro. Endocrinology. 1984 Jun;114(6):2084–2091. doi: 10.1210/endo-114-6-2084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadley R. W., Hume J. R. An intrinsic potential-dependent inactivation mechanism associated with calcium channels in guinea-pig myocytes. J Physiol. 1987 Aug;389:205–222. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Byerly L. Calcium channel. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1981;4:69–125. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.04.030181.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Miyazaki S., Moody W., Patlak J. Blocking effects of barium and hydrogen ions on the potassium current during anomalous rectification in the starfish egg. J Physiol. 1978 Jun;279:167–185. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Ohmori H. Studies of single calcium channel currents in rat clonal pituitary cells. J Physiol. 1983 Mar;336:649–661. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G., Veselovsky N. S., Fedulova S. A. Ionic currents in the somatic membrane of rat dorsal root ganglion neurons-II. Calcium currents. Neuroscience. 1981;6(12):2431–2437. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90089-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Steinberg I. Z., Walton K. Presynaptic calcium currents in squid giant synapse. Biophys J. 1981 Mar;33(3):289–321. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84898-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lux H. D., Nagy K. Single channel Ca2+ currents in Helix pomatia neurons. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Sep;391(3):252–254. doi: 10.1007/BF00596179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason W. T., Rawlings S. R. Whole-cell recordings of ionic currents in bovine somatotrophs and their involvement in growth hormone secretion. J Physiol. 1988 Nov;405:577–593. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason W. T., Sikdar S. K. Characterization of voltage-gated sodium channels in ovine gonadotrophs: relationship to hormone secretion. J Physiol. 1988 May;399:493–517. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason W. T., Waring D. W. Electrophysiological recordings from gonadotrophs. Evidence for Ca2+ channels mediated by gonadotrophin-releasing hormone. Neuroendocrinology. 1985 Sep;41(3):258–268. doi: 10.1159/000124186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason W. T., Waring D. W. Patch clamp recordings of single ion channel activation by gonadotrophin-releasing hormone in ovine pituitary gonadotrophs. Neuroendocrinology. 1986;43(2):205–219. doi: 10.1159/000124529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matteson D. R., Armstrong C. M. Na and Ca channels in a transformed line of anterior pituitary cells. J Gen Physiol. 1984 Mar;83(3):371–394. doi: 10.1085/jgp.83.3.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mentrard D., Vassort G., Fischmeister R. Calcium-mediated inactivation of the calcium conductance in cesium-loaded frog heart cells. J Gen Physiol. 1984 Jan;83(1):105–131. doi: 10.1085/jgp.83.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitra R., Morad M. Two types of calcium channels in guinea pig ventricular myocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5340–5344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Stevens C. F. Conductance fluctuations and ionic pores in membranes. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1977;6:345–381. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.06.060177.002021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowycky M. C., Fox A. P., Tsien R. W. Three types of neuronal calcium channel with different calcium agonist sensitivity. Nature. 1985 Aug 1;316(6027):440–443. doi: 10.1038/316440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto H., Takahashi K., Yoshii M. Two components of the calcium current in the egg cell membrane of the tunicate. J Physiol. 1976 Feb;255(2):527–561. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quandt F. N., Narahashi T. Isolation and kinetic analysis of inward currents in neuroblastoma cells. Neuroscience. 1984 Sep;13(1):249–262. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90275-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shangold G. A., Murphy S. N., Miller R. J. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone-induced Ca2+ transients in single identified gonadotropes require both intracellular Ca2+ mobilization and Ca2+ influx. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6566–6570. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. E., Wakefield I., King J. A., Naor Z., Millar R. P., Davidson J. S. The initial phase of GnRH-stimulated LH release from pituitary cells is independent of calcium entry through voltage-gated channels. FEBS Lett. 1987 Dec 10;225(1-2):247–250. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81167-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


