Abstract
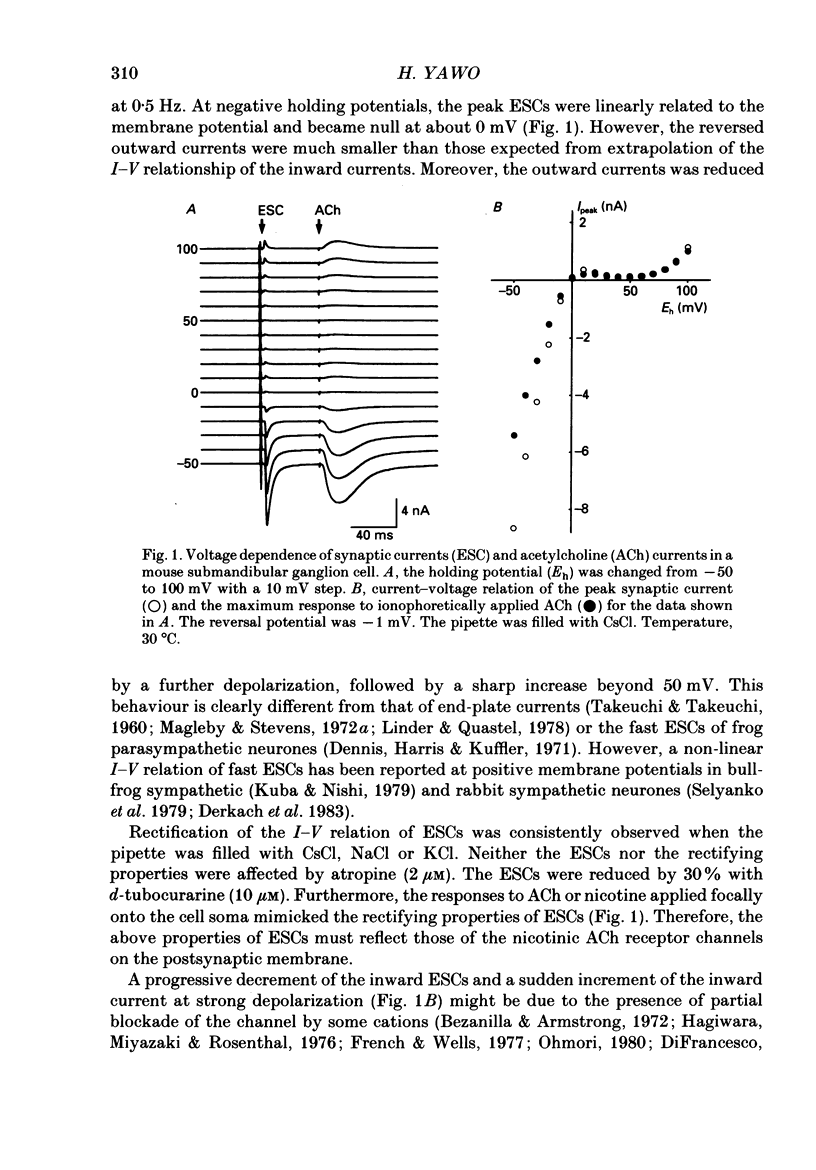
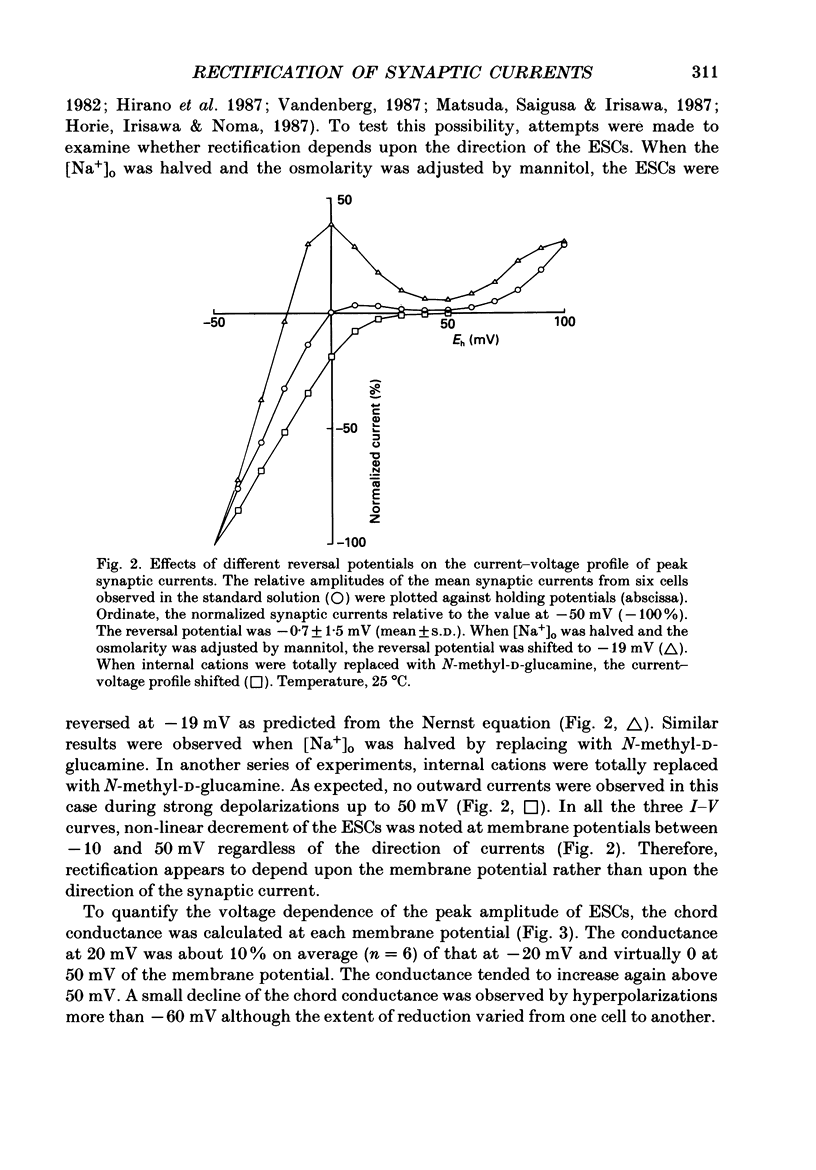
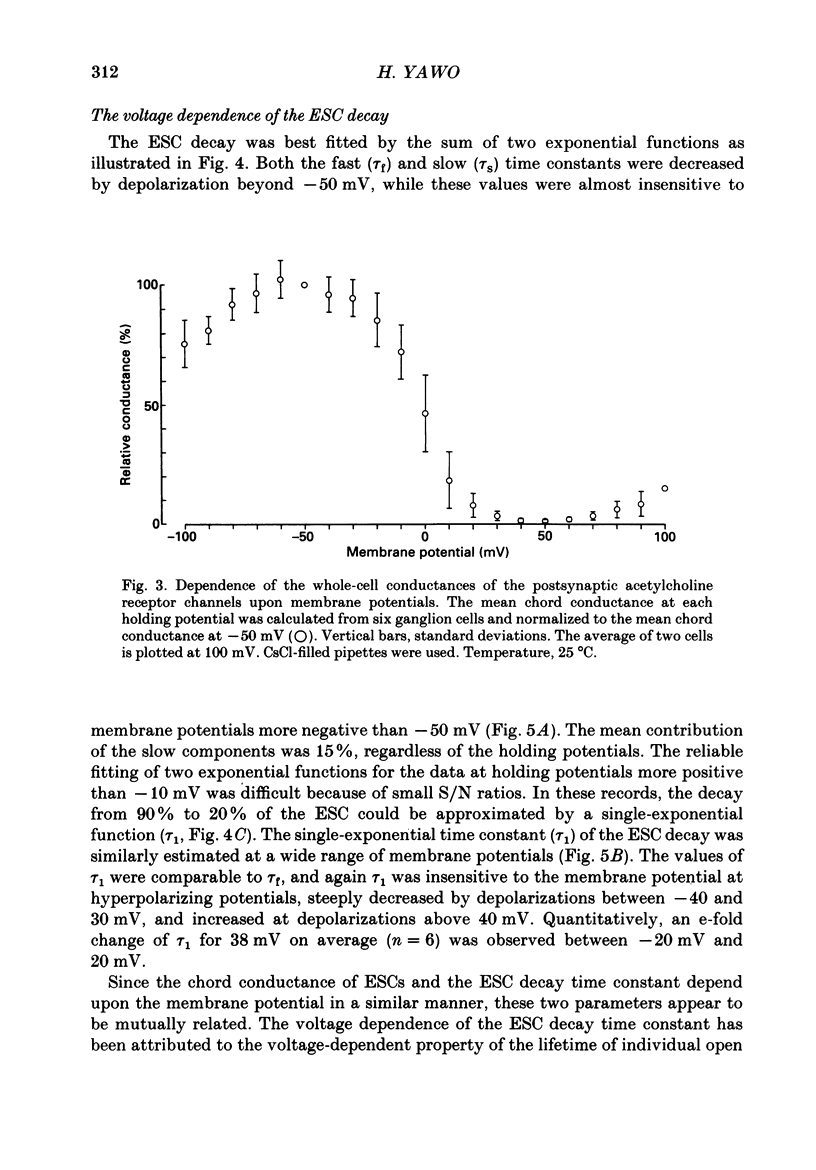
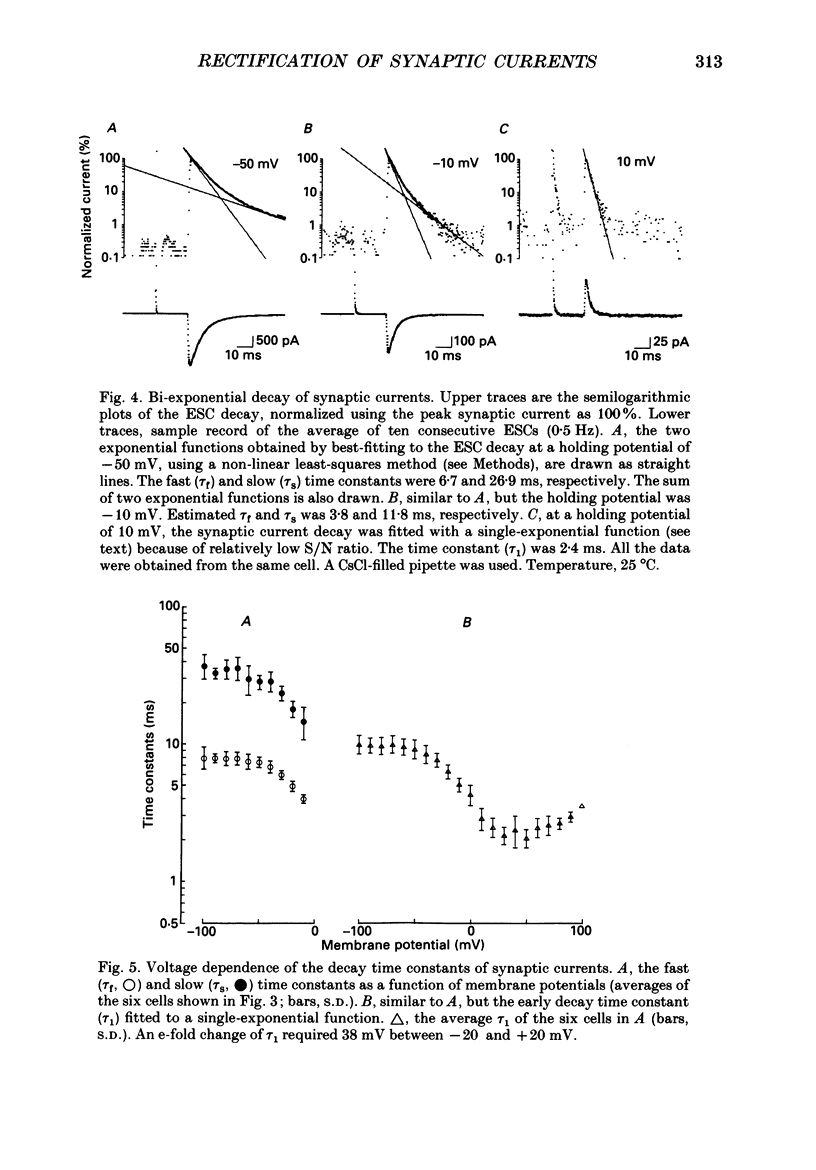
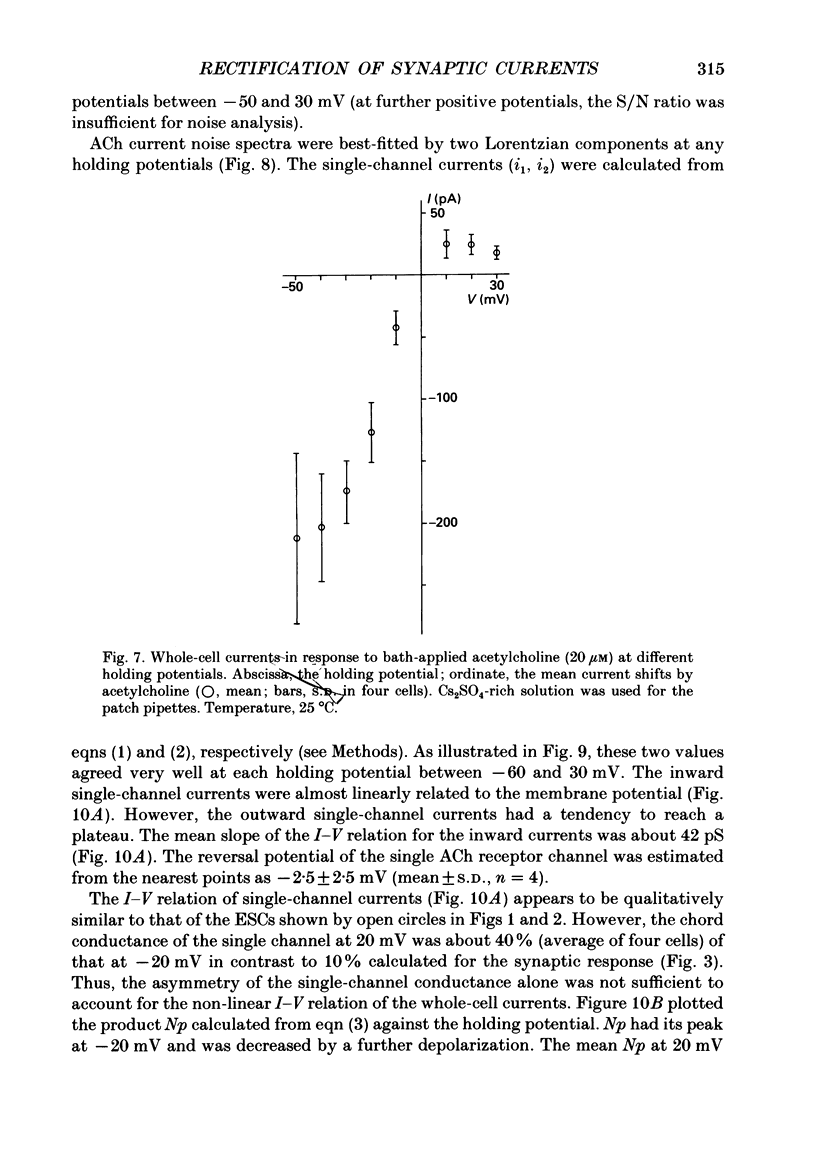
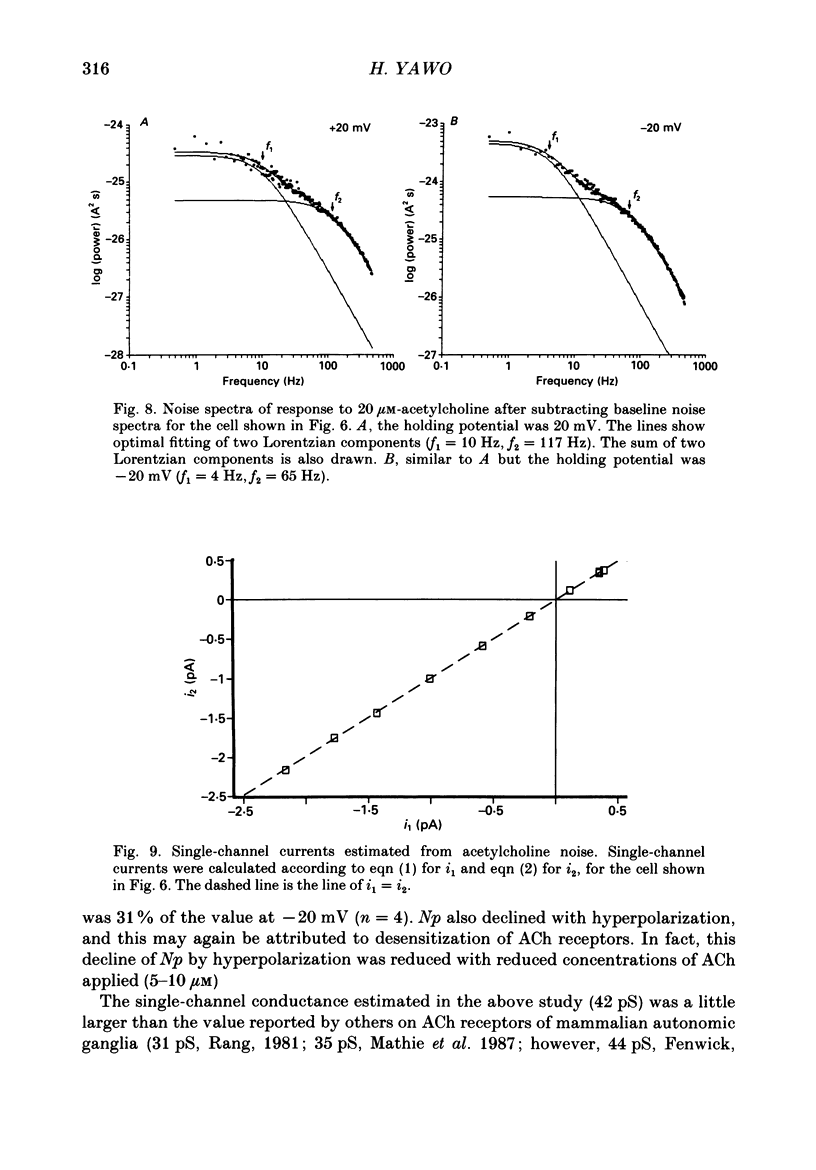
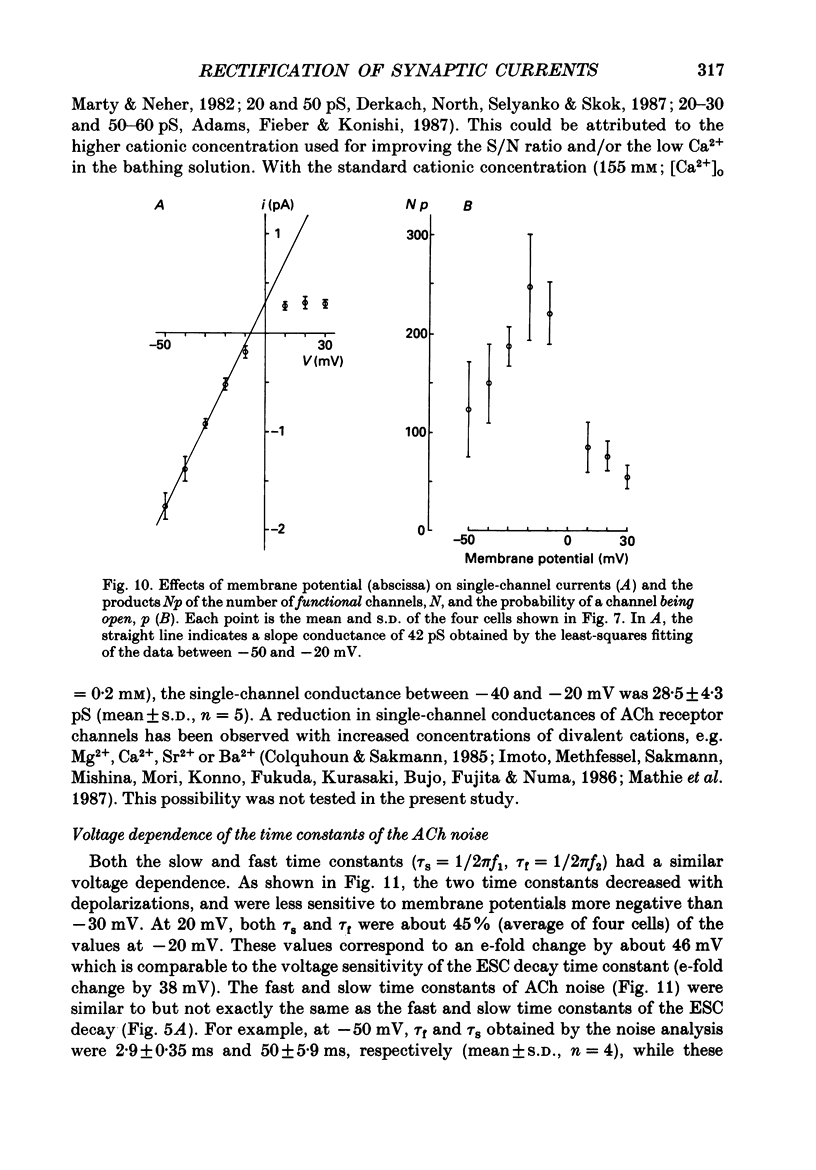
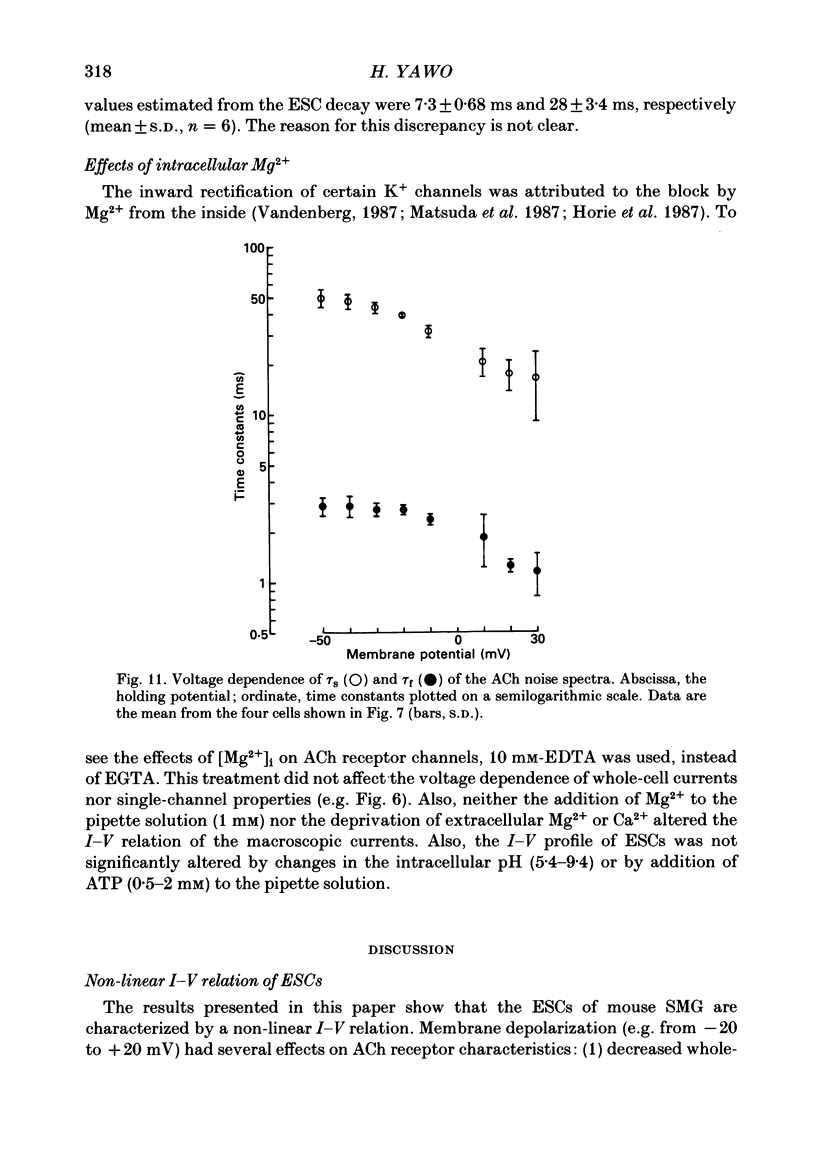
1. Synaptic currents and responses to acetylcholine (ACh) were recorded from mouse submandibular ganglion (SMG) cells under whole-cell voltage clamp. 2. The peak amplitude of excitatory synaptic currents (ESCs) as well as the currents evoked by the ionophoretic application of ACh followed a unique non-linear current-voltage (I-V) relation. The chord conductance of the whole-cell currents decreased with depolarization of the membrane potential and became virtually 0 at 50 mV. 3. The decay of ESCs was described by two exponential functions. Both the fast (tau f) and slow (tau s) time constants were sharply decreased at depolarizing potentials beyond -40 mV, being insensitive to hyperpolarizing potentials more than -50 mV. 4. Single ACh receptor channels were characterized by the whole-cell current noise analysis. The single-channel currents followed Ohm's law at negative membrane potentials but tended to reach a plateau at positive membrane potentials. The mean slope conductance measured between -40 and -20 mV was 28.5 pS. 5. The product of the number of functional channels (N) and the probability of a channel being open (p) showed a steep voltage dependence. The value of Np at 20 mV was only 31% of that at -20 mV. 6. The noise power spectrum was best fitted by a double-Lorentzian function. Both the fast (tau f) and slow (tau s) time constants were sharply decreased by depolarizations beyond -20 mV. being less sensitive to membrane potentials more negative than -30 mV. 7. The non-linear I-V relation of ESCs was attributed in part to the voltage dependence of p and in part to the voltage dependence of the single-channel conductance (gamma) of ACh receptor channels.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson C. R., Stevens C. F. Voltage clamp analysis of acetylcholine produced end-plate current fluctuations at frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1973 Dec;235(3):655–691. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ascher P., Large W. A., Rang H. P. Studies on the mechanism of action of acetylcholine antagonists on rat parasympathetic ganglion cells. J Physiol. 1979 Oct;295:139–170. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballivet M., Nef P., Couturier S., Rungger D., Bader C. R., Bertrand D., Cooper E. Electrophysiology of a chick neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor expressed in Xenopus oocytes after cDNA injection. Neuron. 1988 Nov;1(9):847–852. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90132-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezanilla F., Armstrong C. M. Negative conductance caused by entry of sodium and cesium ions into the potassium channels of squid axons. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Nov;60(5):588–608. doi: 10.1085/jgp.60.5.588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Dreyer F., Sheridan R. E. The actions of tubocurarine at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1979 Aug;293:247–284. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Hawkes A. G. Relaxation and fluctuations of membrane currents that flow through drug-operated channels. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Nov 14;199(1135):231–262. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1977.0137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Sakmann B. Fast events in single-channel currents activated by acetylcholine and its analogues at the frog muscle end-plate. J Physiol. 1985 Dec;369:501–557. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull-Candy S. G., Howe J. R., Ogden D. C. Noise and single channels activated by excitatory amino acids in rat cerebellar granule neurones. J Physiol. 1988 Jun;400:189–222. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis M. J., Harris A. J., Kuffler S. W. Synaptic transmission and its duplication by focally applied acetylcholine in parasympathetic neurons in the heart of the frog. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1971 Apr 27;177(1049):509–539. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1971.0045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derkach V. A., North R. A., Selyanko A. A., Skok V. I. Single channels activated by acetylcholine in rat superior cervical ganglion. J Physiol. 1987 Jul;388:141–151. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derkach V. A., Selyanko A. A., Skok V. I. Acetylcholine-induced current fluctuations and fast excitatory post-synaptic currents in rabbit sympathetic neurones. J Physiol. 1983 Mar;336:511–526. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiFrancesco D. Block and activation of the pace-maker channel in calf purkinje fibres: effects of potassium, caesium and rubidium. J Physiol. 1982 Aug;329:485–507. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P., KATZ B. An analysis of the end-plate potential recorded with an intracellular electrode. J Physiol. 1951 Nov 28;115(3):320–370. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick E. M., Marty A., Neher E. A patch-clamp study of bovine chromaffin cells and of their sensitivity to acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:577–597. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French R. J., Wells J. B. Sodium ions as blocking agents and charge carriers in the potassium channel of the squid giant axon. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Dec;70(6):707–724. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.6.707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Miyazaki S., Rosenthal N. P. Potassium current and the effect of cesium on this current during anomalous rectification of the egg cell membrane of a starfish. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Jun;67(6):621–638. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.6.621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T., Kidokoro Y., Ohmori H. Acetylcholine dose-response relation and the effect of cesium ions in the rat adrenal chromaffin cell under voltage clamp. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Apr;408(4):401–407. doi: 10.1007/BF00581136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horie M., Irisawa H., Noma A. Voltage-dependent magnesium block of adenosine-triphosphate-sensitive potassium channel in guinea-pig ventricular cells. J Physiol. 1987 Jun;387:251–272. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe J. R., Colquhoun D., Cull-Candy S. G. On the kinetics of large-conductance glutamate-receptor ion channels in rat cerebellar granule neurons. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1988 May 23;233(1273):407–422. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1988.0030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imoto K., Methfessel C., Sakmann B., Mishina M., Mori Y., Konno T., Fukuda K., Kurasaki M., Bujo H., Fujita Y. Location of a delta-subunit region determining ion transport through the acetylcholine receptor channel. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):670–674. doi: 10.1038/324670a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The statistical nature of the acetycholine potential and its molecular components. J Physiol. 1972 Aug;224(3):665–699. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuba K., Nishi S. Characteristics of fast excitatory postsynaptic current in bullfrog sympathetic ganglion cells. Effects of membrane potential, temperature and Ca ions. Pflugers Arch. 1979 Jan 31;378(3):205–212. doi: 10.1007/BF00592737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtman J. W. The reorganization of synaptic connexions in the rat submandibular ganglion during post-natal development. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(1):155–177. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder T. M., Quastel D. M. A voltage-clamp study of the permeability change induced by quanta of transmitter at the mouse end-plate. J Physiol. 1978 Aug;281:535–558. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loring R. H., Zigmond R. E. Characterization of neuronal nicotinic receptors by snake venom neurotoxins. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Feb;11(2):73–78. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90168-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loring R. H., Zigmond R. E. Ultrastructural distribution of 125I-toxin F binding sites on chick ciliary neurons: synaptic localization of a toxin that blocks ganglionic nicotinic receptors. J Neurosci. 1987 Jul;7(7):2153–2162. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-07-02153.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magazanik L. G., Vyskocil F. Dependence of acetylcholine desensitization on the membrane potential of frog muscle fibre and on the ionic changes in the medium. J Physiol. 1970 Oct;210(3):507–518. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magazanik L. G., Vyskocit F. The effect of temperature on desensitization kinetics at the post-synaptic membrane of the frog muscle fibre. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(2):285–300. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Pallotta B. S. A study of desensitization of acetylcholine receptors using nerve-released transmitter in the frog. J Physiol. 1981 Jul;316:225–250. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Stevens C. F. A quantitative description of end-plate currents. J Physiol. 1972 May;223(1):173–197. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Stevens C. F. The effect of voltage on the time course of end-plate currents. J Physiol. 1972 May;223(1):151–171. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathie A., Cull-Candy S. G., Colquhoun D. Single-channel and whole-cell currents evoked by acetylcholine in dissociated sympathetic neurons of the rat. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1987 Nov 23;232(1267):239–248. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1987.0072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda H., Saigusa A., Irisawa H. Ohmic conductance through the inwardly rectifying K channel and blocking by internal Mg2+. Nature. 1987 Jan 8;325(7000):156–159. doi: 10.1038/325156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purves D., Lichtman J. W. Synaptic sites on reinnervated nerve cells visualized at two different times in living mice. J Neurosci. 1987 May;7(5):1492–1497. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-05-01492.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purves D., Voyvodic J. T., Magrassi L., Yawo H. Nerve terminal remodeling visualized in living mice by repeated examination of the same neuron. Science. 1987 Nov 20;238(4830):1122–1126. doi: 10.1126/science.3685967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rang H. P. The characteristics of synaptic currents and responses to acetylcholine of rat submandibular ganglion cells. J Physiol. 1981 Feb;311:23–55. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selyanko A. A., Derkach V. A., Skok V. I. Fast excitatory postsynaptic currents in voltage-clamped mammalian sympathetic ganglion neurones. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1979 Dec;1(2):127–137. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(79)90011-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snider W. D. The dendritic complexity and innervation of submandibular neurons in five species of mammals. J Neurosci. 1987 Jun;7(6):1760–1768. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-06-01760.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEUCHI A., TAKEUCHI N. On the permeability of end-plate membrane during the action of transmitter. J Physiol. 1960 Nov;154:52–67. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenberg C. A. Inward rectification of a potassium channel in cardiac ventricular cells depends on internal magnesium ions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2560–2564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


