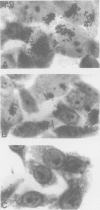
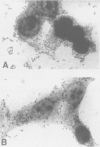
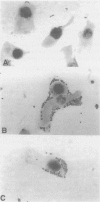
Abstract
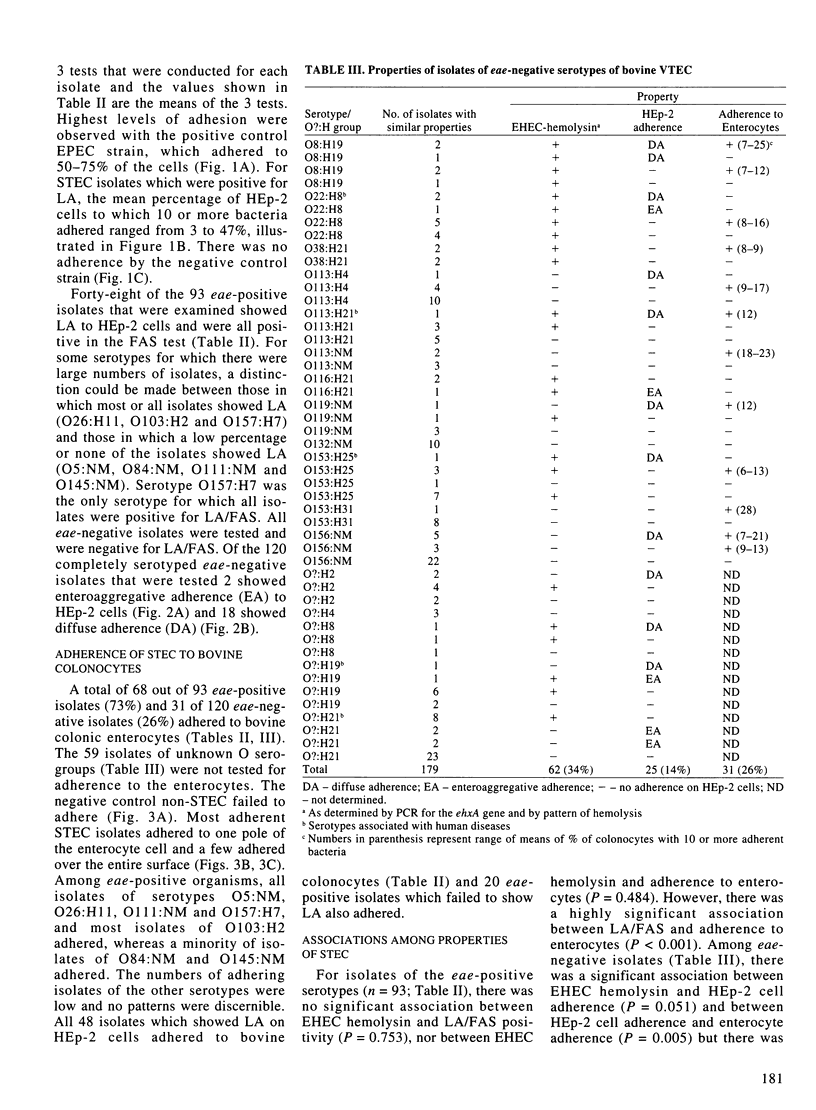
This study identified potential virulence markers in 93 eae-positive and 179 eae-negative Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC), isolated from a random sampling of healthy cattle in southwestern Ontario. PCR amplification was used to identify genes for enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC)-hemolysin, the EAF plasmid, and bundle-forming pili (Bfp); adherence to HEp-2 cells and to bovine colonocytes, and the fluorescent actin staining (FAS) test were used to characterize interaction of the bacteria with epithelial cells. The EHEC-hemolysin sequences were detected in 98% of eae-positive isolates compared with 34% of eae-negative isolates. All isolates were negative for EAF and bfp sequences. There was 100% correlation between localized adherence (LA) to HEp-2 cells and the FAS test. Forty-eight (52%) of the eae-positive isolates were LA/FAS-positive, whereas none of the 179 eae-negative isolates was positive in either test. Among the eae-negative isolates, 20 (11%) showed diffuse adherence and 5 (2.8%) showed enteroaggregative adherence to HEp-2 cells. Seventy-three percent of the eae-positive isolates adhered to bovine colonocytes, whereas only 26% of 120 eae-negative isolates that were tested adhered. All 13 O157:H7 isolates were positive for eae and EHEC-hemolysin gene sequences, LA/FAS, and adherence to bovine colonocytes. It is concluded that possession of genes for eae and EHEC hemolysin is correlated with the serotype of STEC, that production of EHEC hemolysin was highly correlated with serotypes implicated in human disease, and that none of the potential markers that were examined can be used to predict the potential virulence of an isolate.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrett T. J., Kaper J. B., Jerse A. E., Wachsmuth I. K. Virulence factors in Shiga-like toxin-producing Escherichia coli isolated from humans and cattle. J Infect Dis. 1992 May;165(5):979–980. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.5.979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer M. E., Welch R. A. Characterization of an RTX toxin from enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7. Infect Immun. 1996 Jan;64(1):167–175. doi: 10.1128/iai.64.1.167-175.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutin L., Aleksic S., Zimmermann S., Gleier K. Virulence factors and phenotypical traits of verotoxigenic strains of Escherichia coli isolated from human patients in Germany. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1994 Feb;183(1):13–21. doi: 10.1007/BF00193627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutin L., Geier D., Zimmermann S., Karch H. Virulence markers of Shiga-like toxin-producing Escherichia coli strains originating from healthy domestic animals of different species. J Clin Microbiol. 1995 Mar;33(3):631–635. doi: 10.1128/jcm.33.3.631-635.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutin L., Montenegro M. A., Orskov I., Orskov F., Prada J., Zimmermann S., Stephan R. Close association of verotoxin (Shiga-like toxin) production with enterohemolysin production in strains of Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Nov;27(11):2559–2564. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.11.2559-2564.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutin L., Zimmermann S., Gleier K. Human infections with Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli other than serogroup O157 in Germany. Emerg Infect Dis. 1998 Oct-Dec;4(4):635–639. doi: 10.3201/eid0404.980415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke R. C., McEwen S. A., Gannon V. P., Lior H., Gyles C. L. Isolation of verocytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli from milk filters in south-western Ontario. Epidemiol Infect. 1989 Apr;102(2):253–260. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800029927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn C. R., Scotland S. M., Smith H. R., Willshaw G. A., Rowe B. Properties of Vero cytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli of human and animal origin belonging to serotypes other than O157:H7. Epidemiol Infect. 1989 Aug;103(1):83–95. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800030387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dytoc M. T., Ismaili A., Philpott D. J., Soni R., Brunton J. L., Sherman P. M. Distinct binding properties of eaeA-negative verocytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli of serotype O113:H21. Infect Immun. 1994 Aug;62(8):3494–3505. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.8.3494-3505.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke J., Franke S., Schmidt H., Schwarzkopf A., Wieler L. H., Baljer G., Beutin L., Karch H. Nucleotide sequence analysis of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) adherence factor probe and development of PCR for rapid detection of EPEC harboring virulence plasmids. J Clin Microbiol. 1994 Oct;32(10):2460–2463. doi: 10.1128/jcm.32.10.2460-2463.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girón J. A., Donnenberg M. S., Martin W. C., Jarvis K. G., Kaper J. B. Distribution of the bundle-forming pilus structural gene (bfpA) among enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1993 Oct;168(4):1037–1041. doi: 10.1093/infdis/168.4.1037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin P. M., Tauxe R. V. The epidemiology of infections caused by Escherichia coli O157:H7, other enterohemorrhagic E. coli, and the associated hemolytic uremic syndrome. Epidemiol Rev. 1991;13:60–98. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyles C., Johnson R., Gao A., Ziebell K., Pierard D., Aleksic S., Boerlin P. Association of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli hemolysin with serotypes of shiga-like-toxin-producing Escherichia coli of human and bovine origins. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1998 Nov;64(11):4134–4141. doi: 10.1128/aem.64.11.4134-4141.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hicks S., Frankel G., Kaper J. B., Dougan G., Phillips A. D. Role of intimin and bundle-forming pili in enteropathogenic Escherichia coli adhesion to pediatric intestinal tissue in vitro. Infect Immun. 1998 Apr;66(4):1570–1578. doi: 10.1128/iai.66.4.1570-1578.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ismaili A., McWhirter E., Handelsman M. Y., Brunton J. L., Sherman P. M. Divergent signal transduction responses to infection with attaching and effacing Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1998 Apr;66(4):1688–1696. doi: 10.1128/iai.66.4.1688-1696.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karaolis D. K., McDaniel T. K., Kaper J. B., Boedeker E. C. Cloning of the RDEC-1 locus of enterocyte effacement (LEE) and functional analysis of the phenotype on HEp-2 cells. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1997;412:241–245. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4899-1828-4_36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A. Infection by verocytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jan;2(1):15–38. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny B., DeVinney R., Stein M., Reinscheid D. J., Frey E. A., Finlay B. B. Enteropathogenic E. coli (EPEC) transfers its receptor for intimate adherence into mammalian cells. Cell. 1997 Nov 14;91(4):511–520. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80437-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutton S., Baldwin T., Williams P. H., McNeish A. S. Actin accumulation at sites of bacterial adhesion to tissue culture cells: basis of a new diagnostic test for enteropathogenic and enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1290–1298. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1290-1298.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M. Escherichia coli that cause diarrhea: enterotoxigenic, enteropathogenic, enteroinvasive, enterohemorrhagic, and enteroadherent. J Infect Dis. 1987 Mar;155(3):377–389. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.3.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Xu J. G., Kaper J. B., Lior H., Prado V., Tall B., Nataro J., Karch H., Wachsmuth K. A DNA probe to identify enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli of O157:H7 and other serotypes that cause hemorrhagic colitis and hemolytic uremic syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jul;156(1):175–182. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.1.175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mainil J. G., Jacquemin E. R., Kaeckenbeeck A. E., Pohl P. H. Association between the effacing (eae) gene and the Shiga-like toxin-encoding genes in Escherichia coli isolates from cattle. Am J Vet Res. 1993 Jul;54(7):1064–1068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDaniel T. K., Kaper J. B. A cloned pathogenicity island from enteropathogenic Escherichia coli confers the attaching and effacing phenotype on E. coli K-12. Mol Microbiol. 1997 Jan;23(2):399–407. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1997.2311591.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy B., Whipp S. C., Imberechts H., Bertschinger H. U., Dean-Nystrom E. A., Casey T. A., Salajka E. Biological relationship between F18ab and F18ac fimbriae of enterotoxigenic and verotoxigenic Escherichia coli from weaned pigs with oedema disease or diarrhoea. Microb Pathog. 1997 Jan;22(1):1–11. doi: 10.1006/mpat.1996.0085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nataro J. P., Kaper J. B., Robins-Browne R., Prado V., Vial P., Levine M. M. Patterns of adherence of diarrheagenic Escherichia coli to HEp-2 cells. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1987 Sep;6(9):829–831. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198709000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philpott D. J., McKay D. M., Mak W., Perdue M. H., Sherman P. M. Signal transduction pathways involved in enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli-induced alterations in T84 epithelial permeability. Infect Immun. 1998 Apr;66(4):1680–1687. doi: 10.1128/iai.66.4.1680-1687.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandhu K. S., Clarke R. C., McFadden K., Brouwer A., Louie M., Wilson J., Lior H., Gyles C. L. Prevalence of the eaeA gene in verotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains from dairy cattle in Southwest Ontario. Epidemiol Infect. 1996 Feb;116(1):1–7. doi: 10.1017/s095026880005888x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scaletsky I. C., Silva M. L., Trabulsi L. R. Distinctive patterns of adherence of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli to HeLa cells. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):534–536. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.534-536.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt H., Beutin L., Karch H. Molecular analysis of the plasmid-encoded hemolysin of Escherichia coli O157:H7 strain EDL 933. Infect Immun. 1995 Mar;63(3):1055–1061. doi: 10.1128/iai.63.3.1055-1061.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt H., Plaschke B., Franke S., Rüssmann H., Schwarzkopf A., Heesemann J., Karch H. Differentiation in virulence patterns of Escherichia coli possessing eae genes. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1994 Feb;183(1):23–31. doi: 10.1007/BF00193628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt H., Rüssmann H., Schwarzkopf A., Aleksic S., Heesemann J., Karch H. Prevalence of attaching and effacing Escherichia coli in stool samples from patients and controls. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1994 Aug;281(2):201–213. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8840(11)80571-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scotland S. M., Willshaw G. A., Smith H. R., Rowe B. Properties of strains of Escherichia coli O26:H11 in relation to their enteropathogenic or enterohemorrhagic classification. J Infect Dis. 1990 Nov;162(5):1069–1074. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.5.1069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willshaw G. A., Scotland S. M., Smith H. R., Rowe B. Properties of Vero cytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli of human origin of O serogroups other than O157. J Infect Dis. 1992 Oct;166(4):797–802. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.4.797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winsor D. K., Jr, Ashkenazi S., Chiovetti R., Cleary T. G. Adherence of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli strains to a human colonic epithelial cell line (T84). Infect Immun. 1992 Apr;60(4):1613–1617. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.4.1613-1617.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]