Abstract
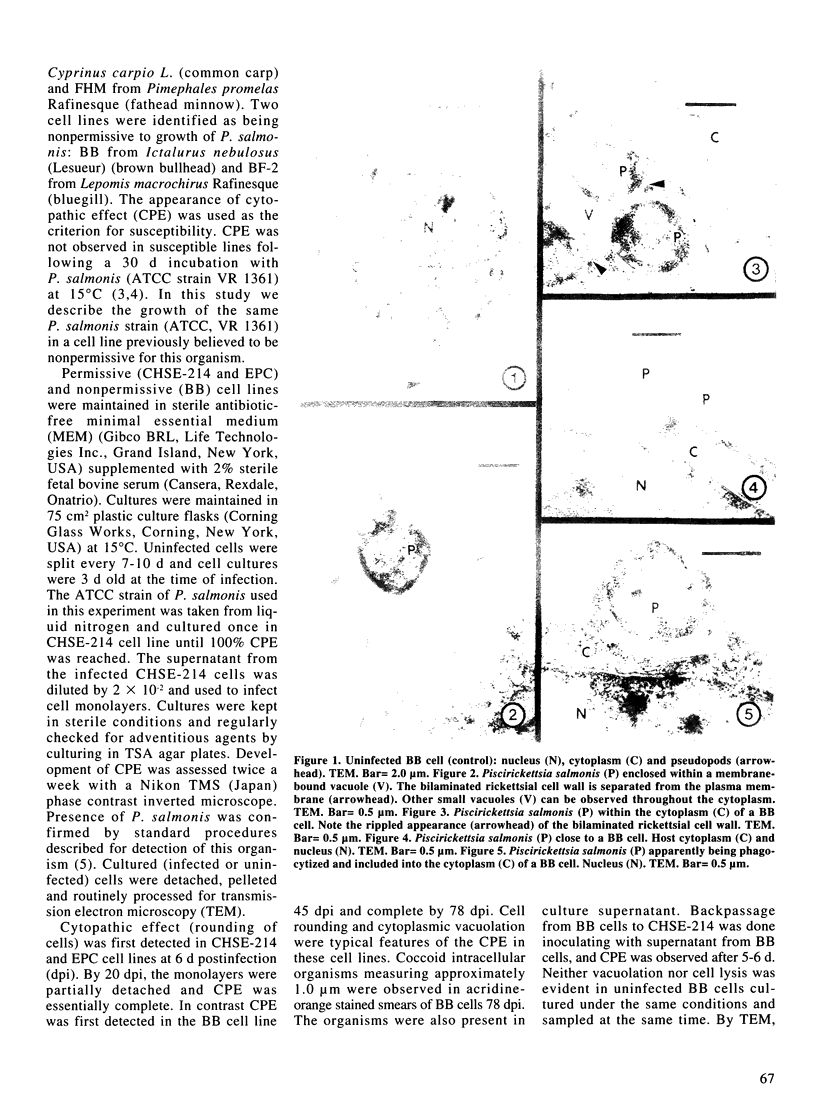
Piscirickettsia salmonis, the etiologic agent of salmonid rickettsial septicemia (SRS), affects several species of salmonids. Previous reports using the appearance of cytopathic effect (CPE) as the criterion for susceptibility, showed that Piscirickettsia salmonis (ATCC strain) can be grown in vitro in some cells lines derived from salmonid fish, but not in BB cells from brown bullhead (Ictalurus nebulosus) and BF-2 cells from bluegill (Lepomis macrochirus). In this study we describe growth of P. salmonis (ATCC strain VR 1361) in a cell line previously believed to be nonpermissive for this organism. CPE was first detected in chinook salmon embryo (CHSE-214) and epithelioma papulosum ciprini (EPC) cell lines at 6 d postinfection (dpi). In contrast, using BB cell line, CPE was first detected 45 dpi and the monolayer completed CPE by 78 dpi. Electron microscopic examination of BB cells 78 dpi revealed free, intracytoplasmic and extracellular localization of the agent. P. salmonis was also observed within membrane-bounded vacuoles in BB cells, similar to that described in CHSE 214 cells. Contrary to earlier reports, results from the present study show that the BB cell line, is susceptible to Piscirickettsia salmonis infection. The delayed onset of CPE in BB cells in comparison to other permissive cell lines suggests that BB cells are not ideal hosts for P. salmonis. Interestingly, however, these results demonstrate that P. salmonis can infect non-salmonid cell lines, and raises the possibility that non-salmonid fish may play a role in the persistence and transmission of SRS in the natural environment.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fryer J. L., Lannan C. N., Giovannoni S. J., Wood N. D. Piscirickettsia salmonis gen. nov., sp. nov., the causative agent of an epizootic disease in salmonid fishes. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;42(1):120–126. doi: 10.1099/00207713-42-1-120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]